Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Autotrophic nutrition helps organisms produce their own food using simple inorganic materials like water, carbon dioxide, solar energy, and salt minerals, in the presence of sunlight. All living organisms need energy and food to have steady growth and reproduction.
Key Terms: Autotrophic Nutrition, Nutrition in Plants, Photosynthesis, Chemosynthesis, Sunlight, Carbon dioxide, Chlorophyll
What is Autotrophic Nutrition?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
| “Autotrophic nutrition is a process where organisms prepare their own food from simple inorganic materials like water, mineral salts, carbon dioxide and sunlight.” |
Autotrophic nutrition is observed in autotrophs. Autotrophs are organisms that are capable of producing nutritive compounds with the help of inorganic materials. Some examples of autotrophs are Algae, Phytoplankton, Seaweed, Wheat, Grass, Maize plant, bacteria, blue-green algae, and Cyanobacteria.
All plants have a mode of autotrophic nutrition to keep producing their own food. The two types of autotrophic nutrition are:
- Photosynthesis
- Chemosynthesis
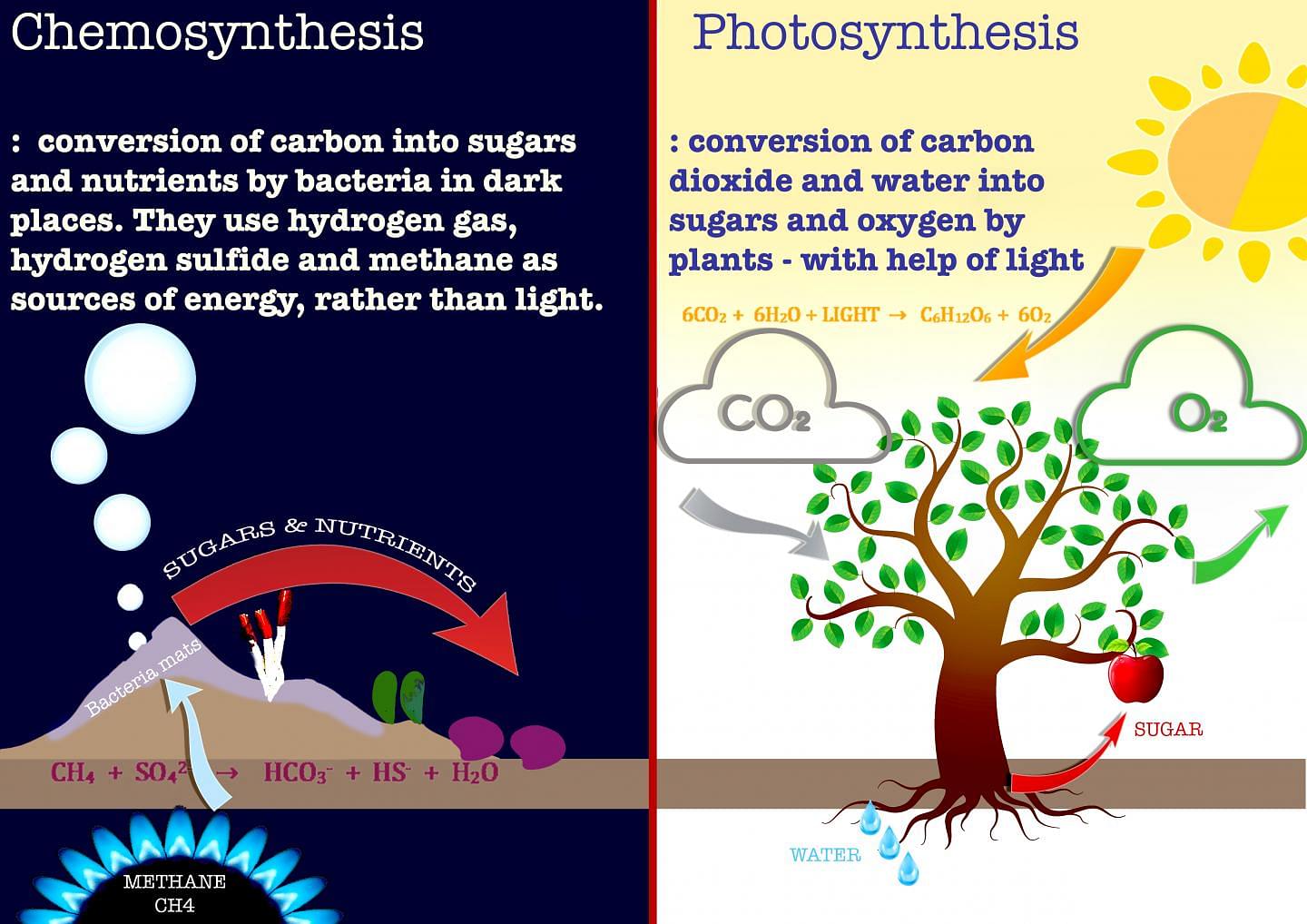
Chemosynthesis vs. Photosynthesis
Check out:
What is Photosynthesis?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Photosynthesis is the process of using carbon dioxide and water and converting them into nutrients in the presence of sunlight. It is used by plants, organisms, bacteria, and protists.
- All Autotrophic organisms have a green pigment called chlorophyll which is present in a structure known as chloroplast that helps in absorbing light and storing it as energy.
- Leaves, stomata, and roots are the major parts of plants that play a huge role in the process of photosynthesis.
- The plants and organisms that prepare their own food, with the help of photosynthesis, are called photoautotrophs.
- The energy produced is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar).
- Photosynthesis is the only source for all plants sustaining life processes and the sole way to get energy.
- Photosynthesis helps to maintain the carbon cycle between oceans, plants, animals, and the earth.
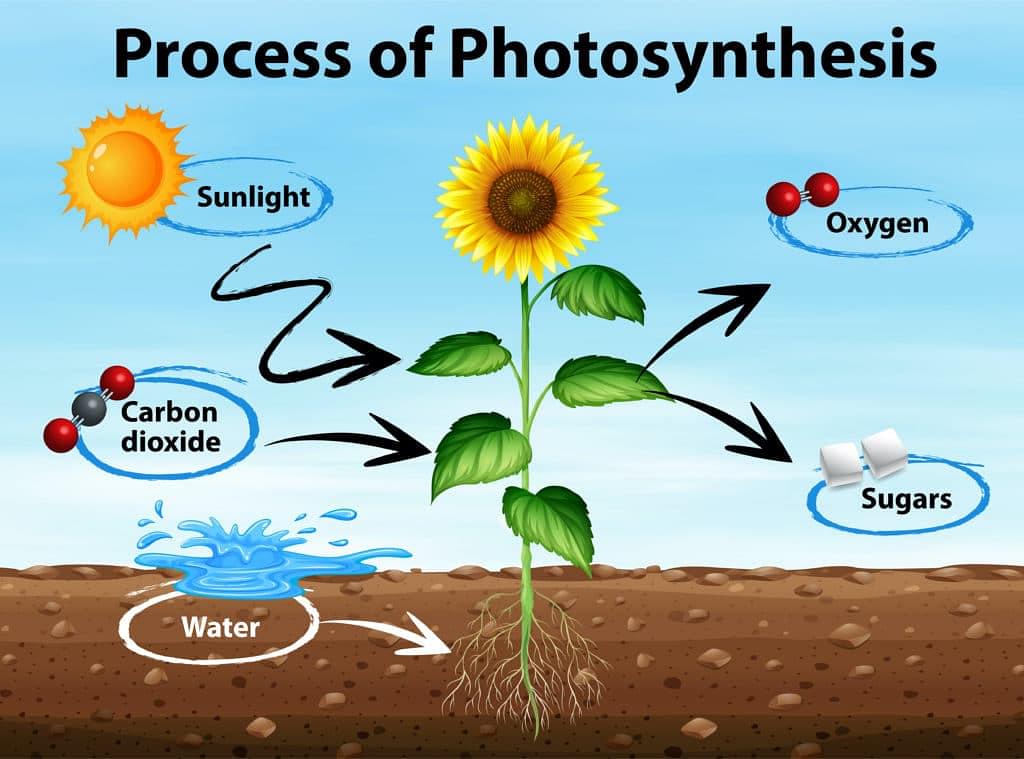
What is Photosynthesis?
