Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Dominant trait is a common term referred to in genetics. In biology, genetics is a field of study that takes a close look at inheritance and variation of character. When two genes are in contact, the gene that emerges dominant is called the dominant gene. The dominant gene masks or covers up the weaker gene and is responsible for dominant traits. Some examples of the concept are dark hair dominant over blond hair, cleft chin, baldness.
What are Character and Traits?
Character is the feature of an individual while a trait is the distinguishable feature of a character and its delectable variant. For example, the hair color would be a character while black hair is a trait.
What is Allele?
In the simplest terms, an allele is two or more versions of a gene. A person inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. If two alleles are the same, we can say that the person is homozygous for that particular gene. If the two alleles are different we can say that the person is heterozygous for that particular gene.
Mendel’s Experiments
Gregor Johann Mendel’s experiments were a huge breakthrough in the field of genetics. He was the first scientist to give a scientific explanation for inheritance and variation of character through hybridization experiments. Mendel wasn’t the first person to conduct these experiments, however. He simply modified them. Kingsley and Goss were the first. Mendel considered two or three genes at a time in his experiments much to his great success.
Mendel conducted his experiments on garden peas. They were chosen because of the following reasons:
- They had a large number of traits to consider.
- They showed self-pollination and cross-pollinating them was easy. Cross-pollination produced fertile hybrids.
- They completed their growth in one season.
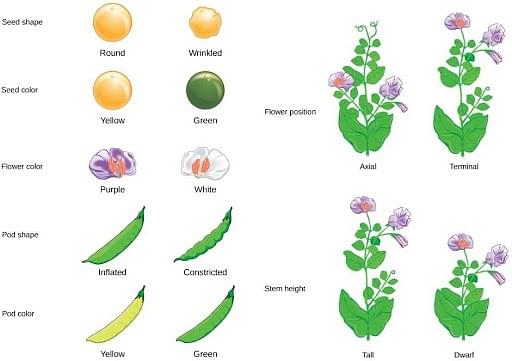
Mendel’s Experiments
Mendel chose 14 plants to study and selected 7 characters to study throughout generations of crossbreeding. The characters considered for the study were:
- Seed shape
- Seed color
- Flower color
- Pod color
- Pod shape
- Stem height
- Flower position
Dominant and Recessive
Based on the results of his experiments, Mendel made the following proposals:
- If two dissimilar characters are present in a person, only one of these characters will carry over to the next generation.
- The characters that express themselves in the next generation are known as dominant and those that do not are termed as recessive.
- The dominant allele prevents or masks the recessive allele from expressing itself.
The characters can be either genotype or phenotype. Genotype means genetic characteristics and phenotype means physical characteristics that can be seen with the naked eye.
Also Read:
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
Based on his observations and the results of his experiments, Mendel made the three laws referred to as laws of inheritance
- Each character of the garden pea is controlled by some discrete units. These discrete units are called factors and they always occur in pairs. When two dissimilar kinds of factors occur together, one factor expresses itself while the other can’t. The factor that expresses itself is called the dominant factor and the factor that can’t express itself is called the recessive factor. This is called the law of dominance but it is not a universal law.
- The Law of segregation is when two members of a pair of alleles separate during gamete(gametes are reproductive cells) formation. Hence, gametes carry only one factor of a character. It is to ensure the purity of gametes. This law is universal.
- The Law of independent assortment states that alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, during gamete formation, one pair of traits separate from another pair of traits independently.
Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete dominance happens when neither allele is completely dominant over the other. As a result, a phenotype that is a combination of both alleles occurs. After Mendel’s experiments on garden peas, scientists repeated the experiment on other plants. They observed variation in the law of inheritance. Plants showed properties that neither belonged to either parent but was a combination of both.
Incomplete dominance can be observed with the example of snapdragon flowers.

Incomplete Dominance
As can be seen in the picture, crossing red and white snapdragon flowers make pink snapdragon flowers. In humans, an example would be the child of a straight-haired parent and a curly-haired parent having wavy hair.
