Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
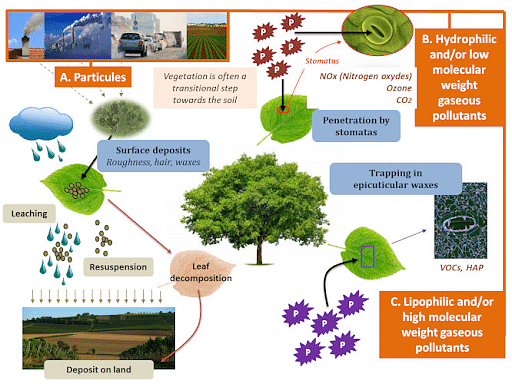
Effects of Air Pollution on plants is vast. Air Pollution deposits a layer of dust and dirt on the surface of the leaves thereby blocking the respiration process through stomata. As plants completely depend on the atmosphere for their survival, pollutants such as ozone, sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen dioxide, etc are the primary cause for the stunted growth and death of plants.
Read Also: Our Environment: Types, Components and Functions
| Table of Content |
Key Terms:- Air pollution, Pollution, pollutants, respiration, living organisms, health, stomata, Air, ozone, sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen dioxide, atmosphere
Read Also: Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Substances
What is Air Pollution?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Air Pollution is an undesirable change in the atmosphere that is caused by substances known as pollutants. Air Pollution has a negative effect on all living and non-living organisms. It affects the health of human beings in many degrees. But it affects the plants the worst as plants completely depend on the atmosphere for their survival.

Air Pollution
Read Also: Ozone Layer Depletion
Pollutants that affect Plants
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the pollutants that affect the well-being of plants are as follows.
Ozone: Ozone is beneficial for life on earth, it stops ultraviolet rays to pass through the atmosphere. However, it can cause a lot of health issues such as breathing problems, congestion, throat irritation etc if found on the ground. Ozone causes oxidative damage to the cell membranes of the plant which results in the loss of integrity and function for the plant cell membrane, it also affects photosynthesis.

Oxidative Damage
Sulphur Dioxide: Plants get affected by sulphur dioxide because of acid rain. It results in the discoloration of the leaves, disrupts certain mechanisms of photosynthesis. Furthermore, sulphur dioxide affects the opening of the stomata resulting in excessive loss of water.
Read Also: Food Chains and Webs
Damages on Plants due to Pollution
Nitrogen Dioxide: It is formed from the combustion of fossil fuels and emissions from refining petroleum. Nitrogen Dioxide is quite toxic and stunts the growth of plants.
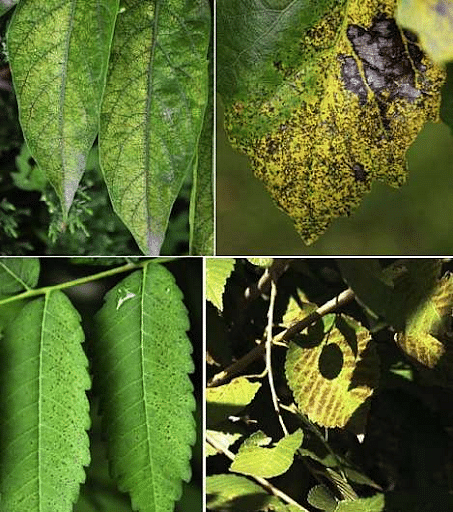

Effect of pollutants on plants
Lead and Heavy metals: Aerosols of lead and other toxic heavy metals contribute to air pollution. This can cause plugging of stomata which would decrease the gas diffusivity rate. It also affects the net photosynthesis rate.
Read Also: Components of Ecosystem
Causes of Air Pollution
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Anything humans do that involves burning things, using chemicals or producing piles of dust has the potential that can cause air pollution. Some of the causes of air pollution are as follows.
Industrial Burning: Heavy industries such as thermal power industries and refining factories release a huge amount of poisonous gases in to the atmosphere and contribute to an increase in air pollution.
Automobiles: Around 27% of the emission of greenhouse gases are due to automobiles. The emission of poisonous gases from automobiles takes a heavy toll on the quality of the air.
Read Also: Air Pollution Control

