Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Density describes how much space an object takes up in relation to its mass. The density of a substance can be calculated as its mass per unit of volume. Water is an odorless, tasteless, colorless, and transparent chemical substance that is the main constituent of the lakes, oceans, and streams on the planet. The density of water is approximately 1 gram per cubic centimeter (1 gm/cm3).
- A molecule of water (H2O) is made up of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen bound by 2 covalent bonds.
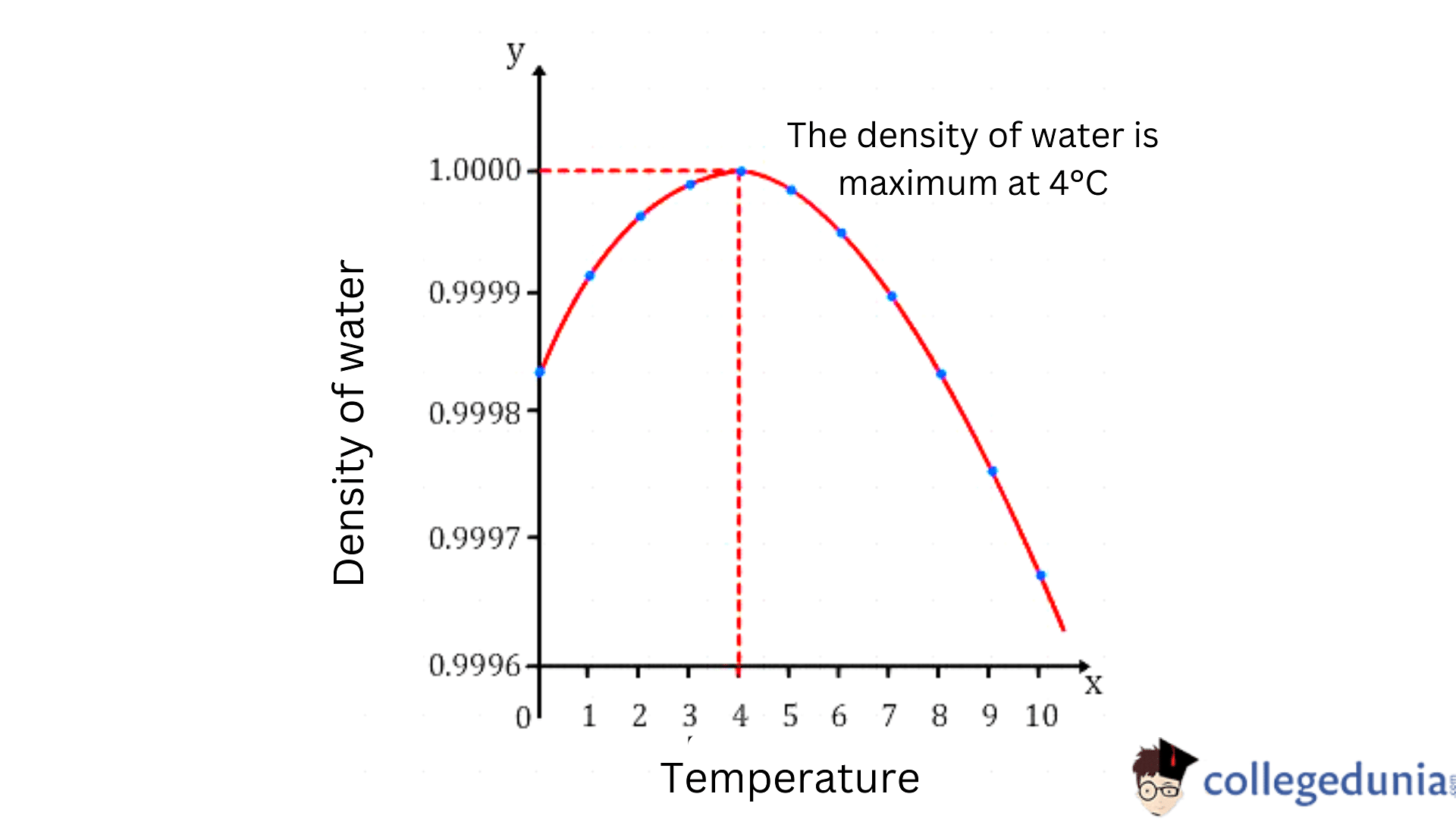
- The density of water is maximum at 4°C as at this temperature, two opposing effects (thermal expansion and the hydrogen bond formation) are in equilibrium.
