Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
A wiring system is a network of wires that connect various accessories for the distribution of electrical energy from the supplier metre board to a variety of electrical energy consuming devices such as lamps, fans, and other domestic appliances via regulating and safety devices. Various types of wiring are used in homes, including Electrical wiring for lighting and power distribution, telephone, heating etc. Appliances at our homes, draw electricity through wires and convert it to mechanical energy.
| Table of Content |
Also Read: Types of Switches
Related Links
- Appearing for JEE Main, Download JEE Mains PYQ for all sabjects
- Appearing for NEET, Download NEET PYQ for all subjects
Key Takeaways: Electrical Wiring, Domestic Wiring, Live Wire, Earth Wire, Neutral Wire
What is Electrical Wiring?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A wiring system is a network of wires that connect various accessories for the distribution of electrical energy from the supplier metre board to a variety of electrical energy consuming devices such as lamps, fans, and other domestic appliances via regulating and safety devices.

Electrical Wiring
Electrical Wires
A wire is a single electrical conductor or channel capable of carrying electricity. A wire's conductor is composed of copper or aluminium, or copper-sheathed aluminium coated in a non-conductive plastic coating. A cable, on the other hand, is the assembly of one or more of these wires in a different fashion for the purpose of transmitting an electric current.
Read More: Notes on Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
Types of Electrical Wiring
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The different types of electrical wiring are as follows.
Tee system or Joint box system
This wiring is used to connect appliances together. It uses a small amount of cable and is inexpensive, making it perfect for temporary installations.
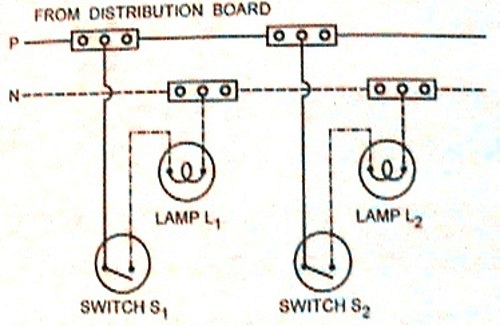
Tee System Wiring
Loop-in system
This system is set up in such a way that the lighting and other appliances are connected in parallel, allowing each device to be controlled separately. Thus, it makes it easier to find a flaw such as a damaged wire in such a system.

Loop in System Wiring
Read More: Intrinsic Semiconductors
Cleat Wiring
This wiring is made up of regular VIR or PVC insulated wires that are braided and placed on the walls and ceilings using porcelain cleats, wood, or plastic. It is a sort of makeshift system that's not fit for residential use, however perfect for temporary settings such as buildings under construction.

Cleat Wiring
Batten Wiring
TRS cables with single, double, and three cores are used in this type of wiring. These wires can withstand steam, chemicals, and water. In comparison to any other electrical wiring method in an electric circuit, it is inexpensive.

Batten Wiring System
Read More: Electric charges and field
Casing and Capping Wiring
The VIR cables are encased in hardwood casings in this wiring. It has become obsolete in recent years. When the phase and neutral wires are put in slots individually, repair is simple.

Casing and Capping wiring
Lead Sheathed Wiring
This has electrical wires with an outer sheath consisting of a 95 per cent lead alloy aluminium alloy. The cables are protected from air corrosion, moisture, and mechanical damage by this covering.

Lead Sheathed Wiring
Read More: Application of Gauss Law
Conduit Wiring
Surface conduit wiring and concealed conduit wiring are two types of this type of wiring.

