Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
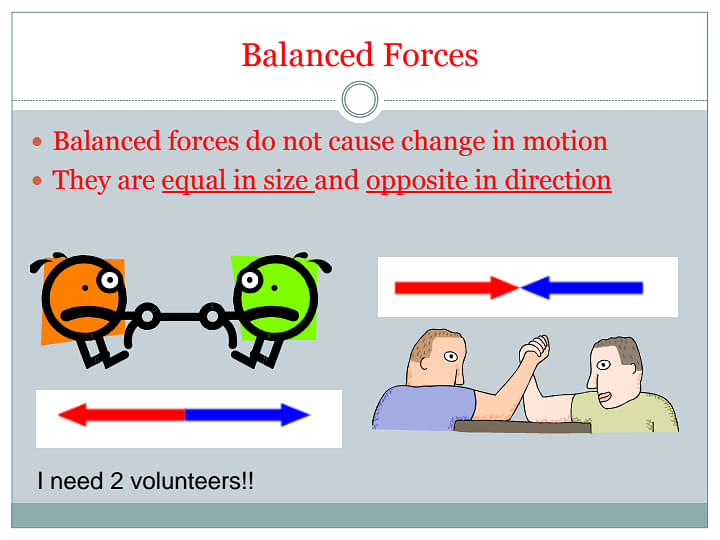
Balanced force can be defined as a force that is opposite in direction and equal in size. Balanced forces are usually present in the state of equilibrium. Some of the characteristics of Balanced forces are:
- The magnitude of balanced forces are same.
- Forces present in a balanced system are equal in size.
- Balanced forces act on an oject in opposite directions.
There is no change in direction when the forces are balanced. For a balanced force, any stationary body is going to continue to be in the stationary position, whereas a moving object will continue to move at the same speed and direction. An example of balanced force is when an apple hangs from a tree, the force exerted by the branch on the apple balances the weight of the apple. While an apple falls from the tree, the net force on it becomes unbalanced.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Force, Balanced Force, Unbalanced Force, Newton’s First Law of Motion, Equilibrium, Speed
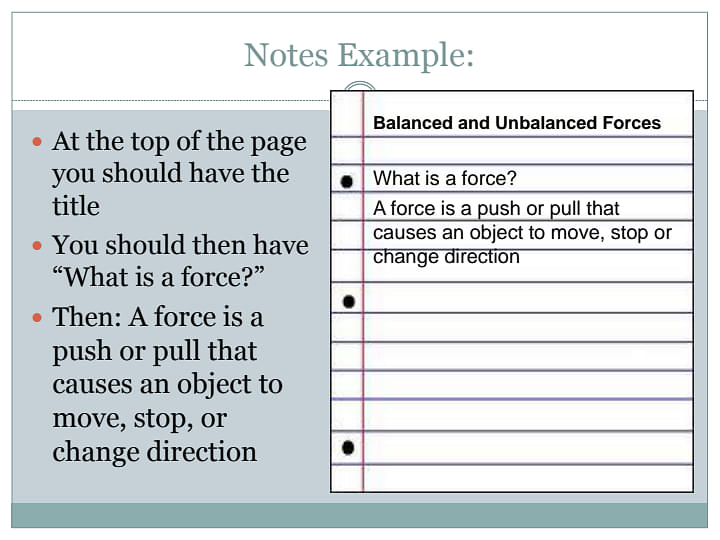
What is Force?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A force can be both a push and a pull. For example, when you push a door open, you must apply force to the door. To open a drawer, you must also exert force. When a force is applied to an object, it can change its:
- Speed
- Direction of movement
- The form of movement (for example, an elastic band gets longer if you pull it)
Force can be defined as:
| “The push or pull exerted on an object with mass which causes it to change its velocity.” |

Force
Forces can be contact forces, in which two objects must come into contact with each other to exert a force. Other forces are non-contact forces, in which objects do not have to come into contact with one another. These are some examples: gravity, magnetism, static electricity causes forces.
