The CUET PG History exam in 2025 is scheduled for 26th March during Shift 2. After the exam, candidates can access the question paper, answer key, and detailed solution PDF. The test evaluates knowledge in art history, techniques of History, aesthetics, Indian and Western art forms, and creative expression.
Candidates must attempt 75 questions within 60 minutes, totaling 300 marks. Each correct answer awards 4 marks, while 1 mark is deducted for every incorrect response.
CUET PG 2025 History Question Paper with Solutions PDF
| CUET PG 2025 History Question Paper with Solutions PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
Which Mughal emperor was so concerned about tobacco's addiction that he banned it?
View Solution
Tobacco was introduced into India during the Mughal period, towards the end of Akbar’s reign.
Among the Mughal emperors, Jahangir was particularly concerned about the harmful effects of tobacco consumption.
Jahangir believed that tobacco was addictive and injurious to health. He observed its increasing use among people and felt that it weakened both physical health and moral discipline. Due to these concerns, he issued strict orders banning the use and sale of tobacco in his empire. He also prescribed punishments for those who disobeyed the ban.
Although the ban was not always strictly enforced across the empire, Jahangir’s actions clearly show his strong opposition to tobacco on health and social grounds.
Therefore, the correct answer is Jahangir. Quick Tip: Remember that Jahangir is known for his personal interest in social reforms and public welfare. His ban on tobacco is a commonly asked fact in Mughal history questions.
Who authored Muntakhab-ul-lubab?
View Solution
Muntakhab-ul-lubab is an important Persian historical work related to the Mughal period.
It was authored by Khafi Khan, whose full name was Muhammad Hashim Khafi Khan.
Khafi Khan lived during the late Mughal period and his work provides a detailed account of Mughal history, particularly from the reign of Aurangzeb to the early 18th century. The book is especially valuable because it critically describes the administrative policies, political conditions, and decline of the Mughal Empire.
Other options can be eliminated as:
Abdullah Khan and Zulfikar Khan were nobles and military commanders, not historians.
Ghulam Husain Salim authored \textit{Riyaz-us-Salatin, not \textit{Muntakhab-ul-lubab.
Hence, the correct answer is Khafi Khan. Quick Tip: Match historians with their works: Khafi Khan — \textit{Muntakhab-ul-lubab Ghulam Husain Salim — Riyaz-us-Salatin Such pairings are frequently asked in exams.
Mitra Mela started in
View Solution
Mitra Mela was a secret revolutionary organization founded by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar in 1899.
The organization was established in Nasik with the objective of spreading nationalist ideas among the youth and preparing them for revolutionary activities against British rule.
Mitra Mela emphasized physical training, patriotic education, and the study of revolutionary literature.
It later evolved into a more organized revolutionary group known as \textit{Abhinav Bharat, which played a significant role in the Indian revolutionary movement.
Since Mitra Mela was founded in Nasik, the correct answer is Nasik. Quick Tip: Remember important revolutionary organizations and their places of origin: Mitra Mela — Nasik Abhinav Bharat — Maharashtra Such factual questions are common in competitive examinations.
Who popularized the view that the Revolt of 1857 was `a conflict between civilization and barbarism'?
View Solution
The interpretation of the Revolt of 1857 has varied widely among British and Indian historians.
One early British viewpoint portrayed the revolt as a violent uprising lacking any legitimate political or national character.
T. R. Holmes, a British historian, popularized the view that the Revolt of 1857 was essentially a ``conflict between civilization and barbarism.''
According to this interpretation, the British represented order, progress, and civilization, while the Indian rebels were depicted as barbaric and destructive.
This perspective was used to justify British rule in India and to delegitimize the revolt by denying its nationalist or popular character.
Later Indian historians strongly criticized this view and reinterpreted the revolt as an early expression of resistance against colonial rule.
Hence, the correct answer is T. R. Holmes. Quick Tip: British historians often interpreted the Revolt of 1857 to justify colonial rule. Remember: T. R. Holmes — ``Conflict between civilization and barbarism'' Indian historians — Revolt as an early nationalist uprising
In ancient and early medieval period, a digest of Hindu laws on inheritance which became extremely influential in Bengal was known as
View Solution
In ancient and early medieval India, Hindu laws relating to inheritance and succession were interpreted through different legal schools. Among these, the \textit{Dayabhaga school became especially influential in Bengal.
The \textit{Dayabhaga was a digest of Hindu law composed by the jurist Jimutavahana around the 12th century. Unlike the Mitakshara system followed in most parts of India, the Dayabhaga system emphasized inheritance based on religious efficacy, particularly the capacity to offer funeral rites (\textit{shraddha) to ancestors.
According to the Dayabhaga system, sons did not acquire a right to ancestral property by birth. Instead, inheritance was determined after the death of the father. This interpretation gave greater flexibility in property rights and also allowed widows certain inheritance rights, which were not commonly recognized under other Hindu law schools.
Due to its rational interpretation and regional acceptance, the Dayabhaga system became the dominant legal authority governing inheritance laws in Bengal.
Therefore, the correct answer is Dayabhaga. Quick Tip: Remember the regional application of Hindu law schools: Dayabhaga — Bengal (inheritance after father's death) Mitakshara — Most other parts of India (birthright in property) Such distinctions are frequently tested in history exams.
The names of the Chapekar brothers who attacked Mr. Rand in Poona in 1897 were:
View Solution
In 1897, Poona (Pune) was severely affected by a plague epidemic. To control the situation, the British government appointed W. C. Rand as the Chairman of the Plague Committee. The committee adopted harsh and intrusive measures, including forced inspections of houses and mistreatment of Indian residents, which caused widespread resentment among the people.
The Chapekar brothers, who were young revolutionary nationalists, strongly opposed these oppressive actions. To protest against British tyranny and humiliation of Indians, Damodar Hari Chapekar and Balkrishna Hari Chapekar planned an attack on Mr. Rand.
On 22 June 1897, while returning from the Diamond Jubilee celebrations of Queen Victoria, Rand was attacked. Although Rand initially survived, he later succumbed to his injuries. This incident marked one of the earliest revolutionary acts against British officials in India and inspired later revolutionary movements.
Thus, the correct answer is Damodar and Balkrishna. Quick Tip: Important revolutionary facts to remember: Chapekar brothers — Damodar, Balkrishna, and Vasudev Target — W. C. Rand (Plague Commissioner, Poona) Year — 1897 Such questions are frequently asked in modern Indian history.
Strachey Commission was related to
View Solution
The Strachey Commission was appointed by the British government in India to examine the recurring problem of famines and to suggest measures for their prevention and management.
The commission was headed by Sir Richard Strachey and submitted its report in 1880. It studied the causes of famines, administrative shortcomings, and relief measures adopted during periods of scarcity. One of its major conclusions was that famines in India were not merely due to natural causes like drought, but were aggravated by administrative failures, lack of timely relief, and inadequate transport and storage of food grains.
Based on the recommendations of the Strachey Commission, the British government formulated a more systematic famine policy. This later contributed to the development of Famine Codes, which laid down guidelines for relief work, grain distribution, and employment during famine conditions.
Therefore, the Strachey Commission was related to famine. Quick Tip: Remember important commissions and their focus: Strachey Commission — Famine Hunter Commission — Education Simon Commission — Constitutional reforms Such matches are commonly asked in competitive examinations.
The minting of coins as a prerogative of the state power began in India with the:
View Solution
In ancient India, the earliest coins were punch-marked coins, which were initially issued by local authorities, merchants, and guilds. However, the systematic minting of coins as an exclusive prerogative of the central state power began during the Mauryan period.
Under the Mauryas, especially during the reign of Chandragupta Maurya and Ashoka, coinage came under strict state control. The Arthashastra of Kautilya clearly mentions the office of the Superintendent of Mint (\textit{Lakshanadhyaksha), indicating that the state regulated the production, quality, and circulation of coins.
This centralized control over minting reflected the highly organized administrative system of the Mauryan Empire and marked an important stage in the economic history of ancient India.
Hence, the correct answer is Mauryas. Quick Tip: Key points to remember about ancient Indian coinage: Mauryas — State-controlled minting Punch-marked coins — Earliest coins Arthashastra — Mentions mint administration Such economic history questions are common in exams.
Under which king, Mewar attained the greatest height of its power?
View Solution
Mewar attained the greatest height of its political power, territorial expansion, and cultural prosperity during the reign of Rana Kumbha (1433–1468 CE).
Rana Kumbha successfully defended Mewar against repeated attacks by the Sultanates of Malwa and Gujarat and emerged as one of the most powerful rulers of 15th-century Rajputana. Through military victories, he expanded the boundaries of Mewar and consolidated its position as a dominant regional power.
Apart from his military achievements, Rana Kumbha was also a great patron of art, architecture, and learning. He constructed several forts and temples, the most notable being the Kumbhalgarh Fort, which later became a UNESCO World Heritage Site. His reign is also remembered for architectural contributions such as the Vijay Stambha (Tower of Victory) at Chittor.
While Rana Sanga later challenged the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughals, the overall territorial extent, stability, and cultural achievements of Mewar were at their peak under Rana Kumbha.
Therefore, the correct answer is Rana Kumbha. Quick Tip: Remember key rulers of Mewar: Rana Kumbha — Greatest extent and cultural zenith Rana Sanga — Military resistance against Delhi Sultanate Rana Pratap — Symbol of Rajput valor and resistance Such distinctions are often tested in medieval Indian history.
Razmanama, is painted translation of:
View Solution
The Razmnama (also spelled Razmanama) is the Persian translation of the Indian epic \textit{Mahabharata. It was commissioned during the reign of the Mughal emperor Akbar as part of his policy of promoting cultural integration and mutual understanding among different religious traditions.
Akbar set up a translation bureau known as the \textit{Maktab Khana, where scholars translated major Sanskrit works into Persian, the official language of the Mughal court. The \textit{Razmnama was not only translated into Persian but was also richly illustrated with miniature paintings, making it a painted translation.
The work played a significant role in introducing the stories and philosophical ideas of the \textit{Mahabharata to Persian-speaking elites of the Mughal Empire and helped foster Indo-Persian cultural synthesis.
