The CUET PG Computer Science exam 2025 was conducted on 18th March 2025. After the test, students can download the question paper, official answer key, and detailed solution PDFs for all sets. The test focuses on topics such as data structures, algorithms, computer networks, operating systems, database management systems, software engineering, theory of computation, and programming languages like C/C++/Java/Python.
The exam has 75 questions to be attempted in 60 minutes, totaling 300 marks. Each correct answer gets 4 marks, and 1 mark is deducted for every incorrect one.
CUET PG Computer Science 2025 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| CUET PG Computer Science Question Paper with Solutions PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
CUET PG Computer Science 2025 Question Paper with Solutions
One term in the given number series is wrong. Find out the wrong term.
Find the next two terms of the series:
The given series is: \( A, C, F, J, ? \).
(A) O
(B) U
(C) R
(D) V
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Door is related to bang in the same way as chain is related to
In a certain code, VISHWANATHAN is written as NAAWTHHSANIV. How is KARUNAKARANA written in that code?
Find the number of triangles in the given figure.

Identify the missing number (?) from the following figure.

Introducing a man to her husband, a woman said, "His brother's father is the only son of my grandfather." How is the woman related to this man?
Find the missing word (?) which is similar to the given words.
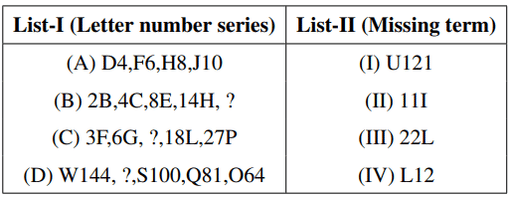
Choose the missing term (?) of the following series.
\( 2, 27, 107, 427, ? \).
In an examination, a student scores 4 marks for every correct answer and loses 1 mark for every wrong answer. If she/he attempts all 60 questions and secures 130 marks, the number of questions she/he attempts wrongly are?
In the following question, there is a certain relationship between two given words on one side of "::" and one word is given on another side of "::" while another word is to be found from the given options, having the same relation with this word as the words of the given pair bear. Choose the correct option to replace the '?'.
Milk : Emulsion :: Butter : ?
Consider the following four words, out of which three are alike in some manner and one is different.
(A) Arrow
(B) Missile
(C) Sword
(D) Bullet
Choose the combination that has alike words.
Consider the following alphabet series:
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
If the second half of the given alphabet series is written in reverse order, which letter will be seventh to the right of the twelfth letter from the left end?
If \( \frac{1}{9!} + \frac{1}{10!} = \frac{x}{11!} \), then the value of \( x \) is:
Out of 5 consonants and 4 vowels, how many words of 3 consonants and 3 vowels can be made?
From the given sets, which is an infinite set:
A fair coin is tossed three times. Let A be the event of getting exactly two heads and B be the event of getting at most two tails, then \( P(A \cup B) \) is:
If \( a, b, c \) are in Geometric Progression and \( a^x = b^y = c^z \), then \( x, y, z \) are in:
If \( (x - 1) \) is a factor of \( 2x^2 - 5x + k = 0 \), then the value of \( k \) is:
If \( x = \left( 2 + \sqrt{3} \right)^3 + \left( 2 - \sqrt{3} \right)^{-3} \) and \( x^3 - 3x + k = 0 \), then the value of \( k \) is:
If \[ \frac{1}{a(b + c)} + \frac{1}{b(c + a)} + \frac{1}{c(a + b)} = k, then the value of k is: \]
The length of major axis and coordinate of vertices for the ellipse \( 3x^2 + 2y^2 = 6 \) respectively are:
The center and radius for the circle \( x^2 + y^2 + 6x - 4y + 4 = 0 \) respectively are:
