Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Refraction of Light is the phenomenon that involves the bending of light when it travels from medium to another. In refraction of light, a change in velocity of the light and direction of propagation occurs. When light travels through a substance with a different refractive index, refraction of light takes place.
- The cause behind the change in direction is the change in speed.
- Some natural phenomena of refraction of light in nature are the twinkling of stars, rainbows, the formation of mirages, optical illusions, and many more.
- The Refractive index enables us to understand how fast light travels through a medium.
Also read: Light: Reflection and Refraction Important Question
Key Terms: Refraction, refraction of light, refractive index, laws of refraction, Snell’s Law, Rarer medium, Denser Medium
What is Refraction of Light?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]Refraction refers to the change in the direction of a wave that passes from one medium to another. Light is a form of energy that undergo various phenomena like diffraction, reflection, refraction, interference, and polarisation. Refraction of light is one of the most commonly observed phenomena, but sound waves and water waves also experience refraction.
- Refraction of light is the bending of the light wave when it passes from one medium to another, due to the difference in the density of the two mediums.
- Refraction makes it possible for us to have optical instruments such as magnifying glasses, lenses, and prisms.
- If you observe a pencil dipped into water, you’ll notice that it seems to be tilted at an angle at the interface of air and water, or the bottom of a tub or a tank that contains water seems to be raised.
