Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
A solar cooker is used for the purpose of cooking food using the energy that is radiated by the Sun, i.e. the solar energy. We often use stoves and ovens for cooking vegetables, meat, and rice. Solar cooker helps us in cooking the same food but instead of utilizing gas or electricity, we use a naturally abundant resource, our sunlight. It works on the principle of converting light energy into heat energy. In this article, we will have a look at the working of a solar cooker, its working principle, construction, and the pros and cons of using a solar cooker.
| Table of Content |
What is a Solar Cooker?
Solar Cooker is a device used for cooking food with the energy of direct sunlight, usually employing reflective panels to focus the light on a dark-colored pot in an insulated box.
Sunlight refers to the electromagnetic radiation which is produced by changing electric and magnetic fields. When photons from light waves contact molecules in a substance, they convert sunlight to heat. Energy is included in the electromagnetic radiation released by the Sun. When they hit, the energy causes the matter molecules to vibrate. The molecules become energized and rise to new heights. Heat is produced as a result of this process.
Solar Cooker
In this way, we use the energy generated by the Sun to cook our food in a solar cooker that makes use of the concave mirror. Concave mirrors are used as they reflect the light from the sun to a single point known as the focus. The solar cooker operates on the concept that sunshine warms the pot in which the food is cooked. The pot gets warmed by turning light energy into heat energy. The concave mirror concentrates the sun's rays onto a receiver, such as a cooking pan, in this case. UV light rays enter a solar cooker, which is subsequently transformed into longer infrared light rays that cannot escape.
Also Read: Uses of Solar Panels
Solar cooker Working Principle
- Sunlight Concentration: To concentrate and channel light from the sun into a tiny cooking space, a mirror surface with a high specular reflection is used. The magnitude of the sunlight can even melt salt and metal but these high temperatures are not required for solar cooking in the home. Therefore, in the market solar cookers are designed to reach temperatures ranging from 650°C to 4000°C.
- Converting Light Energy into Heat Energy: The concentrated sunlight is focused onto a receiver, such as a cooking pan. In order to maximize absorption, solar cooker pots and pans should be matte black. The interaction of light energy with the receiver transforms it into heat through conduction.
- Trapping Heat Energy: Using a glass lid on the pot increases light absorption from the top of the pan, reduces convective energy loss, and improves the cooker's heat holding ability. The glazing allows infrared thermal rays to pass through but is opaque to incoming sunlight.
Also Read: Some Natural Phenomena due to Sunlight

Working of a Solar Cooker
Types of Solar cooker
Solar cookers are divided mainly into two categories:
- Box Type
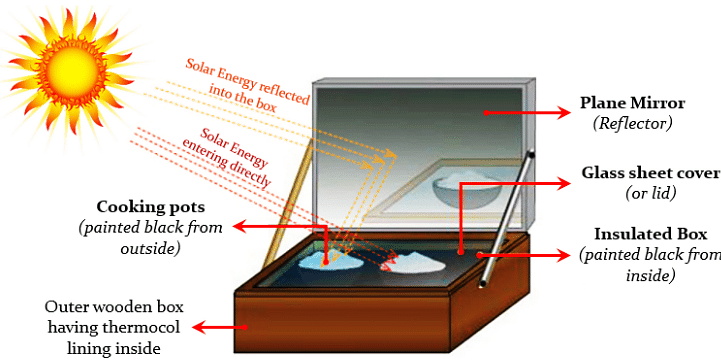
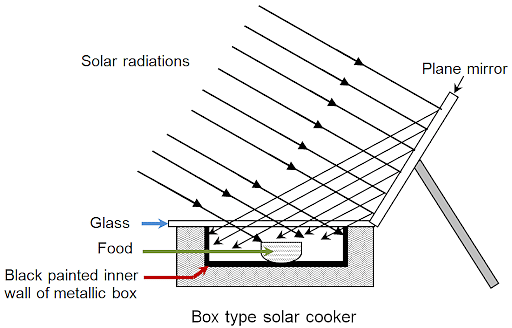
Heat is reflected by a reflector into a box in this style of the cooker, and then trapped by the top glass, creating a greenhouse effect that heats the cooking utensils. It consists of:
- Black Box
- Glass Cover
- Cooking Containers
- Plane Mirror Reflector
???
- Parabolic Type
The heat converges at a spot where the cooking tools are stored; it heats up and cooks the food in this type.
Other subcategories include:
- Cookers in boxes (often called box ovens)
- Cookers with a parabola
- Cookers in tubes
Also Read: Photoelectric Effect
Box-type solar cooker
The box-type solar cooker is the most common type of solar cooker. The following are the components of a box-type solar cooker:
- The black box is a heat-absorbing insulated metal or wooden box that is painted black on the inside.
- As a cover for box B, a cover constructed of two sheets of toughened glass joined together in an aluminum frame is employed.
- The plane mirror reflector is hinge-affixed to box B. The mirror reflector can be angled towards the box at any angle. The mirror is set up in such a way that the reflected sunlight falls on the box's glass lid.