Causes of Pollution
Wildfire: The smoke produced by the forest fire contains carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde - all known for warming the planet.
Volcano eruption: Giant volcanic eruptions spew ashes and a huge amount of sulfur gases, as well as carbon dioxide. The sulfur gases when combined with water vapour in the atmosphere from sulfur and sulfuric acid which are detrimental to humans, plants and animals. The magma from the volcanoes destroys all the vegetation coming in their way.
Read Also: Montreal Protocol
Most affected Plants by Air Pollution
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
As plants heavily depend on the atmosphere for their survival, they end up consuming all the air pollutants such as ozone, nitrogen oxides, heavy metals, smoke and particulate matter. Some of the plants that are most affected and very sensitive to these pollutants are listed below.
- Trees: American Quaking Aspen, Phantom Orchid, Honeylocust, Walnut, Poplar, Oak, Colombo, Green Dragon, Rosewood, Willow, etc.
- Crops: Wheat, Rice, Tomato, Tobacco, Soybeans, Cantaloupe, Beets, Sunflower, Carrots, Sweet corn, Gourds, Green Peas, Muskmelon, Alfalfa, Turnips, Grapes, Peaches, Watermelon, Squash Potato, and Strawberries.

Effects of pollution on tomato leaves
- Shrubs: Crabapple, Ponderosa pine, and citrus
- Leafy greens: Spinach and Celery
Read Also: Air Pollution prevention and control act
Things to Remember
- Air Pollution is an undesirable change in the atmosphere that is caused by substances known as pollutants.
- Ozone causes oxidative damage to the cell membranes of the plant which results in the loss of integrity and function for the plant cell membrane, it also affects photosynthesis.
- Plants get affected by sulphur dioxide because of acid rain which results in discolouration.
- Nitrogen Dioxide is quite toxic and stunts the growth of plants.
- Aerosols can cause plugging of stomata which would decrease the gas diffusivity rate.
- Wheat, Rice, Tomato, Tobacco, Soybeans, Cantaloupe, Beets, Sunflower, Carrots, Sweet corn, Gourds, Green Peas, Muskmelon, Alfalfa, Turnips, Grapes, Peaches, Watermelon, Squash Potato, and Strawberries are some of the crops that are affected by air pollution.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. Explain the significant environmental effects of Air Pollution? (2 marks)
Ans. Acid rain harms trees and causes soils and water bodies to ferment, making water harmful for some fish and other natural life. Depletion of the ozone layer is causing UV radiation to arrive at earth causing skin cancer and also harms crops for example soybeans. It also prompts a decrease in the horticultural yield.
Ques. What do you mean by acid rain? How does it affect both living and non-living things? (5 marks)
Ans. Due to fossil fuel and industrial combustions that mostly emit nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere. Water vapour present in the atmosphere reacts with these gases to form nitric acid and sulphuric acid. Normal rainwater is slightly acidic with a pH range of 5.3-6.0 because carbon dioxide and water present in the air react together to form carbonic acid, which is a weak acid. When the pH level of rainwater falls below this range due to combining with these acids in the atmosphere, it becomes acid rain.
Acid rain has significant effects on the world environment and public health.
- Effect on aquatic environment: Acid rain lowers pH level below 5, most fish eggs cannot hatch. Lowering in pH can also kill adult fish.
- Effect on forests: It makes trees vulnerable to disease, extreme weather, and insects by destroying their leaves, damaging the bark and arresting their growth.
- Effect on soil: Acid rain highly impacts soil microbes and biological activity as well as soil chemical compositions. Thus affecting crop production.
- Effect on architecture and buildings: Acid rain on buildings, especially those constructed with limestone, react with the minerals and corrode them away. This leaves the building weak and susceptible to decay. Irreplaceable damage can be caused to the old heritage buildings.
- Effect on public health: When in the atmosphere, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide gases, degrades visibility and can cause accidents, leading to injuries and deaths. Intensified levels of acid depositions in dry form in the air can cause lung and heart problems such as bronchitis and asthma.
- Other effects: Acid rain leads to weathering of buildings, corrosion of metals, and peeling of paints on surfaces. Acid rain also corrodes metals like steel, bronze, copper and iron.
Ques. Which air pollutants mostly affect the plants? (2 marks)
Ans. Major pollutants are hydrofluoric acid, sulphur oxides, acid rain. The hydrofluoric acid leads to a cellular metabolism disruption of calcium. Sulphur oxides lead to the disturbing mechanism of chlorophyll and acid rain causes deficiencies of minerals which leads to yellowing of the leaves due to leaching of rainwater of the Ca, K and Mg mineral elements.
Ques. Discuss the causes and effects of global warming. What measures need to be taken to control global warming? (3 marks)
Ans. An increase in the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases has resulted in the rise of atmospheric temperature by 0.6 C . Causes of global warming :