Functions of Photosynthesis
|
Process of Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis occurs in the following way:
- Chlorophyll helps in absorbing light energy.
- Light energy is then converted into chemical energy which results in the splitting of the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates takes place.
Photosynthesis Equation
The equation of photosynthesis is:
| 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Six Carbon dioxide molecules + Six water molecules → Sugar molecules + Oxygen molecules (with the help of photosynthesis and chlorophyll) |
- Oxygenic Photosynthesis - 6CO2 + 12H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
- Anoxygenic Photosynthesis - CO2 + 2H2A + Light Energy → [CH2O] + 2A + H2O
Components of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis consists of two components as reactants and products.
- Reactants: ATP, Carbon dioxide, Oxygen, NADPH, Water, and Chlorophyll
- Products: Oxygen, water, and GA3P
What is Chemosynthesis?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some rare autotrophs do not use energy from light to produce their own food but use chemical reactions instead. Organic compounds are synthesized by living organisms, generally in the absence of sunlight by deriving energy through chemical reactions.

Chemosynthesis
Examples of Autotrophs
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The examples of autotrophs are as follows:
- Plants
- Algae (Green algae and Red algae)
- Bacteria such as cyanobacteria
Read More:
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Autotrophic nutrition is self nutrition wherein the organisms prepare their own food from simple inorganic materials in the presence of sunlight.
- Autotrophic nutrition is observed in autotrophs, i.e. organisms who synthesise their own food
- There are two methods of autotrophic nutrition: Chemosynthesis and photosynthesis.
- In photosynthesis, sunlight is converted to food. Green plants engage in photosynthesis
- The reaction of photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
- In chemosynthesis, chemicals are used instead of light in order to produce food.
Autotrophic Nutrition PDF
Sample Questions
Ques: Why is Photosynthesis considered so important for life on earth? (All India 2012)
Ans. Photosynthesis works as the only way for plants, organisms, and algae to get food and energy. Photosynthesis is the sole process that provides oxygen in the atmosphere.
- All living organisms need food and energy to lead a healthy and long life.
- Photosynthesis is useful for humans too as, during the process of photosynthesis, oxygen is released by plants as a waste product.
- During Photosynthesis plants are taking in carbon dioxide and in return release oxygen which helps in sustaining all life forms on earth.
Ques: What is the role played by different parts of a plant during the process of photosynthesis? (Delhi 2017)
Ans. The role played by different parts of a plant during the process of photosynthesis are:
- Leaf: Leaf is the part where all the food is stored and produced. The green pigment chlorophyll on leaves helps to capture light energy which is then used to make food by using photosynthesis.
- Stomata: Stomata are the tiny pores present in a plant to regulate the flow of gases and water vapour. They’re usually in the leaves of the plant but can also be found in the stem sometimes. Stomata work as the regulator of water as it allows how much water leaves and enters the plant. It is also responsible for absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
- Roots: Roots help in absorbing nutrients and water from the soil. The root is the first base that truly attaches the plant to the soil because if the roots weaken then the survival of the plant will be very difficult. The growth of the plant depends on the roots as it provides nutrients, minerals, and water to the whole plant.
Ques: Why can't photosynthesis occur at night time? (All India 2015)
Ans. The process of photosynthesis needs light to perform the whole process.
Several other factors that affect photosynthesis are:
- Insufficiency of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
- The environment is too cold or too hot for the plant
Ques. Why are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related to each other? (All India 2015)
Ans. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are biochemical processes that help each other to complete their process.