- In box B, you'll find a set of blackened aluminum containers.
The solar cooker is set up in the sun with a plane mirror reflector so that a strong beam of sunlight enters the box via the glass sheet. The heat created by the infrared radiation absorbed by the blackened metal surfaces in the wooden box elevates the temperature of a blackened metal surface to around 100°C.
Solar Cooker Pros and cons
Pros
- Solar cookers do not require any fuel and thus it helps us save money and protect the environment by preventing pollution.
- Cooking without carbon dioxide-based fuels reduces carbon footprint.
Cons
- In cloudy conditions, solar cookers are less effective.
- Food takes longer to cook in some solar cookers than it does in a standard stove or oven.
- Cooking some thick dishes, such as huge roasts and loaves of bread, may be difficult.
- Strong gusts of winds might influence some solar cookers, slowing down the cooking process.
Construction of solar cooker
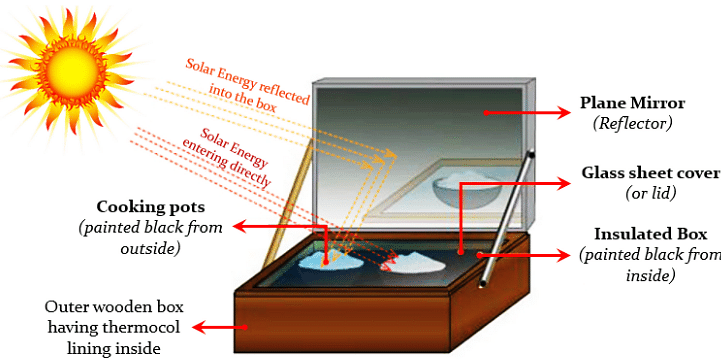
Step 1: Make a box out of an aluminum sheet using a wooden box as a template.
Step 2: Use black paint to paint the inside of the aluminum box.
Step 3: Place this aluminium box into the wooden box.
Step 4: Attach the mirror to the lid, then secure the lid to the wooden box using the hinges.
Step 5: Place a glass sheet on top of the box.
Step 6: To prepare the food, paint the containers in which we intend to cook, as well as the tools, black from the outside.
Step 7: Fill these containers with food and place them inside the box.
As a result, the glass sheet serves to trap heat inside the box, while the mirror converges light into the box, heating it, and the solar cooker is ready to prepare meals.
Construction of a Solar Cooker
Things to Remember
- When photons from light waves contact with molecules in a substance, they convert sunlight to heat.
- We use the energy generated by the Sun to cook our food in a solar cooker.
- The solar cooker operates on the concept that sunshine warms the pot in which the food is cooked.
- When light strikes the concave mirror, all of the Sun's UV rays are concentrated into a single focal point on the cooker, causing the cooker to heat up and aiding in the cooking process.
- The solar cooker functions as a mystical weapon in the fight against environmental challenges such as air pollution.
Sample Questions
Ques. Define Solar cooker. (1 mark)
Ans. A device used for cooking food with the energy of direct sunlight, usually employing reflective panels to focus the light on a dark-colored pot in an insulated box is known as a solar cooker.
Ques. Which type of mirror, concave, convex, or plane, is used in a solar cooker, and why? (3 marks)
Ans. A concave mirror is mostly used in the solar cooker as it is a converging mirror. When light strikes the mirror, all of the Sun's UV rays are concentrated into a single focal point on the cooker, causing the cooker to heat up and aiding in the cooking process.
Ques. What are the benefits of using a Parabolic Cooker? (3 marks)
Ans. The following are some of the benefits of parabolic solar cookers:
- They are not harmful to the environment.
- They focus light on a smaller area to achieve high temperatures of around 350 degrees Celsius (662 degrees Fahrenheit), allowing the food to be cooked.
Ques. Is Solar Cooking Good for health? (3 marks)
Ans. Yes, the food cooked in a solar cooker is good for health as:
- The essential vitamins and other nutrients in the food are not lost.
- In addition, the meal is free of mutagens and carcinogens created by standard high-heat cooking procedures.
Ques. How Can Solar Cooking Aid In Illness Prevention? (2 marks)
Ans. The solar cooker doesn't produce ash and can be used to replace traditional cooking methods that are harmful to the environment and therefore by the preservation of our environment, helps us in staying healthy.
Ques. What are the cons of using a solar cooker? (3 marks)
Ans. Some of the disadvantages of using a solar cooker are:
- Food takes longer to cook in some solar cookers than it does in a standard stove or oven.
- It might not work properly in cloudy conditions.
- Cooking some thick dishes, such as huge roasts and loaves of bread, may be difficult.
Ques. Name types of solar cookers. (5 marks)
Ans. There are mainly two types of solar cookers:
- Box type
- Parabolic type
Other subcategories include:
- Cookers in boxes (often called box ovens)
- Cookers with a parabola
- Cookers in tubes









Comments