Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
The carbon atom was discovered by Antoine Lavoisier. Carbon, denoted with the symbol C and atomic number 6, is a tetravalent and nonmetallic chemical element with four electrons. It sits on group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon is a readily available element. It makes up to 0.025 percent of the Earth's crust. Carbon is extremely versatile and resilient. It has distinguished properties and it is one of the most universally present elements. Its compounds, formed through atomic bonds, can have opposite properties. For example, Diamond, a carbon compound, is non-combustible and cannot conduct electricity, whereas Graphite, also a carbon compound, is highly combustible and can conduct electricity.
| Table of Contents |
The term Carbon is derived from the Latin word ‘carbo’ which means charcoal. All organic substances existing in the world have abundant carbon present inside them, which is why the study of carbon is essential. This chapter is a part of unit 1 chemical substances nature and behaviour and carries a total of 25 marks and 55 periods.
Properties of Carbon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some of the important properties of Carbon are:
- Carbon takes four electrons to make a covalent bond.
- Through catenation, Carbon can quickly form bonds with other atoms and give rise to large molecules.
- Due to its valency, carbon can bond with other atoms of carbon and some mono-valent elements.
- The carbon bonds which are formed with other elements are really strong. This makes these compounds extraordinarily stable.
Cause of the versatile nature of Carbon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are multiple reasons behind the versatility in nature of carbon -
-
Tetravalency of Carbon
Carbon is present in all organic substances of nature, living or non-living, making it the 4th most abundant element in the world. Due to its atomic number and composition, Carbon follows the octet rule. The carbon atom has four electrons in its shell, which is why it four forms of covalent bonds. Hence, carbon is tetravalent.
-
Catenation of Carbon
Catenation is the self-linkage of carbon atoms done by the covalent bonds to construct branched chains, straight chains, or rings of various sizes. It is a unique phenomenon, performed only by carbon.
-
Multiple Bond Formation
The smallest size of carbon enables the formation of multiple bonds with its own atoms as well other elements. Carbon can form double or triple bonds, hence it can form a lot of carbon compounds.
- Isomerism
Carbon compounds with the same molecular formula can possess different properties and structures. This phenomenon is called isomerism.
Read Also : Carbon and its compounds
Allotropes of Carbon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Allotropy is the phenomenon that states that two elements exist with two or more different physical states but similar chemical properties.

Carbon and its allotropes:
- Diamond
- Graphite
- Buckminster Fullerene
Covalent Bonds
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Carbon always forms covalent bonds. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. The electron pairs are called bonding pairs. Covalent bonds establish a stable balance of repulsive and attractive forces between atoms. Covalent bonds are much more common than ionic bonds, as the electronic configuration of each atom allows the sharing of electrons to attain the equivalent of a full outer shell.
Covalent bonds include metal-to-metal bonding, σ-bonding, π-bonding, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds, and agostic interactions. Through nomenclature, covalent bonding means the "co" sharing of atoms and their valency, which is also called the valence bond theory.
Types of covalent bonds
- Polar Covalent Bonds: Bonds in which the electrons are shared unequally by the atoms as they have an intense attraction to one nucleus than the other. Due to the unequal distribution, a positive (δ+) or negative (δ-) charge develops between the electrons.
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: Bonds in which the electrons are shared equally.
Carbon Compounds
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
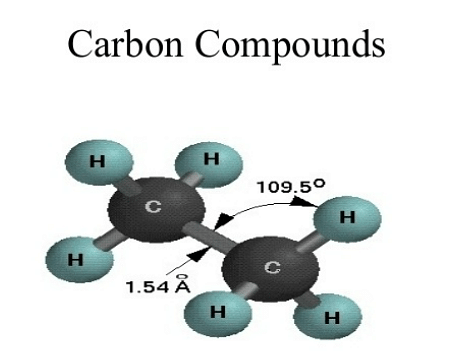
Carbon compounds are chemical substances in which a carbon atom bonds to another element. Through catenation and tetravalency, carbon is capable of making a mind-boggling number of compounds. Carbon has organic(bonded with Hydrogen) and inorganic compounds(bonded without Hydrogen). These compounds are unique, strong, and stable. Carbon compounds differ on grounds of origin, saturation, and covalency. The physical properties of carbon compounds can also be distinguished as per their origin and formation.
Classification of Carbon compounds
-
Saturated carbon compounds:
Compounds formed by a single bond between two elements are called saturated compounds. The most common example of a saturated carbon compound is Ethane (C2H6). Saturated hydrocarbons are bonded with as many hydrogen atoms as possible.
- Unsaturated carbon compounds:
Compounds formed by double or triple bonds are unsaturated carbon compounds. The most common example of an unsaturated carbon compound is Ethene (C2H4).
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Combustion: Through the evolution of heat and light, compounds can combust to form carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
- Oxidation: Carbon compounds can oxidize through an oxidizing agent.
- Addition reaction: In the presence of catalysts, unsaturated hydrocarbons subdue additional reactions.
- Substitution reaction: Saturated hydrocarbons can supplement substitute reactions. For example, methane, in the presence of sunlight, undergoes chlorination.
Checkout Important Question: Homologous Series
Frequently Asked Questions
Ques: What are the four types of carbon compounds? (2 marks)
Ans: The four types of carbon compounds are-
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids.
Ques: ?What are oxidizing agents? (2 marks)
Ans: An oxidizing agent is a chemical element that accepts the electrons of other substances through a chemical reaction. The most common oxidizing agents are Hydrogen, Halogens, and Hydrogen Peroxide.
Ques: What is the chemical oxidization reaction? (2 marks)
Ans: In the presence of oxygen, carbon compounds get oxidized through a combustion reaction. Although not all oxidation reactions are carried out through oxygen as it is carried out by oxidizing agents which are oxidants.
Ques: What are covalent bonds? (2 marks)
Ans: A covalent bond is formed by sharing electron pairs with atoms. These electrons are called bonding pairs or shared pairs. Covalent bonds execute a stable balance of repulsive and attractive forces between atoms sharing electrons.
Ques: What are the most commonly used carbon compounds? (2 marks)
Ans: 18% of the entire human body is made of carbon compounds such as sugar, protein, and glucose. Carbon is used in jewelry, paints, inks, and many other daily life things.
Read Also:








Comments