Thus, the correct answer is Mahabharata. Quick Tip: Remember important Mughal translations: Razmnama — Persian translation of \textit{Mahabharata Ramayana — Translated into Persian during Akbar’s reign Maktab Khana — Translation bureau under Akbar Such cultural history facts are commonly asked in exams.
Which ancient Indian University was the most renowned learning centre of Buddhism and compared with modern Oxford or Harvard?
View Solution
Nalanda University was the most renowned centre of Buddhist learning in ancient India and is often compared with modern institutions like Oxford or Harvard due to its scale, academic excellence, and international reputation.
Established around the 5th century CE during the Gupta period, Nalanda flourished under royal patronage, particularly from Gupta and later Pala rulers. It attracted students and scholars from all over Asia, including China, Korea, Japan, Tibet, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia.
Nalanda was a residential university with thousands of students and teachers. It offered advanced studies in Buddhist philosophy, logic, metaphysics, medicine, mathematics, astronomy, and grammar. Admission was highly competitive, and only the most capable students were accepted after rigorous oral examinations.
The university had vast libraries, the most famous being Dharmaganja, which housed an enormous collection of manuscripts. Nalanda continued to thrive for several centuries until it was destroyed in the 12th century.
Therefore, the correct answer is Nalanda University. Quick Tip: Ancient Indian universities to remember: Nalanda — Greatest Buddhist learning centre Vikramshila — Advanced Tantric Buddhism Taxila — Early centre of Brahmanical and secular studies Such comparisons are frequently asked in history examinations.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I \hfill List-II
(A) Dhakar Itihas \hfill (I) R. C. Majumdar
(B) Hindu Colonies in the Far East \hfill (II) Kedarnath Majumdar
(C) A Social History of Museums \hfill (III) Ronald Inden
(D) Imagining India \hfill (IV) Kenneth Hudson
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of books with their respective authors is as follows:
Dhakar Itihas was written by R. C. Majumdar, a prominent historian known for his works on ancient and medieval Indian history.
Hindu Colonies in the Far East was authored by Kedarnath Majumdar, which discusses Indian cultural expansion in Southeast Asia.
A Social History of Museums was written by Kenneth Hudson, focusing on the evolution and social role of museums.
Imagining India was authored by Ronald Inden, who examined the construction of Indian identity in historical writings.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A) - (I), \quad (B) - (II), \quad (C) - (IV), \quad (D) - (III) \]
Hence, option (3) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: For match-the-following questions, first identify well-known author–book pairs. Such questions often test familiarity with historians and their major works.
Who is known as the `Liberator of the Indian Press'?
View Solution
Charles Metcalfe is known as the ``Liberator of the Indian Press'' because of his role in removing restrictions on the press during British rule in India.
In 1835, when Metcalfe was the acting Governor-General of India, he passed the Press Act of 1835. This act abolished the system of prior censorship and licensing of newspapers, which had earlier been imposed by British authorities. As a result, newspapers were allowed to be published without seeking prior permission from the government.
This measure greatly encouraged the growth of the Indian press and helped the spread of political ideas, public opinion, and social reform movements. The freedom granted to the press under Metcalfe laid the foundation for the emergence of a vibrant nationalist press in India.
Therefore, Charles Metcalfe earned the title ``Liberator of the Indian Press.'' Quick Tip: Remember important press-related reforms: Charles Metcalfe — Liberator of the Indian Press (Press Act, 1835) Lord Wellesley — Censorship of Press Act, 1799 Vernacular Press Act — 1878 Such questions are frequently asked in modern Indian history.
Consider the following statements and identify the correct ones
(A) The Indian Museum, Calcutta was founded in 1814.
(B) James Fergusson travelled in India between 1935 and 1942 and documented the examples of ancient Indian monuments in \textit{The History of Asia and Eastern Architecture.
(C) Rajendra Lal Mitra published \textit{Buddha Gaya: The Hermitage of Sakya Muni in 1878.
(D) The Indian Government passed the Treasure Trove Act, giving the public the right to acquire all objects of archaeological interest.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is correct. The Indian Museum in Calcutta was founded in 1814 by the Asiatic Society and is regarded as the oldest museum in India.
Statement (B) is incorrect. James Fergusson travelled in India between 1835 and 1842, not between 1935 and 1942. He documented Indian architectural monuments in works such as \textit{The History of Indian and Eastern Architecture.
Statement (C) is correct. Rajendra Lal Mitra published \textit{Buddha Gaya: The Hermitage of Sakya Muni in 1878, which is an important work in the study of Buddhist archaeology.
Statement (D) is incorrect. The Treasure Trove Act empowered the government, not the general public, to claim ownership or control over objects of archaeological interest discovered in the ground.
Hence, only statements (A) and (C) are correct. Quick Tip: For statement-based questions, verify dates, titles of works, and the intent of laws carefully. Minor factual errors often make a statement incorrect.
Who wrote the `Environment and Ethnicity in India: 1200–1991'?
View Solution
\textit{Environment and Ethnicity in India: 1200–1991 is a significant work in the field of Indian environmental history. It was written by Ramchandra Guha, a well-known historian and environmental thinker.
In this book, Guha examines the long-term interaction between environment, ethnicity, and social groups in India over several centuries. He analyzes how ecological changes, state policies, colonial interventions, and economic developments affected different ethnic communities, particularly forest-dwelling and pastoral groups.
The work highlights how environmental exploitation and administrative control contributed to social conflicts and shaped ethnic identities from the medieval period through colonial rule and into post-independence India. This book is widely regarded as a foundational text in Indian environmental historiography.
Other options can be eliminated as:
Sejal Nagpal is not associated with this work.
Mahesh Rangarajan is known for studies on wildlife and environmental history but did not author this book.
Sumit Guha has written extensively on Indian history and environment but not this specific work.
Therefore, the correct answer is Ramchandra Guha. Quick Tip: Remember key authors in Indian environmental history: Ramchandra Guha — Environment, ecology, and social history Mahesh Rangarajan — Wildlife and conservation history Sumit Guha — Environmental and regional history Author–book matching is a common exam theme.
In which year did the Dutch establish factories in Nizampatan?
View Solution
The Dutch were among the earliest European trading powers to establish commercial settlements on the eastern coast of India. After setting up their first factory at Masulipatnam in 1605, they soon expanded their trading activities along the Coromandel Coast.
Nizampatan (also known as Nizampatnam), located near the mouth of the Krishna River, emerged as an important port for Dutch trade. The Dutch established their factory at Nizampatan during the years 1605–06 to facilitate trade in textiles and other goods.
This early establishment helped the Dutch strengthen their commercial network in the Deccan region and compete effectively with other European trading companies such as the English and the Portuguese.
Hence, the correct answer is 1605--06. Quick Tip: Important early Dutch factories in India: Masulipatnam — 1605 Nizampatan — 1605--06 Pulicat — Major Dutch headquarters on the Coromandel Coast Dates of European factories are frequently asked in history exams.
The English detached the Maratha and the Nizam from the side of Haider. Undaunted, Haidar faced the British but suffered defeat in 1781 in the battle of
View Solution
During the Second Anglo-Mysore War (1780–1784), Haidar Ali initially achieved significant success against the British. However, through diplomatic efforts, the English succeeded in detaching the Marathas and the Nizam of Hyderabad from Haidar Ali’s alliance, thereby isolating Mysore.
Despite this setback, Haidar Ali continued to confront the British forces with determination. In 1781, a major battle was fought at Porto Novo (Parangipettai) between Haidar Ali and the British army led by Sir Eyre Coote. In this battle, Haidar Ali suffered a decisive defeat due to the superior organization and tactics of the British forces.
The Battle of Porto Novo marked a turning point in the war, weakening Mysore’s position and strengthening British dominance in southern India, although the conflict continued until the Treaty of Mangalore in 1784.
Therefore, the correct answer is Porto Novo. Quick Tip: Key battles of the Anglo-Mysore Wars: Porto Novo (1781) — Defeat of Haidar Ali Pollilur (1780) — Major Mysore victory Mangalore (1784) — Treaty ending the war Such battle-related questions are common in modern Indian history.
Arrange the following in chronological order
(A) Data Ganj Bakhsh in Punjab
(B) Kabir in Uttar Pradesh
(C) Sundarmurti in Tamil Nadu
(D) Muktabai in Maharashtra
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
To arrange the given personalities in chronological order, we consider the time period in which each lived:
Sundarmurti (Sundarar) was a Shaiva saint of Tamil Nadu and one of the 63 Nayanars. He lived around the 7th–8th century CE, making him the earliest among the given figures.
Data Ganj Bakhsh (also known as Ali Hujwiri) was a renowned Sufi saint who lived in the 11th century CE and played an important role in spreading Islam in the Punjab region.
Muktabai was a prominent Bhakti saint from Maharashtra and the sister of Sant Dnyaneshwar. She lived in the 13th century CE.
Kabir was a famous Bhakti saint and poet from Uttar Pradesh who lived during the 15th century CE.
Thus, the correct chronological order is: \[ (C), (A), (D), (B) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: For chronology questions, first identify the century of each personality. Bhakti and Sufi saints are often asked in timeline-based questions.
Pataliputra was established in which era?
View Solution
Pataliputra was established during the 5th century BCE. It was founded by Ajatashatru, the ruler of the Haryanka dynasty of Magadha, initially as a fortified village named Pataligrama.
The strategic location of Pataliputra at the confluence of major rivers such as the Ganga, Son, and Gandak made it an ideal administrative and military center. Over time, it developed into a major city and later became the capital of powerful empires such as the Mauryas and the Guptas.
Classical accounts by Greek writers like Megasthenes describe Pataliputra as a magnificent and well-planned city, highlighting its importance in ancient Indian political and urban history.
Therefore, the correct answer is 5th century BCE. Quick Tip: Key facts to remember: Founder of Pataliputra — Ajatashatru Original name — Pataligrama Major capital of — Maurya and Gupta Empires Such foundational facts are frequently asked in ancient Indian history.
Mohammad Bin Qasim put his foothold in Sind in the year
View Solution
Mohammad Bin Qasim, a young Arab general of the Umayyad Caliphate, led an expedition into Sind in 712 CE. He was sent by the Umayyad governor Hajjaj bin Yusuf to punish the ruler of Sind, Raja Dahir, for alleged acts of piracy against Arab ships.
