Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
The conservation of natural resources are important for healthy and sustainable life. Natural resources are the resources that are derived from nature without the absence of human intervention. This comprises sources of value such as commercial and industrial utility, aesthetic value, scientific curiosity, and cultural worth. It encompasses the sun, the atmosphere, water, land, all minerals, all plants, and all animal life on Earth.
These resources can be safeguarded in natural reserves as part of our natural heritage if every individual along with the government take the necessary steps to conserve nature. In this article, we will look at ways for conservation of natural resources, the importance of conservation, and the types of natural resources.
Related Links
What are Natural Resources?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
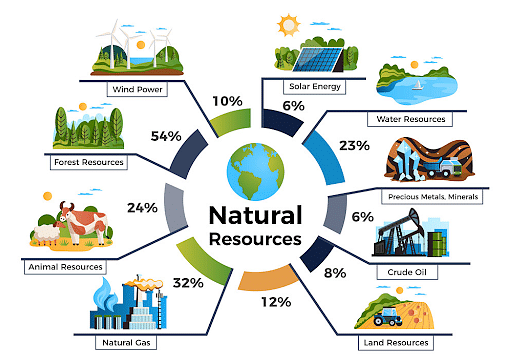
A natural resource might be any kind of material that are derived from nature and can be used by people. These include coal, oil, metals, natural gas, stone, and sand. Air, sunshine, soil, and water are all examples of natural resources. Food, fuel, and raw materials for manufacturing are all made from natural resources. Plants and animals provide all of the food that people consume. Heat, light, and electricity are provided by natural resources such as coal, natural gas, and oil.
The conservation of natural resources is very important as our daily needs are also fulfilled by nature for example-water that we drink, food that we eat, and air that we breathe, as well as clothing, automobiles, televisions, computers, and refrigerators. Natural resources may be used to get a variety of essential items. The following are some examples:
- Wind energy is generated by blowing air.
- Food, clothing
- (wool, silk), and other products are made from animals.
- Coal is utilized in the power generation process.
- Plants are used to make food, paper, and timber, among other things.
- Water is utilized for a variety of purposes, including drinking, washing, and hydroelectricity.
- Photosynthesis, solar electricity, and other processes rely on sunlight.
Natural resources
Type of Natural Resources
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
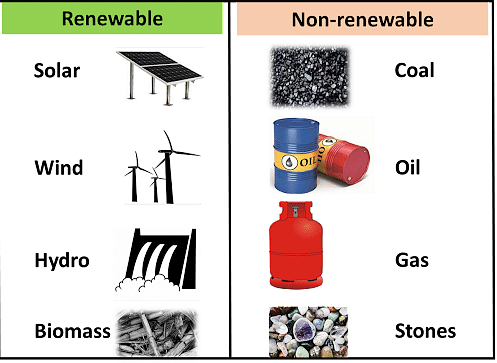
Natural Resources can be classified mainly into two types, Renewable, and Non-renewable resources.
- Renewable resources are natural resources that can be renewed at roughly the same rate as they are consumed, such as trees, water, sun, and wind. Renewable resources, on the other hand, can be exhausted if they are not managed or protected appropriately.
- Non-renewable resources are natural resources that are exhausted faster and that can not be replenished. Oil and natural gas are fossil fuels that have been created over millions of years. Nonrenewable resources are gone for good once they've been extracted and used up.
Natural resources can also be classified as biotic and abiotic resources:
- Natural resources that come from the biosphere are known as biotic natural resources (organic and living materials). These include animals, woods (vegetation), and various things that may be obtained from them. Because they are made up of decomposed organic matter, fossil fuels like petroleum, oil, and coal are included in this category.
- The non-organic and non-living natural resources are referred to as abiotic natural resources. Water, land, air, and heavy metals such as iron, copper, silver, gold, and others are examples of abiotic natural resources.
Nature also has metallic and non-metallic resources:
- Minerals that include metals are known as metallic minerals. They are tougher, more lustrous, and may be melted to create new items. Iron, copper, and tin are some examples.
- Metals are absent from non-metallic minerals. They are softer and lack lustre. Clay and coal are two examples.
Renewable vs Non-renewable resources
Conservation of Natural Resources
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Everything we need in our daily lives are derived from the natural resources accessible to us. Furthermore, even artificial resources are derived from natural resources that are readily available in nature. We never consider, however, that if we utilize these resources carelessly, they would ultimately be depleted. Global population growth, increasing urbanization, and industrialization have all resulted in higher demand for available resources.
Conservation of Natural Resources refers to the practice of minimizing the waste of natural resources and ensuring the needs of the present are met with a consideration of the needs of the future. The contemporary lifestyle and technological advancements have had a significant negative influence on natural resources. Natural resources such as coal and petroleum are rapidly dwindling, and once they are consumed, we will have to rely on other energy sources. As a result, it is critical that we humans operate in a manner that ensures the conservation of natural resources. Natural resource conservation can be accomplished in a variety of ways. The basic principle behind conservation is to maximize the utilization of natural resources while avoiding waste.

