CUET 2023 Physics Answer Key for all shifts is made available for download here. NTA to release CUET Answer Key 2023 PDF for Physics soon on cuet.samarth.ac.in. Download CUET 2023 Physics Question Paper PDF
Candidates can download the answer key and question paper PDFs for CUET UG 2023 Physics exam using the links given below.
CUET 2023 Physics Answer Key and Question Paper with Solutions PDF
| CUET 2023 Physics Question Paper with Answer Key | Check Solution |

CUET 2023 Physics Questions with Solutions
Question 1:
Choose the correct statements from the following:
A. The total charge in any isolated system remains constant.
B. When some charge is transferred to a conductor, it stays at the same place without getting distributed over the entire surface.
C. One Coulomb of negative charge is the total charge of \(6.25 \times 10^{18}\) electrons.
D. Electric field is a scalar field.
E. Permanent dipole means that the dipole moment \(\vec{P}\) exists irrespective of external electric field \(\vec{E}\).
Choose the correct alternative from the following:
Choose the correct answer from the following:
If three charged particles are collinear and are in equilibrium, then:
An isolated sphere has a capacitance of 60 pF, what is the radius of the sphere?
The electric field intensity due to an infinite thin plane sheet of surface charge density \(\sigma\) is:
Three capacitors of capacitances 3 \(\mu\)F, 6 \(\mu\)F and 12 \(\mu\)F are connected in series. Find the potential difference across the 6 \(\mu\)F capacitor, if a battery of 7 V is connected across this combination:
Kirchhoff's Second Law is based on law of conservation of:
Identify the graph from the following showing the temperature dependence of resistivity for a typical semiconductor?

In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of 1.5 V gives a balance point at 45.0 cm length of the wire. If the cell is replaced by another cell and the balance point shifts to 75.0 cm, what is the emf of the second cell?
A room heater is rated 750 W, 220 V. An electric bulb rated 200 W, 220 V is connected in series with this heater. What will be the power consumed by the bulb and the heater respectively, when the supply is at 220 V?
A cell of constant emf is first connected to a resistance \(R_1\) and then to \(R_2\). If power delivered in both cases are same, then the internal resistance of the cell is:
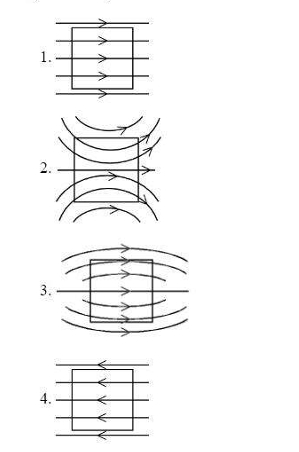
A uniform magnetic field, parallel to the plane of the paper existed in space initially directed from left to right. When a bar of soft iron is placed in the field parallel to it, the lines of force passing through it will be represented by:
To protect galvanometer from possible damages due to large current, which of the following should be connected to its coil:
The charge which is a source of electric field but not of magnetic field is:
There is a thin conducting wire carrying current. The value of magnetic field induction at any point on the conductor would be:
The coercivity of a bar magnet is 140 A m\(^{-1}\). To demagnetize it, it is placed inside a solenoid of length 1.6 m and number of turns 112. What is the current flowing through the solenoid?
Magnetic field \(|B|\) at a point \(P\) in the following network is:

Which one out of the following is not an application of eddy currents?
In an a.c. circuit, the rms voltage is \(100\sqrt{2}\) V. The peak value of voltage would be:
A square loop of copper wire is pulled through a region of uniform magnetic field as shown. Rank the pulling forces \(F_A\), \(F_B\), \(F_C\), and \(F_D\) that must be applied to keep the loop moving with constant speed (\(\vec{v}\)):

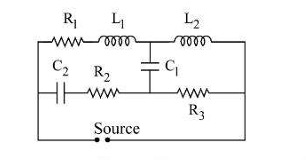
Find the effective impedance in the circuit if the source is:
a) DC source and b) High frequency AC source
In AC circuits, the relation that holds is \( Z = \frac{E_U}{I_U} \), where:
When 100 V dc is applied across a solenoid, a current of 1 A flows in it. When 100 V ac is applied across the same solenoid the current drops to 0.5 A. If the frequency of the ac source is 50 Hz, the impedance and inductance of the solenoid are:
Match List I with List II
LIST I LIST II
A. X-rays I. \(1 \times 10^{16} - 3 \times 10^{21} \, Hz\)
B. Microwaves II. \(1 \times 10^{9} - 3 \times 10^{11} \, Hz\)
C. Radiowave III. \(1 \times 10^{8} - 5 \times 10^{22} \, Hz\)
D. \(\gamma\)-rays IV. \(5 \times 10^{5} - 10^{9} \, Hz\)
An electromagnetic wave going through vacuum is described by \( E = E_0 \sin(kx - \omega t) \), \( B = B_0 \sin(kx - \omega t) \), then:
Light is traveling from one medium to another medium as given in the options. In which of the following options total internal reflection will be possible?
A slit of width \(e\) is illuminated by light of wavelength \(\lambda\). What should be the value of \(e\) to obtain the first maximum at an angle of diffraction \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)?
In Young's double slit experiment, yellow light of wavelength 640 nm produces fringes of width 0.8 mm. What will be the fringe width if the light source is replaced by another monochromatic source of wavelength 720 nm and the separation between the slits is made thrice?
An astronomical telescope consists of an objective of focal length 50 cm and eyepiece of focal length 2 cm is focused on the moon so that the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision (25 cm). Assuming angular diameter of the moon as \( \frac{1}{2^\circ} \) at the objective, the angular size of image is:
A spherical air lens of radii \( R_1 = R_2 = 10 \, cm \) is cut from a glass (\(\mu = 1.5\)) cylinder as shown in the figure. Its focal length is \( f_1 \). If a liquid of refractive index \( \mu_2 \) is filled in the space, then the focal length of the liquid lens becomes \( f_2 \). Calculate \( f_1 \) and \( f_2 \). Choose the correct options from the following.

