CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2024 PDF (Set 1 - 56/1/2) is available for download here. CBSE conducted the Chemistry exam on February 27, 2024, from 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM. The total marks for the theory paper are 70. The question paper contains 20% MCQ-based questions, 40% competency-based questions, and 40% short and long answer type questions.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2024 (Set 2 - 56/1/2) with Answer Key
| CBSE Class 12 2024 Chemistry Question Paper with Answer Key | Check Solution |
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2024 with Solution

Section A
The most stable oxidation state of Iron is:
The product formed as a result of reaction of CH\(_3\)MgBr and CO\(_2\) followed by hydrolysis is:
Nucleotides are composed of:
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo S\(_N\)1 reaction most readily?
Phenol dimerises in benzene having van’t Hoff factor 0.54. Its degree of association is:
A reaction A\(_2\) + B\(_2\) → 2AB occurs by the following mechanism:
A\(_2\) → A + A (slow)
A + B\(_2\) → AB + B (fast)
A + B → AB (fast)
Its order would be:
Decarboxylation of sodium benzoate on heating with soda lime gives:
The IUPAC name of CH\(_3\)–C(=O)–CH\(_2\)–C(=O)–H is:
Dehydration of tertiary alcohols with Cu at 573 K gives:
In the Arrhenius equation, when log k is plotted against 1/T, a straight line is obtained whose:
Phenol on reaction with aqueous bromine at room temperature gives:
The specific sequence in which amino acids are arranged in a protein is called:
Assertion (A): Aniline is a stronger base than ammonia.
Reason (R): The unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom in aniline becomes less available for protonation due to resonance.
Assertion (A): The pK\(_a\) of O\(_2\)N–CH\(_2\)–COOH is lower than that of CH\(_3\)–COOH.
Reason (R): The –NO\(_2\) group shows an electron-withdrawing effect, which increases the acidic character of O\(_2\)N–CH\(_2\)–COOH.
Assertion (A): Transition metals have high enthalpy of atomization.
Reason (R): This is because transition metals have low melting points.
Assertion (A): When NaCl is added to water, elevation in boiling point is observed.
Reason (R): Elevation in boiling point is a colligative property.
(a) Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions:
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
Br\(_2\) water
Write the chemical equations when:
Pentan-3-one is treated with H\(_2\)N–NH\(_2\) followed by heating with KOH in high boiling solvent such as ethylene glycol.
Calculate the potential of the iron electrode in which the concentration of Fe\(^{2+}\) ion is 0.01 M.
\[ (E^\circ_{Fe^{2+}/Fe} = -0.45 V at 298 K) \] \[ [Given: log 10 = 1] \]
Compound (A) \( \left( C_6H_{12}O_2 \right) \) on reduction with LiAlH\textsubscript{4 gives two compounds (B) and (C). The compound (B) on oxidation with PCC gives compound (D) which upon treatment with dilute NaOH and subsequent heating gives compound (E). Compound (E) on catalytic hydrogenation gives compound (C). The compound (D) is oxidized further to give compound (F) which is found to be a monobasic acid (Molecular weight = 60). Identify the compounds (A), (B), (C), (D), (E) and (F).
Answer the following: (any three)
(a) What is peptide linkage?
(c) Which one of the following is a polysaccharide? Sucrose, Glucose, Starch, Fructose
(d) Give one example each for water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins.
Write the mechanism of the following reaction: \[ CH_3CH_2OH \xrightarrow{H^+ \, 443\, K} CH_2 = CH_2 \]
Write the main product in each of the following reactions:
(a) Write the formula for the following coordination compound:
Potassium tetrahydroxidozincate (II)
(b) Arrange the following complexes in the increasing order of conductivity of their solution: \[ [Cr(NH_3)_5Cl] Cl_2, \, [Cr(NH_3)_3Cl_3], \, [Cr(NH_3)_6Cl_3] \]
(c) Identify the type of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes:
(i) \( [Co(NH_3)_5NO_2]^{2+} \)
(ii) \( [Co(en)_3]Cl_3 \)
(a) Which of the following is an allylic halide?
(i)
(ii)
(b) Out of chlorobenzene and 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene, which is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution and why?
(c) Which isomer of C4H9Cl has the lowest boiling point?
The following initial rate data were obtained for the reaction: \[ 2NO (g) + Br_2 (g) \rightarrow 2 NOBr (g) \]
(a) What is the order with respect to NO and \(Br_{2}\) in the reaction?
(b) Calculate the rate constant (k).
(c) Determine the rate of reaction when the concentrations of NO and \(Br_{2}\) are 0.4 M and 0.2 M, respectively.
When a certain conductivity cell was filled with 0.05 M KCl solution, it has a resistance of 100 ohms at 25°C. When the same cell was filled with 0.02 M \(AgNO_{3}\) solution, the resistance was 90 ohms. Calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of \(AgNO_{3}\) solution.
Given:
Conductivity of 0.05 M KCl solution = \( 1.35 \times 10^{-2} \, \Omega^{-1} \, cm^{-1} \)
(a) What is crystal field splitting energy?
(b) Give reason for the violet colour of the complex \( [Ti(H_2O)_6]^{3+} \) on the basis of crystal field theory.
(c) \( [Cr(NH_3)_6]^{3+} \) is paramagnetic while \( [Ni(CN)_4]^{2-} \) is diamagnetic. Explain why.
Question 30:
Explain why \( [Fe(CN)_6]^{3-} \) is an inner orbital complex, whereas \( [Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3+} \) is an outer orbital complex.
(1) The melting and boiling points of Zn, Cd, and Hg are low.