Forces are of two types:
- Balanced force
- Unbalanced force
Newton’s First Law of Motion
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Newton’s First law of Motion claims that:
| “A body at rest or motion at a constant speed in a straight line, it will remain in an unchanged position unless an external force is applied to it.” |
Simply, it states that unless acted upon by an external force, an object in uniform motion will remain in uniform motion. And an object at rest will remain at rest unless and until it is acted upon by an external force.

Newton's First law of Motion
What is Balanced Force?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A balanced force is defined as two equal-magnitude but opposite-direction forces acting on a body. Forces that are equal and opposing cancel each other out. As a result, a body at rest will remain at rest. And, once in motion, a body will remain in motion.
- Balanced forces cannot alter the state or direction of motion.
- They have the ability to change the shape of an object.
- Under the influence of balanced forces, the body will remain in its initial state of motion. Because of their opposing directions, the forces cancel each other out.
Balanced Force in Terminal Velocity: Terminal velocity is considered a very good example of balanced force since, here, the gravitational force and the air resistance balance ome another. The terminal velocity is reached in the case force of gravity is equivalent to the drag force on the object.
Balanced Forces Diagram
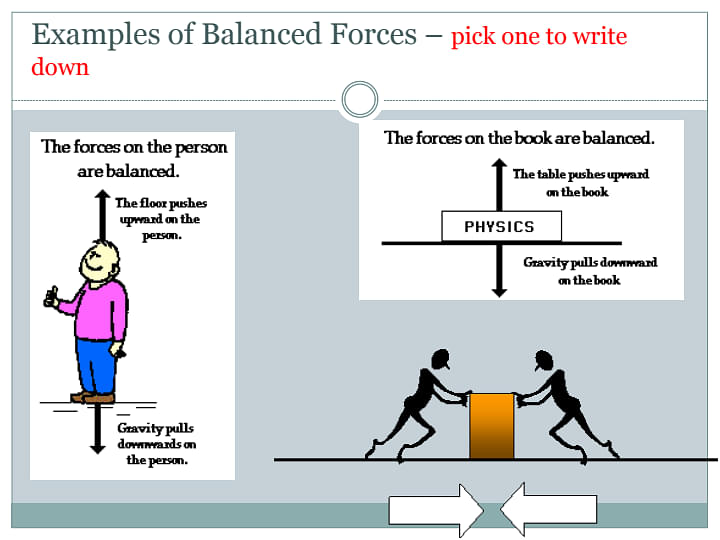
In a game of tug of war between equally matched opponents, neither of the teams can pull the opposing team towards themselves due to balanced forces.

Balanced Force Example
When is a Force Balanced?
Forces will be balanced at any given point of time, unless and until any external force is added to them.
- For instance, consider the two forces acting on a book placed on a table.
- One force, which is the Earth's gravitational pull, can be observed to exert a downward force.
- Whereas, the other force, wherein the book pushes on the table (also often referred to as a normal force).
- Since these two forces have equal magnitude and can be found in opposite directions, they balance one another.
- Thus, the book can be found in a state of equilibrium.
- There is no unbalanced force which acts upon the book, helping it maintain a state of motion.
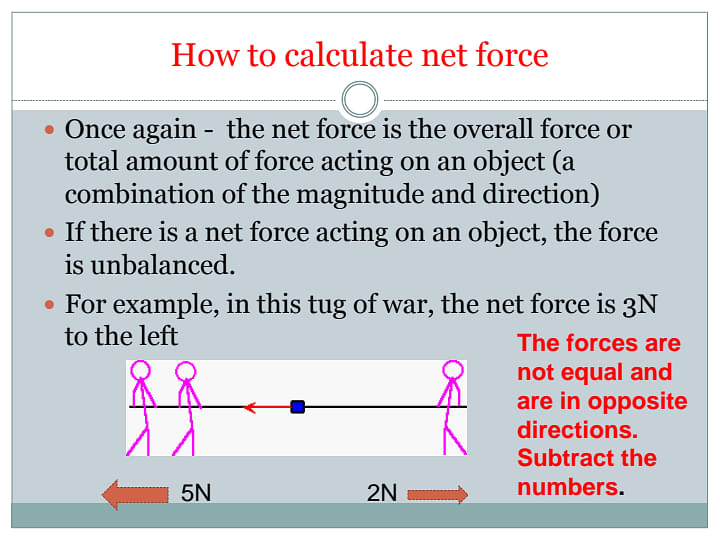
Resultant Force and Balanced ForceForces possess direction and size. When an object has different forces acting upon it, the force’s effect is the same as one force in a distinct direction. This is known as the Resultant Force. Assuming that the resultant force is zero the force on the object is balanced. A resultant force is required in order to change the velocity of a given body. Assuming that the forces on an object are balanced, the object is going to be stationary. However in the case that it is moving, then it is going to continue to move at a steady speed in the same direction. |
Examples of Balanced Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Some examples of Balanced Force are:
- The weight of an object is balanced against the usual force operating on a body. Due to gravity, the weight acts downward, whereas the normal force acts in the opposite direction with equal magnitude.