In 712 CE, Mohammad Bin Qasim successfully invaded Sind and defeated Raja Dahir. This marked the first permanent establishment of Arab rule in the Indian subcontinent. After his victory, he consolidated Arab control over important towns such as Debal, Nerun, and Multan.
The conquest of Sind laid the foundation for the spread of Islam and Islamic administration in the north-western regions of India and represents a significant event in early medieval Indian history.
Therefore, the correct answer is 712. Quick Tip: Important early medieval dates to remember: 712 CE — Arab conquest of Sind by Mohammad Bin Qasim Raja Dahir — Ruler defeated in Sind Hajjaj bin Yusuf — Governor who sent the expedition Chronological questions are commonly asked in history exams.
Which of the following revolutionary leaders organized the Chittagong Armoury Raid?
View Solution
The Chittagong Armoury Raid was a major revolutionary action against British rule in India, carried out on 18 April 1930. The raid aimed at seizing arms and ammunition from the British armouries in Chittagong and disrupting British authority.
This daring operation was organized and led by Surya Sen, popularly known as \textit{Masterda. He was a prominent revolutionary from Bengal and a member of the Indian Republican Army (Chittagong branch). Surya Sen believed in armed struggle as a means to overthrow British rule and inspire mass uprising.
Under his leadership, revolutionaries attempted to capture the police and auxiliary force armouries and destroy communication lines. Although the immediate objective was not fully successful, the raid became a landmark event in the revolutionary movement and inspired many young nationalists.
Other options are incorrect because:
Jatin Das was a revolutionary martyr known for his hunger strike.
C. R. Das was a moderate nationalist leader and freedom fighter.
Rash Bihari Bose was associated with the Ghadar movement and the Delhi conspiracy.
Hence, the correct answer is Surya Sen. Quick Tip: Important revolutionary events to remember: Chittagong Armoury Raid (1930) — Surya Sen Kakori Conspiracy — Ram Prasad Bismil Ghadar Movement — Lala Hardayal Leader–event matching is a common exam pattern.
Which of the following was NOT a patron of the Kangra School of painting:
View Solution
The Kangra School of painting flourished in the Himalayan region during the 18th century and is best known for its lyrical beauty, delicate colors, and themes drawn from Vaishnavism, especially the love of Radha and Krishna.
This school of painting received strong patronage from the rulers of Kangra, particularly from the Katoch dynasty. Raja Sansar Chand was the greatest patron of the Kangra School and played a decisive role in its development and refinement. Other members of the ruling family, such as Ghamand Chand and Aniruddha Chand, also extended patronage to artists and supported the growth of this artistic tradition.
Roop Chand, however, is not known to have been associated with or a patron of the Kangra School of painting.
Therefore, the correct answer is Roop Chand. Quick Tip: Key patrons of the Kangra School: Sansar Chand — Greatest patron Ghamand Chand — Early supporter Aniruddha Chand — Continued patronage Remembering patron–art school associations helps in art and culture questions.
Nalayira Divyaprabandham, described as a Tamil Veda, is one of the major anthologies of compositions by
View Solution
The Nalayira Divyaprabandham is a celebrated collection of 4,000 Tamil devotional hymns and is revered as the ``Tamil Veda.'' It is one of the most important texts of the Bhakti movement in South India.
These hymns were composed by the Alvars, who were Vaishnavite saint-poets devoted to Lord Vishnu. The Alvars lived between the 6th and 9th centuries CE and expressed intense personal devotion through their poetry. Their compositions emphasize love, surrender, and devotion to Vishnu and his incarnations.
The compilation of the \textit{Nalayira Divyaprabandham is traditionally credited to Nathamuni, who collected and systematized the hymns of the Alvars. The text continues to play a central role in Vaishnavite worship, especially in South Indian temples.
The other options are incorrect because:
Nayanars composed Shaivite hymns collected in the \textit{Tevaram.
Virshaivas were associated with later Lingayat traditions.
Jaina literature is distinct from Bhakti devotional anthologies.
Therefore, the correct answer is Alvars. Quick Tip: Bhakti literature to remember: Alvars — Vaishnavite hymns (\textit{Nalayira Divyaprabandham) Nayanars — Shaivite hymns (Tevaram) Such distinctions are frequently asked in cultural history.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
(A) The Muslim League passed Pakistan Resolution
(B) Churchill became British Prime Minister
(C) Germany invades Poland, which marks the beginning of World War II
(D) Japan's attack on Pearl Harbour
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
To arrange the events in correct chronological order, let us note their respective years:
Germany invades Poland — September 1939, which marked the beginning of World War II.
Pakistan Resolution — Passed by the Muslim League in March 1940 at Lahore.
Winston Churchill became British Prime Minister — May 1940.
Japan's attack on Pearl Harbour — December 1941, leading to the entry of the United States into World War II.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (C), (A), (B), (D) \]
Hence, option (4) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: For chronology questions, always note the exact year (and month if needed) of major world events. World War II timelines are frequently tested in modern history questions.
The first Round Table Conference in London was held between
View Solution
The First Round Table Conference was convened in London by the British government to discuss constitutional reforms in India. It was held from 12 November 1930 to 19 January 1931.
The conference was attended by representatives of the British government, Indian princes, and various political groups. However, the Indian National Congress did not participate in this conference because it was engaged in the Civil Disobedience Movement at that time.
The discussions focused on issues such as federal structure, representation of princely states, and minority safeguards. Although no final agreement was reached, the conference laid the groundwork for subsequent constitutional negotiations.
Therefore, the correct answer is 12--19 November, 1930. Quick Tip: Key facts about Round Table Conferences: First RTC — Nov 1930 to Jan 1931 (Congress absent) Second RTC — 1931 (Gandhi attended) Third RTC — 1932 Chronology of national movement events is frequently asked in exams.
Despite Gandhi's protest, in which year Subhash Chandra Bose was elected President of the Congress again?
View Solution
Subhash Chandra Bose was first elected President of the Indian National Congress in 1938 at the Haripura session. His views, however, increasingly differed from those of Mahatma Gandhi and the Congress high command, particularly regarding the pace and methods of the struggle against British rule.
Despite strong opposition from Gandhi and his supporters, Bose contested the presidential election again in 1939 at the Tripuri session. He defeated Gandhi-backed candidate Pattabhi Sitaramayya, thereby securing re-election as Congress President.
Although Bose won the election, he soon faced severe organizational resistance from the Congress Working Committee, most of whose members resigned. This political deadlock eventually led to Bose resigning from the presidency later in 1939 and forming the Forward Bloc.
Therefore, the correct answer is 1939. Quick Tip: Key Congress sessions to remember: Haripura Session (1938) — Bose elected President Tripuri Session (1939) — Bose re-elected despite Gandhi's opposition Forward Bloc — Formed by Bose in 1939 Such leadership-related questions are common in modern Indian history.
The All India Kisan Sabha was formed at Lucknow in:
View Solution
The All India Kisan Sabha (AIKS) was formed in April 1936 at Lucknow with the objective of organizing peasants across India and addressing their economic and social grievances.
The formation of the Kisan Sabha marked an important development in the agrarian movement during the Indian national struggle. It aimed to fight against high rents, illegal exactions by landlords, and oppressive colonial agrarian policies. Leaders like Swami Sahajanand Saraswati played a key role in shaping the organization and mobilizing peasants.
The All India Kisan Sabha worked closely with the Indian National Congress and other left-oriented groups to bring peasant issues into the mainstream of the freedom movement.
Therefore, the correct answer is April 1936. Quick Tip: Important peasant organizations and dates: All India Kisan Sabha — April 1936 (Lucknow) Eka Movement — 1921–22 Bardoli Satyagraha — 1928 Agrarian movements are frequently asked in modern Indian history.
The Ghadar Party was formed at
View Solution
The Ghadar Party was formed in 1913 at San Francisco by Indian revolutionaries living abroad, mainly in the United States and Canada. The party aimed to overthrow British rule in India through armed revolution.
It was founded by leaders such as Lala Hardayal, Sohan Singh Bhakna, and other Indian expatriates. The party published a revolutionary newspaper titled \textit{Ghadar, which openly called for rebellion against British imperialism and inspired Indians, especially soldiers, to rise against colonial rule.
San Francisco became the headquarters of the Ghadar Party because of the large Indian immigrant population on the west coast of the United States and the relatively greater political freedom available there compared to British India.
Thus, the correct answer is San Francisco. Quick Tip: Key facts about the Ghadar Party: Founded — 1913 Place — San Francisco Leader — Lala Hardayal Aim — Armed overthrow of British rule Such factual questions are common in revolutionary movement topics.
Which of the following traveller was amazed by the efficiency of the postal system during the Delhi Sultanate, and described Delhi as a vast city with a great population?
View Solution
Ibn Battuta, the famous Moroccan traveller, visited India during the reign of Sultan Muhammad bin Tughlaq in the 14th century. He served as a Qazi (judge) in Delhi and stayed in the Sultanate for several years, which gave him first-hand experience of its administration and society.
In his travel account, the \textit{Rihla, Ibn Battuta expressed admiration for the highly efficient postal system of the Delhi Sultanate. He described the existence of both horse-post (\textit{ulagh) and foot-post (\textit{dawa), which enabled rapid transmission of news and official correspondence across vast distances.
Ibn Battuta also described Delhi as a magnificent and vast city with a very large population, highlighting its prosperity, administrative sophistication, and urban scale.
Therefore, the correct answer is Ibn Battuta. Quick Tip: Important travellers and their observations: Ibn Battuta — Delhi Sultanate, postal system, Muhammad bin Tughlaq Marco Polo — South India during the Pandya period Abdur Razzaq — Vijayanagara Empire Traveller accounts are key sources for medieval Indian history.
During the Mughal period, the peshkash (tribute) levied on forest people, often included a supply of:
View Solution
During the Mughal period, forest regions were inhabited by various tribal and forest-dwelling communities. These groups were often not brought under direct administrative control but were instead linked to the Mughal state through the payment of \textit{peshkash (tribute).
