Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Molar Mass and Molecular Mass are both important terms in science yet both words are sometimes used interchangeably. However, it is important to note that the distinction is really important to understand the concepts of chemistry. When referring to the mass of a single or well-defined molecule, the term molecular mass is more often used. Whereas, the molar mass is an average value of several different versions of the compound, which might vary in different isotopes. Molar mass gives us the mass of a mole of a substance while molecular mass on the other hand gives us the mass of a molecule of a substance. In this article, we will have a look at the molar and the molecular mass and understand the difference between the two.
Read More: Ions Definition
Read More: Combustion and Flames
What is Molar Mass?
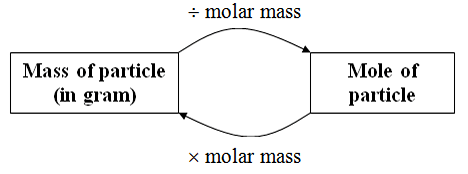
Molar mass is the mass of a mole of a substance. It is the mass of a compound divided by a specific amount of substance. The SI unit used to represent molar mass is g/mol. This specifies the number of molecules, atoms, or compounds that one mole of a substance contains. The molar mass of a chemical, in g/mol, is numerically equivalent to the average mass of one molecule, in daltons (for all practical purposes). The average mass of a water molecule is approximately 18.0153 daltons, and the molar mass of water is approximately 18.0153 g/mol.
\(Molar mass = \frac{ Mass of a substance (in kg)} {Amount of the substance (mol)} \)
The relative atomic mass of an element multiplied by the molar mass constant helps to determine the molar mass of that element. Standard relative atomic masses are dimensionless values (i.e., pure numbers), whereas molar masses contain units. Multiplying by the molar mass constant assures that the computation is dimensionally valid (in this case, grams per mole).
Molar mass
Checkout Important Question on: Molar Mass of Magnesium
What is Molecular Mass?
Molecular mass refers to the mass of one molecule of a compound. Because of the isotopes, the molecular mass varies. The unit used to quantify molecular mass is amu. The abbreviation amu stands for atomic mass units. Molecular weight is often considered identical with molecular mass; nonetheless, it is also very changeable in practice, as are the units used in association with it.
Read Also:
| Difference Between Atom and Molecule | Difference Between Element and Compound |
| Difference Between Physical and Chemical Changes | Chemical Change |
\(Molecular mass = \frac{Molar Mass (in g)}{Number of moles of the substance}\)
The units Da or u are used mostly to determine molecular mass. Atomic and molecular masses are commonly expressed in daltons, which is measured in comparison to the mass of the isotope 12C (carbon 12), which is 12 Da by definition.

Molecular mass
Difference between Molar Mass and Molecular Mass
Some of the significant differences between Molar Mass and Molecular Mass are tabulated below:
| Point of Difference | Molar Mass | Molecular Mass |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Mass of a mole of a substance | Mass of molecules |
| Alternate Meaning | It’s also referred to as molecular weight. | It helps to determine the mass of a sole molecule. |
| Denotation | For high-level equations, the SI unit is g/mol. | It is denoted in amu |
| Definition | The mass of Avogadro number of atoms/molecules or compounds. | The total sum of atomic masses of all the atoms present in a molecule of a substance. |
| Measurement | Compounds, atoms, or molecules are measured. | It is measured specifically in molecules. |
| Accuracy | It is less accurate than the molecular mass | It is accurate to be used in higher computations |
| Numerical Example | Mass of 1 mole of oxygen is 15.9994 grams. Therefore, the molar mass = 15.9994 g/mol | Molecular mass of Ca(OH)2 = 74 atomic mass units |
Things to Remember
- The mass of one molecule is defined as the molecular mass of a compound.
- Molar mass is the mass of a substance in a particular quantity.
- Compounds, atoms, or molecules are measured in molar mass.
- Molecular mass is measured specifically for molecules.
- g/mol is the SI unit for molar mass.
- Da or u is the SI unit of molecular mass.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is the molar mass of H2O? (5 marks)
Ans. A substance's molar mass is the mass of one mole of the substance. The atomic mass of each substance is multiplied by the subscript of that element in the chemical formula to obtain the molar mass. After that, all of the elements' masses are added.