- This phenomenon is caused due to the process of refraction of light.
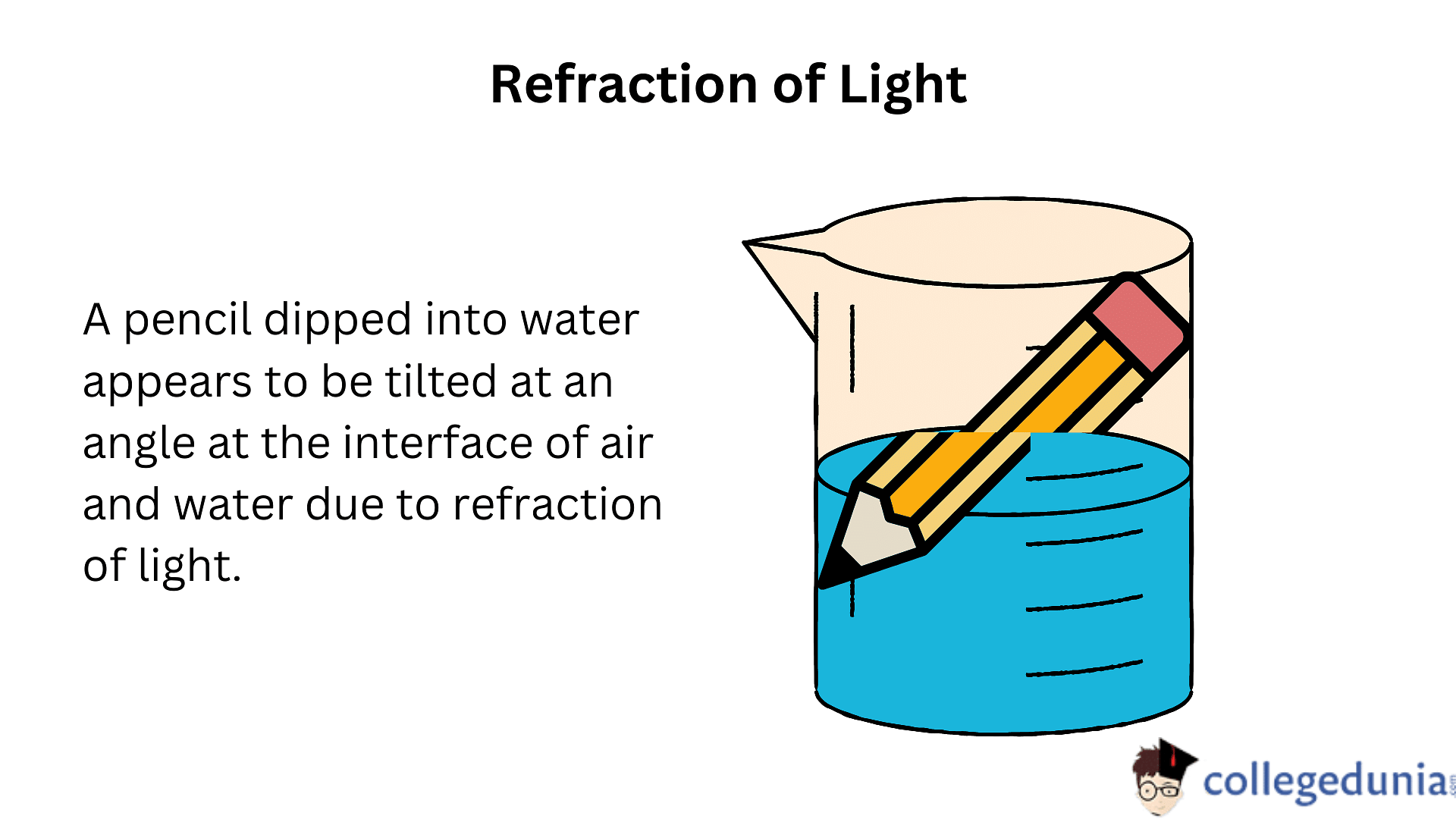
The refraction of light is a commonly observed phenomenon. Refraction makes it possible to have optical instruments like magnifying glasses, lenses, and prisms. The light is focused on our retina also due to the refraction of light.
Read More:
Causes of Refraction
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The main cause of refraction of light is the difference in the velocity of light when it enters different mediums.
- The speed of light in air is faster than that of water.
- Thus, the speed of light increases when it travels from water to air, and similarly, the speed decreases when it travels from air to water.
- When the light travels from air to glass, the speed gets reduced and the light moves toward the normal, that is the light rays move towards the NN’ normal from its original path.
- Likewise, when the light ray travels from glass to air, its speed gets increased and it moves away from the normal.
When light travels from a rarer substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends towards the normal line. When light travels from denser to rarer substances, the refracted light bends away from the normal.
- A light ray refracts when it travels into a medium of a different refractive index.
- If the light wave approaches the boundary or interfaces in a perpendicular direction, the ray of light doesn’t refract even though the speed changes.
- This change in speed also leads to a change in direction.
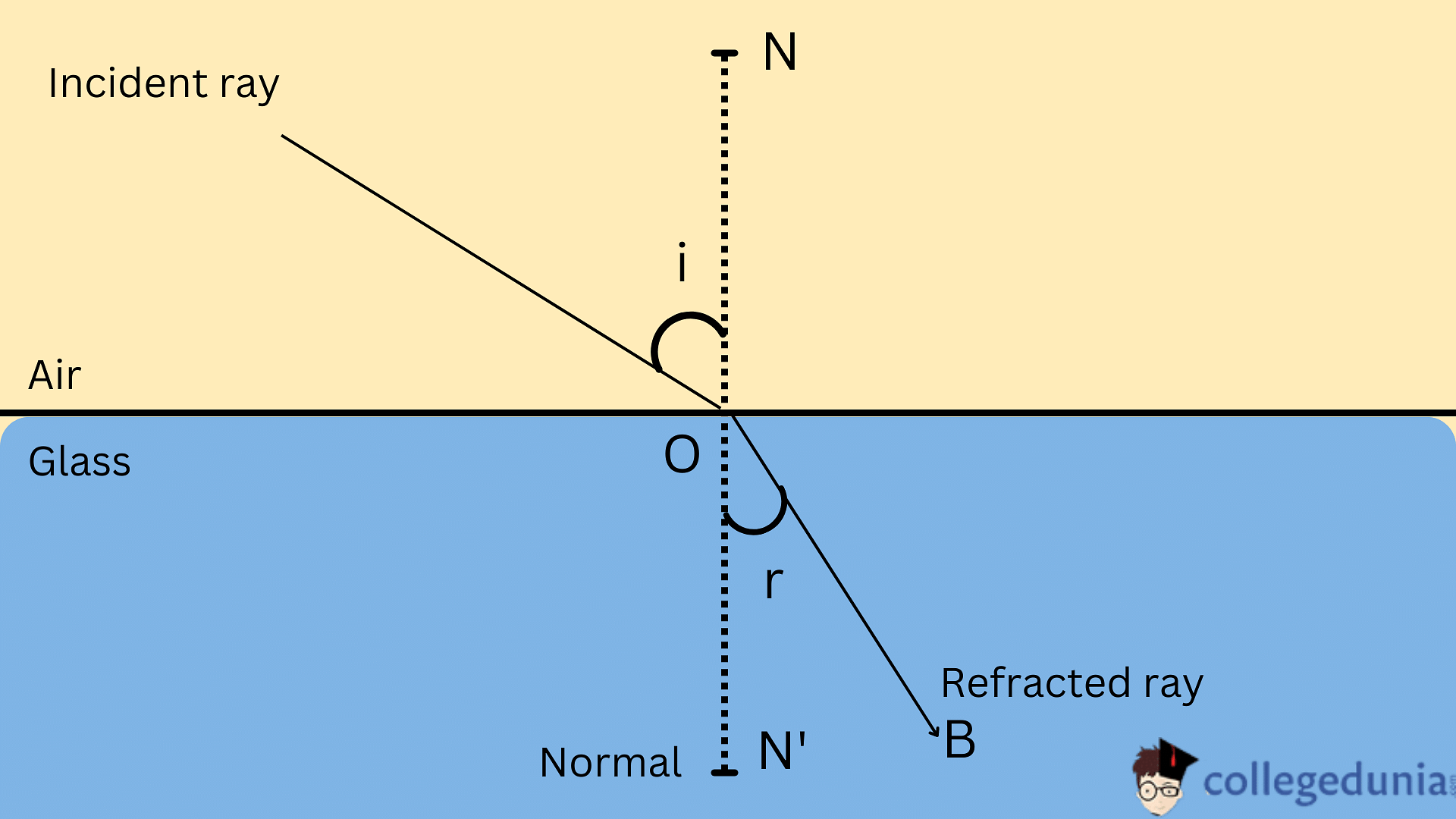
Causes of Refraction