A significant component of this tribute frequently included elephants. Elephants were highly valued by the Mughal rulers for their use in warfare, transport, royal processions, and hunting expeditions. Since elephants were primarily found in forested regions, the Mughal state depended on forest chiefs and tribal groups for their supply.
Historical records, including Mughal chronicles, indicate that forest people paid tribute not mainly in cash but in kind, with elephants being one of the most important items. This arrangement also helped integrate forest societies into the imperial political structure without completely disrupting their way of life.
Therefore, the correct answer is Elephants. Quick Tip: Remember Mughal terms and practices: Peshkash — Tribute paid by local chiefs or forest people Forest regions — Major source of elephants Elephants — Crucial for Mughal military and royal use Such socio-economic details are frequently asked in medieval history questions.
One of the important aspects of Buddha's teaching patichcha-samuppada refers to
View Solution
\textit{Patichcha-samuppada, also known as \textit{Pratityasamutpada, is one of the most fundamental doctrines of Buddhism. It refers to the law of dependent origination, which explains the causal relationship governing existence and suffering.
According to this doctrine, all phenomena arise dependent upon conditions, and nothing exists independently or permanently. The Buddha explained that suffering arises due to a chain of causes—ignorance leads to desire, desire leads to attachment, and attachment leads to suffering. When these causes are removed, suffering also ceases.
This teaching rejects the idea of a permanent soul or eternal substance and emphasizes impermanence and interdependence. It forms the philosophical foundation of other Buddhist concepts such as impermanence (\textit{anicca), suffering (\textit{dukkha), and non-self (\textit{anatta).
Hence, \textit{patichcha-samuppada refers to the law of dependent origination. Quick Tip: Core teachings of Buddhism: Four Noble Truths — Nature and cessation of suffering Eightfold Path — Way to liberation Patichcha-samuppada — Law of dependent origination Conceptual clarity is essential for philosophy-related questions.
The British Government of India charged I.N.A. soldiers, and trials were held at the Red Fort of Delhi. Which of the following was NOT an accused in these trials?
View Solution
The Indian National Army (I.N.A.) trials were conducted by the British government at the Red Fort in Delhi during 1945–46. These trials created widespread public sympathy for the INA soldiers and intensified nationalist sentiments across India.
The most prominent accused in the Red Fort trials were:
Shah Nawaz Khan
P. K. Sehgal
Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon
They were charged with treason for having taken up arms against the British government during World War II under the leadership of Subhash Chandra Bose.
T. B. Sapru, however, was not an accused. He was a senior lawyer and nationalist leader who played a role in public life but had no association with the INA trials as a defendant.
Therefore, the correct answer is T. B. Sapru. Quick Tip: Remember the INA Red Fort Trial trio: Shah Nawaz Khan P. K. Sehgal Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon These names are frequently asked together in examination questions.
In which type of the Gupta coins, the king is represented, dressed for the first time in an Indian waistcoat and turban?
View Solution
Gupta coinage marks an important stage in the evolution of Indian numismatics, not only in terms of artistic excellence but also in reflecting changes in royal ideology and cultural identity.
In the archer type coins, the Gupta king is depicted standing, holding a bow in one hand and an arrow in the other. Significantly, in this type the ruler is shown wearing an Indian waistcoat and turban for the first time, instead of foreign or Central Asian-style dress seen in earlier coinage.
This change in attire symbolized the growing assertion of indigenous Indian culture and political confidence during the Gupta period. The archer type coins are most commonly associated with rulers like Samudragupta and Chandragupta II.
Other coin types such as the battle axe, tiger slayer, and kacha types emphasize martial prowess or royal authority but do not introduce this distinctive Indian style of dress.
Therefore, the correct answer is the archer type. Quick Tip: Key Gupta coin types to remember: Archer type — Indian dress (waistcoat and turban) Tiger slayer type — Royal valor Battle axe type — Military power Questions on Gupta art and coinage often focus on symbolism and attire.
Terracotta models of the plough have been found at which one of the following Harappan sites?
View Solution
Kalibangan, an important site of the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization located in present-day Rajasthan, provides significant evidence of early agricultural practices.
Archaeological excavations at Kalibangan revealed terracotta models of the plough, along with a well-preserved ploughed field showing a distinctive criss-cross pattern of furrows. This indicates the use of plough-based agriculture by the Harappans and suggests advanced knowledge of farming techniques.
The presence of plough models strengthens the interpretation that agriculture was a well-developed and organized activity in the Harappan civilization. No such clear evidence of plough models has been found at Lothal, Banawali, or Dholavira.
Therefore, the correct answer is Kalibangan. Quick Tip: Important Harappan sites and their significance: Kalibangan — Ploughed field and terracotta plough models Lothal — Dockyard Dholavira — Advanced water management Banawali — Planned settlement Linking sites with archaeological findings is a common exam strategy.
The site of Jhukar is situated in which province of Pakistan?
View Solution
Jhukar is an archaeological site associated with the late phase of the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization, commonly referred to as the Jhukar culture.
The site is located in the Sindh province of present-day Pakistan. Archaeological evidence from Jhukar shows a continuation and transformation of Harappan cultural traits, including pottery styles and settlement patterns, after the decline of the mature Harappan phase.
Since Jhukar lies in lower Indus regions, it is geographically and historically linked with Sindh rather than the mountainous or north-western regions of Pakistan.
Therefore, the correct answer is Sindh. Quick Tip: Late Harappan cultural sites to remember: Jhukar — Sindh (Late Harappan phase) Cemetery H — Punjab region Rangpur — Gujarat Regional classification of archaeological sites is frequently tested.
Which of the following was an early capital of Harshvardhana?
View Solution
Harshvardhana initially ruled from Thaneshwar (also known as Thanesar), which was the early capital of his kingdom. Thaneshwar was the ancestral seat of the Pushyabhuti dynasty to which Harsha belonged.
After consolidating his power and expanding his empire over large parts of northern India, Harshvardhana later shifted his capital to Kannauj. Kannauj then became a major political and cultural center during his reign.
Thus, while Kannauj is often associated with Harsha’s mature rule, Thaneshwar was his early capital.
Therefore, the correct answer is Thaneshwar. Quick Tip: Key facts about Harshvardhana: Early capital — Thaneshwar Later capital — Kannauj Dynasty — Pushyabhuti Capital cities and dynastic centers are common exam questions.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I (Symbols of worship in Buddhism) \hfill List-II (Meant to / Associated with)
(A) Empty seat \hfill (I) Mahaparinibbana
(B) Stupa \hfill (II) Enlightenment
(C) Wheel \hfill (III) Indicates the meditation of Buddha
(D) Bodhi Tree \hfill (IV) First sermon of Buddha
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Early Buddhist art followed an aniconic tradition, where the Buddha was not depicted in human form. Instead, symbols were used to represent key events of his life and teachings.
The Empty seat symbolizes the meditation of the Buddha and his spiritual presence.
The Stupa represents the Mahaparinibbana (final liberation) of the Buddha and often contains relics.
The Wheel (\textit{Dharmachakra) symbolizes the first sermon of the Buddha at Sarnath.
The Bodhi Tree is associated with the Enlightenment of the Buddha at Bodh Gaya.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(III),\ (B)-(I),\ (C)-(IV),\ (D)-(II) \]
Hence, option (1) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Key Buddhist symbols to remember: Bodhi Tree — Enlightenment Wheel — First sermon Stupa — Mahaparinibbana Empty seat — Meditation / spiritual presence Symbol–event associations are frequently tested in art and culture questions.
Who is the author of the book titled `The Other Side of Silence: Voices from the Partition of India'?
View Solution
The Other Side of Silence: Voices from the Partition of India is a seminal work on the social history of the Partition of India. It was authored by Urvashi Butalia, a prominent historian, feminist scholar, and oral historian.
In this book, Butalia shifts the focus from high politics and official narratives to personal experiences of ordinary people affected by Partition. Using oral testimonies, memoirs, and interviews, she highlights themes of displacement, violence, gendered suffering, memory, and silence.
The work is especially notable for foregrounding women’s experiences and examining how trauma and loss were remembered—or deliberately forgotten—in the aftermath of Partition. It has become a foundational text in Partition studies and subaltern historiography.
The other options are incorrect because:
Anita Inder Singh focuses mainly on diplomatic and political history.
Gyanendra Pandey wrote \textit{Remembering Partition.
Mushirul Hasan worked extensively on Partition politics and Muslim identity.
Therefore, the correct answer is Urvashi Butalia. Quick Tip: Important books on Partition: Urvashi Butalia — \textit{The Other Side of Silence Gyanendra Pandey — Remembering Partition Mushirul Hasan — Studies on Partition and Muslim politics Author–book matching is a frequent exam theme.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
(A) S. R. Rao begins excavation at Lothal
(B) R. S. Bisht begins excavation at Dholavira
(C) M. S. Vats begins excavation at Harappa
(D) B. B. Lal and B. K. Thapar begin excavations at Kalibangan
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
To arrange the excavations in chronological order, consider the years when these archaeological works began:
M. S. Vats began excavation at Harappa in the early 1920s, making it the earliest among the given excavations.
S. R. Rao started excavation at Lothal in 1954, which revealed the famous dockyard of the Harappan civilization.
B. B. Lal and B. K. Thapar began excavations at Kalibangan in the early 1960s.
R. S. Bisht initiated excavation at Dholavira much later, in 1990.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (C), (A), (D), (B) \]
Hence, option (1) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Link archaeologists with sites and approximate decades: Harappa — 1920s Lothal — 1950s Kalibangan — 1960s Dholavira — 1990s Chronology of excavations is a common archaeology exam theme.
Who wrote the book `Histories'?
View Solution
Histories is a famous work written by Herodotus, a Greek historian of the 5th century BCE, who is often regarded as the \emph{Father of History.
The book \textit{Histories primarily deals with the Greco-Persian Wars and also provides detailed accounts of the geography, customs, traditions, and histories of various ancient civilizations, including Egypt, Persia, and parts of India. Herodotus combined storytelling with inquiry, aiming to preserve the memory of past events and explain their causes.
The other options are incorrect because:
Megasthenes wrote \textit{Indica.
Plato wrote philosophical dialogues such as \textit{The Republic.
