There are a total of 14 chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics. These 14 chapters are divided into two parts. Part 1 contains 8 chapters, and Part 2 has 6 chapters. The whole 14 chapters are further categorised into 9 units on the basis of their relation to the topics in the chapters.
The National Council for Education Research and Training (NCERT) has divided the Class 12 physics syllabus into 2 parts for the periodic convenience of teaching and logical flow.
- Part I covers foundational and electromagnetic theories of physics.
- Part II covers quantum mechanics, atomic models, nuclear physics, and semiconductors.
- Both parts are equally important for the board examination.
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapters are also used for NEET, JEE, UPSC, and several competitive exams.
- For the Class 12 CBSE board examination, the chapters have 7-16 each.
- Though the number of chapters and the subtopics under each chapter is from 5 to 15, both parts equally cover 50% of the complete physics syllabus.
- Part 1 covers classical physics
- Part 2 covers modern physics
Also Read

Key Summary
- Total Class 12 CBSE Physics units: 9
- Total Class 12 CBSE Physics chapters: 14
- Total Class 12 CBSE Physics syllabus parts: 2
- Theory exam: for 70 marks.
- Internal/practical marks: 30 marks
- Chapter-wise weightage: 7-16 questions.
- Total teaching hours: 160
- Exam duration: 3 hours
- Passing mark: 33% in both internals and externals, i.e., 23+10=33 out of 100.
- These chapters are also used for JEE, NEET, UPSC, BITSAT, NDA, CUET, and NSEP, and many more examinations.
How many chapters in CBSE class 12 Physics
- CBSE Class 12 Physics has 14 chapters divided across 2 parts.
- 14 chapters are grouped into 9 units based on the topics’ relativity.
- Topics like Electrical charges and Fluids, Electrostatic potential, Capacitance, Current Electricity, Moving charges and Magnetism have more subtopics listed.
- Electromagnetic Induction, Alternating Current, Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Wave Optics, Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Atoms, Nuclei, and Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits have 7-8 subtopics listed under each.
- Magnetism and Matter, and Electromagnetic Waves have 4-5 subtopics listed.
- Weightage of each chapter ranges around 7-16 questions for the CBSE Class 12 board exam.
| NCERT Class 12 Physics all Chapters-Part 1 Full Text Book |
|---|
| NCERT Class 12 Physics all Chapters-Part 2 Full Text Book |
Total chapters in Class 12 Physics
- Overall, 14 chapters are in Class 12 Physics.
- 14 chapters are grouped into 9 units.
- These 19 units have 4 minimum and 30 maximum hours allocated for teaching.
- These 9 units are further divided into Part 1 and Part 2 for periodic assessment and evaluation purposes.
- All these chapters will be evaluated in the board exam for a 70+30 marks division for externals and internals.
How many chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics: Chapter list
| Unit No. | Unit Name | Chapter No. | Chapters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit:1 | Electrostatics | 1 | Electrical Charges and Fields |
| 2 | Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | ||
| Unit:2 | Current Electricity | 3 | Current Electricity |
| Unit:3 | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | 4 | Moving Charges and Magnetism |
| 5 | Magnetsism and Matter | ||
| Unit:4 | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | 6 | Electromagnetic Induction |
| 7 | Alternative Current | ||
| Unit:5 | Electromagnetic Waves | 8 | Electromagnetic waves |
| Unit:6 | Optics | 9 | Ray Optics and Optical Instruments |
| 10 | Wave Optics | ||
| Unit:7 | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 11 | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter |
| Unit:8 | Atoms and Nuclei | 12 | Atoms |
| 13 | Nuclei | ||
| Unit:9 | Electronic Devices | 14 | Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits |
Also Read
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper with Solution (2025-2015): Download PDFHow many chapters in CBSE Class 11 Physics
- Total chapters in Class 11 Physics are 14, which are grouped in 10 units across 2 parts.
- In the exams, the questions from each unit range from 10-23.