- Unlike normal liquids, the density of water decreases from 4° to 0° Celsius.
- Above 4 degrees, water’s density decreases as the temperature increases.
- This behavior of water is called “density anomaly”.
- Typically, in SI units, the density of water at 4°C is 1000 kg.m-3.
- At room temperature i.e. 22° C, the density of water is 997.77 kg/m3.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Density of Water, Mass, Volume, Density, Water, Density Anomaly, Temperature, Hydrogen Bonds, Thermal Energy
What is the Density of Water?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The density of water can be defined as the weight of water per its unit volume, which is dependent on the temperature of the water.
- The density of any substance is defined as its mass per unit volume.
- Density is a measure of the way matter is packed together.
- Water has a maximum density of 998.97 kg/m3 at 4°C or 39°F.
Density explains the relation between the mass of a substance and the volume it occupies. In different units, the density of water can be demonstrated as:
| Unit | Water Density |
|---|---|
| Density of water in g/cm3 | 1 g/cm3 |
| Density of water in g/mL | 0.9998395 g/ml |
| Density of water in kg/m3 | 1000 kg/m3 |
| Density of water in lb/ft3 | 62.4 lbs/ft3 |
Do you know?Why density of water is the highest at 4oC? As the water molecules become close together, the density of the liquid increases. When the temperature of warm water drops, the water molecules slow down, and the density of water increases. Therefore, at 4°C, the density of water is maximum. |
Read More:
Density of Water in Room Temperature
At normal temperature, water’s density is 998.2 kg/m3.
- Density of pure water – 1g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3.
- Density of freshwater – 1g/cm3 or 1000kg/m3.
- Density of ocean water - 1027 kg/m3.
- Density of distilled water – 0.99823g/ml
-
Density of seawater – 1023.6 kg/m3 at a 25 °C temperature, 35 g/kg salinity, and 1 atm pressure.
Absolute Density is the mass of a substance per unit volume of a material.
Water does not have any absolute density as the density of water varies with its temperature. At normal temperature, water has a density of 0.99823 g/ml.
Density of Water Formula
Density is calculated by the formula d = M/V, where d is density, M is mass, and V is volume. The density of a substance is usually measured in grams per cubic centimeter.
Properties of Water
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Some properties of water are as follows:
| Properties of Water | Values |
|---|---|
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
Water Density Anomaly
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Water is abundantly available in the world and is found in three forms (solid, liquid, and gas). When the temperature decreases, water converts into solid, and when the temperature increases, water converts into gas.
Above 4oC
When water is cooled from a high temperature, the thermal energy of the molecules of water reduces. The molecules come closer and therefore the density increases.
Below 4oC
In this range of temperature, the water molecules come closer and they are able to make stable Hydrogen bonds. Due to the lack of thermal motion, more and more hydrogen bonds are formed. This prevents the water molecules from coming closer and therefore the density of water decreases.
At 4oC
At a temperature of 4 degrees, the thermal expansion and the hydrogen bond formation tend to balance each other in order to give a stationary behavior for the density. So, the density of water at 40C is the maximum and the specific volume is the minimum.
Frequently Asked QuestionsQues. Mention the density of water in SI units. (1 mark) Ans. The density of water in SI units is 1000 kg/m3. Any substance's density can be expressed by its mass per unit volume. Ques. Consider that the relative density of mercury is 13.6. Justify what it means. (1 mark) Ans. Considering that the relative density of mercury is 13.6, mercury is 13.6 times as heavy as an equivalent volume of water. |
Properties of Density of Water
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
The behavior of water density is unusual. Once other materials transform from gas to liquid and liquid to solid-state, the density increases. However, the density of water increases when it transforms from gas to liquid and it decreases when water becomes solid. Due to this unusual behavior of density, ice floats in liquid water.

Some of the properties of the Density of Water are:
- The density of water fluctuates with temperature.
- As the temperature decreases, the water’s density increases and reaches its maximum value of 1000 kg/m3 at a temperature of 4oC.
- When the temperature further decreases, it tends to expand and becomes less dense.
- At 0°C, water becomes ice; the water molecules form a rigid but open pattern.
- As this structure is less dense as compared to normal water, therefore, ice floats on the surface of the water.