Do you know?As light from a star passes through our atmosphere, it bounces through the different layers, bending the light before you see it. The bending of the light changes as well since the hot and cold layers of air keep moving, which causes the star's appearance to twinkle. Hence, stars twinkle due to atmospheric refraction of light. Read More: Why do stars twinkle? |
What is the Refractive Index?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]A refractive index is a number that explains how fast light travels when passed through a material.
- The Refractive index or the index of refraction gives the speed of light when it passes through a medium.
- The refractive Index is dimensionless.
- The Refractive index can be found by calculating the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum(c) to the ratio of the speed of light in a medium(v). It is denoted by µ.
| Refractive Index µ = c/v |
- The light ray changes its direction depending on the refractive index of the medium, or it bends at the junction while separating the two media.
- If the light ray travels from one medium to another with a higher refractive index, it bends towards the normal, else it bends away from the normal.
Read More: Uses of Plane Mirrors
Laws of Refraction of Light
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
There are two Laws of Refraction. They are:
- The incident ray, the normal to the interface of two media, and the refracted ray, all lie on the same plane.
- Snell's Law: Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sine of the incident angle to the sin of refracted is constant. It describes the relationship between angles of refraction and angles of incidence. The equation of Snell’s law is given by,
sin i/ sin r = constant
Also read: Calculation of change in velocity
Refraction of Light – Solved ExampleExample: Light that travels in air enters an optical fiber of 1.44 refractive index.