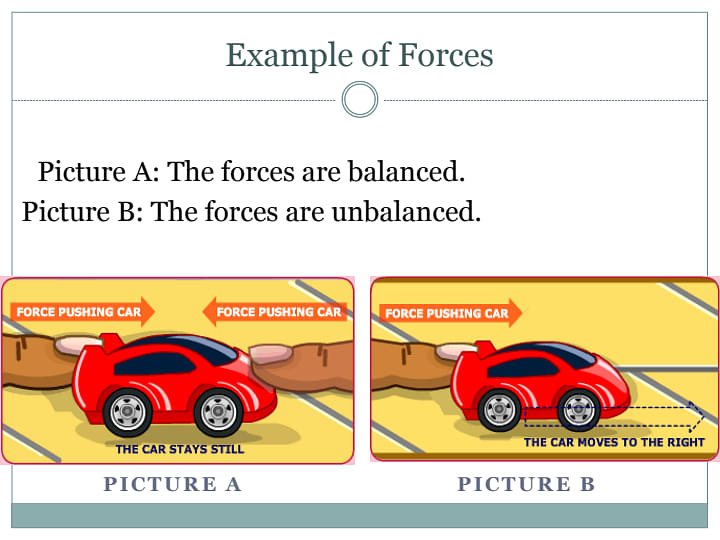
- A car that is pushed with equal force from both sides. The automobile will only be in its resting state. It's not going to move.
- A vertically positioned lizard on a wall. Due to the force of gravity, the lizard's weight should drag it down. Friction, on the other hand, balances it out with a force of equal size.
- A rope suspends a ball. The tension created by the rope balances the weight of the object. The stress is equal and in the opposite direction.
- A weighing balance in which the weights in both pans are the same.
- In a car, cruise control is used. Due to balanced forces, the car maintains a constant speed.
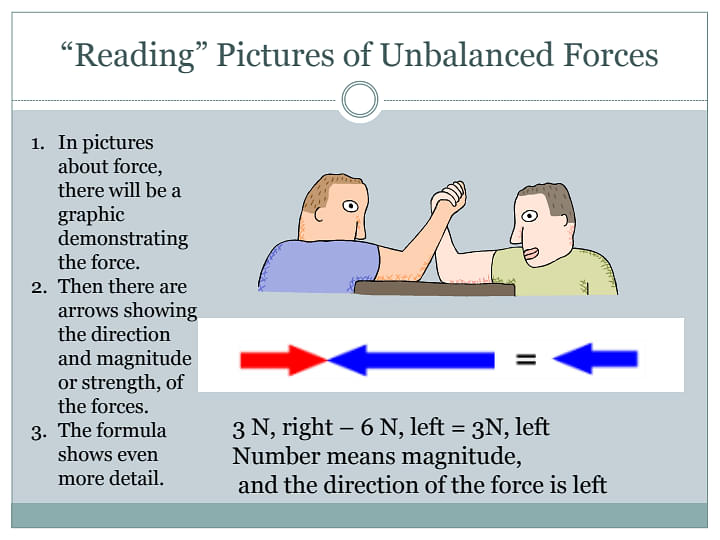
- In a game of arm wrestling, two opponents are evenly matched.
- An airplane in level flight with steady wings is in balance. The weight of the airplane balances the lift, and the drag balances the thrust.
The majority of balanced force examples can be divided into a few groups as well.
