Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
An element is the simplest form of matter that can not be converted into simpler substances or built from simpler substances by any ordinary chemical or pysical method. Elements can further be classified into metals, non-metals and metalloids depending on their properties, which are correlated with their placement in the periodic table. We are aware of the usefulness of the metals and non-metals but we are not that much familiar with their properties. In this article, we will look into the physical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Metals, Non-metals, Metalloids, Elements, Sulphur, Carbon, Halogens, Phosphorus, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Selenium, Nitrogen, Noble gases
Definition
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The physical properties of metals and non-metals are a way of identifying their characteristics. This identification can further help us in recognizing their applications. Various types of elements, metals, and non-metals, are omnipresent in our day-to-day lives and are provided to us by the environment at different stages. Our only concern is to identify them and recognize their optimal applications. The chapter on the physical properties is an intrinsic part of the syllabus of class 9th and 10th. The chapter tries to give a detailed analysis of the prominent characteristics and features of metals and non-metals that will help in developing your understanding and knowledge about the topic. This article will give you a brief overview of the chapter.
Read More:-
| Chapter Related Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ester Hydrolysis | Fehling Test | Iodoform Test |
| Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction | Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction | Butyric Acid |
| Resonance | Grignard Reagent | Enantiomers |
Metals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The periodic table is majorly composed of metals. The metals therein are separated by non-metals through a zigzag line starting from Carbon to Radon. The elements that exist between the two elements are phosphorus, selenium, and iodine. The elements present on the left-hand side of the periodic table are termed as metals. There are various types of metals such as alkali metals, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides, and alkaline earth metals.
Non-metals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The zig-zag elements and the elements existing to the right of them in the periodic table are non-metals. Elements such as sulphur, carbon, all halogens, phosphorus, hydrogen, oxygen, selenium, nitrogen, and noble gases are categorized as non-metals. Therefore, the periodic table has very few elements that are non-metals. The elements that are present in between metals and non-metals are termed semimetals or metalloids. These will have the combined properties of both metals and non-metals.
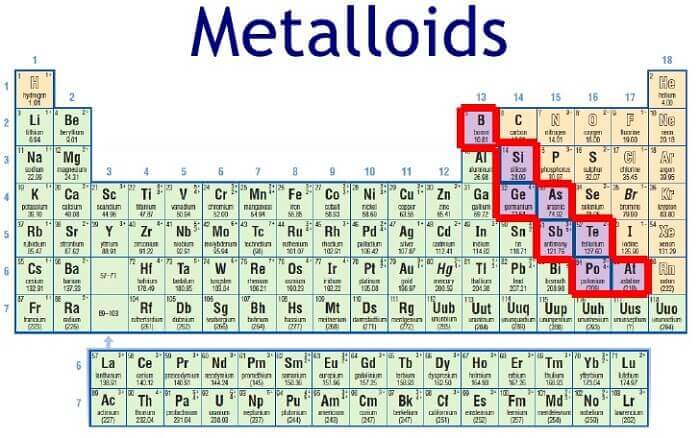
Metalloids
Physical Properties of Metals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The planet Earth is a storehouse of metals. In fact, the entire composition of the inner core of the Earth consists of iron and nickel which are classified as metals. These metals have different characteristics and properties which ultimately make them liable for some specific utilisations. Some of the properties of metals are as follows.
Metals are heavy-weight due to their high density. They also have a very high melting and boiling point because of the stronger bond they carry. The most important property of any metals is that they are a very good conductor of electricity. This is very well exhibited through the application of the copper wires in wiring. Metals could be easily used to conduct the electricity because of the presence of the free negative charges in them. Thus, making it different from non-metals.Metals are also a good conductor of heat. That’s why pots, pans, vessels are made up of metals.
All the metals are generally hard. Although, the intensity of their hardness varies from metal to metal. Due to this property, they can’t be broken easily and hence require a lot of energy and strength for the same, therefore making it difficult to change their shapes. For example, iron is used to make cars, buildings, ships, etc. All the pure metals have shiny surfaces. This gives them the property of metallic lustre. This allows its application in jewelry making such as Gold. Metals do not have flexibility but they have tensile strength. They cannot be stretched. These metals are high on ductility which allows them to be drawn into a thin wire. For instance, gold is very high on ductility as one gram of gold can draw 2 kilometers of a wire.
Physical Properties of Non-Metals
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
We all are very much familiar with the most common non-metals which are oxygen and hydrogen. Although, when the earth was formed about 4.5 billion years ago oxygen was absent, but now it has become an important non-metal vital for our existence. Apart from this, various other important non-metals also exist and in order to make their optimum utilization, it is important to understand their physical properties. Non-metals could be found in any state – solid, liquid, or gaseous. They are extremely weak and brittle and sometimes do not possess much weight due to low density. Hence, they tend to easily break or shatter.
Moreover, Non-metals have high ionization energies. And they are also insulators. Unlike metals, non-metals are poor conductors of electricity. This also makes non-metals a poor conductor of heat. They’re poor thermal conductors because they have the property of gaining electrons very easily. They do not shine like metals. Thus, the non-metals are pale and dull. One of the most effective properties of non-metals is that they are capable of forming acidic oxides. Thus, it makes them good oxidizing agents.
Read More:-
Sample Questions
Q1. Where are metals in the periodic table?(1 mark)
Ans. The periodic table is majorly composed of metals. The metals therein are separated by non-metals through a zigzag line starting from Carbon to Radon. The elements that exist between the two elements are phosphorus, selenium, and iodine. The elements present on the left-hand side of the periodic table are termed as metals.
Q2. What is the meaning of malleability and ductililty?(1 mark)
Ans. Malleability refers to a property in which a metal is hammered down to a thin sheet without any breaking. For example, gold and silver are metals having malleable properties.
While on the other hand, ductility refers to a property in which a metal is drawn into a thin wire. For example, gold is a highly ductile metal.
Q3. Mention the name of the metal which is liquid at room temperature?(1 mark)
Ans. Mercury is the only metal that is found in a liquid form at room temperature.
Q4. Which metal is resistant to any reaction with steam?(1 mark)
Ans. Silver is a metal that has a property that prevents it from even reacting with heat.
Q5. What is formed after a metal reacts with oxygen?(1 mark)
Ans. Basic oxides are formed when metals (except Al and Zn) react with oxygen.
Q6. Mention a non-metal that also acts as a conductor?(1 mark)
Ans. Graphite is a non-metal that is also a good conductor of electricity.
Ques: (a) Due to which property of metals are metallic foils prepared?
(b) State the uses of aluminium foils.(2 marks)
Ans: (a) The metallic foils are prepared by making use of the malleable property of metals.
(b) The uses of aluminium foils are,
- Wrapping chocolates and food staffs
- to prepare hydrogen
Ques: Why do some metals like, Na, K, Ca, Mg not occur in nature as free elements?(2 marks)
Ans: Metals like Na, K, and all the alkali metals and Ca, Mg and all other alkaline earth metals are very reactive due to which they react with oxygen and carbon dioxide and alos with other nonmetals like sulphur present in the earth’s crust to form compounds like oxide, carbonates, sulphates, sulphides, chlorides. Therefore, they are not found in free state but in the form of the above compounds.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Check:




Comments