(2) Of the \( d^4 \) species, Cr\(^{2+}\) is strongly reducing while Mn\(^{3+}\) is strongly oxidizing.
(3) \( E^0 \) value of Cu\(^{2+}\)/Cu is \( +0.34 \) V.
(b) Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(i) At the same temperature, \( CO_2 \) gas is more soluble in water than \( O_2 \) gas. Which one of them will have a higher value of \( K_H \) and why?
(ii) How does the size of blood cells change when placed in an aqueous solution containing more than 0.9% (mass/volume) sodium chloride?
(iii) 1 molal aqueous solution of an electrolyte \( A_2B_3 \) is 60% ionized. Calculate the boiling point of the solution.
(i) The vapour pressures of A and B at 25°C are 75 mm Hg and 25 mm Hg, respectively. If A and B are mixed such that the mole fraction of A in the mixture is 0.4, then calculate the mole fraction of B in the vapour phase.
(ii) Define colligative property. Which colligative property is preferred for the molar mass determination of macromolecules?
(iii) Why are equimolar solutions of sodium chloride and glucose not isotonic?
(a) N,N-diethylbenzenesulphonamide is insoluble in alkali. Give reason.
(b) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction. Why?
(c) Write a simple chemical test to distinguish between methylamine and aniline.
(d) Write the chemical reaction involved in Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
(e) How will you convert aniline to p-bromoaniline?
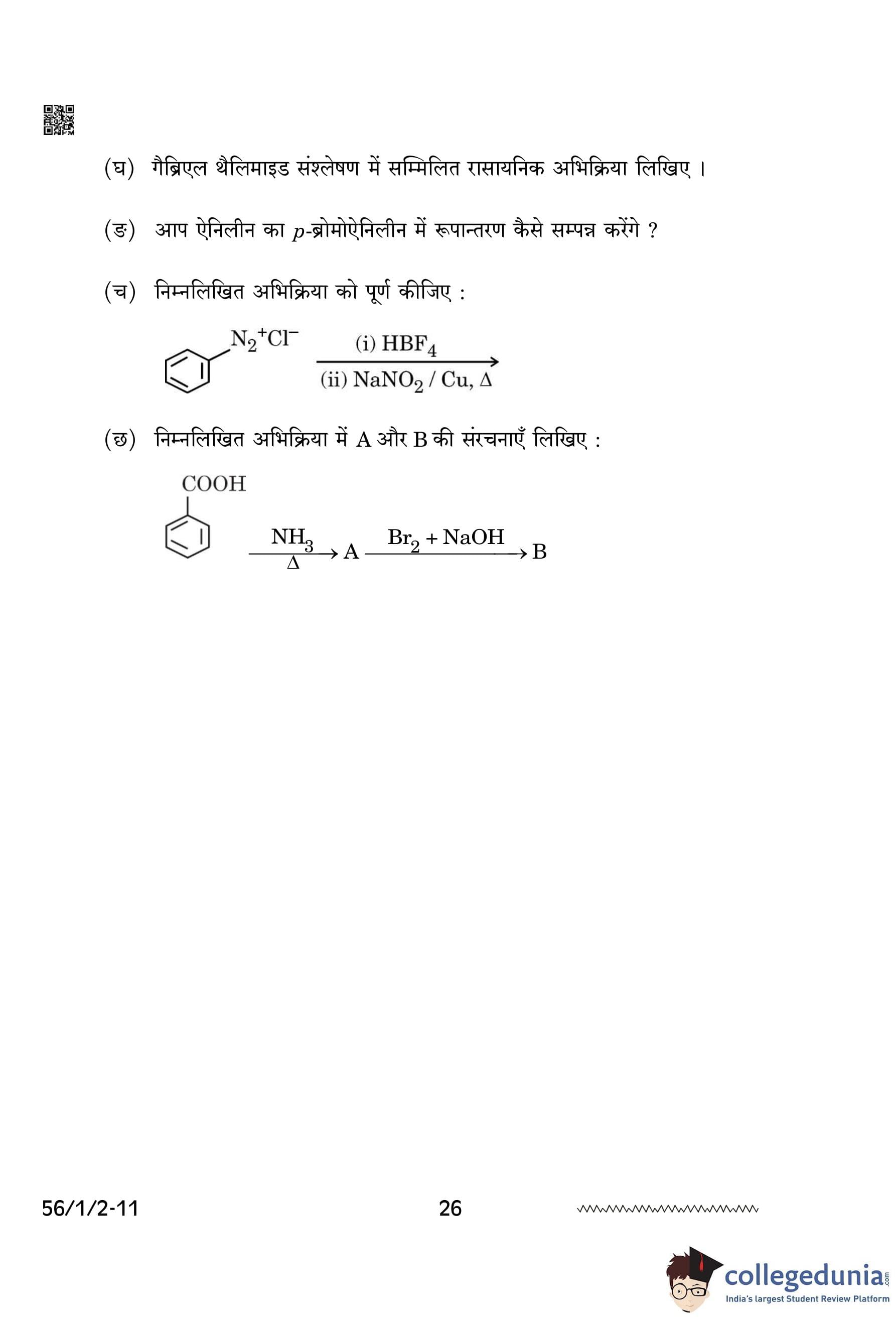
(f) Complete the following reaction:
\[ C_6H_5N_2^+Cl^- \xrightarrow{(i) HBF_4} \xrightarrow{(ii) NaNO_2/Cu, \Delta} \quad ? \]
(g) Write the structures of A and B in the following reaction:
\[ C_6H_5COOH \xrightarrow{NH_3, \Delta} A \xrightarrow{Br_2/NaOH} B \]





























Comments