Solution:
We will take air as medium 1 and optical fibre as medium 2. Therefore, n1 = 1, n2 = 1, and θ1= 22o. Substituting the values in the equation: (1.00) sin 22o = 1.44 sin θ2 sin θ2 = (1.00/1.44) sin 22o = 0.260 θ2 = sin-1 (0.260) = 15o |
Types of Refraction
[Click Here for Sample Questions]There are mainly two types of refraction:
Refraction from denser to rarer medium
When a light ray travels from a medium of higher refractive index to a lower refractive index medium, the light ray bends towards the normal. The relative refractive index, in this case, is less than 1 and the angle of incidence is less than the angle of refraction. For example, the refraction from glass to air.
Refraction from rarer to the denser medium
When light travels from a medium with a lower refractive index to a higher refractive index medium, it bends away from the normal. In this case, the relative refractive index is greater than 1. The angle of incidence is also greater than the angle of refraction. For example, the refraction of light in water from the air.
Read More: Transmission, Absorption, and Reflection of Light
Refraction of Light in Real Life
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Some of the examples of refraction of light in real life are as follows –
- One of the most prominent examples of refraction is the formation of a rainbow. A Rainbow is formed as a result of refraction through the bending of sun rays through the raindrops.
- Mirage and looming are optical illusions, which are the result of the refraction of light.
- The band of seven colors obtained when white light is passed through a prism is a result of refraction.
- A swimming pool always looks shallower than it really is. This is because the light coming from the bottom of the pool bends at the surface due to the refraction of light.
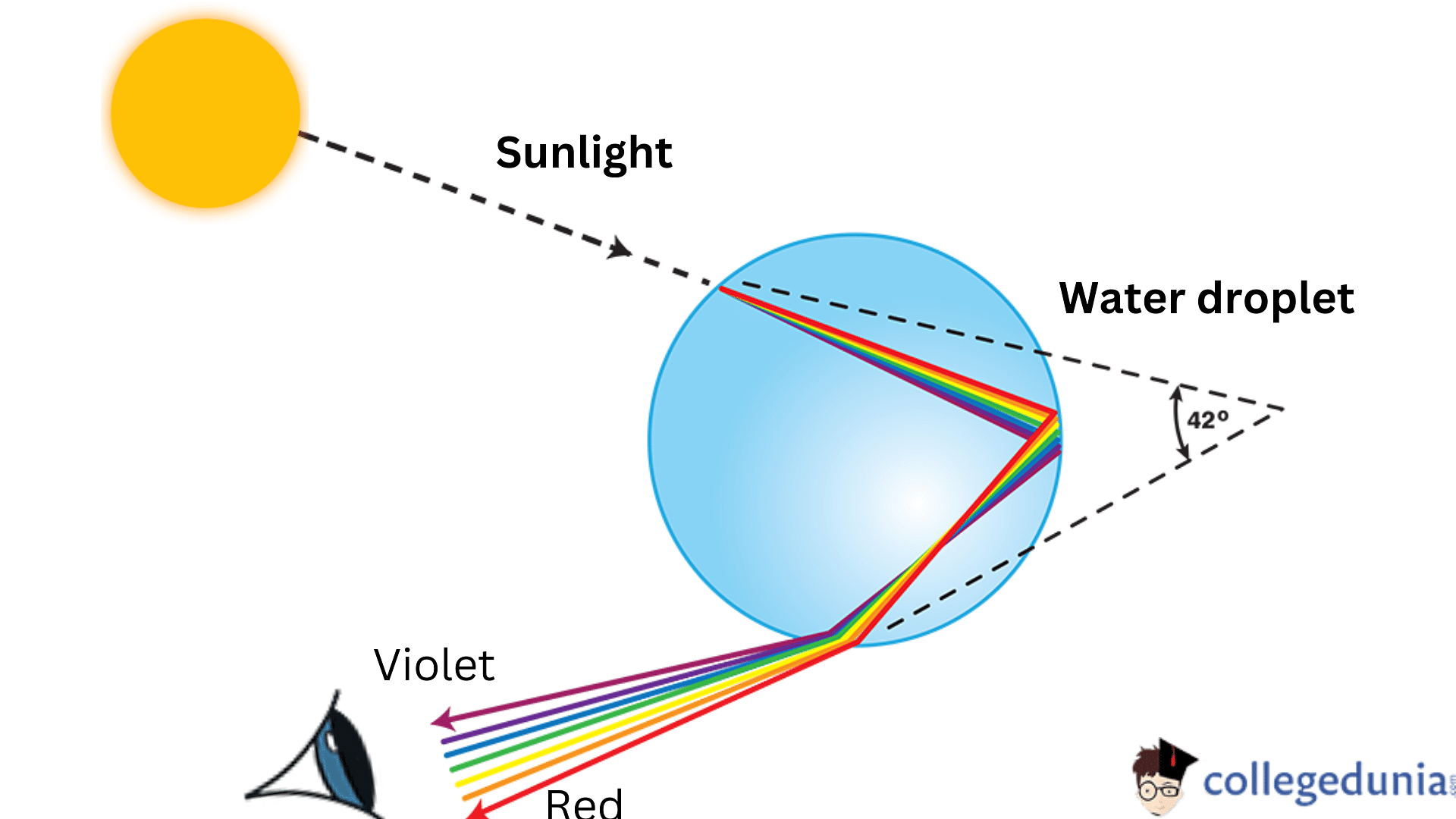
Applications of Refraction of Light
[Click Here for Sample Questions]The applications of refraction of light are –
- Refraction is used by a lens to serve various purposes such as magnification.
- A person with poor eye vision wears spectacles and is able to view the world clearly with the help of the refraction of light through the spectacles.