What is Unbalanced Force?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
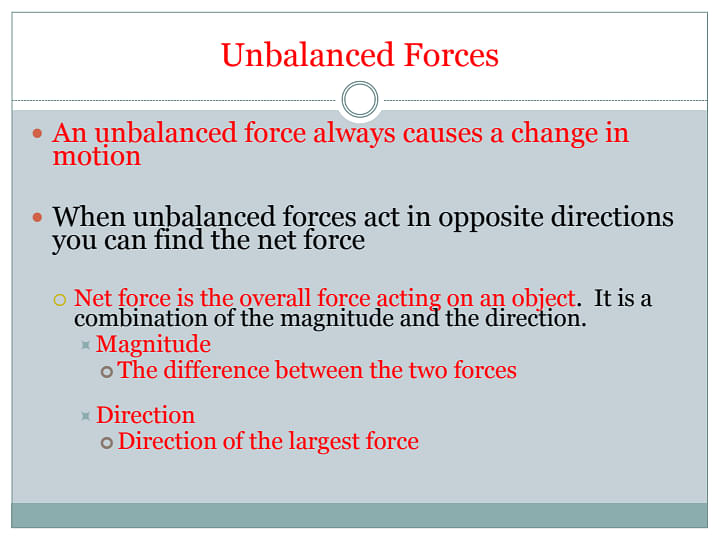
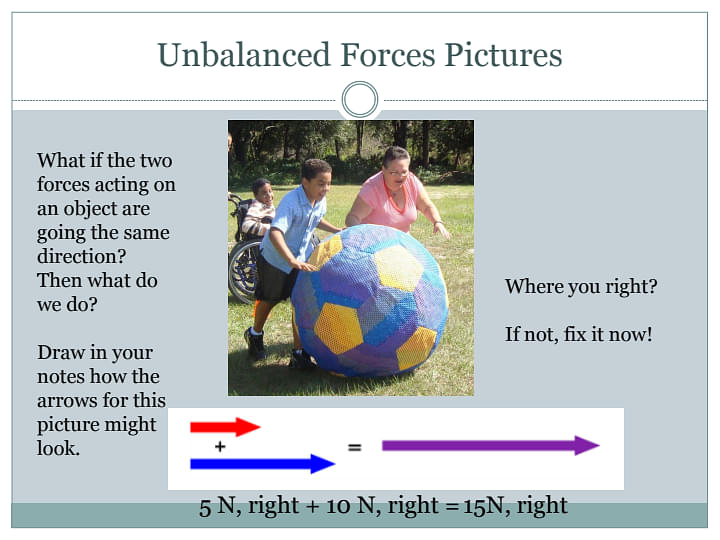
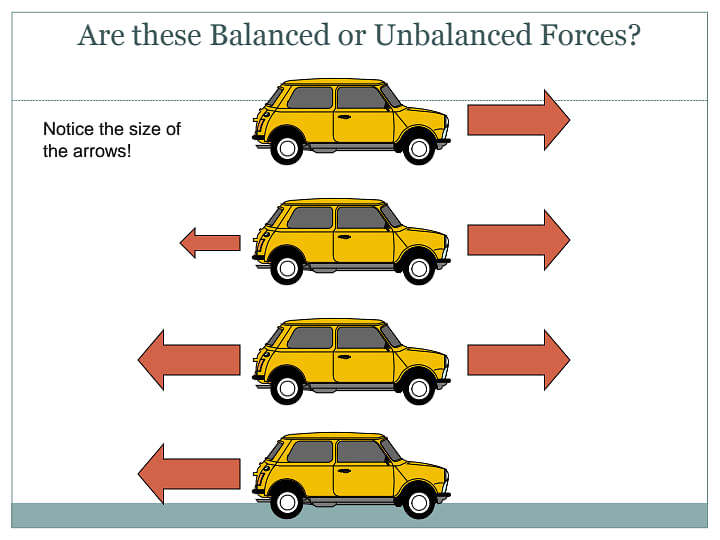
An unbalanced force is a force where two forces acting in opposing directions on a body and are not equal in magnitude and in size. Simply, the resultant of two opposite forces are seen to act on an object, thus bringing it to motion. These opposite forces are known as Unbalanced forces.