If the line through \( (3, y) \) and \( (2, 7) \) is parallel to the line through \( (-1, 4) \) and \( (0, 6) \), then the value of \( y \) is:
The points \( (K, 2 - 2K), (-K + 1, 2K) \) and \( (-4 - K, 6 - 2K) \) are collinear if:
(A) \( K = \frac{1}{2} \)
(B) \( K = -\frac{1}{2} \)
(C) \( K = \frac{3}{2} \)
(D) \( K = -1 \)
(E) \( K = 1 \)
If \( x^2 = -16y \) is an equation of a parabola, then:
(A) Directrix is \( y = 4 \)
(B) Directrix is \( x = 4 \)
(C) Co-ordinates of focus are \( (0, -4) \)
(D) Co-ordinates of focus are \( (-4, 0) \)
(E) Length of latus ***** is 16
The value of \(\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty}\left(1+\frac{2}{3x}\right)^{x}\) is:
If  then \(f(x)\) is
then \(f(x)\) is
\[ \int \frac{2x+1}{x^{2}+x+2}\, dx \ is \]
Bag \(A\) contains 3 Red and 4 Black balls while Bag \(B\) contains 5 Red and 6 Black balls. One ball is drawn at random from one of the bags and is found to be Red. Then, the probability that it was drawn from Bag \(B\) is:
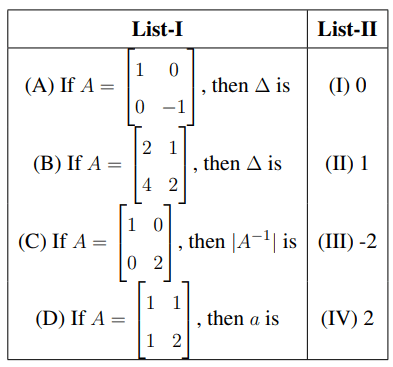
Match List-I with List-II:
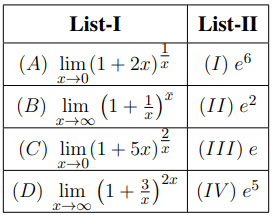
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following scheduler/schedulers is/are also called CPU scheduler?
(A) Short Term Scheduler
(B) Long Term Scheduler
(C) Medium Term Scheduler
(D) Asymmetric Scheduler
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A situation where two or more processes are blocked, waiting for resources held by each other is called:
External fragmentation occurs .................. .
Which disk scheduling algorithm looks for the track closest to the current head position?
Which CPU scheduling algorithm prefers the process with the shortest burst time?
The Dining Philosopher problem can be solved by:
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct option.
For a deadlock to occur, the four conditions namely Mutual Exclusion, Hold and Wait, No preemption, Circular wait __________.
Which of the following is a way to recover from the deadlock which has already occurred?
Details of a paging system for memory management are as follows:
Logical address space: 32 KB
Page Size: 4 KB
Physical Memory size: 64 KB
The number of pages in the logical address space and number of page frames in physical memory, respectively, are:
Consider a page reference string as:
7, 0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 4, 2, 3, 0, 3, 2.
Assume that there are 3-page frames available.
Calculate the total number of page faults for the above reference string if LRU policy is used for page replacement.
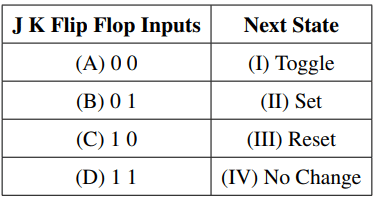
Match List-I with List-II:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match List-I with List-II:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider a typical process P in the critical section. Arrange the following statements of code to make a valid general structure.
(A). Critical section
(B) . Remainder section
(C) . Entry section
(D) . Exit section
Arrange the following layers of MS DOS operating system starting from inner most to outer most.
(A). ROM BIOS Device drivers
(B) . Resident System Program
(C) . MS DOS Device Drivers
(D) . Application Program
Which of the following is not an application of DFS?
Match List-I with List-II:
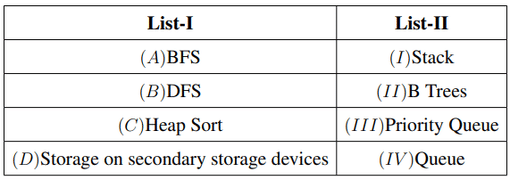
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In a binary search tree, the worst case time complexity of inserting and deleting a key is:
Match List-I with List-II:
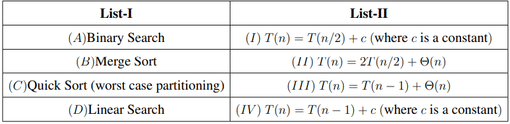
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Arrange the following time complexities in increasing order.
