The CUET Physics 2025 exam was conducted between 13th May and 3rd June, and the question paper, answer key, and solution PDF are available for download here.
According to the revised exam pattern, students must attempt all 50 questions within 60 minutes, with the total marks being 250. Each correct response carries +5 marks, while each incorrect answer incurs a –1 mark penalty.
CUET UG Physics 2025 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| CUET UG Physics Question Paper with Solutions PDFs | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
CUET UG Physics 2025 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
If the protons and electrons are the only basic charges in the universe, all the observable charges have to be integral multiples of e. Thus, if an object contains x electrons and y protons, the net charge on the object will be
A charge of magnitude \(3 \times 10^{-7}\) C is located at a distance of 0.09 m from a point P. Obtain the work done in bringing a charge of \(2 \times 10^{-9}\) C from infinity to the point P.
In a series combination of capacitors connected across a battery
Two point charges, 4 µC and -3 µC (with no external field) are placed at (-6 cm, 0, 0) and (6 cm, 0, 0), respectively. The amount of work required to separate the two charges infinitely away from each other will be
If the net flux through a cube is 1.05 N m\(^2\) C\(^{-1}\), what will be the total charge inside the cube? (Given: The permittivity of free space is \(8.85 \times 10^{-12}\) C\(^2\) N\(^{-1}\) m\(^{-2}\)).
A parallel plate capacitor having plate area 200 cm² and separation 2.0 mm holds a charge of 0.06 µC on applying a potential difference of 60 V. The dielectric constant of the material filled in between the plates is.
The electric potential due to an electric dipole
(A) depends on r, where r is the magnitude of position vector \(\vec{r}\)
(B) depends on the angle between the position vector \(\vec{r}\) and the dipole moment vector \(\vec{p}\)
(C) falls off at long distances, as \(1/r^2\)
(D) does not depend upon the distance separating the charges
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Two point charges placed a distance d apart in vacuum exert a force of magnitude F on each other. One of the two charges is doubled. To keep the magnitude of force same the separation between the charges should be changed to
Conductors develop electric currents in them
Resistivity of a conductor depends on
In the (i) absence of electric field, and in the (ii) presence of electric field, the paths of electrons between successive collisions with the positive ions of the metal, are
A resistor develops 800 J of thermal energy in 20 s on applying a potential difference of 20 V. Its resistance is
A wire of resistance 4 \(\Omega\) is used to make a coil of radius 7 cm. The wire has a diameter of 1.4 mm and the resistivity of its material is 2 x 10\(^{-7}\) \(\Omega\) m. The number of turns in the coil will be
A battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 3 \(\Omega\) is connected to an external resistor. If the current in the circuit is 0.6 A, the voltage across the external resistor will be
A uniform wire of resistance 12 \(\Omega\) is cut into three pieces in the ratio of length 1: 2: 3. Now the three pieces are connected to form a triangle. A cell of emf 8 V and internal resistance 5 \(\Omega\) is connected across the highest of the three resistors. The current through the circuit is:
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 5.0 A m² has poles 20 cm apart. The pole strength would be
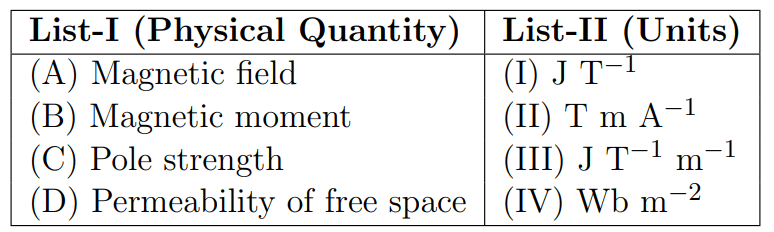
Match List-I with List-II
A long wire with a small current element of length 1 cm is placed at the origin and carries a current of 10 A along the x-axis. The magnitude of the magnetic field, due to the element, on the y-axis at a distance 0.5 m from it, would be
A conductor is placed along z-axis carrying current in z direction in uniform magnetic field directed along y-axis. The magnetic force acting on the conductor is directed along:
A galvanometer of resistance 520 \(\Omega\) is shunted with 20 \(\Omega\) resistance to convert it into an ammeter. The resistance of the ammeter will be
The magnitude of magnetic field inside a solenoid of length 0.3 m having 800 turns carrying a current of 6 A is
A charged particle accelerated through a potential difference of V volts acquires a speed u. The particle is then made to enter perpendicularly in a uniform magnetic field B. The radius of the circular path followed by the charged particle will be proportional to
Figure shows a coil C connected to a galvanometer G. When the North-pole of a bar magnet is pushed towards the coil, the pointer in the galvanometer deflects. Regarding this set up, the following statements are given:
(A) It indicates the presence of electric current in the coil.
(B) The deflection is found to be smaller when the magnet is pushed towards the coil faster.
(C) There is repulsion in the moving magnet and the magnetic pole induced in the coil facing towards the N pole of the magnet.
(D) If the bar magnet does not move, there is no induced current in the coil.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

Figure shows a rectangular conductor PQRS in which the conductor PQ is free to move. The conductor PQ is moved towards the left with a constant velocity V as shown in the figure. Assume that there is no loss of energy due to friction. What will be the magnetic flux linked with the loop PQRS and the motional emf?