Read More: Heating effect of Electric Current
Domestic Electric Circuits
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Electric circuit wiring in residences and buildings is known as domestic circuits. A pair of insulated copper or aluminium wires transport electricity to our dwellings.
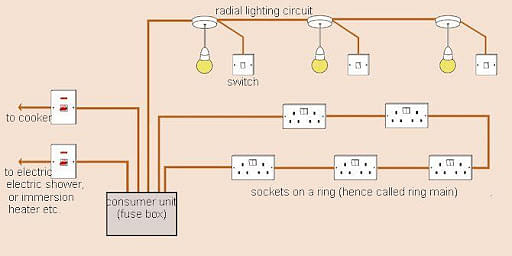
Domestic Wiring
The 3 types of wires used in a domestic electric circuit are as follows:
- Live wire
- Neutral wire
- Earth wire
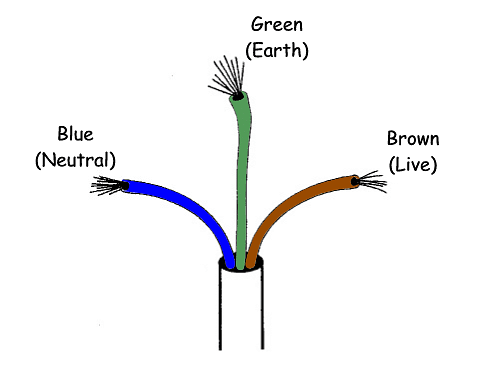
Live wire
- A live wire is one that conducts electricity.
- It is responsible for carrying the high voltage and delivering it to the appliances.
- It's also known as phase wire or hot wire.
- It is red in colour.
- The circuit breaker will blow if something goes wrong inside the machinery or circuit, the live wire is then linked to a metal part, protecting the user from electrocution or even a small shock.
- When a live wire makes contact with a neutral wire, the circuit's resistance drops dramatically and a big amount of current flows through it.
Wire Types
Read More: Resistors
Neutral wire
- The wire having zero potential is called neutral wire.
- This wire completes the circuit by providing a path for the current to return to the power source.
- It is black in colour.
Earth wire
- It is green in colour.
- A precautionary connection created in AC connections to prevent harm due to fluctuations is known as the earth or ground.
- The primary purpose of earthing is to protect people from electrical shock.
- The earth wire connects the metallic body of electric appliances to the earth, allowing any leakage of electric current to be transported to the ground.
Note: The potential difference (or voltage) supplied in our country is 220V
Difference Between Earth Wire and Neutral Wire
The key differences between earth wire and neutral wire are tabulated below.
| Earth Wire | Neutral Wire |
|---|---|
| The wire, when connected, provides a low-resistance path to protect against harm caused by leakage of current. | It is a conducting wire that provides a return path for the flow of electrical current in an AC circuit. |
| It doesn't have any current flowing through it. During any power disconnections, it only has minor electricity. | It always carries current. |
| It acts as a grounding point for electrical current. | It serves as a point of return for the flow of power. |
| The earthing connection can be made independently or via a neutral line. | A neutral line must be used to link it. |
Things To Remember
- Electrical Wiring is a wiring system that is a network of wires that connect various accessories for the distribution of electrical energy from the supplier metre board to a variety of electrical appliances.
- A wire is a single electrical conductor capable of carrying electricity, usually made of aluminium.
- There are different types of electrical wiring systems such as tee system, Loop-in system, cleat wiring, batten wiring, casing and capable wiring, lead Sheathed wiring and conduit wiring.
- Electric circuit wiring in residences and buildings is known as domestic circuits.
- The three types of wires used in a domestic electric circuit are live ire, a neutral wire and earth wire.
Read More: Van de graff generator
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the difference between a live wire and a neutral wire? [2 marks]
Ans.
- The live wire brings in the current while the neutral wire provides the return path for the current.
- The live wire is red in colour while a neutral wire is black in colour.
- Live wire carries a positive charge while neutral wire carries a negative charge.
Ques. When does an electric short circuit occur? [2 marks]
Ans. When the live and neutral wires in a domestic circuit come into direct touch with each other without any resistance, a short-circuit occurs. The circuit's resistance drops to zero, allowing an excessive amount of electricity to flow through it.
Ques. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances? [2 marks]
Ans. The earth wire is a safety feature that provides a low-resistance current conductor. The live wire might come into direct contact with the metallic cover of the appliances owing to excessive heat or wear and tear, causing an electric shock if touched. To prevent shock, the metallic component is connected to the earth via a three-pin connection, which allows electricity to pass to the earth when a short circuit occurs.
Earthing metallic appliances are required because it assures that if there is any current leakage in the metallic cover, the appliance's potential equals that of the earth. The earth's potential is zero. Thus, no current passes and the person doesn't get any electric shock.
Ques. Derive the formula for the force acting on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field. [3 marks]
Ans. The force acting on a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is,
F = B × I × L
The current I is the rate of flow of charge.
Now, if a charge Q flows in time t then the current I = Q/t. Hence substituting for I in
the above equation, we get,
F = (B × Q × L)/t
Suppose the particle carrying the charge Q travels a length L in time t, then the velocity
v = L/t. So substituting this value, we get
Force on moving charge F = B × Q × v.
Ques. Give two reasons why different electrical appliances in a domestic circuit are connected in parallel. [2 marks]
Ans.
(i) If one of the appliances is turned off or fuses, the other appliances are unaffected and continue to function.
(ii) All electrical appliances can use the same voltage from the mainline.
Ques. What is a fuse wire? What is the advantage and disadvantage of using a thick fuse wire? [2 marks]
Ans. A fuse is a critical component in the protection of electric circuits. It's a wire constructed of metal with a low melting point, such as tin or tin alloy.
Due to short-circuiting or overloading, the fuse wire is heated or melts when a strong current travels through a circuit. As a result, the circuit is broken, and the current ceases to flow. This saves all of the circuit's appliances.
Ques. Explain what is short-circuiting and overloading in an electric supply. [3 marks]
Ans.
Short circuiting
If the live and neutral wires' plastic insulations are torn, the two wires will come into contact. Short-circuiting occurs when the live and neutral wires come into direct contact. The current flowing through the circuit made by these wires is quite high, resulting in a significant heating effect that could result in a fire.
Overloading
The amount of current flowing through household wiring at any given time is determined by the power ratings of the appliances in use. When a large amount of high-power electrical appliances are turned on at the same time, the circuit draws a tremendous amount of current. This is referred to as overloading. The copper wires in residential wiring heat up to a very high temperature as a result of the huge current passing through them, which might cause a fire.
Check-Out:




Comments