Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
Human Reproduction is a form of sexual reproduction in which fertilization in human occurs. It is typically a process in which male and female gets involved in sexual intercourse. During that intercourse, the reproductive systems of male and female result in the fertilisation of the female's ovum by male’s sperm.
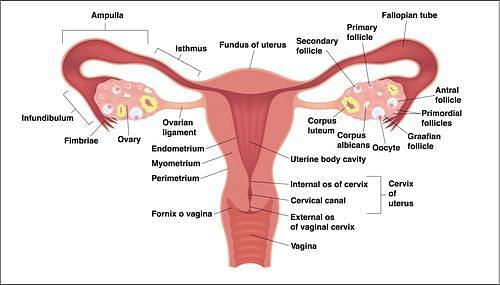
Human Reproductive System - Female
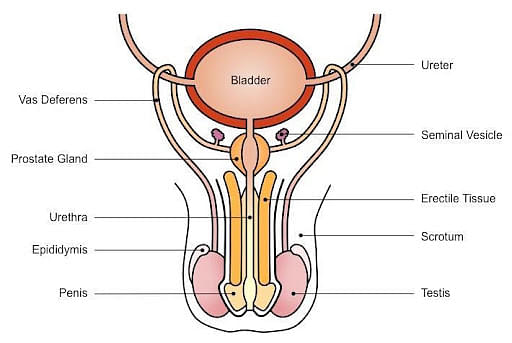
Human Reproductive System - Male
Question 1: The process of the releasing of eggs from the female ovary is known as:
- Gestation
- Plantation
- Parturition
- Ovulation
Click here for the answer
Answer: d. Ovulation
Explanation: Ovulation in a human female can be defined as the release of a mature egg from one of the two ovaries present in the female body. This occurs when the follicles of the ovary rupture. It occurs at around the 14th day of the 28-day menstrual cycle. In this process after the release of eggs, it travels through the fallopian tube which is the place where fertilization takes place.
Question 2: Which part of the human sperm plays a key role during the penetration of the egg membrane?
- Tail
- Allosome
- Autosome
- Acrosome
Click here for the answer
Answer: d. Acrosome
Explanation: An acrosome is an organelle that has an oval-shaped head as well as a cap-like covering in a normal sperm cell. Acrosomes have the necessary enzymes that aid the process of breaking down the outer membrane of a female egg cell. This thus facilitates the fertilization of the mature egg cell.
Question 3: The accessory genital gland of a human male is/are:
- Prostate gland
- Cowper’s gland
- Seminal gland
- All of the above
Click here for the answer
Answer: d. All of the above.
Explanation: All of these glands, namely Prostate gland, Cowper’s gland and Seminal gland, secrete the necessary fluids that help in the lubrication of the reproductive system of males and its sperms. The sperms then get distributed in the fluid which in turn aid in the transportation of sperms into the female body.
Question 4: Which hormone influences ovulation inside the female body?
- Luteinising hormone
- Estrogen
- Follicle-stimulating hormone
- Progesterone
Click here for the answer
Answer: a. Luteinising hormone
Explanation: Luteinising hormone (LH) is a hormone secreted by the gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. These are also known as gonadotropic hormones. They also aid the stimulation of corpus luteum for the production of progesterone while also stimulating the estrogen and progesterone production from the ovary. This hormone thus plays a key role in the menstrual cycle of human females.
Question 5: The cell division does not occur in which of the following processes?
- Oogenesis
- Spermiogenesis
- Spermatogenesis
- Embryogenesis
Click here for the answer
Answer: a. Oogenesis
Explanation: Oogenesis can be defined as the growth process wherein a primary egg cell (also known as the ovum) present inside a human female grows to become a mature ovum. These cells are also known as the primary ova. They stay dormant till the time ovulation begins and the mature egg is made to release from either one of the ovaries. It can also be called a cell maturity process. Thus, this is a process that does not involve any cell division.
Question 6: What is the outermost layer of a blastocyst known as?
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Trophoblast
- Mesoderm
Click here for the answer
Answer: c. Trophoblast
Explanation: Trophoblasts are a group of cells that collectively form the outermost layer of a blastocyst. These can be seen in the four days after the fertilization process occurs in the human body. These are very important as they provide the necessary nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They help in the implantation of the embryo and its interaction with the decidualized maternal uterus.
Question 7: Spermiation can be defined as the process of the release of sperms from
- Vas Deferens
- Epididymis
- Seminiferous tubules
- Prostate gland
Click here for the answer
Answer: c. Seminiferous tubules
Explanation: Spermiation can be defined as the process in which the mature sperms from the seminiferous tubules. This process takes place over a period of several days at the apical edge of the seminiferous epithelium and also includes a range of discrete steps. This is a determinant of the sperm count that enters the epididymis. It is accomplished by multiple coordinated interactions between various structures, cellular processes and also adhesion complexes that together make up the spermiation machinery.
Question 8: The temperature of the male scrotum that is essential for the normal functioning of the testis is always ___ below the body temperature.
- 8 °C
- 6 °C
- 4 °C
- 2°C
Click here for the answer
Answer: d. 2 °C
Explanation: Scrotum, which is the sac-like structure that stays suspended from the root of the penis, aids in the maintenance of temperature that is required by spermatogenesis. This is achieved by locating the testes outside the body cavity. The scrotum also acts as a climate control system for the testes to maintain the temperature fit for sperm production i.e., 34 °C. This temperature is nearly 2 °C lower than the ideal body temperature that is about 36.5 °C.
Question 9: What is the name of the last part of the oviduct?
- Ampulla
- Fimbriae
- Isthmus
- Infundibulum
Click here for the answer
Answer: c. Isthmus
Explanation: The last part of the oviduct is known as the Isthmus. It is the inferior-posterior part of the uterus. It is connected to the uterus and also has a narrow lumen. It is the connection between the body and the cervix. It has the potential to become highly compressible during the times of pregnancy due to increased rates of production of the progesterone hormone. It also serves the purpose of forming a reservoir for sperms.
Question 10: Which group of cells in the male gonad from the following groups represent the haploid cells?
- Primary spermatocytes
- Secondary spermatocytes
- Germinal epithelial cells
- Spermatogonial cells
Click here for the answer
Answer: b. Secondary spermatocytes
Explanation: Haploid can be defined as a quality of a cell that has a single set of chromosomes i.e., half of the normal number of chromosomes (23 chromosomes in humans). Secondary spermatocytes are a group of haploid cells that undergo the second meiotic division and give rise to two spermatids that differ from the secondary spermatocytes because of smaller nuclei and homogeneously distributed chromatin.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments