Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
The oxidation-reduction reaction, also called the redox reaction, is any chemical reaction wherein the oxidation number of a participating chemical species changes by gaining or losing an electron. Redox reactions are common in some of the basic functions of life, like photosynthesis, respiration, corrosion or rusting, and combustion. After the discovery of electrons, chemists became convinced that oxidation-reduction reactions involved the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
Read Also: Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways: Oxidation and reduction, redox reactions, loss of electron, gain of electron, ion, atom, molecule, combustion reaction.
What is Oxidation?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of an ion, atom, or certain atoms in a molecule. It is also described as a reaction where an element combines with oxygen. For instance, oxidation of magnesium involves a chemical reaction between magnesium metal and oxygen to form magnesium oxide. It is the job of oxidizing agent to add oxygen from another substance.

Oxidation
The video below explains this:
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Detailed Video Explanation:
Read more:
What is Reduction?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The word reduction comes from a Latin word that means “to lead back”. Reduction means the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state of an ion, atom, or certain atoms in a molecule. The reaction between magnesium oxide and carbon to form magnesium metal and carbon monoxide at 20000 Celsius is an example of the reduction of magnesium oxide to magnesium metal. It is the job of the reducing agents to remove the oxygen from another substance.

CO2 Reduction
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Oxygen Transfer
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In chemistry, oxidation and reduction are associated with the transfer of oxygen. Oxidation means a gain of oxygen and Reduction means loss of oxygen. Reduction reaction is defined as anything that leads back to a free metal state. Magnesium undergoes both oxidation and reduction processes.
| 2Mg (s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO (s) is a Oxidation reaction MgO (s) + C (s) → Mg (s) + CO (g) is a Reduction reaction. |
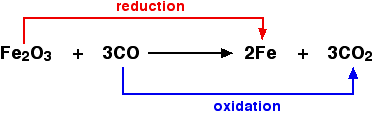
Read more : Important Questions on Chemical Equations
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Hydrogen Transfer
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
With the help of this procedure, ethanol can be oxidised to ethanal:

In order to remove the hydrogen from ethanol, an oxidizing agent is required. A commonly used oxidizing agent is potassium dichromate (VI) solution acidified with dilute sulfuric acid. Again, ethanal can be reduced back to ethanol by adding hydrogen. Here, the possible reducing agent is sodium tetrahydridoborate, NaBH4.

Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Electron Transfer
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons while Reduction means the gain of electrons. Both Oxidation and Reduction reactions are always interlinked as electrons are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. Therefore, they occur together in pairs and it is impossible to have one without another. Magnesium is a good example to explain this concept. Magnesium gets oxidized by losing two electrons to oxygen which gets reduced by accepting two electrons from magnesium.
| 2 Mg + O2 → 2 [Mg2+] [O2-] |
Since oxidation and reduction cannot occur individually, as a whole they are called Redox reactions. The reactant that oxidizes the other reactant is called an oxidizing agent and the reactant that reduces is called the reducing agent. To learn whether oxidizing agents either accept or give away electrons, it is essential to follow these steps one by one: An oxidizing agent oxidizes other reactants. It means that oxidizing agent is getting reduced. Oxidation is the loss of electrons. Therefore, the oxidizing agent must gain electrons.
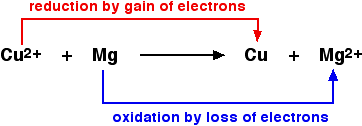
Redox Reactions
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Many reactions in organic chemistry are classified as Redox reactions. They occur due to changes in the oxidation state that occur without the independent transfer of electrons. It is also known as an oxidation-reduction reaction and is defined as a reaction in which one reactant undergoes oxidation while the other gets reduced during the course of the reaction. For instance, the Oxidation state of carbon atoms in the wood increases during the combustion of wood with molecular oxygen, and oxygen atoms decrease with the production of carbon dioxide and water. Thus, the oxygen atoms are reduced while receiving electrons while carbon atoms are oxidized, losing electrons. Therefore, oxygen is the oxidizing agent and carbon is the reducing agent in the above example. Another example is the reaction of zinc oxide and carbon.
| ZnO + C = Zn + CO. |
Common Redox Reactions
- Combustion Reaction: It is defined as a type of redox reaction that occurs between molecular oxygen and compound to form oxygen-containing products. 2 2C8H18+ 25O2 → 16CO2(g) + 18H2O
- Disproportionation Reaction: It is defined as a type of redox reaction where a single reactant is simultaneously reduced and oxidized. It is also known as an auto-oxidation reaction.
3ClO-(aq) → ClO3-(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)
- Single replacement Reaction: It is a type of redox reaction where one element is substituted or switched for another element within a compound. This reaction is also called a single displacement reaction.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
How to Balance Redox Reaction?
The steps that need to be followed to balance redox reactions are as follows:
- Assign elements with oxidation numbers
- Write half-reactions for reduction and oxidation
- Multiplication of half reaction number to equalize
The redox reaction is when a chemical reaction, where one of the reactants is decreased and the other is oxidized. Oxidation and Reduction apply to the transition between elements or compounds of electrons, which are characterized by the state of oxidation.
As the amount of oxidation increases, an atom is oxidized and it is reduced when the amount of oxidation reduces. The functions of life like photosynthesis and breathing include redox reaction. One of the most critical steps in balancing a redox reaction is to determine if there is still a redox reaction.
Oxydation versus Reduction
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Oxidation is the process when a reactant loses electrons during a reaction. Whereas, when a reactant accumulates electrons during a reaction. A reduction-oxidation, which is also referred to as a redox reaction, is a type of chemical reaction wherein reduction and oxidation occurs at the same time. In this process, the reduced species receive electrons and the oxidized species lose them. Moreover, despite its name, the oxidation process does not require the presence of oxygen.
Read more:
Things to Remember
- Oxidation, according to the electronic concept, can be defined as the process in which an atom or ion loses one or more electrons.
- Based on electronic concept, reduction is the process in which an atom or ion gains one or more electrons.
- Oxidising agent is the substance that brings about oxidation.
- Reducing agent is a substance that brings about reduction.
- Every chemical reaction has to be balanced according to the “Law of conservation of mass”.
Sample Questions
Ques: The reduction is gain of which among the following?
Electrons
Protons
Neutrons
Oxygen (1 mark)
Answer. A(Electrons)
Ques: Which among the following is defined as the gain of oxygen?
Oxidation
Reduction
Chlorination
Halogenation (1 mark)
Answer. A(Oxidation)
Ques: The reaction in which oxidation and reduction take place at the same time is known as?
Oxidation reaction
Reduction reaction
Redox reaction
None of the above (1 mark)
Answer. C(Redox reaction)
Ques: In the reaction of formation of magnesium oxide, magnesium undergoes which among the following?
Reduction
Hydrogenation
Oxidation
None of the above (1 mark)
Answer. C(Oxidation)
Ques: Rusting of Iron occurs due to?
Sublimation
Reduction
Oxidation
Hydrogenation (1 mark)
Answer: C(Oxidation)
Ques: What is the difference between Oxidation and Reduction? (1 mark)
Ans: Oxidation occurs when a reactant loses electrons during reaction while Reduction occurs when a reactant gains electrons during the reaction.
Ques: What are the examples of gradual oxidation? (1 mark)
Ans: The gradual oxidation examples are rusting of iron and wood.
Ques: What is a reduction reaction? (1 mark)
Ans: The reaction in which oxygen is lost or hydrogen is gained is known as a reduction reaction.
Ques: What is the importance of oxidation and reduction? (1 mark)
Ans: Oxidation and reduction reactions are biological and artificial energy sources on our planet. Oxidation of molecules releases a large amount of energy by removing hydrogen and replacing it with oxygen.
Ques: Write any two applications of displacement reactions. (2 marks)
Ans: In displacement reaction, a more reactive metal will displace a less reactive metal from its solution. Some of the applications of the displacement reactions are,
(i) It is used in the refining or silver
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
(ii) It is also used in antacid which causes relief from acidity problem or indegestion. An antacid (Calcium hydroxide) neutralizes stomach acid i.e, the hydrochloric acid.
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O
Ques: Write any two industrial application of combination reaction. (2 marks)
Ans: The two important industrial application of combinations are:
(i) Reaction of quick lime with water that form slaked lime used in white washing,
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(s)
(ii) Manufacture of HCl gas feom H2 and Cl2.
H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
Ques: Can corrosion be considered as an oxidation reaction? (3 marks)
Ans: Corrosion is a natural process through which a refined metal is transformed into more chemically stable form, like its oxide, hydroxide or sulfide. Corrosion involves the oxidation of substances by oxygen as well. Ans oxidation is the reaction of any metal and non-metal with oxygen to form the oxide of that metal or non-metal.
4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3
The metal atoms lose electrons when they form the rust compound known as metal oxide which is written as,
2Fe + O2 → 2Fe2+ + 2O2-
By taking only the reaction of iron into account we get,
2Fe → 2Fe2+ + 2e-
Therefore, oxidation is one form of corrosion of metals.
Ques: What is the link between oxidation and oxidising agent in a redox reaction? Write an example of redox reaction that shows the relationship of the same. (3 marks)
Ans: Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of an ion, atom, or certain atoms in a molecule. It is also described as a reaction where an element combines with oxygen. While, oxidising agent is a substance that accepts electrons and causes other substances to lose electrons. At the same time, it undergoes reuction and oxidises the other substance. Maeaning, an oxidising agent add oxygen to another substance and remove hydrogen from it.
For example: Fe2O3 + 3Mg → 2Fe + 3MgO
Here, the oxidation of magnesium (by adding oxyden) and reduction of iron oxide (removal of oxygen) takes place. Thus, magnesium is the reducing agent and iron oxide is the oxidising agent.
Ques: What is precipitation reaction? Explain with example. (2 marks)
Ans: When two reactants react and their product formed remains insoluble and settles as a solid, it is known as a precipitate. The reactions in which precipitate is formed are called precipitation reactions.
When aqueous solution of sodium sulphate is mixed with the aqueous solution or barium chloride, barium sulphate comes in the form of white precipitate.
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(↓) + 2NaCl(aq)
Do Check Out:



Comments