- The house doors, camera, movie projections, and telescope uses the concept of refraction of light.
Check Out:
Things to Remember
- Refraction of light is the bending of the light wave when it passes from one medium to another, which is caused due to the difference in the density of the two mediums.
- Refraction makes it possible for us to have optical instruments such as magnifying glasses, lenses, and prisms.
- The main cause of refraction is the variation in the velocity of the light or refractive indices when it enters different mediums.
- The first law of refraction states that the incident ray, the normal to the interface of two media, and the refracted ray, all lie on the same plane.
- Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sine of the incident angle to the sin of refracted is constant which describes the relationship between angles of refraction and angles of incidence.
-
Snell’s law equation is given by \(\frac{sin \ i}{sin \ r} \)= Constant
Previous Years’ Questions
- A lens forms real and virtual images of an object when the object is at… [AP EAPCET 2018]
- A convex lens is dipped in a liquid whose refractive index is equal to the… [NEET 2003]
- A bulb is located on a wall. Its image is to be obtained on a parallel wall with the help of a convex lens… [NEET 2002]
- A bubble in the glass slab (μ=1.5) when viewed from one side appears at 5 cm… [NEET 2000]
- The frequency of a light ray is 6×104Hz. Its frequency when it propagates in a… [DUET 2003]
- The size of the image of an object, which is at infinity, as formed by a convex lens of focal length… [JEE Advanced 2003]
- A point object O is placed in front of a glass rod having a spherical end with a radius of… [BITSAT 2008]
- When a light ray enters from oil to glass on the oil glass interface. The velocity of light… [JIPMER 2019]
- An isosceles prism of angle 120∘ has a refractive index of 1.44. Two parallel rays of… [JEE Advanced 1995]
- Two beams of red and violet color are made to pass separately through a prism with angle of prism… [UPSEE 2019]
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the reason for the refraction of light? (1 mark)
Ans. The main cause of the refraction of light is the change in the velocity of light while traveling in a different medium.
