Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
To understand what is the relative density first of all we must have to understand what is density. Density is defined as the total amount of mass present in a unit volume of any matter. The density of any matter varies according to the substance; every substance has a different density.
Read More: Dalton’s atomic theory
Read More: Intermolecular Forces
Relative Density
At room temperature and pressure, the difference between specific gravity and density is 1gm per 1 cubic cm is the density of water and this density is used as a standard density and density of other substances calculated relative to this density that's why it is called relative density.
Let's see the densities of different substances.
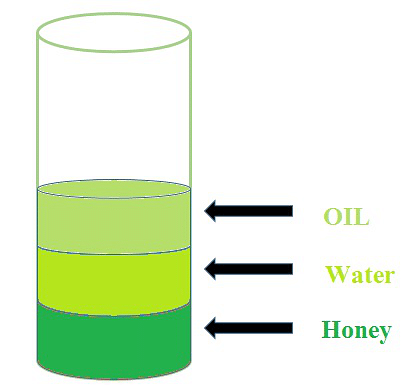
Let's take a test tube or glass cup and put some water in it. Then take some honey and oil and pour it into the glass. Now you can see that honey is settled at the bottom and oil is at the top. Why did this happen? The answer is simple: due to the density, the honey has more density than oil that why does it settle at the bottom this shows that every substance has a different density.
| Substances | Density (gm/ cm3) |
|---|---|
| Honey | 1.42 |
| Milk | 1.03 |
| Water | 1.0 |
| Lamp oil | 0.8 |
| Maple syrup | 1.37 |
| Liquid soap | 1.06 |
| Rubbing alcohol | 0.79 |
| Baby oil | 0.83 |
Let's understand the specific gravity. Specific gravity is the ratio of a substance's mass to the reference substance. Let suppose the milk has a density of 1.03 g /cm3 so now we can easily calculate its specific gravity that is -
1.03 / 1 = 1.03.
The specific gravity is a ratio that's why it does not have any unit; it is a quantity that doesn't have a dimension.
By measuring the specific gravity of any substance we can know that the substance is going to float on water or is going to sink. If the specific density of a substance is more than 1 then it will submerge and if it is less than 1 then it will float.
By using the above table you can easily know which substance is going to sink in the water and which is going to float.
Read Also:
| Difference Between Atom and Molecule | Difference Between Element and Compound |
| Difference Between Physical and Chemical Changes | Chemical Change |
The Formula of the Relative Density
Due to the temperature and pressure, the density of any substance may vary. That's why it is necessary to mention the temperature and pressure at which the density of the substances is to be determined.
Generally by ignoring factors like changing weather patterns and other things the measurement is done at 1 atmosphere that is 101.325 kPa. As we measure the relative density compared to the water it is highly incompressible and this thing does not happen with other substances like petroleum. These substances usually show the variation in density due to the pressure. So we have to neglect this to measure the relative density.
Now the relative density formula or R.D = Density of the substance / Density of the water
R.D = ρsubstance / ρrefrence
As we have earlier mentioned that if the relative density is more than 1 then the substance will sink into the water and if the relative density is less than 1 then the substance will float on the water so by using this statement we can write relative density formula such as
R.D. ( Relative Density) = weight loss of solid in air/weight loss of solid in water
Read More: Properties Of Matter
Factors affecting Relative Density
There re a number of factors that affect relative density. Let us look at each one of them in detail.
Temperature: Generally solid substances do not affect due to temperature so that corresponding density change is not relevant. But according to Archimedes principle while deciding the density of a liquid or solid material we have to consider temperature because the temperature change affects liquid in a greater way that is it can be in the range of 0.1 to 1 per °c
Air bubbles: If the air bubbles are stuck to the solid object it will increase the relative density when the object goes into the liquid. The air bubbles that have a diameter of 1 mm can yield up to a 0.5 mg increase and if the diameter is 2 mm it can yield up to 4 mg.
The volume of solid: If the solid substance has a large volume emersed in the liquid it will increase the level of fluid.
Pressure: Imagine that an astronaut has brought a glass of water to space as there is no pressure in space the water will vaporize as soon as possible and its density will decrease because its volume is increasing. And if started to increase the pressure the density of water will increase because due to the pressure the attraction in the water molecules will increase, thus increasing the density. Hence it is proved that the density is directly proportional to the pressure.
There are different ways to calculate the relative density like using the hydrometer, hydrostatic balance, oscillating densitometer, pycnometer method, Immersed body method, etc.
Read More: Relation Between Normality and Molarity
Relative Density Applications
- The application of relative density is in the various fields like when hydrocarbons that have a heavy molecular weight are converted to the low molecular weight hydrocarbon this chemical process takes place using the measurement of relative density.
- It can also be used to determine the density of unknown substances relative to the density of known substances.
- Geologist also uses the relative density to know the mineral content of the rock.
- In petroleum industry also has measure uses. In the petroleum industry, the products obtained are majorly due to the measurement done according to the relative density of the liquid.
Read More: Lewis Dot Structures
Things to remember
- Density is defined as the total amount of mass present in a unit volume of any matter.
- The density of any matter varies according to the substance; every substance has a different density.
- Specific gravity is the ratio of a substance's mass to the reference substance.
- The specific gravity is a ratio that's why it does not have any unit; it is a quantity that doesn't have a dimension.
- The relative density formula or R.D = Density of the substance / Density of the water
R.D = ρsubstance / ρrefrence
- Factors affecting the density- Temperature, air bubbles, pressure, and volume of solid.
Read More: Variable Valency
Sample Questions
Ques. Define density.
Ans. Density is defined as the total amount of mass present in a unit of volume of any substance.
Ques. Define relative density.
Ans. Relative density is defined as the density calculated relative to the water.
Water has a density of 1 gm/cm3 . Relative density is the dimensionless quantity.
Ques. You have a relative density of sliver is 10.8 and density of water is 1000kgm-3 then calculate the density of silver.
Ans. Data: Density of water - 1000Kgm-3
Relative density of silver - 10.8
As we know that
Relative density = density of sliver/density of water
The density of silver = Relative density × density of water
= 10.8 × 1000
The density of silver = 10800 km-3
Ques. Name the S.I. unit of density. How it is related to g/cm3?
Ans. S.I. unit of density is kg/m3. Relationship of kg/m3 with g/cm3 is 1 g/cm3 = 1000 kg/m3.
Ques. The density of brass is 8.4 g/cm3. What do you mean by this statement?
Ans. The density of brass is 8.4 g/cm3 it means that a block of brass having a volume 1 cm3 contains a mass of 8.4 g.
Ques. What is the unit of relative density?
Ans. It has no unit as it is the ratio of two similar quantities.
Ques. Why does a piece of ice float on water?
Ans. The density of ice is 0.9 g/cm3 is less than the density of water i.e. 1 g/cm3. Hence a piece of ice floats on water.
Read Also:








Comments