Read More:
Factors Affecting Water Density
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Three factors that affect the density of water are as follows:
- Purity of Water
- Temperature of Water
Purity of Water
- In pure water, lowering the temperature reduces thermal motion. It allows the water molecules to make more hydrogen bonds preventing the molecules from returning closer to each other
A hexagonal structure forms and leaves some space between the molecules which leads to a decrease in density. Due to this structure, ice is less dense as compared to liquid water.
- In the case of impure water, water density increases with reference to impurity. For example, in the case of saline water, an increase in salinity makes the water dense. Seawater may be an example of saline water.
Seawater density also varies with depth and temperature. It is denser than pure water as it contains many chemicals packed within it.
Temperature of Water
- The density of water is approximately 1 gram/centimeter (1 g/cm3). It is temperature-dependent, but this relation is -linear and unimodal in nature instead of monotonic.
- With an increase in temperature, the water gets warmer and molecules open up. When the temperature goes down, the seawater becomes dense.

- When water is cooled from room temperature, it tends to become increasingly dense. Approximately at about 4°C, pure water reaches its maximum density.
- As it gets cooled further, the water tends to expand and becomes less dense.
- This unusual negative thermal expansion is related to the strong intermolecular forces or interactions and it is observed in the form of molten silica.
- Deep Water is denser than shallow water. Within the deep, water molecules are more packed and tightly adhere to each other because the weight of water above them pushes them down.
- An example of the high density of seawater is the Dead Sea.
- In this sea, the density is so high that objects float on its surface. Its average density is 1240kg/m3 which is extremely high and swimming in this sea is like floating.
Also Read: Difference between Density and Specific Gravity
Water Density vs Temperature
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Water does not have an absolute density as the density of water varies with its temperature. Water has a higher density in its liquid state than solid. The relation between temperature and water is as demonstrated below:

- As we know, the density of water fluctuates with temperature.
- It increases when the temperature decreases and reaches its maximum value at a temperature of 40C.
- When the temperature further goes down, the density of water becomes less.
- Due to this, ice floats on the surface.
- This property of water benefits living creatures within the sea whose surface is frozen but under the surface, water temperature is at 4oC, which helps certain sea creatures in their survival.
Water Density Experiment
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
To understand the density of water, let’s do a little experiment. We’ll need a tall glass cup, honey, water, copra oil, and coloring,
- Pour a one-quarter cup of honey,
- Now, pour a one-quarter cup of colored water gently into the honey.
- Pour a one-quarter cup of copra oil on top of the colored water.

Now, notice that different substances showcase a different density, which suggests for an equivalent volume different substances weigh differently, as they weigh differently heavier substances tend to settle at rock bottom, like honey and lighter material like oil tends to float at the highest.
Using liquids with different specific gravities, we get their density as –
- Rubbing Alcohol – 0.79
- Lamp Oil – 0.8
- Baby Oil – 0.83
- Water – 1.0
- Milk – 1.03
- Liquid Soap – 1.06
- Corn Syrup – 1.33
- Maple Syrup – 1.37
- Honey – 1.42
Density of Water at Different Temperatures Scales
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
There are several factors that may affect the density of a substance. Some factors which affect the density of water are given within the points below.
| Temperature | Density in kg/m3 |
|---|---|
| 100 °C | 958.4 |
| 80 °C | 971.8 |
| 60 °C | 983.2 |
| 40 °C | 992.2 |
| 30 °C | 995.65 |
| 25 °C | 997.04 |
| 22 °C | 997.77 |
| 20 °C | 998.2 |
| 15 °C | 999.1 |
| 10 °C | 999.70 |
| 4 °C | 998.97 |
| 0 °C | 999.83 |
| -10 °C | 998.12 |
| -20 °C | 993.547 |
| -30 °C | 983.854 |
Previous Year Questions
- The time period of a satellite on earth is 5 hours. If the separation between the… [BITSAT 2019]
- The molecular formula of a commercial resin used for exchanging ions … [JEE Mains 2015]
- There is a shell of mass M and the density of the shell is uniform… [BITSAT 2013]
- The alum is used for purifying water …
- Four identical particles of equal masses 1kg made to move along the… [JEE Main 2021]
- Four identical particles of equal masses 1kg made to move along the… [JEE Main 2021]
- Acceleration due to gravity is g on the surface of the earth. Then the value of… [JKCET 2004]
- There is a shell of mass M and the density of the shell is uniform… [BITSAT 2013]
- If the earth shrinks such that its density becomes 8 times the present value… [AP EAPCET]
- Acceleration due to gravity is g on the surface of the earth… [JKCET 2004]
Things to Remember
- Water is a colorless, odorless, transparent, tasteless liquid found in abundance on the planet
- The density of water is the weight of water per its unit volume, while dependent on the temperature of the water.