Photosynthesis requires the products (Carbon dioxide and water) of cellular respiration and cellular respiration requires the end products (Glucose and oxygen) of photosynthesis.
Both these reactions help the atmosphere by maintaining the cycle of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
Ques: What is autotrophic nutrition? Give examples. (3 Marks)
Ans. Autotrophic nutrition is a process in which an organism is able to produce or create its own food. These organisms use inorganic materials such as water, solar energy, and CO2 to make their food.
There are two types of autotropic nutrition: Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis.
Examples of autotrophic nutrition include Auto-Green Plants, Algae, Phytoplankton, Seaweed, Wheat, Grass, Maize plant, bacteria, blue-green algae, and Cyanobacteria.
Ques: What are heterotrophic and autotrophic nutrition? (3 Marks)
Ans. Autotrophs are the organisms that prepare their own food while heterotrophic organisms are those that cannot prepare their own food.
Heterotrophic organisms depend upon autotrophs for nutrition.
- Autotrophic Nutrition Examples (Autotrophs): Plants, Algae, Bacteria, and Plankton
- Heterotrophic Nutrition Examples (Heterotrophs): Cows, buffaloes, tigers, horses, and humans
Ques: Which are the most essential components in autotrophic nutrition? (1 Mark)
Ans. For photosynthesis, autotrophic nutrition, solar energy, water, chlorophyll, and carbon dioxide are the most essential components.
Ques: How many types of autotrophic nutrition are there? (1 Mark)
Ans. There are two types of autotrophic nutrition namely Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis.
- In photosynthesis, sunlight is used to prepare food. Green plants engage in photosynthesis.
- Chemicals are used instead of light in order to produce food in Chemosynthesis; for example bacteria.
Ques: Are fungi autotrophic? (1 Mark)
Ans. No, fungi are not autotrophic organisms. Fungi are parasites and belong to eukaryotic organisms. They get the energy they need to live from other organisms.
Ques: What molecules are produced by autotrophs? (2 Marks)
Ans. There are two types of autotrophs: photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
- In photosynthesis, solar energy is used as the main component that converts water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air into a nutrient called glucose and oxygen.
- In Chemosynthesis, bacteria use energy stored in the chemical bonds of hydrogen sulfide and methane to make glucose from water and carbon dioxide. As by-products, Pure sulfur and sulfur compounds are produced.
Ques: Why producers are also called autotrophs? (1 Mark)
Ans. Autotrophs create or produce their own food using sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals. This is because producers are also called autotrophs. Plants are the most important type of producer.
Ques: Does chemosynthesis require oxygen? (1 Mark)
Ans. Yes, Chemosynthesis requires oxygen. As in place of sunlight, the chemical oxidation of sulfide (H2S) by oxygen (O2) fuels the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) to organic carbon by chemosynthetic bacteria.
Ques: What is the difference between photosynthetic and chemosynthetic bacteria? (2 Marks)
Ans. Photosynthesis uses solar energy as the main source of making food. While chemicals are used instead of solar energy to manufacture their food by chemosynthetic bacteria.
- Examples of photosynthetic bacteria: Purple bacteria are the most common type of photosynthetic bacteria; cyanobacteria
- Examples of chemosynthetic bacteria: bacteria and methanogenic archaea living in deep-sea vents.
Ques: Why are green plants called producers? (2 Marks)
Ans: The green plants trap the sun’s energy and the raw materials in food molecules. They form the basis of sustenance for all the organisms directly or indirectly. They are also called the producers as they produce food for all other organisms.
Ques: From where do the green plants get carbon dioxide? (2 Marks)
Ans: Many processes like respiration, combustion, volcanic activity, etc. release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This carbon dioxide of the atmosphere is used by the terrestrial plants and the hydrophytes use the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water.
Ques: What type of nutrition is shown in amoeba? What does it diet include? (2 Marks)
Ans: Amoeba shows holozoic nutrition. Its diet includes bacteria, microscopic plants like the diatoms, minute algae, and microscopic animals like other protozoa, nematodes and even dead organic matter.
