Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
The topic Periodic Classification of Elements covers some important subsections. Before moving on to important questions, let us recap the different ways elements have been classified. These are:
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newlands’s Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table
Dobereiner’s Triads
One of the early classifications, this method involves arranging the elements in the increasing order of their atomic mass. A triad of elements with similar properties are formed. Among the three, the atomic mass of the element in the middle would be around the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements. The downside of this classification is that it is not applicable to all known elements.
Eg: Li (6.9), Na(23), K(39)
Newland’s Law of Octaves
Here elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic masses and every 8th element shows the same physical and chemical properties as the first.

Newland’s Law of Octaves
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Medeleev’s periodic law provides the basis for this table and it states that “the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses''. The elements show a repetition of properties occurring at certain intervals called Periodicity of Properties.
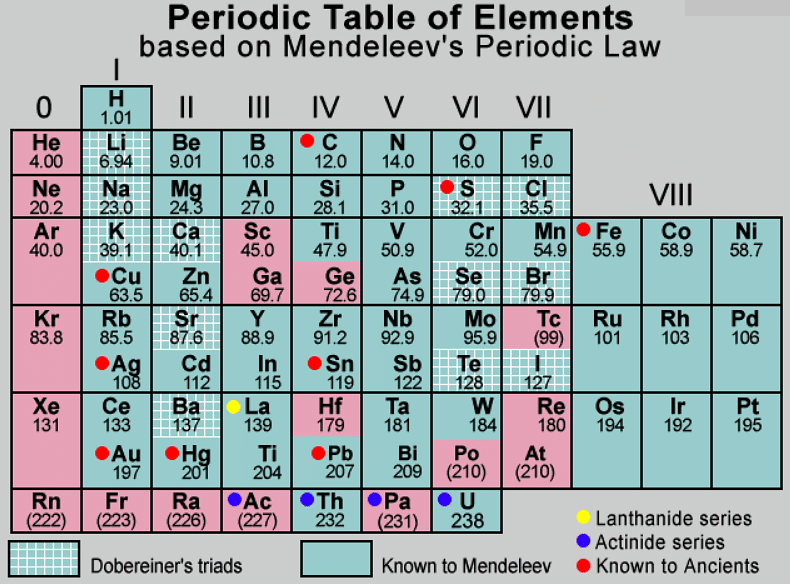
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
The Modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic law states that the chemical and physical properties of elements form the periodic function of their atomic number. The Atomic Number (Z) would be equal to the number of protons present within the nucleus of an atom.
There are groups which form the 18 vertical columns and periods form the 7 horizontal rows.