Ques. The refractive index (µ) of water is 1.33 and in air, the speed of light(c) is measured to be 3 x 108 ms-1. With the given values calculate the speed of light in the water.(1 mark)
Ans. µ= c/v
1.33 = 3 x 108 ms-1/v
v = 3 x 108 ms-1/1.33
= 2.25 x 108 ms-1
Ques. If it is given that the refractive index of carbon disulfide is 1.63, how is the speed of light in air and in the medium related?(1 mark)
Ans. As µ= c/v, we can say that the speed of light in the medium of carbon disulfide is 1/1.63 times the speed of light in the air.
Ques. How should a ray of light be incident on a rectangular glass slab so that it comes out from the opposite side of the slab without being displaced?(1 mark)
Ans. The ray of light should be incident at a 0° angle, in order to make the ray pass through the glass slab without being displaced.
Ques. Light traveling in air enters into an optical fiber of refractive index 1.44. State the answers: (3 marks)
a) In which direction does the light bend?
b) If the angle of incidence on one end of the fiber is 22o, then find the angle of refraction.
Ans:
a) As the light travels from a rarer medium(air) to a denser medium(optical fiber). Therefore, the refracted ray will bend towards the normal.
b) The angle of refraction can be calculated with the steps given below:
Let air be medium 1 and optical fibre be medium 2.
Therefore, n1 = 1.00, n2 = 1.44, and θ1= 22o.
Now, substituting the values in the equation as follows:
(1.00) sin 22o = 1.44 sin θ2.
sin θ2 = (1.00/1.44) sin 22o = 0.260
θ2 = sin-1 (0.260) = 15o
Ques. The light traveling through the optical fiber reaches the end of the optical fiber and exits into the air. Find the angle of refraction outside the fiber if the angle of incidence at the end of the tube is 30o. (3 marks)
Ans. Let us assume the fiber is medium 1 and air is medium 2.
Hence, n1 = 1.44, n2 = 1.00, and θ,1 = 30o.
Substituting the values in the equation, we get
(1.44) sin 30o = 1.00 sin θ2
sin θ2 = (1.44/1.00) sin 30o = 1.44 (0.500) = 0.720
θ2 = sin-1 (0.720) = 46o
Here, the angle of refraction is larger than the angle of incidence. This indicates that the light is bending away from the normal as it enters a rarer material.
Ques. What is the difference between refraction and reflection of light? (3 marks)
Ans. Reflection of light occurs when the light bounces off a medium. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection if the medium has a smooth surface. While refraction of light is the change in the direction of light as it passes from one medium to another.
Ques. What do you mean by refractive index? (2 marks)
Ans. The refractive index can be defined as the measure of the bending of a light ray when it passes from one medium to another. It can also be described as the ratio of the velocity of a light ray in an empty space to the velocity of light in a substance, n = c/v.
Ques. What is meant by dispersion of light? (2 marks)
Ans. Dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting a beam of white light into its seven constituent colors when passed through a transparent medium such as a prism. The refractive index of materials varies with the wavelength and frequency of light.
Ques. What do you mean by the reflection of light? (3 marks)
Ans. Reflection of light is the phenomenon that takes place when a ray of light approaches a smooth polished surface and the light ray bounces back. The incident light ray that lands on the surface are reflected off the surface. The ray that bounces back is called the reflected ray.
Ques. What is total internal reflection? (3 marks)
Ans. Total internal reflection is defined as the complete reflection of a light ray within a medium such as water or glass from the surrounding surfaces back into the medium. The phenomenon takes place if the angle of incidence is greater than a certain limiting angle, called the critical angle.
Ques. What are the two laws of reflection of light? (Delhi 2011)
Ans. Laws of reflection of the light state that:
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Ques. When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is
(a) real
(b) inverted
(c) virtual and inverted
(d) virtual and erect (2020)
Ans. The correct answer is (d) An enlarged virtual and erect image is formed behind the mirror when an object is placed between the principal focus and pole of a concave mirror.
Ques. Draw a labeled ray diagram showing the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror. Also, mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it. (AI 2019)
Ans.

Read More:




Comments