Linear magnification produced by a mirror is +1.5. What is the correct mirror and object position?
The type of wavefront that emerges from a distant light source is:
A proton, a deuteron, an electron, and an \(\alpha\)-particle have the same energy. Their deBroglie wavelengths are \( \lambda_p \), \( \lambda_d \), \( \lambda_e \), and \( \lambda_{\alpha} \), respectively. Which of the following is correct?
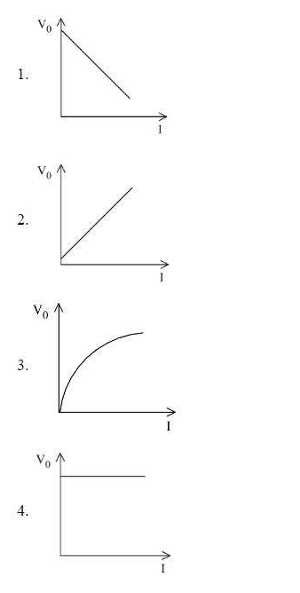
The correct curve between stopping potential \( V_0 \) and intensity of incident radiation \( I \) at constant frequency is:
Which of the following statements are correct?
A. Photoelectric current depends on the intensity of light.
B. The stopping potential is directly related to the maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted, which is dependent on the intensity of incident radiation.
C. Photoelectric emission from a metal surface occurs due to absorption of a photon by an electron.
D. Photoelectric effect follows the law of conservation of energy.
What will be the energy released in the fusion process of two lighter nuclei of masses \( m_1 \) and \( m_2 \) into a nucleus of mass \( M \)?
Select the correct statement for nuclear force:
The energy diagram of a hydrogen atom is given below. Arrange the wavelengths corresponding to different emissions in increasing order.

Match List I with List II
LIST I LIST II
A. Rn^{222}_{86} \rightarrow Po^{218}_{84} III. \alpha particle
B. Bi^{214}_{83} \rightarrow Po^{214}_{84} I. \beta^- particle
C. Th^{234}_{90} \rightarrow U^{234}_{92} I. \beta^- particle
D. Na^{22}_{11} \rightarrow Na^{22}_{10} II. \beta^+ particle
Which of the following statements is NOT correct:
Identify the logic operation carried out by the following circuit.

In the figure, the potential difference between A and B is:

Match List I with List II
LIST I LIST II
A. Zener Diode II. Voltage Regulator
B. LED III. Remote Control
C. Rectifier IV. AC to DC
D. Photo diode I. Detect optical signals
The height of a TV tower is 180 m. To what distance the transmission can be made from this tower, if the radius of earth is \(6.4 \times 10^6\) m?
Match List I with List II:
LIST I LIST II
A. Modulation I. Retrieval of information from the carrier wave at the receiver
B. Baseband signals II. Frequency range over which an equipment operates
C. Demodulation III. Superimposition of a signal on a high frequency wave
D. Bandwidth IV. Band of frequencies representing the original signal
Two point charges \(q\) and \(-3q\) are kept 12 cm apart. The distance of the point from \(q\) on the line between two charges at which potential due to this system of charges is zero will be:
Mobility of electrons
The displacement current due to time varying electric field is given by
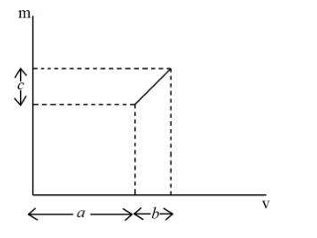
The graph shows the variation of the magnification (m) produced by a thin lens with image distance (v). The focal length of the lens is:
Match List I with List II using Bohr's atomic model:
LIST I LIST II
A. Radius of electron orbit I. directly proportional to \( n^2 \)
B. Angular momentum of electron II. directly proportional to \( n \)
C. Velocity of electron III. inversely proportional to \( n \)
D. Energy of electron IV. inversely proportional to \( n^2 \)




















































CUET Answer Key 2023 PDF for Other Subjects
Also Check:





Comments