| Unit No | Unit Name | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit:1 | Physical world and measurement | 1 | Units and Measurements |
| Unit:2 | Kinematics | 2 | Motion in a Straight Line |
| 3 | Motion in a Plane | ||
| Unit:3 | Laws of motion | 4 | Laws of Motion |
| Unit:4 | Work, energy, and power | 5 | Work, Energy, and Power |
| Unit:5 | Motion of systems of particles and rigid body | 6 | System of Particles and Rotational Motion |
| Unit:6 | Gravitation | 7 | Gravitation |
| Unit:7 | Properties of bulk matter | 8 | Mechanical Properties of Solids |
| 9 | Mechanical Properties of Fluids | ||
| 10 | Thermal Properties of Matter | ||
| Unit:8 | Thermodynamics | 11 | Thermodynamics |
| Unit:9 | Behavior of perfect gases and kinetic theory of gases | 12 | Kinetic Theory |
| Unit:10 | Oscillation and waves | 13 | Oscillation |
| 14 | Waves |
Also Read
Important Questions for Class 12 Physics with AnswersHow many chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics: Class 12 Physics chapters PDF-PART 1
| Chapter Name | |
|---|---|
| Chapter 1 | Electrical Charges and Fields |
| Chapter 2 | Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance |
| Chapter 3 | Current Electricity |
| Chapter 4 | Moving Charges and Magnetism |
| Chapter 5 | Magnetsism and Matter |
| Chapter 6 | Electromagnetic Induction |
| Chapter 7 | Alternative Current |
| Chapter 8 | Electromagnetic waves |
How many chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics : Class 12 Physics chapters PDF-PART 2
| Chapter Name | |
|---|---|
| Chapter 9 | Ray Optics and Optical Instruments |
| Chapter 10 | Wave Optics |
| Chapter 11 | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter |
| Chapter 12 | Atoms |
| Chapter 13 | Nuclei |
| Chapter 14 | Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits |
How many chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics : Physics NCERT class 12 Index Part 1
| Chapter 1: Electrical Charges and Fields | |
|---|---|
| 1.1 | Introduction |
| 1.2 | Electric charge |
| 1.3 | Conductors and insulators |
| 1.4 | Basic properties of electric charge |
| 1.5 | Coulomb's law |
| 1.6 | Forces between multiple charges |
| 1.7 | Electric field |
| 1.8 | Electric field lines |
| 1.9 | Electric flux |
| 1.10 | Electric dipole |
| 1.11 | Dipole in a uniform external field |
| 1.12 | Continuous charge distribution |
| 1.13 | Gauss's Law |
| 1.14 | Application of Gauss's law |
| Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | |
| 2.1 | Introduction |
| 2.2 | Electrostatic potential |
| 2.3 | Potential due to a point charge |
| 2.4 | Potential due to an electric dipole |
| 2.5 | Potential due to a system of charges |
| 2.6 | Equipotential surfaces |
| 2.7 | Potential energy of a system of charges |
| 2.8 | Potential energy in an external field |
| 2.9 | Electrostatics of conductors |
| 2.10 | Dielectrics and polarization |
| 2.11 | Capacitors and capacitance |
| 2.12 | The parallel plate capacitor |
| 2.13 | Effect of a dielectric on capacitance |
| 2.14 | Combination of capacitors |
| 2.15 | Energy stored in a capacitor |
| Chapter 3:Current Electricity | |
| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Electric current |
| 3.3 | Electric currents in conductors |
| 3.4 | Ohm's law |
| 3.5 | Drift of electrons and the origin of resistivity |
| 3.6 | Limitations of Ohm's law |
| 3.7 | Resistivity of various materials |
| 3.8 | Temperature dependence of resistivity |
| 3.9 | Electrical energy, power |
| 3.10 | Cells, emf, Internal resistance |
| 3.11 | Cells in series and in parallel |
| 3.12 | Kirchhoff's rules |
| 3.13 | Wheatstone Bridge |
| Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism | |
| 4.1 | Introduction |
| 4.2 | Magnetic force |
| 4.3 | Motion in a magnetic field |
| 4.4 | Magnetic field due to a current element, Biot-Savart law |
| 4.5 | Magnetic field on the axis of a circular current loop |