Aristotle authored works on philosophy, politics, and science, such as \textit{Politics and \textit{Poetics.
Therefore, the correct answer is Herodotus. Quick Tip: Important ancient authors and their works: Herodotus — \textit{Histories Megasthenes — Indica Thucydides — History of the Peloponnesian War Author–book questions are common in ancient world history.
Which king is mentioned in the Barikot inscription of Swat Valley?
View Solution
The Barikot inscription, discovered in the Swat Valley region, is an important epigraphic source for the early medieval history of north-western India. The inscription mentions Jaipal Dev, a ruler of the Hindu Shahi dynasty.
Jaipal Dev ruled in the late 10th century CE and is known for his resistance against the incursions of Mahmud of Ghazni into the north-western regions of the Indian subcontinent. The Hindu Shahis controlled territories covering parts of present-day eastern Afghanistan and north-western India, including the Swat Valley.
The reference to Jaipal Dev in the Barikot inscription helps historians establish the political influence of the Hindu Shahi rulers in this region and provides valuable insight into the historical geography and power structure of the time.
The other options are incorrect because:
Dharampal was a Pala ruler of eastern India.
Vijaypal was a later Hindu Shahi ruler but is not mentioned in this inscription.
Muhammad Ghori belonged to a much later period (12th century CE).
Therefore, the correct answer is Jaipal Dev. Quick Tip: Important points to remember: Barikot inscription — Swat Valley Dynasty — Hindu Shahis Jaipal Dev — Resistance against Ghaznavid invasions Epigraphic evidence is a key source for early medieval Indian history.
Which of the following Chola rulers first conquered the Maldives?
View Solution
Rajendra I, the illustrious son of Rajaraja I, was one of the greatest rulers of the Chola dynasty and is well known for his extensive overseas expeditions. During his reign in the early 11th century CE, the Chola navy emerged as a dominant maritime power in the Indian Ocean.
Rajendra I was the first Chola ruler to conquer the Maldives. This naval expedition was part of his larger overseas campaign aimed at controlling important maritime trade routes and asserting Chola supremacy over regions connected to Indian Ocean commerce. The conquest of the Maldives strengthened Chola influence over sea trade between India, Southeast Asia, and the Arabian world.
The other options are incorrect because:
Rajaraja I expanded Chola power in South India and Sri Lanka but did not conquer the Maldives.
Vijayalaya was the founder of the Chola dynasty and ruled much earlier.
Kulottunga I focused mainly on internal administration and regional consolidation.
Therefore, the correct answer is Rajendra I. Quick Tip: Key achievements of Rajendra I: Overseas naval expeditions Conquest of Maldives Expansion into Southeast Asia Chola naval power is a frequently tested topic in medieval Indian history.
Who gave the title of Sher Khan to Sher Shah?
View Solution
Sher Shah Suri was originally known as Farid Khan. He received the title Sher Khan from Bahar Khan Lohani, the Afghan ruler of Bihar, whom Farid served early in his career.
According to historical accounts, Farid Khan earned this title after he killed a tiger (or lion) with great bravery, thereby impressing Bahar Khan Lohani. As a mark of admiration for his courage and military ability, Bahar Khan Lohani conferred upon him the title ``Sher Khan,'' meaning ``Lion Lord.''
This title later became closely associated with his identity, and after establishing his rule in North India, he became known as Sher Shah Suri. His administrative reforms and governance left a lasting impact on Indian history.
The other options are incorrect because:
Hemu was a later contemporary during the Mughal–Sur interlude.
Bairam Khan was a Mughal noble under Akbar.
Babur was the founder of the Mughal Empire and had no role in conferring this title.
Therefore, the correct answer is Bahar Khan Lohani. Quick Tip: Key facts about Sher Shah Suri: Original name — Farid Khan Title ``Sher Khan'' — Given by Bahar Khan Lohani Known for — Administrative and revenue reforms Such biographical details are commonly asked in medieval Indian history.
Shahbazgarhi inscription of Ashoka is written in which script?
View Solution
The Shahbazgarhi inscription is one of the Major Rock Edicts of Emperor Ashoka and is located in the present-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa region of Pakistan.
Ashoka’s inscriptions were written in different scripts depending on the region. In the north-western parts of the Indian subcontinent, including Shahbazgarhi and Mansehra, the inscriptions were written in the Kharoshthi script. This script was written from right to left and was influenced by the Aramaic script.
In contrast, Ashokan inscriptions found in most other parts of India were written in the Brahmi script. The use of Kharoshthi at Shahbazgarhi reflects regional linguistic and cultural variations within the Mauryan Empire.
Therefore, the correct answer is Kharoshthi. Quick Tip: Ashokan inscriptions and scripts: Shahbazgarhi, Mansehra — Kharoshthi Most of India — Brahmi Language used — Prakrit Script–region matching is a common exam topic in ancient Indian history.
Mirabai's husband Yuvraj Bhojraj was the son of:
View Solution
Mirabai, the celebrated Bhakti saint and devotee of Lord Krishna, was married to Yuvraj Bhojraj of Mewar. Bhojraj was the eldest son of Rana Sanga (Rana Sangram Singh), one of the most powerful rulers of the Sisodia dynasty of Mewar.
Rana Sanga ruled Mewar in the early 16th century and is remembered for his valour and resistance against the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughals. Mirabai’s marriage into the royal family of Mewar placed her within a prominent Rajput household, though her deep devotion to Krishna often brought her into conflict with courtly traditions.
Bhojraj died at a young age, after which Mirabai devoted herself entirely to her spiritual life and devotional poetry.
Therefore, the correct answer is Rana Sanga. Quick Tip: Key facts related to Mirabai: Husband — Yuvraj Bhojraj Father-in-law — Rana Sanga Tradition — Krishna Bhakti (Vaishnavism) Biographical links of Bhakti saints are commonly asked in exams.
Which painter was conferred with the title of Nadir-ul-Asr by Jahangir?
View Solution
During the reign of Emperor Jahangir, Mughal painting reached a high level of naturalism and artistic refinement. Jahangir was a great patron of art and personally took interest in the work of court painters.
Ustad Mansoor was one of the most distinguished painters in Jahangir’s court, especially renowned for his exceptional paintings of animals, birds, and flora. Deeply impressed by his artistic excellence and precision in natural history illustrations, Jahangir conferred upon him the title ``Nadir-ul-Asr'', meaning ``Wonder of the Age.''
Abul Hasan, another eminent painter of the Mughal court, was given a different title—Nadir-uz-Zaman (Wonder of the Time). Abu'l Fazl was a historian and scholar, not a painter, while Manohar was a painter but did not receive this specific title.
Therefore, the correct answer is Ustad Mansoor. Quick Tip: Important Mughal painters and titles: Ustad Mansoor — Nadir-ul-Asr Abul Hasan — Nadir-uz-Zaman Basawan, Manohar — Prominent Mughal painters Matching artists with titles is a common question in art and culture.
On whose death Col. Palmer, the British Resident at Poona remarked, `with him departed all the wisdom and moderation of the Maratha Government'?
View Solution
Nana Fadnavis was one of the most able statesmen of the Maratha Confederacy and played a crucial role in Maratha administration and diplomacy during the late 18th century. He was a key member of the Barbhai Council that governed the Maratha state after the death of Peshwa Madhav Rao.
Nana Fadnavis was known for his political wisdom, administrative efficiency, and balanced approach toward both internal Maratha politics and relations with external powers, especially the British. His diplomatic skill helped preserve Maratha autonomy for a considerable period despite growing British influence.
After his death in 1800, Col. Palmer, the British Resident at Poona, famously remarked that “with him departed all the wisdom and moderation of the Maratha Government,” highlighting Nana Fadnavis’s importance as a stabilizing force in Maratha governance.
Therefore, the correct answer is Nana Fadnavis. Quick Tip: Key Maratha statesmen to remember: Nana Fadnavis — Diplomat and administrator Mahadji Sindhia — Military leader and statesman Baji Rao II — Last Peshwa Such quotations-based questions often point to influential administrators.
What is described in Tahqeek-e-Hind?
View Solution
Tahqeek-e-Hind (also known as \textit{Kitab fi Tahqiq ma lil-Hind) was written by the famous scholar Al-Biruni. This work is one of the most valuable historical and cultural accounts of India written by a foreign scholar.
Al-Biruni came to India during the early 11th century along with Mahmud of Ghazni. In \textit{Tahqeek-e-Hind, he provided a detailed and systematic description of Indian society, religion, philosophy, science, mathematics, astronomy, geography, customs, and traditions as they existed during the 11th century.
What makes this work unique is Al-Biruni’s objective and scholarly approach. Instead of criticizing Indian beliefs, he tried to understand them from the Indian point of view, often comparing them with Greek and Islamic ideas.
Thus, \textit{Tahqeek-e-Hind is essentially a comprehensive description of 11th century India. Quick Tip: Important medieval historical works: Al-Biruni — \textit{Tahqeek-e-Hind (11th century India) Ibn Battuta — Rihla Minhaj-us-Siraj — Tabaqat-i-Nasiri Books by foreign travellers are key sources for medieval Indian history.
What were local communities of merchants called in the Vijayanagar empire?
View Solution
In the Vijayanagar Empire, trade and commerce played a vital role in the economy, and various merchant communities were actively involved in internal and overseas trade.
The Kudirai Chettis were an important community of merchants, particularly known for their involvement in the trade of horses. Since good-quality horses were essential for the Vijayanagar army and were largely imported from West Asia, the Kudirai Chettis held a significant position in the economic and military system of the empire.
The other options are incorrect because:
Vellals were primarily an agrarian community.
Ayangar refers to a Vaishnavite sect, not a merchant group.
Kalatikas were associated with artisans and craft production.
Therefore, the correct answer is Kudirai Chettis. Quick Tip: Key merchant communities in South Indian history: Kudirai Chettis — Horse traders in Vijayanagar Manigramam and Ayyavole — Earlier merchant guilds Economic history questions often focus on trader communities and guilds.
Who said about the drainage system of Harappan civilization that `It is certainly the most ancient system as yet discovered'?
View Solution
Sir John Marshall, the Director-General of the Archaeological Survey of India in the early 20th century, played a crucial role in the excavation and interpretation of the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization.
