Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Lithosphere is the “land” sphere of the subsystem. Earth’s system is divided into four overlapping subsystems or spheres, namely "lithosphere" (land), "hydrosphere" (water), "biosphere" (living organisms), and "atmosphere" (air). Composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle, it is the outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet or natural satellite. The lithosphere is an important part of the earth’s four spheres as it assists human life by providing forests, grasslands, minerals, natural resources, etc, and is the reason behind the movement of tectonic plates, volcanos, earthquakes, etc.
What is Lithosphere?
The term lithosphere is derived from the Greek language, composed of the words “lithos” meaning rocky, and the word “sphaira” meaning sphere. It is the outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet or natural satellite. It is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle, which compose the rigid and hard outer layer of the Earth.
The lithosphere reacts to the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere to initiate the soil-forming process called the pedosphere. It can extend to a depth of more than 100 km (or 60 miles) but generally has a thickness between 35 to 50 km in the continental regions.
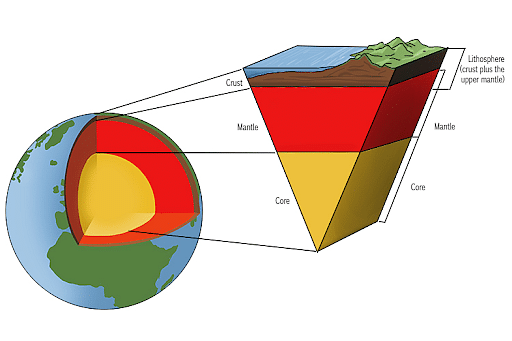
Lithosphere
Composition of Lithosphere
Earth’s lithosphere composition varies depending on whether it lies under oceans or on land. The earth’s crust is made up of several layers of rocks and hence is not a homogeneous substance.
Sedimentary rocks are on the top, metamorphic rocks are in the middle, and at the bottom, we have basaltic rocks, constituting the earth’s crust. The Earth's crust also consists of various large dynamic tectonic plates. These tectonic plates keep moving slowly but continuously at an average rate of around 10 cm.
Also Read:
Types of Lithosphere
Lithosphere can be mainly divided into oceanic and continental lithosphere:
Oceanic Lithosphere
The lithosphere associated with oceanic crust and exists in the ocean basins is called the oceanic lithosphere. It is the portion of the upper mantle and crust present underneath the ocean and seas. The oceanic lithosphere tends to be denser than its counterpart the continental lithosphere.
It thickens as it ages and moves away from the mid-ocean ridge. New oceanic lithosphere is constantly being produced at mid-ocean ridges and thus, the oceanic lithosphere is much younger than the continental lithosphere. The oldest oceanic lithosphere is about 170 million years old.
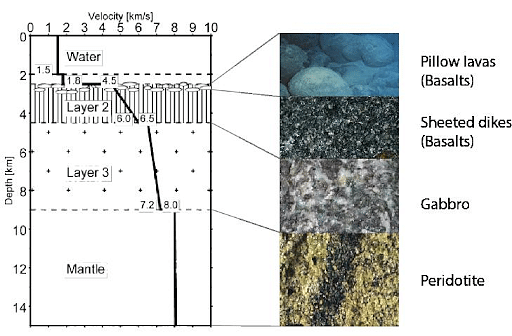
Composition of Oceanic Lithosphere
Continental Lithosphere
Continental lithosphere is linked with continental crust. It has an average thickness range from about 35 to 45 km. It comes into direct contact with the atmosphere. It is composed of a layer of igneous and sedimentary rock that forms the continents. This layer consists mostly of granitic rock.
About 40% of the Earth’s surface is covered by continental lithosphere, but it also makes up about 70% of the volume of Earth’s crust. Most scientists believe that there was no continental crust originally on the Earth, but the continental crust ultimately derived from the fractional differentiation of oceanic crust. The continental lithosphere is billions of years old, much older than the oceanic lithosphere.
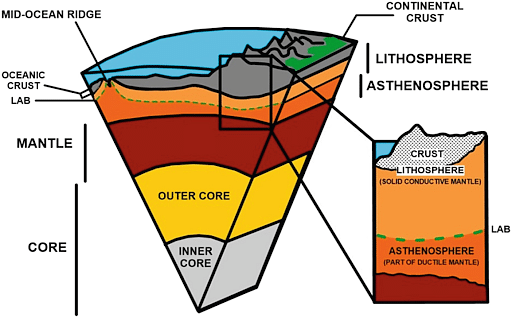
Continental Lithosphere
Importance of Lithosphere
The lithosphere is an integral part of the earth’s four spheres and aids greatly for life to flourish on earth. Following are some points showing the importance of the lithosphere:
- The lithosphere provides our forests, grasslands and is responsible for agriculture, human settlements, and is a rich source of minerals.