| 4.6 | Ampere’s circuital law |
| 4.7 | The solenoid |
| 4.8 | Force between two parallel currents, the Ampere |
| 4.9 | Torque on current loop, magnetic dipole |
| 4.10 | The moving coil galvanometer |
| Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter | |
| 5.1 | Introduction |
| 5.2 | The bar magnet |
| 5.3 | Magnetism and Gauss's law |
| 5.4 | Magnetization and magnetic intensity |
| 5.5 | Magnetic properties of materials |
| Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction | |
| 6.1 | Introduction |
| 6.2 | The experiments of Faraday and Henry |
| 6.3 | Magnetic flux |
| 6.4 | Faraday's Law of Induction |
| 6.5 | Lenz's law of conservation of energy |
| 6.6 | Motional electromotive force |
| 6.7 | Inductance |
| 6.8 | AC generator |
| Chapter 7: Alternative Current | |
| 7.1 | Introduction |
| 7.2 | AC voltage applied to a resistor |
| 7.3 | Representation of AC current and voltage by rotating vectors-Phasos |
| 7.4 | AC voltage applied to an inductor |
| 7.5 | AC voltage applied to a capacitor |
| 7.6 | AC voltage applied to a series LCR circuit |
| 7.7 | Power in an AC circuit: The power factor |
| 7.8 | Transformers |
| Chapter 8: Electromagnetic waves | |
| 8.1 | Introduction |
| 8.2 | Displacement current |
| 8.3 | Electromagnetic waves |
| 8.4 | Electromagnetic spectrum |
How many chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics : Physics NCERT class 12 Index Part 2
| Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments | |
|---|---|
| 9.1 | Introduction |
| 9.2 | Reflection of Light by Spherical Mirrors |
| 9.3 | Refraction |
| 9.4 | Total Internal Reflection |
| 9.5 | Refraction at spherical surfaces and by lenses |
| 9.6 | Refraction through a prism |
| 9.7 | Optical instruments |
| Chapter 10: Wave Optics | |
| 10.1 | Introduction |
| 10.2 | Huygens principles |
| 10.3 | Refraction and reflection of plane waves using Huygens principle |
| 10.4 | Coherent and incoherent addition of waves |
| 10.5 | Interference of light waves and Young's experiment |
| 10.6 | Diffraction |
| 10.7 | Polarization |
| Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | |
| 11.1 | Introduction |
| 11.2 | Electron emission |
| 11.3 | Photoelectric effect |
| 11.4 | Experimental study of the photoelectric effect |
| 11.5 | Photoelectric effect and wave theory of light |
| 11.6 | Einstein's photoelectric equation: Energy quantum of radiation |
| 11.7 | Particle nature of light: The Photon |
| 11.8 | Wave nature of matter |
| Chapter 12: Atoms | |
| 12.1 | Introduction |
| 12.2 | Alpha particles scattering and Rutherford's nuclear model of the Atom |
| 12.3 | Atomic Spectra |
| 12.4 | The Bohr model of a hydrogen atom |
| 12.5 | The line Spectra of the hydrogen atom |
| 12.6 | DE Broglie's explanation of Bohr's second postulate of quantization |
| Chapter 13: Nuclei | |
| 13.1 | Introduction |
| 13.2 | Atomic masses and composition of the nucleus |
| 13.3 | Size of the nucleus |
| 13.4 | Mass-energy and nuclear binding energy |
| 13.5 | Nuclear force |
| 13.6 | Radioactivity |
| 13.7 | Nuclear energy |
| Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits | |
| 14.1 | Introduction |
| 14.2 | Classification of metals, conductors, and semiconductors |
| 14.3 | Intrinsic semiconductor |
| 14.4 | Extrinsic semiconductor |
| 14.5 | P-n Junction |
| 14.6 | Semiconductor diode |
| 14.7 | Application of a junction diode as a rectifier |
Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- Class 12 CBSE Physics has 14 chapters.
- The 14 chapters are grouped into 2 parts and spread across 9 units.
- The board for Physics has a 70+30 distribution, 70 for externals and 30 for internals.
- Around 160 total periods are allocated to cover all chapters; this ranges from 4-30 hours chapter to chapter.
- Each chapter contributes 7-16 for the final exam.
| Stream / Subjects | Theory (Written) | Practical / Internal | Total Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Languages (English, Hindi, etc.) | 80 | 20 | 100 |