(A). Bubble sort (worst case)
(B) . Deleting head node in singly linked list
(C) . Binary search
(D) . Worst case of merge sort
Which of the following statements are TRUE, where \(|E|\) represents the number of edges?
(A). In case of a directed graph, the sum of lengths of all the adjacency list is |E|
(B) . For an undirected graph, the sum of the lengths of all the adjacency list is 2|E|
(C) . For a dense graph, adjacency matrix representation is preferable
(D) . The memory requirement of the adjacency matrix of a graph is dependent on the number of edges
In ................. the search time is independent of the number of elements \(n\).
Consider the task of finding the shortest path in an unweighted graph by using BFS and DFS.
Which of the following statements are true?
(A). BFS always finds the shortest path.
(B) . DFS always finds the shortest path.
(C) . DFS does not guarantee finding the shortest path.
(D) . BFS does not guarantee finding the shortest path.
In case of Binary Search Tree, which of the following procedure’s running time is distinct among all?
All the elements that hash to the same slot are placed into the same linked list in:
The Quicksort and randomized Quicksort procedures differ in:
The statements of pseudocode for searching the first element with key k in the linked list L are given below. Arrange them in the correct order.
(A) while (x != NIL and x.key != k)
(B) x = L.head
(C) x = x.next
(D) return x
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given the index i of a node in a heap, we can not compute:
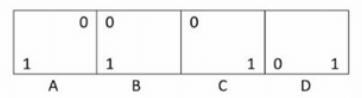
Consider the following Karnaugh Map (K-map). Minimal Function generated by this Karnaugh map is:
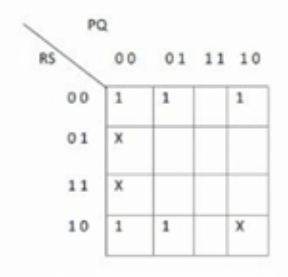
Consider the following types of memories.
(A) Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
(B) Cache Memory
(C) Random Access Memory (RAM)
(D) Registers
Arrange the above memories according to their access speed (from fastest to slowest):
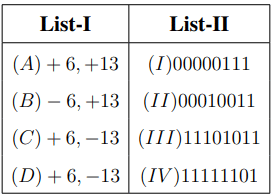
Perform the arithmetic addition of the two decimal numbers given in List-I using the signed-complement system.
Match the corresponding output of List-I with binary number representation given in List-II.
Arrange the following steps in the correct order to understand the functioning of a 3 to 8 line decoder.
(A) The encoder enable input is set to 1.
(B) The decoder activates one of its 8 output lines based on the input code.
(C) The input binary code is applied to the decoder.
(D) The decoder converts the 3-bit binary input into 8 possible outputs.
What should be the minimum Hamming distance \( d_{min} \) to guarantee correction of up to p errors in a given block code?
Consider the following statements.
(A) Combinational logic circuits do not have memory, while sequential logic circuits have memory elements.
(B) Sequential logic circuits depend only on the current inputs, while combinational logic circuits depend on both current and past inputs.
(C) Flip-flops and latches are examples of combinational logic circuits.
(D) Multiplexer is an example of combinational logic circuit.
What is the result of the following operation defined by IEEE754?
\[ (NaN == NaN) \]
Which of the following statement is true about IEEE754 representation of +0 and -0?
Minimum number of 2:1 Multiplexers required to design a 16:1 Multiplexer is?
What should be the output of the following boolean expression after simplifying it to a minimum number of variables? \[ a'b' + ab + a'b \]
To provide a memory capacity of 32K X 16 how many address lines and data lines are required?
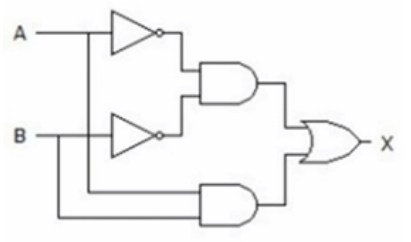
The following circuit generates the same output as?






Comments