H2O is the chemical symbol for water. One oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms make up one water molecule. One mole of oxygen and two moles of hydrogen atoms make up one mole of water. The molecular weight is another name for molar mass. It is the total of the atomic weights of all the atoms in the compound's molecule.
Oxygen and hydrogen have atomic weights of 16 u and 1 u, respectively.
Therefore, Water has a molar mass of 2(1)+16=18 u. A
The letter ‘u' stands for a unified mass unit, which is also known as 'amu' (the atomic mass unit). Another unit that can be used rather than u is g/mol.
Ques. Calculate the molar masses of hydrogen (H2), sulphur (S8), and chlorine (Cl2). Make use of the Molar Mass Formula. (3 marks)
Ans. Molar Mass of (H2) = 2 × 1.00797(7) × 1.000000 g/mol = 2.01588(14) g/mol
Molar Mass (S8) = 8 × 32.065(5) × 1.000000 g/mol = 256.52(4) g/mol
Molar Mass (Cl2) = 2 × 35.453(2) × 1.000000 g/mol = 70.906(4) g/mol.
Ques. Calculate the molar mass of NaCl and C12H22O11. (3 marks)
Ans. The quality mass, relative atomic mass, or the standard relative atomic mass is useful for approximating the relative atomic mass of normal earth samples with typical isotope composition.
Molar Mass (NaCl) = [22.98976928(2) + 35.453(2)] × 1.000000 g/mol
= 58.443(2) g/mol
Molar Mass (C12H22O11) = ([12 × 12.0107(8)] + [22 × 1.00794(7)] + [11 × 15.9994(3)]) × 1.000000 g/mol
= 342.297(14) g/mol.
Ques. Why is the unit of molar mass grams/mole? (3 marks)
Ans. A mole is a unit of measurement for the number of atoms, molecules, ions, or formula units in a chemical compound. It's comparable to other counting units such as a pair (2) and a dozen (12). A mole of a chemical comprises Avogadro's number of molecules or formula units (6.02214076 x 1023 mol). The mass of one mole of a compound and the number of grams per mole of a compound are defined by its molar mass. To put it another way, the molar mass is the total mass in grams of all the atoms that make up a mole of a certain molecule. As a result, molar mass is measured in grams per mole.
Ques. How is molecular mass calculated? (5 marks)
Ans. Molecular mass is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in one molecule of a substance.
For example: Water (H2O)
Atomic mass of H = 1 u
Atomic mass of O = 16 u
Molecular mass of water = 2 x atomic mass of H + 1 x atomic mass of O
= 2 x 1 + 16 x 1
= 18 u
Ques. How is it possible to find the molar mass of a compound? (3 marks)
Ans. There are three steps involved in finding a mass of a compound:
- Calculate the number of atoms in each element in the compound using the chemical formula.
- Multiply each element's atomic weight by the number of atoms present in the compound.
- Add everything up and convert to grams/mole.
Ques. Find out the molar mass of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3. (3 marks)
Ans. Sodium carbonate is made up of two sodium atoms, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms.
Na : 2 x 23.0 = 46
C : 1 x 12.0 = 12
O : 3 x 16 = 48
When the total values are added up i.e, 46 + 12 + 48 = 106
Hence, the molar mass of Na2CO3 is 106 g/mole.
Ques. Find out the molar mass of calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2. (5 marks)
Ans. One atom of calcium, two atoms of nitrogen, and six atoms of oxygen make up calcium nitrate.
Ca: 1 x 40.1 = 40.1
N: 2 x 14.0 = 28
O: 6 x 16.0 = 96
If we add all, 40.1 + 14 + 16 = 164.1
Therefore, the molar mass of Ca(NO3)2 is 164.1 g/mol.
The two nitrate ions are indicated by the subscript two following the parenthesis (NO3)2. Subscripts outside the parentheses are used to multiply the number of atoms. Only the atoms inside the () are affected by subscripts outside the (), not the Ca ion.
Ques. Calculate the molecular mass of HNO3. (2 marks)
Ans. The molecular mass of HNO3 is calculated as:
Molecular mass = the atomic mass of H + the atomic mass of N + 3 × the atomic mass of O
= 1 + 14 + 48
= 63 u.
Read Also:



Comments