- Without the movement of tectonic plates, no mountain ranges and continents would have been formed on earth.
- Numerous types of rocks such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks are also found in the lithosphere.
- The shifting of tectonic plates is responsible for the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and even the continents.
- Volcanoes and earthquakes help in the growth of new vegetation and life as they give rise to fertile soil and lands.
- Organic compounds such as coal, natural gas, oil, etc are biotic remains buried in the lithosphere for millions of years. They curb our energy needs and are integral for producing power.
- Useful minerals and elements, such as iron, aluminum, copper, magnesium, and more are also extracted from the lithosphere.
Also Read:
| Difference Between Mass and Volume | Difference Between Land Breeze and Sea Breeze |
| Difference Between Force and Pressure | Equations of Motion |
Things to Remember
- Composed of the Greek words “lithos” meaning rocky, and the word “sphaira” meaning sphere, the lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell on earth, composed of the earth’s crust and the portion of the upper mantle.
- It is mainly of two types: oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere. The lithosphere underneath the ocean and seas is termed the oceanic lithosphere while the lithosphere layer present on land is known as the continental lithosphere.
- The oceanic lithosphere can go deeper than 100 km while the continental lithosphere is thinner and generally ranges between 35 to 50 km.
- It is an important part of the earth’s four spheres and assists human life by providing forests, grasslands, minerals, natural resources, rocks, etc.
- Interesting Fact: Mount Everest is the highest point of the continental lithosphere and the Mariana Trench is the deepest part of the oceanic lithosphere.
Sample Questions
Ques. Which of the following happens due to tectonic shifts in the Earth’s lithosphere?
- Tsunami
- Volcano
- Earthquake
- All of the above (1 Mark)
Ans. (D) All of the above.
Ques. What is the composition of the lithosphere? (2 Marks)
Ans. The lithosphere composition varies depending on whether it is oceanic lithosphere or continental lithosphere. The earth’s crust is made up of several layers of rocks and hence is not a homogeneous substance.
Sedimentary rocks are on the top, metamorphic rocks are in the middle, and at the bottom, we have basaltic rocks, constituting the earth’s crust. The eath’s crust also consists of various large dynamic tectonic plates which keep moving slowly but continuously.
Ques. Define lithosphere. (3 Marks)
Ans. Lithosphere is the rigid outer layer of the Earth. It is composed of the crust and the solid outermost layer of the upper mantle. The term lithosphere is derived from the Greek language, composed of the words “lithos” meaning rocky, and the word “sphaira” meaning sphere.
The lithosphere reacts to the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere to initiate the soil-forming process called the pedosphere. It can extend to a depth of more than 100 km (or 60 miles) but generally has a thickness between 35 to 50 km in the continental regions.
It is mainly of two types: Oceanic lithosphere and Continental lithosphere.
Ques. Why is the lithosphere important? (3 Marks)
Ans. The lithosphere is where the biosphere (living organisms) inhabit. Following are some points showing the importance of the lithosphere:
- The lithosphere supplies the mother earth’s forests and grasslands and is responsible for agriculture, human settlements.
- It is a rich source of minerals such as iron, aluminum, copper, magnesium, and rocks such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- Organic compounds such as coal, natural gas, oil, etc are biotic remains buried in the lithosphere for millions of years. They curb our energy needs and are integral for producing power.
- The lithosphere is also responsible for the movement of tectonic plates. This shifting of tectonic plates is responsible for the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and even the continents.
- The lithosphere is also responsible for causing volcano eruptions and earthquakes that are dangerous but help in the growth of new vegetation and life as they give rise to fertile soil and lands.
Ques. What are the types of lithosphere? Explain them. (4 Marks)
Ans. Lithosphere is mainly of two types:
1.Oceanic lithosphere: The lithosphere associated with oceanic crust and exists in the ocean basins is called the oceanic lithosphere. It is the portion of the upper mantle and crust present underneath the ocean and seas.
The oceanic lithosphere tends to be denser than its counterpart the continental lithosphere. It thickens as it ages and moves away from the mid-ocean ridge. The oldest oceanic lithosphere is about 170 million years old.
2.Continental lithosphere: Continental lithosphere is linked with continental crust. It has an average thickness range from about 35 to 45 km. It comes into direct contact with the atmosphere. It is composed of a layer of igneous and sedimentary rock that forms the continents. This layer consists mostly of granitic rock.
About 40% of the Earth’s surface is covered by continental lithosphere, but it also makes up about 70% of the volume of Earth’s crust. The continental lithosphere is billions of years old, much older than the oceanic lithosphere.




Comments