The Modern Periodic Table
Periodic Classification of Elements Important Questions
Question. The elements F, Cl and BR have seven valence electrons. Answer the following with justification
(i) Which has the largest atomic radius?
(ii) Which is the most radioactive?
Answer. (i) Bromine has the largest atomic radius. It has 4 shells with electron placements 2,8,18,7
(ii) Due to its small size, Fluorine is the most radioactive as it can easily gain electrons.
Question. What are the limitations of Newland’s Law of Octaves?
Answer. The limitations of Newland’s Law of Octaves are
- This law is only applicable to elements upto Calcium.
- Newland believed that there were only 56 elements and none would be discovered in the future.
- Newland placed Co and Ni in the same slot even though both show different properties
Question. P,Q and Y are three elements showing similar properties. Their atomic masses are X,Y and Z respectively. If the mass of Y is similar to the average mass of X and Z, what is the name of this arrangement? Give examples.
Answer. P,Q and Y belong to Dobereiner’s Triads.
Eg: Li, Na, K
Ca, Sr, Ba
Cl, Br, I
Question. List the merits and demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
Answer. Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
- Mendeleev was open to the idea of new elements being discovered in the future and thus left spaces. For eg: Eka-boron, Eka-aluminium, Eka- silicon etc.
- Based on its position in the table, the properties of many undiscovered elements could be predicted.
- The table could correct the atomic masses of elements which were in doubt.
- The Noble Gases could be placed in the table without disrupting the order.
Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
- Mendeleev’s table could not find a fixed position for hydrogen.
- Isotopes did not have a position. Eg Cl-35, Cl-37
- There was an irregular trend in atomic mass as some elements having higher atomic mass were placed after those with lower atomic mass. Eg Co-58.9 after Ni-58.7
Question. Identify the elements with the following electron configurations
(i) 2,8,2
(ii) 2,8,1
(iii) 2,8,7
(iv) 2,1
Answer. (i) Magnesium (Mg)
(ii) Sodium (Na)
(iii) Chlorine (Cl)
(iv) Lithium (Li)
Question. Given below are the atomic numbers of three elements. Answer along with reason.
| Element | A | B | C |
| Atomic Number | 5 | 7 | 10 |
Question. Which of these elements belong to (i) Group 13 and (ii) Group 15. Also state the period to which they belong.
Answer. (i) A is part of group 13 as its electronic configuration is 2,3 meaning it has 3 valence electrons.
(ii) B belongs to Group 15 with its electronic configuration being 2,5. It has 5 valence electrons.
Both of A and B have 2 shells so they belong in the 2nd period.
Question. Explain why elements belonging to same group show similar properties while those in the same period have different properties?
Answer. The elements of a group have the same valency i.e they have the same number of valence electrons. While the elements in a period have different number of valence electrons thus show different properties.
Question. Answer the questions based on the elements of the third period of the Periodic table as given below:
| Group | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII |
| Period 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl |
Question. a. Which is the bigger atom between Na and Mg. State the reason
b. Identify the most metallic and nonmetallic element
Answer. (a) Na is bigger than Mg. This is because Na has lower nuclear charge than Mg so the force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons are less, making it bigger in size.
(b) The most metallic is Na as it can lose electrons easily because of its larger atomic size while Cl is nonmetallic because it is able to gain electrons easily due to its smaller atomic size.
Question. What physical and chemical properties of elements did Mendeleev use to create his periodic table?
Answer. Mendeleev used atomic mass as a physical property and nature and formulae of hydride and oxide formed as chemical property.
Question. Li, Na and K form a Dobereiner’s triad. If the atomic mass of Li is 7 and K is 39. What is the atomic mass of Na?
Answer.
Dobereiner arranged the elements in increasing order of atomic masses. He found that the atomic mass of the middle element was approximately equal to the arithmetic mean (average) of the atomic masses of the other two elements of that triad when they are arranged in their increasing order of atomic mass.So Li = 7, K = 39
Atomic mass of Na = \(\frac{7+39}{2}= \frac{46}{2}\) = 23
Question. Answer the following
[a]What is Periodicity of properties in relation to the periodic table?
[b] Explain why elements in the same group show similar properties?
[c] If we go from left to right across a period, how will the tendency to gain electrons vary and why?
Answer. (a) The periodicity of properties refers to the nature of elements showing repetition of same properties after definite intervals.
(b) Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons hence showing similar properties.
(c) As we move across a period from left to right,the atomic size keeps decreasing which results in an increase of nuclear charge. Hence the tendency to gain electrons also increases.
Question. The table below shows 8 elements with their atomic numbers and the group and period to which they belong. Answer the questions based on given information. (The letters used for symbols aren't the ones usually used in the periodic table)
| Period | Group 1 | Group 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | A(3) | P(4) |
| 3 | B(11) | Q(12) |
| 4 | C(19) | R(20) |
| 5 | D(37) | S(38) |
Question.
- Give the electronic configuration of Q
- Give number of valence electrons in the atom Q
- What is the number of shells in atom Q
- Arrange P,Q,R and S in decreasing order of atomic size.
- Is Q metallic or nonmetallic?
- Which has the biggest atomic size among B,P and Q?
Answer.
- 1. The electronic configuration of Q is 2,8,2
- Q has 2 valence electrons
- There are 3 shells in Q
- S>R>Q>P is the decreasing order of atomic size.
- Q is a metal
- Among B, P and Q, B has the biggest atomic size.
Question. Explain the relation between the electronic configuration of an atom of an element and its position in the modern periodic table. Give Examples
Answer. The position of an element in the periodic table is dependent on the number of valence electrons, which is in turn dependent on the electronic configuration. Therefore, elements with the same number of valence electrons are in the same group. Group 1 has elements with one valence electron and Group 2 has elements with 2 valence electrons and so on. The period number is therefore the same as the number of shells. If an element has 1 valence electron it belongs to Group 1, if it has 2 valence electrons, it's part of Group 2. For example, consider element A having atomic number 11, the electronic configuration will be 2,8,1. As it has one valence electron, it belongs to Group 1. It has 3 shells so it is part of the third period.
Question. P,Q and R are three elements with atomic numbers 9,11 and 17 respectively. Which two elements will show similar chemical properties and why?
Answer. The electronic configuration of P,Q and R are
P(9): 2,7
Q(11): 2,8,1
R(17): 2,8,7
As P and R have the same number of valence electrons, they will exhibit similar chemical properties.
Question. A and B are 2 elements belonging to Group 1 and 2 respectively and in the same period. Compare them with respect to the periodic table from left to right in regards to the following. Explain why?
- Number of valence electrons in the atoms
- Valencies
- Metallic character
- Atomic size
- Formulae of oxides
Answer.
- 1.A has 1 valence electron while B has 2 valence electrons.
- The valency of A is 1 and B is 2
- A is more metallic than B
- A has bigger atomic size than B
- The formulae of oxides are A2O and BO
Question. If the atomic number of an element is 16. Give
- The number of valence electrons in its atom.
- Valency
- Group number
- Nature of oxide
- Whether it is metallic or nonmetallic
Answer.
- 1. 6
- 2.2
- 3.16
- Acidic Oxide
- Non-metal
Question. What changes occur along a period of the periodic table from left to right in relation to its metallic character?
Answer. As we move along the periodic table from left to right, it is observed that the atomic size decreases. This means the tendency to lose electrons also decreases and thus metallic character also decreases.
Question. From the table below showing electronic configuration of element X, answer the following questions.
| K | L | M |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 8 | 6 |
Question.
- Which group does X belong to?
- Which period is X part of?
- Give the number of valence electrons in X
- Valency of X
Answer.
- X is part of Group 16
- X belongs to the 3rd period
- X has 6 valence electrons
- The valency of X is 2
Question. If the atomic number of an element L is 12, what is its electronic configuration? Also is it metallic or non metallic?
Answer.. The atomic number is 12 hence the configuration will be 2,8,2. L would be a metal.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Check:









Comments