While studying the urban planning of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, John Marshall was particularly impressed by the well-organized and advanced drainage system. The cities had covered drains made of baked bricks, running along the streets and connected to individual houses through soak pits.
Recognizing the sophistication and antiquity of this urban feature, John Marshall remarked that the drainage system of the Harappan civilization was “certainly the most ancient system as yet discovered.” His observation highlighted the high level of civic planning and sanitation achieved by the Harappans.
Therefore, the correct answer is John Marshall. Quick Tip: Key features of Harappan urban planning: Covered brick drains Advanced sanitation system Planned streets and houses Such quotations are often attributed to archaeologists who studied the sites closely.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I \hfill List-II
(A) History of Hindu Mathematics \hfill (I) M. Hiriyanna
(B) Outlines of Indian Philosophy \hfill (II) G. C. Mendis
(C) Ancient Astronomy and Cosmology \hfill (III) A. N. Singh
(D) Early History of Ceylon \hfill (IV) C. P. S. Menon
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of books with their respective authors is as follows:
History of Hindu Mathematics was written by A. N. Singh (along with B. B. Datta), making (A)–(III) correct.
Outlines of Indian Philosophy is a well-known work by M. Hiriyanna, hence (B)–(I).
Ancient Astronomy and Cosmology is associated with C. P. S. Menon, so (C)–(IV).
Early History of Ceylon was authored by G. C. Mendis, giving (D)–(II).
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(III),\ (B)-(I),\ (C)-(IV),\ (D)-(II) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: For match-the-following questions, focus on well-known author–book pairs. Indian philosophy and historiography texts are frequently tested in competitive exams.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I \hfill List-II
(A) Ashoka \hfill (I) Julius Jolly
(B) Hindu Law and Custom \hfill (II) Vincent Smith
(C) Political History of Ancient India \hfill (III) D. R. Bhandarkar
(D) Emperor Ashok \hfill (IV) Hemchandra Raychaudhuri
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of historical works with their authors is as follows:
Ashoka was written by Vincent Smith, a noted historian of ancient India.
Hindu Law and Custom was authored by Julius Jolly, who specialized in ancient Indian legal traditions.
Political History of Ancient India was written by D. R. Bhandarkar, focusing on political developments in early India.
Emperor Ashok was authored by Hemchandra Raychaudhuri, a renowned Indian historian.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(II),\ (B)-(I),\ (C)-(III),\ (D)-(IV) \]
Hence, option (1) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Remember some classic author–book pairs: Vincent Smith — Ashoka Julius Jolly — Hindu Law and Custom D. R. Bhandarkar — Political History of Ancient India H. C. Raychaudhuri — Emperor Ashok Such matches are frequently tested in historiography questions.
Arrange the following kings in chronological order:
(A) Chandra Satakarni
(B) Gautamiputra Satakarni
(C) Yajna Sri Satakarni
(D) Vashishthiputra Pulumayi
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The Satavahana dynasty ruled large parts of the Deccan and played a crucial role in early Indian political history. To determine the correct chronological order, we consider the approximate reigns of the rulers:
Gautamiputra Satakarni (c. 78–102 CE) was the greatest Satavahana ruler, known for defeating the Shakas and restoring Satavahana power.
Vashishthiputra Pulumayi, the son of Gautamiputra Satakarni, succeeded him and ruled in the early 2nd century CE.
Yajna Sri Satakarni ruled later (c. 165–194 CE) and is known from coins and inscriptions showing revived Satavahana strength.
Chandra Satakarni belonged to a later phase of the dynasty and ruled after Yajna Sri Satakarni.
Thus, the correct chronological order is: \[ (B), (D), (C), (A) \]
Hence, option (3) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Key Satavahana rulers in sequence: Gautamiputra Satakarni — Most powerful ruler Vashishthiputra Pulumayi — Immediate successor Yajna Sri Satakarni — Later revival Chronology-based dynasty questions are common in ancient history.
Arrange the following incidents in chronological order:
(A) The Great Wall of China was constructed
(B) Alexander invaded India
(C) The Iranian ruler Darius annexed Punjab and Sindh
(D) The Maurya Empire was finally destroyed by Pushyamitra Shunga
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
To determine the correct chronological order, we note the approximate dates of the given events:
Darius I of Persia annexed Punjab and Sindh around 516 BCE, marking the earliest foreign annexation of parts of north-west India.
Alexander invaded India in 326 BCE during his eastern campaign.
The Great Wall of China was extensively constructed and unified during the reign of Qin Shi Huang around 221–206 BCE.
The Maurya Empire came to an end in 185 BCE when Pushyamitra Shunga overthrew the last Mauryan ruler, Brihadratha.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (C), (B), (A), (D) \]
Hence, option (1) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: For ancient chronology questions: Persian expansion into India — 6th century BCE Alexander — 4th century BCE Maurya decline — 2nd century BCE Always arrange events from earliest to latest using approximate centuries.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
(A) \textit{Natural History in Latin by Pliny
(B) \textit{Indica of Ktesias
(C) Ptolemy's \textit{Geography
(D) \textit{The Kamasutra of Vatsyayana
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct chronological order can be determined by noting the approximate period in which each work was composed:
Indica by Ktesias was written in the 5th century BCE, making it the earliest among the given works.
Natural History by Pliny the Elder was composed in the 1st century CE.
Geography by Ptolemy dates to the 2nd century CE.
The Kamasutra by Vatsyayana is generally dated to the 3rd–4th century CE.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (B), (A), (C), (D) \]
Hence, option (1) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: For chronology questions involving texts: Greek works on India — Mostly pre-Christian era Roman authors — 1st–2nd century CE Classical Indian texts — Mostly early centuries CE Approximate centuries are often sufficient to answer such questions.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I \hfill List-II
(A) Indian Art \hfill (I) Krishna Dev
(B) Temples of North India \hfill (II) V. S. Agrawala
(C) Hinduism and Buddhism \hfill (III) Prithvi Kumar Agrawala
(D) Gupta Temple Architecture \hfill (IV) N. E. Charles Eliot
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of books with their authors is as follows:
Indian Art was written by V. S. Agrawala, a renowned scholar of Indian art, culture, and iconography.
Temples of North India was authored by Krishna Dev, who made significant contributions to the study of Indian temple architecture.
Hinduism and Buddhism was written by N. E. Charles Eliot, focusing on the philosophical and historical development of these religions.
Gupta Temple Architecture was authored by Prithvi Kumar Agrawala, who specialized in Gupta-period art and architecture.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(II),\ (B)-(I),\ (C)-(IV),\ (D)-(III) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Important author–book pairs in Indian art history: V. S. Agrawala — Indian Art Krishna Dev — Temples of North India N. E. Charles Eliot — Hinduism and Buddhism Such matches are frequently asked in art and culture sections.
Consider the following in the context of Subsidiary Alliance and identify the correct statements:
(A) Subsidiary Alliance was a system devised by Lord Wellesley in 1798 and all those states who entered into such an alliance with the British had to accept certain terms and conditions.
(B) The British would not be responsible for protecting their allies from external threats to their power.
(C) In the territory of the ally, a British armed contingent would be stationed.
(D) The ally could enter into agreements with other rulers or engage in warfare.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The Subsidiary Alliance was introduced by Lord Wellesley in 1798 as a key instrument of British imperial expansion in India.
Statement (A) is correct. Lord Wellesley devised the Subsidiary Alliance system, under which Indian states had to accept several restrictive conditions in return for British protection.
Statement (B) is incorrect. Under this system, the British were responsible for protecting their allied states from external aggression.
Statement (C) is correct. One of the main features of the Subsidiary Alliance was the permanent stationing of a British armed contingent within the territory of the allied state, the cost of which was borne by the Indian ruler.
Statement (D) is incorrect. The allied ruler could not enter into treaties with other powers or engage in warfare without British approval.
Thus, only statements (A) and (C) are correct. Quick Tip: Key features of Subsidiary Alliance: Introduced by Lord Wellesley British troops stationed in allied states Allies lost control over foreign policy British provided protection from external threats Statement-based questions often test these core conditions.
Consider the following statements in the context of land revenue and agrarian system of the Mughal Period and identify the correct ones:
(A) Estimation of land revenue was called kankut.
(B) Land held and managed directly by the state was called Matikana.
(C) Rent free land was called sayurghal.
(D) Land allotted in lieu of military service was called taquawi.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is correct. Kankut was a method used in the Mughal period for estimating land revenue based on measurement and assessment of cultivated land.
Statement (B) is incorrect. Land held and managed directly by the Mughal state was known as khalisa, not Matikana. Matikana generally referred to land associated with zamindars.
Statement (C) is correct. Sayurghal referred to rent-free land grants given mainly to religious scholars, saints, and charitable institutions.
Statement (D) is incorrect. Taquawi was not land allotted for military service; rather, it referred to agricultural loans advanced to peasants to help them with cultivation. Land granted in lieu of military service was known as jagir.
Hence, only statements (A) and (C) are correct. Quick Tip: Key Mughal agrarian terms: Kankut — Method of land revenue assessment Khalisa — State-owned land Sayurghal — Rent-free land grants Taquawi — Loans to peasants Conceptual clarity of revenue terms is essential for Mughal administration questions.
Consider the following in the context of the National Anthem of India and identify the correct statements:
(A) Jana-gana-mana was composed originally in Bengali.
(B) Constituent Assembly adopted it as the National Anthem of India in 1946.
(C) It was first sung in 1911 at the Calcutta Session of the Indian National Congress.
(D) It is a part of Rabindranath Tagore's novel \textit{Gora.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is correct. Jana-gana-mana was originally composed in Bengali by Rabindranath Tagore.
Statement (B) is incorrect. The Constituent Assembly adopted Jana-gana-mana as the National Anthem of India on 24 January 1950, not in 1946.
Statement (C) is correct. The song was first sung on 27 December 1911 at the Calcutta Session of the Indian National Congress.
Statement (D) is incorrect. Jana-gana-mana is not part of Tagore’s novel \textit{Gora; it was composed as a separate song.