Codominance
Codominance means that both alleles express themselves in the phenotype. It is different from incomplete dominance in this regard. For example, instead of a red and white flower crossing into a uniformly pink flower(which would be incomplete dominance), the flower would have white and red patches.
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- Character refers to a feature of an individual. Trait means distinguishable features of a character. For example, eye color is a character while blue eyes are a trait.
- Allele means two or more versions of a gene. A person inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent.
- Mendel conducted hybridization experiments on garden peas and carefully documented the results. He used his observations to formulate the laws of inheritance.
- When two dissimilar factors occur together, one factor expresses itself while the other doesn’t. The factor that expresses itself is called the dominant factor and the factor that doesn’t is called the recessive factor. This is called the law of dominance. It is not universal.
- The Law of segregation states that two members of a pair of alleles separate during gamete formation. Hence, one gamete contains only one member of every pair of genes.
- The Law of independent assortment states that one pair of traits separate from another pair of traits independently.
- Mendel’s experiments were a success due to his application of principles of mathematics and statistics, his meticulous recording of observations, large sample data, and forming theoretical explanations based on initial data.
- Incomplete dominance happens when neither allele is dominant over the other. Incomplete dominance can be observed in snapdragon flowers.
- Codominance is different from incomplete dominance in that both alleles express themselves in the phenotype. For example, a white and red flower would cross into a flower with red and white patches.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is an allele? (1 Mark)
Ans. An allele is two or more versions of a gene. A person inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. If two alleles are the same, we can say that the person is homozygous for that particular gene. If the two alleles are different, we can say that the person is heterozygous for that particular gene.
Ques. Give examples of incomplete dominance in humans. (1 Mark)
Ans. Incomplete dominance is rare in humans as humans are genetically complex. The child of a curly-haired parent and a straight-haired parent will have wavy hair. Another example would be eye color.
Ques. What is codominance? (1 Mark)
Ans. Codominance means that both alleles express themselves in the phenotype. It is different from incomplete dominance in this regard. For example, a red and white flower crossing into a flower with white and red patches.
Ques. What do you mean by phenotype and genotype? (1 Mark)
Ans. Genotype means genetic characteristics and phenotype means physical characteristics that can be seen with the naked eye.
Ques. Explain the difference between character and trait. Give examples for both. (2 Marks)
Ans. Character is the feature of an individual while a trait is the distinguishable feature of a character and its delectable variant.
Examples for character: eye color, hair color
Examples for trait: blue eyes, red hair
Ques. Explain the term incomplete dominance. How is incomplete dominance observed in snapdragon flowers? (2 Marks)
Ans. Incomplete dominance happens when neither allele is completely dominant over the other. As a result, a phenotype that is a combination of both alleles occurs.
In snapdragon flowers, when red and white snapdragon flowers are crossed, we get pink snapdragon flowers.
Ques. Why did Mendel choose garden peas for his experiments? (2 Marks)
Ans. Mendel experimented with garden peas for the following reasons :
- They had a large number of traits to consider.
- They showed self-pollination and cross-pollinating them was easy. Cross-pollination produced fertile hybrids.
- They completed their growth in one season.
Ques. What are the three laws of inheritance? (3 Marks)
Ans. Based on his experiments of hybridization on garden peas Mendel made the following observations which came to be called the laws of inheritance.
- Each character of the garden pea was controlled by some discrete units. These discrete units are called factors and they always occur in pairs. When two dissimilar kinds of factors occur together, one factor expresses itself while the other can’t. The factor that expresses itself is called the dominant factor and the factor that can’t express itself is called the recessive factor. This is called the law of dominance but it is not a universal law.
- The Law of segregation is when two members of a pair of alleles separate during gamete formation. Hence, gametes carry only one factor of a character. It is to ensure the purity of gametes. This law is universal.
- The Law of independent assortment states that alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, during gamete formation, one pair of traits separate from another pair of traits independently.




Comments