- The density of a substance is the mass per unit volume.
- The density of water is approximately 1 gram/cubic centimeter (1 g/cm3)
- Water’s density is affected by its purity, temperature, and depth.
Also Check:
Sample Questions
Ques. Why does ice float in water? (2 marks)
Ans: The maximum density of water occurs at around 4° Celsius.
- The density of ice is lower than liquid water, so it floats.
- Upon freezing, density decreases by approx 9%.
Ques. What is the density of seawater? (1 mark)
Ans. At the ocean surface, the density of ocean water is about 1027 kg/m3.
Ques. Why is that the maximum density of water at 4°C? (1 mark)
Ans. The density of water is maximum at 4 °C because, at this temperature, two opposing effects – thermal expansion and formation of hydrogen bonds are in balance.
Ques. At room temperature, what is the density of water? (1 mark)
Ans. The density of water at temperature (i.e., 22°C) in kg/m3 is 997.77.
Ques. Why does water never have an absolute density? (1 mark)
Ans. As its density varies with temperature, water never has an absolute density.
Ques. How is the density of water affected by the temperature? (2 marks)
Ans. The density of water varies with temperature. Lowering the temperature reduces the thermal motion and allows the water molecules to make more hydrogen bonds that prevent the molecules from returning closer to each other.
A hexagonal structure formed leaves some space between the molecules which leads to a decrease in density.
Ques. What are the factors which affect the density of water? (2 marks)
Ans. There are two main factors affecting the density of water i.e. temperature and purity.
- The density of pure water varies with temperature and attains its maximum value at a temperature of 4o C. Impure water density increases with reference to impurity.
- The density of saline water is the best example of this. An increase in salinity makes the water denser.
Ques. Explain the effect of temperature on seawater density? (3 marks)
Ans. The effect of temperature on seawater is often seen in winters. When the temperature goes down the seawater becomes denser as most of the chemicals present within the seawater become denser. The upper layer of seawater is frozen but the temperature of the water layer underneath the surface is 4oC which helps to survive the ocean creatures. And on the opposite hand, when the temperature rises in summer, the seawater becomes less dense. With an increase in temperature, water gets warmer and molecules open up.
Ques. How does water density helpful? (3 marks)
Ans. Water Density is helpful because:
- The density of water fluctuates with temperature.
- It increases when the temperature decreases and reaches its maximum value at a temperature of 40C.
- When the temperature further goes down, the density of water becomes less.
- Due to this, ice floats on the surface.
- This property of water benefits living creatures within the sea whose surface is frozen but under the surface, water temperature is at 4oC, which helps certain sea creatures in their survival.
Ques. Determine the density of metal assuming that density of water is 10, and its relative density is 5. (3 marks)
Ans. According to the question given, the following can be deduced:
The Density of water = 103
The Relative density = 5
Therefore, with the given formula below, we can say:
Relative density = \(\frac{Density \ of \ Metal}{Density \ of \ Water}\)
Thus, after value substitution, we get,
⇒ 5 = \(\frac{(Density \ of \ Metal)}{10^3}\)
⇒ (Density of metal) = 5 x 103 kg/m3
Ques. The relative density of gold is 19.3. Assuming that the density of water is 1000 kg/m3, determine the density of gold in SI unit. (2 marks)
Ans. According to the formula, Relative density = \(\frac{Density \ of \ Substance}{Density \ of \ Water}\)
The Relative density of gold = 19.3
The Density of Water = 1000 kg/m³
Thus Density of Gold = Density of Water × Relative density
= 1000 × 19.3
= 19300 kg/m³
Ques. “Oil is denser than water. State reason. (2 marks)
Ans. Oil is considered denser than alcohol, however, it is less dense than water. The molecules of oil are typically larger than those that compose water. Thus, they cannot pack as tightly as water molecules. Hence, they consume more space per unit area and are generally less dense.
Ques. Which liquid has a mass density less than water but is yet optically denser than water? (1 mark)
Ans. Kerosene, which has a higher refractive index, is known to be optically denser than water. However, its mass density is still lesser than water.
Read More:








Comments