| Humanities & Commerce | 80 | 20 | 100 |
| Science (Physics, Chemistry, Bio, etc.) | 70 | 30 | 100 |
| Mathematics / Applied Maths | 80 | 20 | 100 |
| Fine Arts / Music / Dance | 30 | 70 | 100 |
| Skill/Vocational Subjects | 50–60 | 40–50 | 100 |
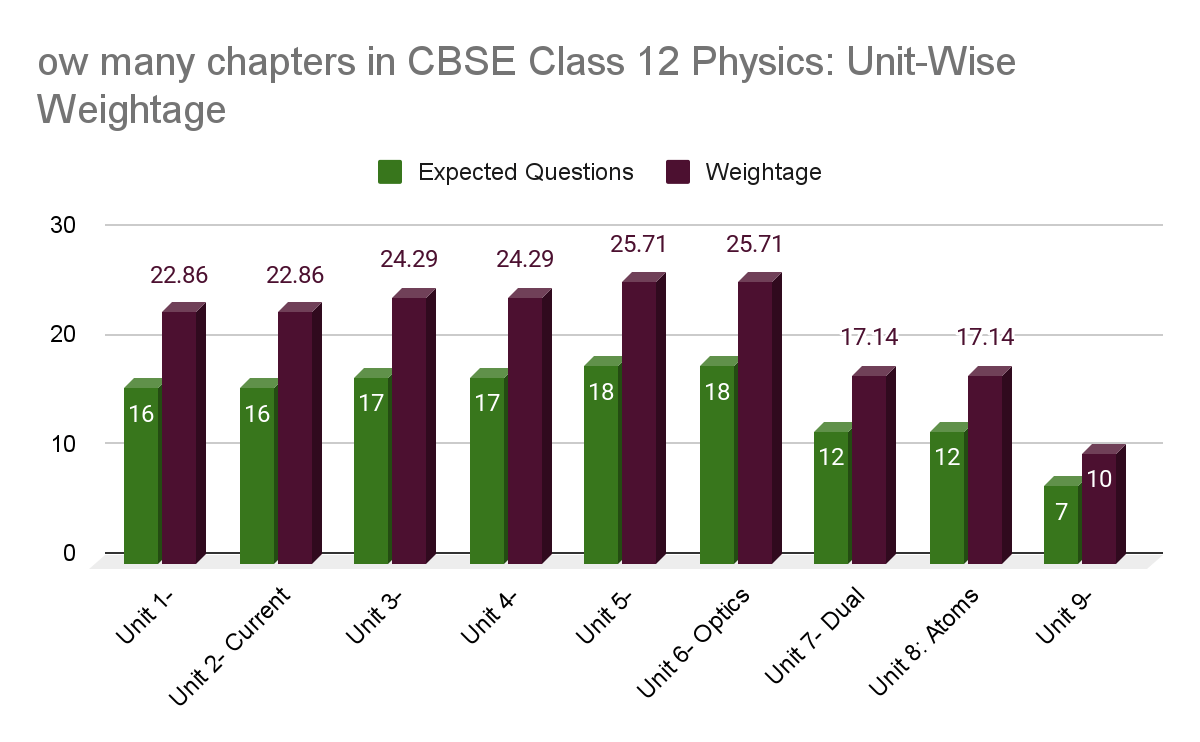
How many chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physics : Class 12 Physics Unit-Wise Weightage
| Unit Name | Expected Questions | Weightage | Chapters | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit 1- Electrostatics | 16 | 22.86% | Electrical Charges and Fields | |
| Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | ||||
| Unit 2- Current Electricity | Current Electricity | |||
| Unit 3- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | 17 | 24.29% | Moving Charges and Magnetism | |
| Magnetsism and Matter | ||||
| Unit 4- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Electromagnetic Induction | |||
| Alternative Current | ||||
| Unit 5- Electromagnetic Waves | 18 | 25.71% | Electromagnetic waves | |
| Unit 6- Optics | Ray Optics and Optical Instruments | |||
| Wave Optics | ||||
| Unit 7- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 12 | 17.14% | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | |
| Unit 8: Atoms and Nuclei | Atoms | |||
| Nuclei | ||||
| Unit 9- Electronic Devices | 7 | 10% | Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits | |
| Total | 70 | 100% | ||
CBSE Class 12 Physics Practical Marks Division
| Practicals | Marks |
|---|---|
| Two experiments: one from each section | 7+7 |
Practical Record:
|
5 |
| One activity from any section | 3 |
| Investigatory project | 3 |
| Viva on experiments, activities, and projects | 5 |
| Total | 30 |
CBSE Class 12 Physics Practical marks division for the visually impaired
| Practicals | Marks |
| Identification/Familiarity with the apparatus | 5 |
| Written test (based on given/prescribed practicals) | 10 |
| Practical Record | 5 |
| Viva | 10 |
| Total | 30 |
How many chapters are in CBSE class 12 Physics-FAQs
Ques: How many chapters are in Physics Class 12 CBSE board?
Ans: There are 14 chapters in Class 12 Physics.
- These are grouped into 9 units across NCERT Part 1 and Part 2.
- They cover both classical and modern physics.
Ques: Which is the biggest chapter in Physics Class 12?
Ans: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments is considered the biggest.
- It is lengthy and has multiple subtopics like reflection, refraction, lenses, and instruments.
- Weightage in boards is also high, making it very important.
Ques: Which chapters are removed from CBSE Class 12 Physics?
Ans: For 2025–26, no complete chapter is removed; only minor topics are trimmed.
- They are embedded in the main topics anyway.
Ques: Which chapter is most important in Physics Class 12 for the board exam?
Ans: Electrostatics, Current Electricity, Ray Optics, Dual Nature, Atoms & Nuclei are high-weightage.
- Together, these cover 40–50% of marks in board exams.
Ques: How many practicals are in Physics Class 12?
Ans: There are 16 practical experiments prescribed.
- 8 from Section A (experiments on electricity & magnetism).
- 8 from Section B (optics, modern physics, semiconductors).
Ques: How many books of Physics are in Class 12?
Ans: There are two books for Class 12 Physics in CBSE.
- Part 1 has 8 chapters
- Part 2 has 6 chapters
Ques: Is Class 12 Physics tough?
Ans: Yes, Physics is considered tough due to its vast syllabus.
- With NCERT examples, PYQs, and practice, it becomes scoring.
Ques: How many marks in numericals come in Physics Class 12?
Ans: 30-35 marks in numericals usually can be expected in Physics class 12.
Ques: How many chapters are in the NCERT Physics overall?
Ans: Class 11 has 15 chapters, Class 12 has 14 chapters.
- Together, NCERT Physics has a total of 29 chapters.



Comments