Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
A two-terminal electrical device that does not allow the electricity to flow freely in a circuit is known as a resistor. A circuit generally consists of load, Power source, wires, switch, and a resistor. The main usage of resistors within a circuit is to reduce flowing current or adjust their levels or diverge voltages. The switch used in a Circuit either makes or breaks the circuit. Many circuits do contain more than one resistor to make a limitation in the flow of the charges in it. The resistors can form two kinds of combination: Series & Parallel. In an electric circuit, there is a stable and constant flow of electricity, and the electric current flows from the higher potential towards the lower potential. A perfect example of this type of circuit in households is the tube light or any other light.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Electrical Device, Electricity, Resistor, Circuit, Voltage, Electric current, Ohm’s law, Potential Drop
Ohm’s Law
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
According to Ohm’s Law,
V = IR
where I denote current
R is constant and denotes resistance
and V denotes the potential difference
Also from the above equation, we get
I = V/R
Hence, the current passing through the resistor is also inversely proportional to its resistance, which means if we double the resistance of the circuit, the current will be halved. A device known as rheostat is generally used in a circuit to change the resistance in it.
Read more: Electricity
Calculation of Resistance in Series Combination
[Click Here for Sample Questions]

Calculation of Resistance in Series Combination
In the case of a series combination, we have the resistors set in series, hence the flow of current in them will pass through the resistors one after another. There is always a chance of a drop of voltage in it.
Again we can use Ohm’s Law to explain the series combination in order to calculate the resistance in the circuit, i.e.
V = IR; where V stands for the Potential Drop.
The circuit construction in series combination is much simpler than Parallel combination circuits. In a series combination, if any kinds of fault or damage take place, it would result in the turning off of the entire circuit.
Read more: Circuit Law
If the number of resistors present in a circuit is 4, then the according to the Ohm’s Law:
V = IR
Rtotal = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4
In the case of the condition where there are ‘n’ numbers of resistors:
The total resistance in the circuit will be: Rtotal = R1 + R2 + ...… + Rn
The total amount of resistance in the circuit is the total amount of individual resistances.
Read Also:
Calculation of Resistance in Parallel Combination
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
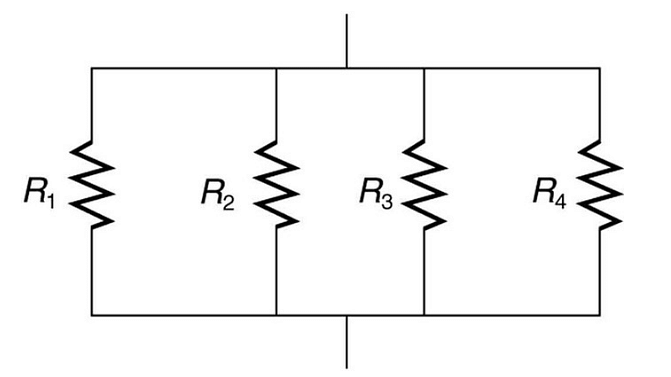
Calculation of Resistance in Parallel Combination
In the case of a Parallel Combination in an electric circuit, the current gets divided itself and flows through different branches, and meets at a common point where the branches meet. While there are many paths for the current to flow, all branches of the parallel circuit may not have the same amount of current flowing through them. So, the resistors in a parallel combination would have a Common Voltage in them. In a parallel circuit, any component or resistor can be easily disconnected or connected and that will not affect the other elements of the circuit.
Read more: Important Formula in electricity
In Parallel arrangement, if four resistors are joined in a circuit, then the total current I, will be calculated by summing up the separate currents flowing through each branch of the arrangement.
I = I1 + I2 + I3 + I4
Using Ohm’s Law to calculate the resistance, we have
I = V/R
Applying this formula on separate resistors- I1 = V/R1
I2 = V/R2
I3 = V/R3
I4 = V/R4
So, V/Rp = V/R1 +V/R2 + V/R3+V/R4 or
I/Rp = I/R1 + I/R2 +I/R3+I/R4
Hence, we can come to the conclusion that the reciprocal of the individual resistances of a parallel circuit are summed up together and is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
In case of n number of resistors joined in a parallel arrangement, the resistance will be
1/Rtotal = 1/ R1+1/R2+......+1/Rn
Read more: Insulators
Sample Questions
Question: What is a circuit composed of? (1 mark)
Answer: An electrical circuit is composed of a power source, conductors (wires), resistor, Load, and a switch to control the flow of current. These components are the major requirement for a circuit to work and the electricity to flow through the circuit.
Read more: Conductor
Question: What is a mixed resistor circuit? (1 mark)
Answer: If resistors are connected in series as well as parallel combinations in the same circuit but in different loops to form a much more complex resistive channel. These types of circuits can be called mixed resistor circuits.
Question: What is the advantage of joining resistors in parallel combinations in a circuit? (1 mark)
Answer: The advantage of joining the resistors of a circuit in parallel combination is that in case if there is any kind of damage, breakage, or fault in any one component of the circuit, the current will still pass and it won’t affect the other components of the circuit. This procedure is not the same in the case of series combinations.
Question: Why in the case of domestic circuits the series combination is not used? (1 mark)
Answer: In series combination, if any component gets damaged, the entire circuit will break and none of the other components will work. As in the case of Parallel arrangement, the entire current gets divided throughout the circuits of electrical appliances, parallel combinations are much safer to use in domestic circuits.
Question: What are the ways to recognize if the resistors are in series or parallel combinations? (1 mark)
Answer: The effective way to understand or recognize whether the resistors are in parallel or series combinations is to look at the joining or junction of the electrical circuit.
- If the resistors are in a series combination, then the head of one resistor will be joined with the tail of another resistor and there will not be any other connection in between the resistors.
- In the case of parallel combination, the heads of two or more resistors will meet at a common joining and the tails will meet in another joining or intersection.
Read Also:








Comments