- A body changes its position in an unbalanced force.
- For instance, we can observe a moving object changing its direction, either increasing the speed or decreasing the speed and a body at rest also starts to move and vice versa.
- While balanced forced do not cause any change in motion, Unbalanced forces do cause a change in motion of an object.
- Unbalanced forces are typically not equal and opposite.
Examples of Unbalanced Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Practically anything that moves is due to the exertion of unbalanced forces on it. Some of the examples of unbalanced force are as follows:
- Apple falling to the ground.
- The up and down movement of the seesaw.
- Kicking a soccer ball.
- The taking-off a rocket.
- Skiing along the mountain slopes.
- Hitting a baseball.
- Drowning of an object.
Also Check:
Difference between Balanced and Unbalanced Force
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are several differences between Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Some of them include:
| Balanced Forces | Unbalanced Forces |
|---|---|
| The forces in Balanced Forces are equal in magnitude. | Unbalanced forces are not equal in magnitude. |
| Opposite in direction. | These forces can be in any direction but opposite. |
| Does not cause any change in the state of the motion of the object. | Causes change in the state of motion of the object. |
Forces of Action and Reaction
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. As a result, the forces are of an identical magnitude and opposing direction. As a result, these forces can be considered balanced forces. Here are a few examples of this type:
- The weight of the object is normally equivalent to the normal force against the ground but in the opposite direction. The normal force and the object's weight cancel each other out.
- When we try to break through a barrier and nothing happens. To offset our force, the wall provides a reaction force in the opposite direction.
A Rope's Tension
A rope's or string's tension is always equal to and opposite to the load applied to it. Here are several examples:
- A ball is hanging from a rope. The ball will remain stationary due to the tension in the rope. The tension is equal to the gravitational force and acts in the opposite direction.
- A tree with an apple dangling from its branches. The tension in the tree branch balances the weight of the apple.
- When both teams use the same level of force in a tug-of-war match. Due to disparities in the stamina of the two sides, the forces become uneven over some time.
In the Water Floating
Objects float in water for a reason.
- The reason for this is that water creates an upthrust force that is equal to and opposes gravitational pull.
- The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the water displaced by the object, according to the Archimedes principle.
- As a result, the object's weight must be equal to the weight of the water displaced to float.
Friction in a Static State
Static friction is a self-adjusting force that adjusts to be equal to and opposite to the force applied to a stationary object. As a result, the object will remain motionless until the applied force exceeds the limiting friction, at which point the forces become imbalanced.
- Brick on a table is an example. Because the static friction adjusts itself to be equal and opposite, it will not move with the slightest push.
- On a hill, an automobile is parked. Gravitational force should ideally pull or slide the cars down because they are parked on an elevation. The static force of friction, on the other hand, provides an equal and opposite force to hold them at rest.
Also Read:
Things to Remember
- When a force is applied to an object, it can change its: speed, the direction of movement, the form of movement.
- Newton’s first law of motion states that unless acted upon by an external force, an object in uniform motion will remain in uniform motion.
- A balanced force is defined as two equal-magnitude but opposite-direction forces acting on a body.
- Example of Balanced Force: A car that is pushed with equal force from both sides. The automobile will only be in its resting state. It's not going to move.
- An unbalanced force is a force where two forces acting in opposing directions on a body and are not equal in magnitude and in size.
- Example of Unbalanced force: Apple falling to the ground, the up and down movement of the seesaw., kicking a soccer ball.
Read Important Force PDF:
















Force PDF
Sample Questions
Ques: How do Forces act on different objects? (1 mark)
Ans: Normal force, or in this case, force is always equivalent in magnitude and opposite in direction to the gravity exerted on objects. This is forces act on different objects.
Ques: What is balanced force equivalent to? (2 marks)
Ans: Forces can be considered as balanced if there are equal forces acting in opposite directions. Balanced forces are equivalent or identical to no force at all. The object will either accelerate or decelerate if the force of an object is unbalanced. Air resistance and friction are forces that oppose the motion.