Ques: How are all plants and animals dependent on green plants? (2 Marks)
Ans: The green plants are fed on by the herbivores which in turn by carnivores. Ultimately, the decomposers derive their nutrition from the dead plants and animals. Thus, all organisms are directly or indirectly dependent on the green plants.
Ques: How is food digested in amoeba? (2 Marks)
Ans: Amoeba is a protozoan and holozoic. Since it is a unicellular organism, the digestion is intracellular. The food taken in remains in a food vacuole or gastric vacuole formed by the cell membrane and a bit of the cytoplasm. The vacuoles are transported deeper into the cells by cytoplasmic movements. Here they fuse with lysosomes that contains enzymes such as amylase and proteinase. Thus, amoeba can digest sugar, cellulose and protein. Fats, however, remain undigested.
Ques: What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by-products? (3 Marks)
Ans: Autotrophic organisms are self-feeders that can synthesise their own food. Green plants are photoautotrophs that can carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a process in which atmospheric carbon dioxide is fixed and combined with water to form glucose and oxygen.
Photosynthesis always takes place in the presence of sunlight which is captured by chlorophyll pigment present in plants.
The equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2+6H2O⟶C6H12O6+6O2
Ques: Write short notes on absorption? (3 Marks)
Ans: Absorption is taking in of digested food by cells and tissues. This involves the absorption of food in the soluble form from the region of digestion into the tissues or in to where it has to be utilized or into the blood stream which transports it to the different tissues. This takes place through the cell membranes.
The absorption may be passive or active. Passive absorption is through diffusion or osmosis without using energy. For example: Water is absorbed by osmosis. Active absorption needs energy. For example, absorption of glucose and sodium ions.
Ques: Give an account of the reaction of the photosynthetic reaction? (4 Marks)
Ans: The reactants of photosynthesis are:
- Carbon Dioxide: During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is converted into carbohydrates and this is called fixing of carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide of the atmosphere is used by the terrestrial plants whereas the hydrophytes use the carbon dioxide dissolved in the water.
- Water: During photosynthesis, hydrogen of water is used to fix carbon dioxide and its oxygen is released. Water is obtained through the root hairs by absorption.
- Chlorophyll: They are pigments capable of absorbing radiant energy of the sun. There are two types of photosynthetic pigments- chlorophyll and carotenoids. Chlorophyll is the main pigments as they are involved in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy. The carotenoids also absorb light energy but they pass it to the chlorophyll molecules.
- Radiant Energy: The radiant energy from the sun is the source of both light and heat energy for photosynthesis. Light energy is harvested by the pigments in order to carry out the breaking down of water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen. The temperature required by the enzymes to function is maintained by the heat energy of the sun.
Previous Year Questions
- The Law of Limiting Factors was proposed by… [KCET 2004]
- In the cell respiration, which of the following conversion… [JIPMER 1998]
- Emerson's enhancement effect and Red drop have been… [NEET 2016]
- The first carbon dioxide acceptor in C4-plants is… [NEET 1990]
- End product of glycolysis is… [NEET 1990]
- A few normal seedlings of tomato were kept in a dark room… [NEET 2014]
- One set of a plant was grown at 12 hours day and 12 hours per night… [NEET 2004]
- The enzymes hexokinase which catalyses glucose to… [NEET 1996]
- Fermentation is anaerobic production of… [NEET 1996]
- Oxidative phosphorylation involves simultaneous oxidation… [NEET 1996]
- Krebs cycle occurs in… [NEET 1996]
- The first step for initiation of photosynthesis will be… [NEET 2000]
- Treatment of seed at low temperature under moist conditions… [NEET 2006]
- Photosynthetic Active Radiation (PAR) has the following… [NEET 2005]
- During which stage in the complete oxidation of glucose are… [NEET 2005]
Also check:









Comments