- Increase in concentration of greenhouse gases
- Increase of automobiles and use of fossil fuel.
- Deforestation and change in land use.
- CFC and aerosol emission from refrigerator and aeroplane.
- Increased particulate matter in the lower atmosphere.
Ques. We should plant trees and nurture the ones already present in the neighborhood. Why? (2 marks)
Ans. Plants absorb carbon dioxide gas and release oxygen. Thus, they play important role in purifying the earth’s atmosphere. By absorbing CO2 they also reduce the chance of global warming. Trees provide habitat to many birds and animals. They maintain the water cycle in nature and also prevent soil erosion.
Ques. What are the Effects of Global Warming? (2 marks)
Ans. - CO2 fertilisation effect.
- Many species of plants, being sensitive to temperature will die with a sudden rise in temperature and their places will be taken over by scrub vegetation.
- Loss of biodiversity
- Rise in sea level
-Possibilities of drought and floods
-Eruption of plant disease and pests.
- Change in rainfall pattern
Ques. Explain how does the inflow of a large number of nutrients like phosphates and nitrates into the water body drastically affects the aquatic life there. Name the phenomenon responsible. (CBSE 2014) (2 marks)
Ans. The inflow of large amounts of nutrients like nitrates and phosphates initially encourages the growth of aquatic organisms, plants and animals. With time as the organic matter increases, debris along with silt piles up at the bottom making the water body shallower and warmer. This leads to the gradual appearance of floating and marshy plants and is eventually converted into the lake. Hence, aquatic life gets severely affected and disrupted.
This phenomenon is called eutrophication. It may be natural or artificial due to the result of human activities.
Ques. How does eutrophication lake take place? Explain. (CBSE 2011) (2 marks)
Ans. The natural ageing of a lake is called eutrophication. In a young lake, there is very little life. Over time, streams drain into it and water becomes enriched with nutrients like phosphate and nitrates.
As a result, phytoplankton and some other plants flourish well. Due to this, the organic matter increases in the lake, water becomes warmer and shallower. Hence, decomposers also start growing.
The high numbers of decomposers make use of the large quantity of oxygen for decomposition. This leads to depletion of dissolved oxygen in the water and mortality of fish and other aquatic organisms. The eutrophied water bodies can lead to Algal Bloom, which further add organic matter to the lake. These consume more oxygen leading to its depletion.
Ques. What are the methods that can reduce the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases? (2 marks)
Ans. - Reducing the greenhouse gas emission by limiting the use of fossil fuels and by developing alternative renewable sources of energy
- Increasing the vegetation cover mainly the forests for photosynthesis utilization of CO2
- Minimizing the use of nitrogen Fertilizers in agriculture for reducing N2O emissions.
- Developing substitutes of chlorofluorocarbons.
Ques. Why does an ozone hole form over Antarctica? How will enhanced ultraviolet radiation affect us? (2 marks)
Ans. Chlorofluorocarbons mainly released in the atmosphere by developed countries, slowly enter the stratosphere and the winds move them towards the poles. Environmental conditions prevailing in Antarctica during winter months, there is no sunlight in Antarctica and extremely low temperature facilitates the formation of ice clouds. During winter, the natural circulation of wind completely isolates Antarctica air from the rest of the world.
The ice clouds provide the catalytic surface for the reaction of chlorine atoms and then ozone. But this degradation of ozone occurs with the return of solar radiation to Antarctica during spring. This results in the thinning of the ozone layer every year over most of Antarctica. This hole disappears in summer due to the warming up of air and mixing up of Antarctica air with that of the rest of the world. Enhanced UV radiations on earth cause: Skin cancer, Blindness and increased chances of cataracts in the eyes, Malfunctioning of the immune system and a higher number of mutations.
Ques. Explain the differences between pure air and polluted air. (2 marks)
Ans. Pure air contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 0.03% CO2. Other gases such as argon, methane, neon, water vapour, etc. are also found in small quantities. When this air is contaminated by unwanted substances which have a harmful effect on both living and non-living things like nitrogen oxide, sulphur oxide, carbon monoxide, etc., is said to be polluted.
Ques. Why does the increased level of nutrients in the water affect the survival of aquatic organisms? (2 marks)
Ans. Increased levels of nutrients in the water affect the survival of aquatic organisms as these act as nutrients for algae to flourish and once these algae die, they serve as food for decomposers like bacteria and a huge amount of oxygen in the water body gets used up. This results in decrease in the oxygen level, which may kill aquatic organisms.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here:https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Do Check Out:




Comments