Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
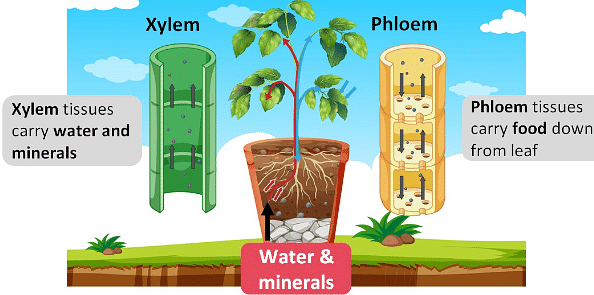
Plants uses chlorophyll, present in the leaves, to photosynthesize energy using CO2. As multicellular organisms, plants have specialized groups of cells performing different functions. The roots absorb raw materials such as phosphorus, nitrogen, and other minerals necessary for the sustenance of the plant. They’re however not responsible for the synthesis occurring in the chlorophyll-containing leaves, located at the opposite end. Thus, plants require a system of transportation for water and minerals to travel from roots to leaves and for the synthesized products from leaves to other parts of the plants. There are two independent systems that carry out these functions. The vascular tissues carrying out these are-
- Xylem
- Phloem.
Key Terms: Transportation of water, Transportation of food, xylem, Phloem
Transportation of Water
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The xylem is responsible for the transportation of water and minerals absorbed by the roots from the soil. Plants can utilize either active or passive absorption to take water
- Active Absorption: This is the process by which root hairs absorb water using metabolic energy. The absorption rate will be slower and is affected by conditions such as temperature and humidity.
- Passive Absorption: Here, the water is absorbed without using metabolic energy. It is faster than active absorption. The transpiration pull is the reason for absorption which is generated in the xylem.
Xylem
Xylem cells are elongated tubes that run from the roots to the leaves. They aren’t living cells. The absorbed water from the roots makes use of the process of osmosis to reach the xylem vessels. Along with the xylem, vessels, and tracheids of roots and leaves form a system that carries out the transportation of water in plants. The water flow in the xylem takes place in one direction only i.e. upwards, from the roots to the leaves via the stem.

Xylem
Water Transportation Process
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The root cells connected to the soil actively procure ions and creates a difference in the concentration of ions between the roots and the soil. To eliminate this difference, water will move from soil into the roots. This pressure created is not enough to bring the water up to the leaves. This is where transpiration comes into play. Plants lose water from the stomata. To replace this water, the suction thus created will pull more water from the xylem. It is also important to remember that the transpiration process occurs during the daytime while water transportation utilizing root pressure is a nightly occurrence. The opening of stomata during the daytime results in a large loss of water. This results in the upward movement of more water from roots to leaves. Transpiration also helps in the regulation of temperature in plants.
Water Transport in Process
Transportation of Food
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Compared to the xylem and its movement of water and minerals, the transportation of food in plants is a bit more complex. Phloem is responsible for the movement of food from leaves to other parts of the plant
Phloem
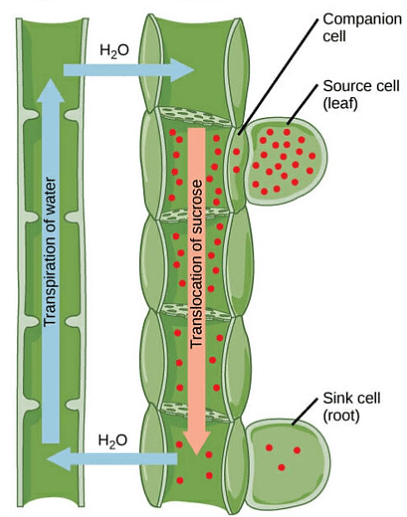
Phloem tissue is inclusive of 3 different types of cells: sieve tubes, companion cells, and vascular parenchyma.
- Sieve tubes are alive, tubular, and have walls called sieve plates. They however lose the nuclei but have operating plasma.
- The companion cells function to load sugar into the sieve elements which are in turn connected to sieve tubes.
Transport of Food
- The locations where food is produced are known as sources and the place where the food is transported to be stored or for consumption is called Sink.
Process of Transporting Products of Photosynthesis
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- The movement of soluble products created after photosynthesis takes place occurs by the phenomenon known as translocation.
- Phloem carries out the process of translocation.
- Additionally, the phloem is also responsible for the transportation of substances like amino acids.
- The movement, which can be both upwards and downwards of synthesized products and substances, occurs in sieve tubes with the aid of companion cells that are located adjacent.
- The phloem makes use of ATP to move substances such as sucrose, which in turn, increases the osmotic pressure and causes the movement of water.
- The pressure difference results in the movement of food materials from the phloem to cells that have less pressure and assures the cells get the necessary products.
- For eg, the sugar stored in the stem or root will be transported to the buds in spring.

Transporting Products of Photosynthesis
Sample Questions
Ques: Differentiate between xylem and phloem? (3 marks)
Ans.
| Xylem | Phloem |
|---|---|
| Xylem conducts water from roots to leaves | Phloem is responsible for transporting materials synthesized from photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant like roots, buds, etc |
| It only has one type of living cell | There are 3 types of living cells |
| Water is transported through tracheids and vessels | Food is moved using sieve tubes |
| Movement is unidirectional | Movement is bidirectional |
Ques: What is root pressure? (3 marks)
Ans. When salts accumulate at the base of roots, it results in the creation of osmotic pressure. This leads to the entry of water into the xylem which forms a column of water. The positive pressure created is called root pressure. Root pressure however is not efficient in transporting water to long distances like in the case of tall trees.
Ques: What is facilitated diffusion? (2 marks)
Ans. Facilitated diffusion uses proteins called permeases to transport materials in plants. It is a passive process and occurs in symport, antiport, and uniport. Only certain molecules are permitted to pass in facilitated diffusion. There are two proteins that aid in this process: porins and aquaporins.
Ques: What are the functions of stomata? (2 marks)
Ans. The stomata perform the following functions:
- The stomata are the site where gases are exchanged between the plant and the atmosphere.
- The stomata also facilitate transpiration
Ques: Is there a difference in how desert plants take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis? (2 marks)
Ans. Yes. Usually, plants carry out transpiration during the day. However, for desert plants, the stomata are closed during the day to preserve water. The stomata are instead opened at night to take in CO2 which is stored in the cells till the sun is out and photosynthesis is carried out during the day.
Ques:. What is the difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition? (3 marks)
Ans. The difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition are:
| Autotrophic | Heterotrophic |
|---|---|
| Organisms prepare food using CO2 and water in the presence of sunlight using chlorophyll | In this case, the organisms are dependant on other living organisms for food |
| Sunlight is the energy source | The energy is from digesting the organic beings like plants that can create their own energy |
| Eg: Plants | Eg. Animals |
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:








Comments