Thus, only statements (A) and (C) are correct. Quick Tip: Key facts about the National Anthem: Composer — Rabindranath Tagore Originally written in — Bengali First sung — INC Session, Calcutta (1911) Adopted as National Anthem — 24 January 1950 Statement-based questions often test dates and original language.
Consider the following in the context of the Revolt of 1857 and identify the correct statements:
(A) The large majority of the sepoys of the Bengal Army were recruited from the villages of Awadh and eastern Uttar Pradesh.
(B) The Rebellion spread throughout North, Deccan and South India.
(C) The control of Indian administration was transferred from the East India Company to the Board of Control by the Government of India Act, 1857.
(D) British newspapers and pictures commemorated the British heroes who saved the English and repressed the rebels, and the rebels were demonized.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is correct. A very large proportion of the Bengal Army sepoys were recruited from Awadh and eastern Uttar Pradesh. These regions were deeply affected by British annexation and revenue policies, which contributed significantly to sepoy discontent.
Statement (B) is incorrect. The Revolt of 1857 was largely confined to North and Central India. It did not spread widely to the Deccan and South India, where British control remained relatively stable.
Statement (C) is incorrect. The transfer of power from the East India Company to the British Crown took place through the Government of India Act, 1858, not 1857, and authority passed to the Crown, not merely to the Board of Control.
Statement (D) is correct. British newspapers, paintings, and illustrations portrayed British officers and civilians as heroic figures while depicting Indian rebels as brutal and barbaric. This narrative helped justify harsh repression and reinforced colonial ideology.
Therefore, only statements (A) and (D) are correct. Quick Tip: Key facts about the Revolt of 1857: Bengal Army recruits — Awadh and eastern U.P. Revolt region — Mainly North and Central India Power transfer — Government of India Act, 1858 British narratives — Rebels demonized in press and art Statement-based questions often include subtle errors in dates and regions.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I (Temple architecture / Symbols in Vijayanagara) \hfill List-II (Associated with)
(A) Mahanavami Dibba \hfill (I) Council chamber
(B) Lotus Mahal \hfill (II) A massive platform
(C) Virupaksha \hfill (III) Guardian deity of kingdom
(D) Pampadevi \hfill (IV) Local mother goddess
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct associations related to Vijayanagara architecture and religious symbolism are as follows:
Mahanavami Dibba was a massive raised platform used for royal ceremonies and celebrations, especially during the Mahanavami (Dussehra) festival.
Lotus Mahal functioned as a council chamber or pleasure pavilion within the royal enclosure.
Virupaksha was regarded as the guardian deity of the Vijayanagara kingdom and was central to its religious identity.
Pampadevi was a local mother goddess associated with the Tungabhadra region and later assimilated into the state cult.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(II),\ (B)-(I),\ (C)-(III),\ (D)-(IV) \]
Hence, option (3) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Key Vijayanagara symbols to remember: Mahanavami Dibba — Royal ceremonial platform Virupaksha — Guardian deity Pampadevi — Local mother goddess Architecture–symbol associations are frequently asked in art and culture sections.
Consider the following and identify the correct matches:
(A) Adi Granth — A philosophical term of Hindus
(B) Anjuman — A Society / An organisation
(C) Advaita — The first book in the Granth Sahib
(D) Ashram — A stage in the life of Hindus
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is incorrect. Adi Granth is the first Sikh scripture and later became part of the \textit{Guru Granth Sahib; it is not a philosophical term of Hinduism.
Statement (B) is correct. Anjuman refers to an association, society, or organization, commonly used in Persian and Urdu contexts.
Statement (C) is incorrect. Advaita is a major philosophical doctrine of Hinduism propounded by Shankaracharya, emphasizing non-dualism. It is not a book of the Granth Sahib.
Statement (D) is correct. Ashram refers to one of the four stages of life (\textit{Ashrama system) in Hindu philosophy—Brahmacharya, Grihastha, Vanaprastha, and Sannyasa.
Hence, only statements (B) and (D) are correctly matched. Quick Tip: Important cultural terms: Adi Granth — Sikh scripture Advaita — Non-dualistic Hindu philosophy Ashram — Stages of life in Hinduism Anjuman — Society or association Concept–definition matching is common in culture-related questions.
Consider the following and identify the correct statements:
(A) There were cultural and economic contacts between the north and the deep south (known as Tamizhakam).
(B) Dakshinapatha was valued for the supply of gold and pearl.
(C) Uttarapatha was less prominent till 2nd century BCE.
(D) Material culture was brought from south to north by traders and missionaries.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is correct. Literary, archaeological, and numismatic evidence shows sustained cultural and economic contacts between north India and the deep south (Tamizhakam), especially through trade networks.
Statement (B) is correct. The Dakshinapatha (southern route) was valued for commodities such as gold, pearls, precious stones, and spices, which were sourced from peninsular India and coastal regions.
Statement (C) is incorrect. The Uttarapatha (northern route) was already prominent well before the 2nd century BCE, facilitating trade and communication across north India and beyond to Central Asia.
Statement (D) is incorrect. Generally, material culture and ideological influences (including Buddhism) spread predominantly from north to south rather than from south to north.
Thus, only statements (A) and (B) are correct. Quick Tip: Ancient Indian trade routes: Uttarapatha — Northern trade route (early prominence) Dakshinapatha — Southern trade route (gold, pearls, spices) Tamizhakam — Deep south with strong overseas trade links Direction of cultural diffusion is a common point of confusion in exams.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I \hfill List-II
(A) Akbarnama \hfill (I) History of Akbar
(B) Tuzuk-i-Baburi \hfill (II) An autobiography of Babur
(C) Tabkat-i-Akbari \hfill (III) Historical book on Mughal period
(D) Gunyatul Muganiya \hfill (IV) Based on Indian music
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of the Mughal-era texts with their descriptions is as follows:
Akbarnama, written by Abul Fazl, is the official chronicle and history of the reign of Emperor Akbar.
Tuzuk-i-Baburi (Baburnama) is the autobiography of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire.
Tabkat-i-Akbari, authored by Nizamuddin Ahmad, is an important historical work on the Mughal period.
Gunyatul Muganiya is a work based on Indian music and musical traditions.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(I),\ (B)-(II),\ (C)-(III),\ (D)-(IV) \]
Hence, option (1) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Important Mughal texts to remember: Akbarnama — Abul Fazl Tuzuk-i-Baburi — Babur Tabkat-i-Akbari — Nizamuddin Ahmad Matching books with their themes is a frequent exam pattern.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I (Name of term) \hfill List-II (Explanation)
(A) Jarib \hfill (I) Bill of exchange
(B) Chacher \hfill (II) System of branding of horses and animals
(C) Dagh \hfill (III) Land out of cultivation for 3--4 years
(D) Hundi \hfill (IV) Land measurement and survey
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of administrative and economic terms used in medieval India is as follows:
Jarib was a measuring rod used for land measurement and survey, especially during the Mughal period.
Chacher referred to land left out of cultivation for 3--4 years to restore fertility.
Dagh was the system of branding horses and animals, introduced to prevent corruption in the military establishment.
Hundi was a traditional bill of exchange used in trade and banking transactions.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(IV),\ (B)-(III),\ (C)-(II),\ (D)-(I) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Important Mughal administrative terms: Jarib — Land measurement Dagh — Branding of horses Hundi — Bill of exchange Chacher — Fallow land Such term–definition matches are common in medieval history exams.
Consider the following terms and their meanings and identify the correct ones:
(A) Rayat — Banker and moneylender
(B) Pahi — Temporary cultivator
(C) Zawabit — Secular laws
(D) Shroff — The payers of land revenue
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is incorrect. A Rayat (or ryot) was a peasant cultivator who actually tilled the land, not a banker or moneylender.
Statement (B) is correct. Pahi referred to a temporary cultivator, often one who migrated seasonally to cultivate land.
Statement (C) is correct. Zawabit were secular regulations or laws framed by the Mughal state, distinct from religious law (Shariat).
Statement (D) is incorrect. A Shroff was a banker or moneychanger who tested and exchanged coins; he was not the payer of land revenue.
Thus, only statements (B) and (C) are correctly matched. Quick Tip: Important Mughal-period terms: Rayat — Peasant cultivator Pahi — Temporary cultivator Zawabit — Secular/state laws Shroff — Banker or moneychanger Clear distinction between agrarian and financial terms helps avoid confusion.
Under whom did the Maratha state reach its territorial zenith extending from `Cuttack to Attock'?
View Solution
The Maratha state reached the greatest extent of its territorial expansion during the period of Balaji Baji Rao (also known as Nanasaheb), who served as the Peshwa from 1740 to 1761.
Under his leadership, the Maratha Confederacy expanded rapidly in all directions. By the mid-18th century, Maratha influence extended from Cuttack (Odisha) in the east to Attock (near the Indus River) in the north-west. This expansion was achieved through a combination of military campaigns, political alliances, and the system of collecting \textit{chauth and \textit{sardeshmukhi.
Although Baji Rao I laid the foundation of Maratha expansion, it was under Balaji Baji Rao that the Maratha state attained its maximum territorial reach. This period marked the zenith of Maratha power before their setback at the Third Battle of Panipat in 1761.
Therefore, the correct answer is Balaji Baji Rao. Quick Tip: Key phases of Maratha expansion: Baji Rao I — Foundation of northward expansion Balaji Baji Rao — Territorial zenith (Cuttack to Attock) 1761 — Third Battle of Panipat Territorial extent questions often distinguish between expansion and peak control.
In the context of the Battle of Plassey who said that `There never was a battle in which the consequences were so vast, so immediate and so permanent'?
View Solution
The quoted statement about the Battle of Plassey was made by G. B. Malleson, a British historian who wrote extensively on the history of British rule in India.
Malleson emphasized the extraordinary significance of the Battle of Plassey (1757), highlighting that its consequences were not only immediate but also far-reaching and permanent. The battle marked the beginning of British political dominance in India by establishing the East India Company as a decisive power in Bengal.
Following Plassey, the Company gained control over Bengal’s revenues and administration, which provided the financial and political foundation for subsequent British expansion across India. Hence, historians regard this battle as a turning point in Indian history.