Problems associated with Natural Resources
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Natural resource extraction, processing, and usage can result in pollution of the air, land, and water, ecosystem disruption or annihilation, and a reduction in biodiversity.
- Carbon dioxide, for example, is a significant greenhouse gas created by burning coal, oil, and natural gas (fossil fuels). The heat from the sun is absorbed and retained by greenhouse gases. Methane, ammonia, sulphur dioxide, and some chlorinated hydrocarbons are examples of greenhouse gases.
- Many scientists think that increasing greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere can lead to global climate change (a change in the average global temperature of the atmosphere near the Earth's surface). This state has the potential to cause global hazards such as floods, drought, and disease.
- Natural resource extraction and use can potentially disrupt ecological interactions. Clearing trees from a field, for example, can disrupt habitats inhabited by numerous animals, forcing them to find other homes.
- Natural resource extraction and use, as well as other human actions, may reduce biodiversity, or the range of creatures that dwell on the planet. Because wild species and natural ecosystems are valuable commodities, reducing the Earth's biodiversity has a significant human cost.
Also check:
Importance of Conservation of Natural Resources
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- In order to safeguard animals
The primary motivation for conservation is to conserve wildlife and increase biodiversity. Protecting wildlife and maintaining it for future generations ensures that the species we care about do not become extinct. This ensures that the ecosystem remains healthy and functional. Some species, such as those seen in zoos and aquariums, cannot thrive outside of their natural environment without human assistance. As a result, the loss of their native habitats is a serious danger to their existence. Furthermore, animals that move and live in several natural habitats are at risk. The preservation of these habitats aids in the protection of the overall ecosystem.
- To safeguard the environment
Climate change is already wreaking havoc on our natural environment, therefore it's no secret that our planet's future must be secured. We must decrease the amount of harm that human activities do to the environment in order to preserve the planet for future generations. And we should do everything we can to help the natural environment.
Nature is our most powerful weapon in the battle against global warming, and we can fully utilize nature's contribution to take the action required to avert a catastrophic rise in temperature through conservation efforts. Everything from tropical forests to our shoreline has a role in combating climate change and ensuring the safety of our communities. As a result, it's critical that we do everything we can to safeguard them.
- For the sake of human health
Conservation of natural resources is important for a variety of reasons, one of which is the influence it has on human health, both in terms of controlling the spread of new diseases and the manufacturing of medications that we rely on.
Animal habitats in the wild act as a deterrent. It keeps new infectious illnesses from spreading from animals to people. Habitats that were formerly untouched have been removed to make place for humans and agriculture. This has brought wild and domestic animals closer, making it easier for illnesses to spread to people.
The Ebola outbreak is one such case. Ebola is a zoonosis (an animal illness that can be transferred to humans), and it is most likely carried by bats.
Many of the drugs we use as humans are made from compounds generated by animals or plants. As a result, by preserving nature, we are also preserving the life-saving pharmaceuticals we rely on, such as anti-cancer treatments.
To put it another way, we can't be healthy in an unhealthy atmosphere. It is in our best interests to protect the natural environment to the greatest extent possible. The exploitation of the natural environment jeopardizes our ability to feed and hydrate the world's population. Pollution, for example, is directly hazardous to human health.

Ways for Conservation of Natural Resources
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Certain actions must be taken to guarantee that we continue to enjoy the benefit of these natural resources, and if we do not, our future generations will face enormous difficulties. Conservation of natural resources guarantees that the ecological equilibrium is maintained. Some of the ways to conserve natural resources are:
- Utilization of alternative energy sources such as solar and wind energy
These alternative energy sources are environmentally benign, especially because they do not emit toxic pollutants that deplete the ozone layer. When compared to fossil fuels such as coal and charcoal, they are superior. They are also inexpensive to use, do not deplete quickly, and are renewable.
- Plant trees to keep soil from eroding.
This comprises planting trees and plants to combat wind and water-induced soil erosion. Trees and plants are necessary for the ecosystem's survival. Most insects, birds, and certain symbiotic plants call them home. This creates a habitat for species, resulting in overall wildlife conservation.
- Using smart water conservation techniques in our houses.
Simple procedures such as ensuring that taps are closed while not in use are part of this. Showering for shorter periods of time saves gallons of water every month. Reusing part of the water in our houses to water our garden is also a good idea.
- Oil should be transported by pipes.
Many oil leaks occur as a result of oil being transported by ship. The oil spills have a negative impact on the environment's vegetation and wildlife. The majority of these species perish as a result of oil spills. Pipelines are one example of current oil transportation methods.
- Treatment of industrial wastes and sewage before discharging them into bodies of water
Wastes that are damaging to the ecology have emerged from rapid industrialization. The direct discharge of these effluents into water bodies has resulted in major water contamination in several parts of the world, particularly in poor nations. To avoid thermal and chemical contamination of water, industrial and human waste should be handled.
- Use energy-saving techniques that are prudent.
Switching off lights and disconnecting electrical equipment while not in use are examples of such measures. Even when not in use, plugged-in equipment use power. Other habits include taking hot showers for shorter periods of time.