The average emf induced in a coil is 2 V when current is changed in 0.4 s
(A) from 5 A to 2 A and the self-inductance of the coil is 0.266 mH
(B) from 4 A to 4 A in the opposite direction, the self-inductance of the coil is 0.10 mH
An inductor of 500 mH is in series with a resistance and a variable capacitor connected to a source of frequency 0.4 kHz. The value of capacitance of the capacitor to get a maximum current will be
A 12 V battery connected to a 6 \(\Omega\), 10 mH coil through a switch drives a constant current in the circuit. The switch is suddenly opened. Assuming that it took 1 ms to open the switch, the average emf induced across the coil would be
For an ac source rated at 220 V, 50 Hz, which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following statements is not correct for electromagnetic induction?
Maxwell's displacement current is
Match List-I with List-II

The electric field E associated with a progressive electromagnetic wave is given by E = E\(_0\)sin(kx - \(\omega\)t). If B\(_0\) is the amplitude of the magnetic field associated with the wave, then
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) All mirrors follow the laws of reflection.
(B) The angle between the ray of incidence and the plane surface of the mirror is equal to the angle between the plane surface of mirror and the ray of reflection for plane mirror
(C) the rays coming parallel to the principal axis will go after reflection through the focus of the curved mirror
(D) the rays coming to the pole of a curved mirror making an angle with axis will be reflected making the equal angle with the axis on the other side of the axis.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(A) The power of a lens is the ability of the lens to converge or diverge the incident rays.
(B) S.I unit of the power of a lens is dioptre while focal length is in centimetres
(C) For a lens of larger focal length, power is smaller
(D) In any combination of lenses, the power of combination is not algebraic addition of power of combined lenses
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In an experiment with a convex lens, the length of an image is 1 cm, and the object length is 5 cm. If the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the lens, then the focal length of the lens is
In a Young's double-slit experiment, two slits are 1.5 mm apart while the screen is 1.2 m away. When a light of wavelength 600 nm is incident on slits, the fringe width will be
The critical angle of incidence \(i_c\) for a ray incident from a denser to rarer medium, is that angle for which
A polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polarizers. The intensity of transmitted light would be maximum, when the angle between the axes of the first polarizer and the polaroid sheet is
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) Total internal reflection occurs when a ray of light travels from a rarer transparent medium to a denser medium.
(B) In total internal reflection, the incident ray of light remains in the same medium after reflection.
(C) In total internal reflection, the angle of incidence inside the denser transparent medium is equal to the angle of reflection in the same medium.
(D) In total internal reflection inside a denser medium there is no angle of refraction
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If focal length of a concave lens is 50 cm, then the power of the lens would be
The photoelectric current is directly proportional to the number of photo electrons emitted per second. This implies that
The de-Broglie wavelength associated with a ball of mass 150 g traveling at 30.0 m/s would be
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) A nucleus of mass number A has a radius R given by the expression R = R\(_0\)A\(^{1/3}\)
(B) Volume of nucleus is proportional to mass number A
(C) The density of nucleus increases with the radius of nucleus.
(D) Density of nuclear matter does not depend on its mass number A
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
An electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom absorbs 12.09 eV energy. The angular momentum of the electron increases by
Which of the following statements are correct?
(A) The electrostatic repulsive force between the protons can be greater than the nuclear force to bind the nucleons together inside a nucleus.
(B) The repulsive electrostatic force between protons in smaller nuclei is much smaller than the nuclear force between nucleons inside a nucleus.
(C) The gravitational force between nucleons is much smaller than the nuclear force between the nucleons inside a nucleus.
(D) The binding energy per nucleon between nucleons is almost constant because the nuclear force is a long range force.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Below given are some statements about electronic devices:
(A) Diodes can be used for rectifying an ac voltage.
(B) For semiconductors, band gap energy E\(_g\) > 3 eV.
(C) By changing the external applied voltage, junction barriers can be changed.
(D) p-n junction is the 'key' to all semiconductor devices.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
On connecting a device X in a series circuit with a battery and a resistor, a current passes through the circuit. On reversing the polarity of the battery, the current in the circuit drops to almost zero. The device X may be a
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true for p-type semiconductors?
(A) Holes are minority carriers and pentavalent atoms are the dopants.
(B) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants.
(C) Holes are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants.
(D) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent atoms are the dopants.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In the following nuclear reaction, \(^1_0n + ^{235}_{92}U \rightarrow ^{140}_{54}Xe + ^b_aSr + 2(^1_0n)\) we have
A proton accelerated through a potential difference of V volts has a de-Broglie wavelength \(\lambda\) associated with it. In order to get the same wavelength associated with an \(\alpha\)-particle, the required accelerating potential is





Comments