Therefore, the correct answer is G. B. Malleson. Quick Tip: Important historical quotations: G. B. Malleson — On the significance of the Battle of Plassey Plassey (1757) — Foundation of British rule in India Buxar (1764) — Consolidation of Company power Quotation-based questions often point to landmark events.
Arrange the following Sufis in chronological order of their death:
(A) Sheikh Nizamuddin Auliya
(B) Sheikh Nasiruddin Chirag-i-Dilli
(C) Khwaja Fariduddin Ganj-i-Shakar
(D) Sheikh Muinuddin Sijzi
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
To arrange the Sufi saints in chronological order of their death, we consider their life spans:
Sheikh Muinuddin Chishti (Sijzi), the founder of the Chishti order in India, died in 1236 CE.
Khwaja Fariduddin Ganj-i-Shakar, a leading Chishti saint and successor in the lineage, died in 1266 CE.
Sheikh Nizamuddin Auliya, one of the most revered Chishti saints, died in 1325 CE.
Sheikh Nasiruddin Chirag-i-Dilli, the last great Chishti saint of Delhi, died in 1356 CE.
Thus, the correct chronological order is: \[ (D), (C), (A), (B) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Chishti Sufi lineage in India: Muinuddin Chishti — Ajmer Fariduddin Ganj-i-Shakar — Punjab Nizamuddin Auliya — Delhi Nasiruddin Chirag-i-Dilli — Delhi Chronology of saints is frequently asked in medieval Indian history.
Match List-I with List-II
List-I (Name of monument) \hfill List-II (Place)
(A) Musamman Burj \hfill (I) Kashmir
(B) Badshahi Masjid \hfill (II) Agra
(C) Chashma-A-Shahi \hfill (III) Lahore
(D) Panchmahal \hfill (IV) Fatehpur Sikri
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct matching of monuments with their locations is as follows:
Musamman Burj is located in Agra and is part of the Agra Fort complex.
Badshahi Masjid is situated in Lahore and was built by Mughal emperor Aurangzeb.
Chashma-A-Shahi is a famous Mughal garden located in Kashmir.
Panchmahal is located at Fatehpur Sikri, built during the reign of Akbar.
Thus, the correct matching is: \[ (A)-(II),\ (B)-(III),\ (C)-(I),\ (D)-(IV) \]
Hence, option (3) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Remember some famous monument–place pairs: Musamman Burj — Agra Badshahi Masjid — Lahore Chashma-A-Shahi — Kashmir Panchmahal — Fatehpur Sikri Such matching questions are common in art and architecture sections.
Arrange the following incidents in chronological order:
(A) The first inscriptional evidence of sati
(B) Emergence of Bhagavatism or the Krishna cult
(C) Visit of Fa-Hien to India
(D) The people of the Eastern Roman Empire learnt the art of growing silk from the Chinese
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The chronological order can be determined by noting the approximate time period of each event:
Emergence of Bhagavatism or the Krishna cult — Developed around the 2nd century BCE, associated with the worship of Vasudeva–Krishna.
First inscriptional evidence of sati — Found in early centuries CE (traditionally dated earlier than Fa-Hien’s visit in standard exam chronology).
Visit of Fa-Hien to India — Took place during 399–414 CE in the Gupta period.
Eastern Roman Empire learning the art of silk production — Occurred in the 6th century CE, when silk-making techniques reached Byzantium from China.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (B), (A), (C), (D) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Helpful timeline markers: Bhagavatism — Pre-Christian era Fa-Hien — Gupta period (5th century CE) Silk in Byzantium — 6th century CE Using broad centuries often helps solve chronology questions.
Consider the following in the context of the expansion of the Mughal Empire by Akbar and identify the correct statements:
(A) Akbar succeeded to the throne of Delhi in 1554 and after his visit to the tomb of Muinuddin Chishti at Ajmer, Bharmal of Amber and Chandrasen of Jodhpur accepted the suzerainty of Akbar.
(B) In 1570, Akbar met huge opposition in occupying Ahmedabad and the great sea port of Surat.
(C) After the fall of Chittor, Akbar captured Ranthambhor and Kalinjar, and when Akbar was at Nagore many states of Rajasthan—Marwar, Bikaner and Jaisalmer—accepted the suzerainty of Akbar.
(D) Rana Pratap refused to bend his knees to the Mughals and had taken to his mountain fortresses after the fall of Chittor.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is incorrect. Akbar ascended the throne in 1556, not 1554. Hence, the statement is factually wrong.
Statement (B) is incorrect. Akbar conquered Gujarat, including Ahmedabad and Surat, during the campaign of 1572–73. The statement about severe opposition in 1570 is inaccurate.
Statement (C) is correct. After the fall of Chittor in 1568, Akbar captured the strategic forts of Ranthambhor and Kalinjar in 1569. Around this period, while at Nagore, several Rajput states such as Marwar, Bikaner, and Jaisalmer accepted Akbar’s suzerainty.
Statement (D) is correct. Rana Pratap refused to submit to Mughal authority and retreated to the hill fortresses of Mewar, continuing resistance against Akbar.
Thus, only statements (C) and (D) are correct. Quick Tip: Key points on Akbar’s expansion: Accession — 1556 Fall of Chittor — 1568 Ranthambhor and Kalinjar — 1569 Rana Pratap — Continued resistance from hill forts Always verify dates and sequences in statement-based questions.
Consider the following statements and identify the correct ones:
(A) The two factions, Bolsheviks and Mensheviks, were related to Russian history.
(B) The Third Reich refers to the government under Hitler.
(C) The French Revolution took place in 1689.
(D) The Soviet Union was formed in 1910.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (A) is correct. The Bolsheviks and Mensheviks were rival factions of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party and played a crucial role in Russian revolutionary history.
Statement (B) is correct. The term Third Reich refers to Nazi Germany under the leadership of Adolf Hitler (1933–1945).
Statement (C) is incorrect. The French Revolution began in 1789, not 1689 (which is associated with the Glorious Revolution in England).
Statement (D) is incorrect. The Soviet Union was officially formed in 1922, not 1910.
Thus, only statements (A) and (B) are correct. Quick Tip: Key historical dates to remember: French Revolution — 1789 Russian Revolution — 1917 Formation of USSR — 1922 Third Reich — Nazi Germany under Hitler Incorrect dates are a common trap in statement-based questions.
Arrange the construction of the following monuments in chronological order:
(A) Buland Darwaja
(B) Sikandra Tomb
(C) Humayun Tomb
(D) Allahabad Fort
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The chronological order can be determined by noting the approximate dates of construction of each monument:
Humayun Tomb was built between 1565–1572 during the reign of Akbar and is the earliest among the given monuments.
Buland Darwaja was constructed in 1575 by Akbar to commemorate his victory over Gujarat.
Allahabad Fort was built by Akbar in 1583 at the confluence of the Ganga and Yamuna.
Sikandra Tomb (Tomb of Akbar) was completed later, around 1613, during the reign of Jahangir.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (C), (A), (D), (B) \]
Hence, option (3) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Key Mughal monuments and dates: Humayun Tomb — 16th century (earliest Mughal tomb) Buland Darwaja — 1575 Allahabad Fort — 1583 Sikandra (Akbar’s Tomb) — Early 17th century Chronology questions often rely on relative reign periods of Mughal emperors.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
(A) The earliest Sanskrit inscription
(B) End of trade with the western part of the Roman Empire
(C) A group of silk weavers from the western coast migrate to Mandsor in Malwa
(D) Jaina texts refer to the existence of eighteen major peoples or nationalities
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct chronological order can be established by placing the events in their approximate historical context:
The earliest Sanskrit inscription refers to the Junagarh inscription of Rudradaman (c. 150 CE), marking the earliest extensive use of classical Sanskrit.
Jaina texts referring to eighteen major peoples or nationalities belong to an early historical phase, broadly dated to the early centuries CE.
Migration of silk weavers to Mandsor is known from the Mandsor inscription (c. 5th century CE), which records the movement of silk weavers from western India to Malwa.
End of trade with the western Roman Empire occurred around the 3rd century CE, following the decline of Roman commercial activity and political instability.
Thus, the correct chronological sequence is: \[ (A), (D), (C), (B) \]
Hence, option (2) is the correct answer. Quick Tip: Helpful timeline cues: Sanskrit inscriptions — Early centuries CE Roman trade decline — 3rd century CE Mandsor inscription — 5th century CE Link inscriptions and economic changes with their broad centuries to solve chronology questions.














































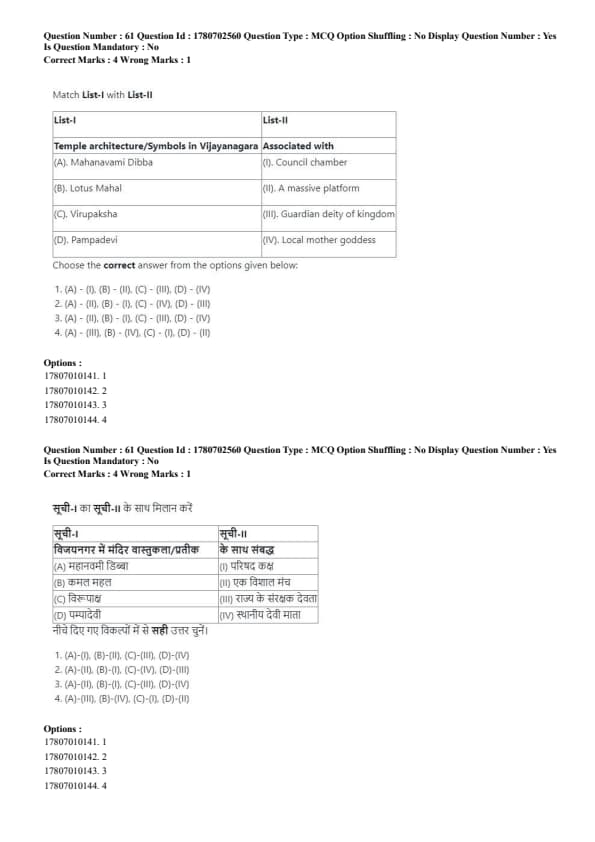



















Comments