- Biogas usage in our homes
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is the most common source of fuel in our houses nowadays all over the world. As a result of continued LPG usage, oil supplies are depleted; biogas is thus a viable alternative. Biogas is mostly made from cow dung, and biogas facilities generate both biogas and manure.
- Make waste recycling a priority.
Plastics and paper bags are among the few pollutants that have resulted in tonnes of rubbish. Recycling is the process of repurposing previously used materials. This minimizes the quantity of garbage accessible, resulting in less contamination of the land and water.
- Instead of plastic and paper bags, use earthbags.
The over-usage of plastic bags is responsible for the majority of the garbage. Every time you go to the grocery shop, bring an earthbag with you. Products should also be packaged in recyclable materials.
- Make crop rotation a habit
Soil fertility is depleted when the same crops are planted over an extended length of time. Crop rotation will replenish and preserve soil fertility, allowing the soil to be conserved.
- Create particular conservation plans for endangered plant and animal species.
This includes botanical gardens and sanctuaries that may be constructed to safeguard endangered species so that future generations might enjoy them.
- Wild animal translocation
Human population growth has resulted in human encroachment on wildlife habitats. This has resulted in a human-animal conflict in which people slaughter wildlife in order to defend themselves from them. Translocation is relocating wild animals to nearby locations and erecting fences to prevent confrontation.
Check out: Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Things to Remember
- A natural resource might be any kind of material that exists in nature that can be used by people.
- Humans rely on natural resources for survival, either directly or indirectly.
- Air, soil, water, sunshine, coal, plants, animals, and minerals are examples of natural resources.
- Furthermore, nature is the sole supply of our most basic necessities, such as food, clothes, and shelter.
- Natural resources are limited in supply and non-renewable.
- Natural resources are becoming scarce as the world's population grows, thus conservation is critical. This enables us, as well as future generations, to maximize the use of natural resources.
- Conservation of Natural Resources is being undertaken in a number of ways.
- By refusing to chop down trees.
- Plastic consumption should be reduced.
- Using alternative energy sources such as solar, wind, and tidal energy, among others.
- Making use of public transportation.
- Rainwater conservation is important.
- Pollution reduction.
- Not dumping industrial effluents into water resources.
- Reducing, Recycling and Reusing.
Read More: Plants Growing in Soil
Sample Questions
Ques. What do you mean by conservation of natural resources? (3 marks)
Ans. Natural resources are those that are found naturally on the planet. These resources may be obtained without the intervention of humans. All living species on the planet rely on these resources. Natural resources include sunshine, air, and water, which are directly used by living creatures. Many of these natural resources can be replenished over time. These materials are recyclable and reusable. However, many natural resources are rapidly depleting due to a variety of factors. It is for this reason that natural resource conservation is vital so that living creatures can maintain and utilize them as needed.
Ques. What is the significance of natural resources? Why is it critical to protect them? (3 marks)
Ans. In our daily lives, we rely on natural resources. Almost all of the things we use on a daily basis are derived from natural resources. Air, water, sunshine, coal, minerals, forests, and land are some examples of natural resources that we utilize. Nature contributes to the overall environmental balance and fully meets all human requirements.
Ques. Recognize the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy resources. (3 marks)
Ans. Renewable resources and non-renewable resources are distinguished as:
- Renewable Resource: Resources that can be renewed in a reasonable amount of time.
Solar and wind energy, for example.
- Non-renewable resources: Ecological mechanisms are unable to renew these resources.
Coal and petroleum are two examples.
Ques. What are Mineral Resources? (2 marks)
Ans. Mineral resources are substances that exist naturally and have certain chemical and physical qualities.
Identified resources, unknown resources, and reserves are the different types of resources.
Ques. What role does a person play in natural resource conservation? (2 marks)
Ans. It is the responsibility of each individual to protect natural resources in such a way that they will be available to future generations as well. As a result of advances in technology and population increase, the modern world is confronted with a slew of issues relating to natural resource depletion. As an individual, one can ensure that no waste of natural resources is done from their end and an environment-friendly approach should be adopted.
Ques. What are some of the negative consequences of land degradation? (2 marks)
Ans. Negative impacts of land degradation include deterioration of soil structure and texture, loss of soil fertility owing to the loss of essential nutrients, increased waterlogging, and salinity, alkalinity, and acidity issues.
Ques. What is the role of farmlands in the conservation of natural resources? (2 marks)
Ans. On the farm, conservation methods play a significant role in reducing food safety issues. By minimizing the migration of viruses, fertilizers, and pesticides into streams, rivers, and lakes, stream-side vegetation, grassed filter strips, and wetlands, farmlands can help in keeping our water supply clean.
Ques. What can we do to protect natural resources? (2 marks)
Ans. The three R's — Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle – are the golden rules of conservation. Reduce resource usage and waste. The second phase entails repurposing materials rather than discarding them after one usage. Recycling helps to decrease pollution and energy and raw material waste.
Also Read:



Comments