Ques: Why does an object float on water? Explain. (2 marks)
Ans: Objects float in water for a reason. The reason for this is that water creates an upthrust force that is equal to and opposes gravitational pull. The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the water displaced by the object, according to the Archimedes principle. As a result, the object's weight must be equal to the weight of the water displaced to float.
Ques: State Newton’s first law of motion. (2 marks)
Ans: A body which is at rest or motion at a constant speed in a straight line, it will remain in an unchanged position unless an external force is applied to it.
It states that unless acted upon by an external force, an object in uniform motion will remain in uniform motion. And an object at rest will remain at rest unless and until it is acted upon by an external force.
Ques: What is meant by balanced forces? (2 marks)
Ans: A balanced force is defined as two equal-magnitude but opposite-direction forces acting on a body. Forces that are equal and opposing cancel each other out. As a result, a body at rest will remain at rest. And, once in motion, a body will remain in motion.
- Balanced forces cannot alter the state or direction of motion.
- They have the ability to change the shape of an object.
- Under the influence of balanced forces, the body will remain in its initial state of motion. Because of their opposing directions, the forces cancel each other out.
Ques: A net-zero external unbalanced force is applied to an object. Is it possible for the item to have a velocity other than zero? If you answered yes, describe the constraints that must be applied to the magnitude and direction of the velocity. If not, please explain why. (3 marks)
Ans: An object with a net-zero external imbalanced force has a balanced force.
In balanced force,
- The stationary object does not move.
- A moving object continues to move.
-
As a result, the object can travel with a velocity greater than zero. It is only possible if the velocity of the object remains constant, i.e.
- The magnitude of velocity remains constant.
- The object's direction does not change.
Ques: Write some examples of balanced force. (3 marks)
Ans: Examples of balanced force are as follows:
- The weight of an object is balanced against the usual force operating on a body. Due to gravity, the weight acts downward, whereas the normal force acts in the opposite direction with equal magnitude.
- A car that is pushed with equal force from both sides. The automobile will only be in its resting state. It's not going to move.
- A vertically positioned lizard on a wall. Due to the force of gravity, the lizard's weight should drag it down. Friction, on the other hand, balances it out with a force of equal size.
Ques: Differentiate between balanced and unbalanced forces. (3 marks)
Ans: The differences between balanced and unbalanced forces are:
| Balanced forces | Unbalanced forces |
|---|---|
| The forces are equal in magnitude | These are unequal in magnitude |
| Opposite in direction | These forces can be in any direction but opposite |
| Does not cause any change in the state of the motion of the object | Causes change in the state of motion of the object |
Ques: Is air resistance a balanced force? (3 marks)
Ans: When a car moves at a constant speed i.e, uniform motion, the driving force from the engine is balanced by resistive and friction in the car’s moving parts. Here, the resultant force on the car is zero. An object that is falling at terminal velocity experiences the same air resistance as its weight. Similarly, a runner at the top speed experiences the same air resistance. And an object falling at the terminal velocity undergoes the same air resistance as its weight. So, if the force acting on an object is balanced, the resultant force is zero.
Ques: What do you mean by forces? (5 marks)
Ans: A force can be both a push and a pull. For example, when you push a door open, you must apply force to the door. To open a drawer, you must also exert force. You can't see a force, but you can often see what it does. When a force is applied to an object, it can change its:
- Speed
- Direction of movement
- The form of movement (for example, an elastic band gets longer if you pull it)
Forces can be contact forces, in which two objects must come into contact with each other to exert a force. Other forces are non-contact forces, in which objects do not have to come into contact with one another. These are some examples: gravity, magnetism, static electricity causes forces.
Ques: What is an unbalanced force? Write some examples. (5 marks)
Ans: An unbalanced force is a force where two forces acting in opposing directions on a body and are not equal in magnitude and in size. A body changes its position in an unbalanced force. For instance, we can observe a moving object changing its direction, either increasing the speed or decreasing the speed and a body at rest also starts to move and vice versa.
Some of the examples of unbalanced force are as follows:
- Apple falling to the ground.
- The up and down movement of the seesaw.
- Kicking a soccer ball.
- The taking-off a rocket.
- Skiing along the mountain slopes.
Also Check:



Comments