
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Neptunium was first created in the year 1940 by Edwin McMillan and Philip Abelson of Berkeley, California. It came from a uranium target that had been hit with slow neutrons and released strange beta-rays, indicating the presence of a novel isotope. Abelson demonstrated that a new element was present. Neptunium is a radioactive actinide metal and is considered to be the first transuranic element. It is silver in colour and when exposed to air it starts getting tarnished.
| Table of Contents |
Key Takeaways: Neptunium, Element, Atoms, Periodic Table, Radioactive
What is Neptunium?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Neptunium is a radioactive, ductile, silvery metal. Neptunium can be used to make a variety of chemical compounds. It is highly reactive chemically and is reactive with oxygen, steam, and acids, but not alkaline solutions. It can be found in a wide variety of oxidation states, ranging from neptunium (IV) to neptunium(VI).
Neptunium is found between the elements uranium and plutonium on the periodic table. The nuclei of all three elements are massive enough to undergo nuclear fission, in which larger nuclei split into smaller and lighter nuclei. Neptunium is not as frequently used as uranium or plutonium because it was found much later.
Neptunium is the first of the synthetically developed heavy elements, Uranium is the last naturally occurring element. Synthetic elements do not naturally occur on the surface, they have to be created by bombarding with heavier elements so these are man-made. It is one of the by-products of radiating nuclear fuel, it is one of the actinides that are produced, it must be controlled within the Purex process. Among all the elements in the periodic table, it has the largest liquid range(from going from liquid phase to gas phase).
Neptunium’s name is inspired by the planet Neptune and is placed between Uranium and Plutonium in the periodic table just like the planet is placed between Uranus and Pluto in the solar system. A.C. Wahl and Glenn Seaborg discovered the longer-living isotope, neptunium-237, with a half-life of 2.14 million years. Because Martin Klaproth established the trend of naming uranium after the planet Uranus and plutonium after the planet Pluto, McMillan and Abelson named the new element after the planet Neptune, which is located between Uranus and Pluto.
Neptunium
Also Read:
Neptunium Atomic Number and Electronic Configuration
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
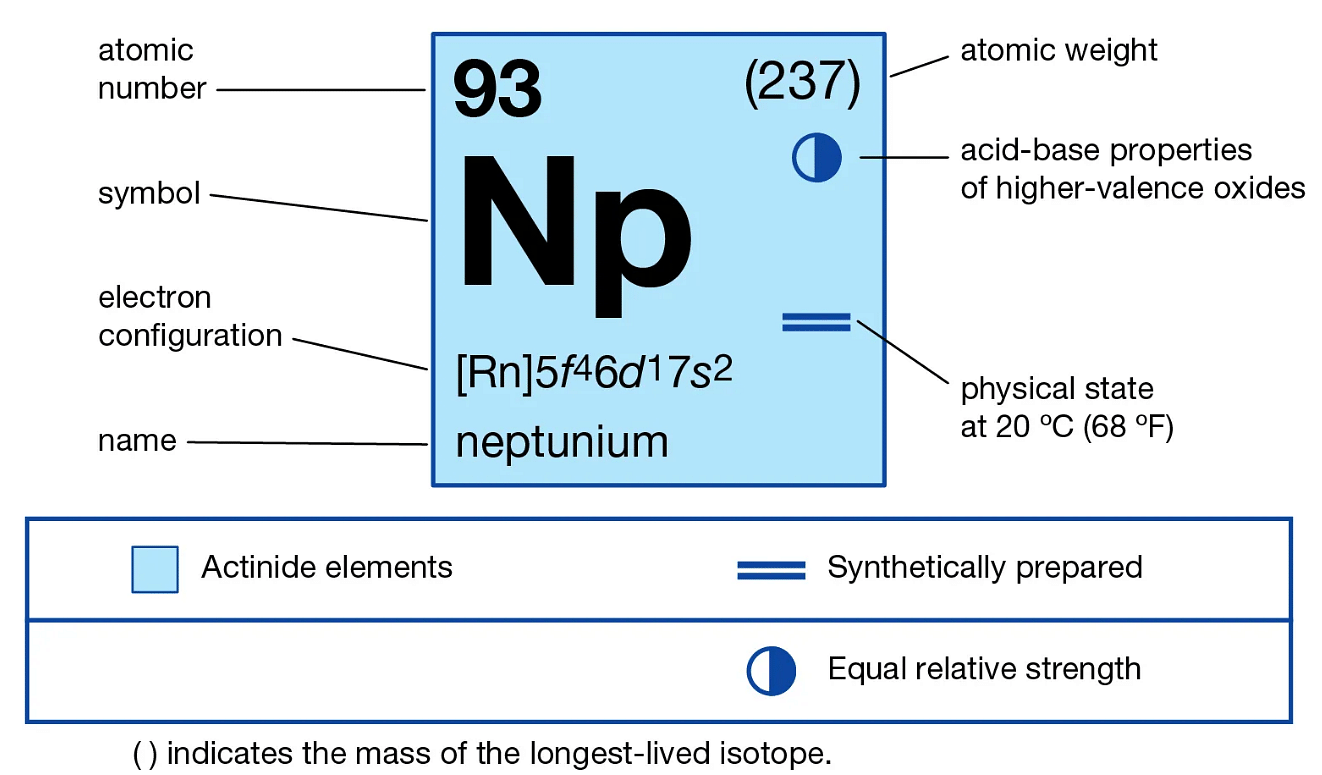
The atomic number of Neptunium in the periodic table is 93. It has an equal number of protons and electrons - 93.
The electronic configuration is → 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 5f4 6d1 7s2 or it can be written as Rn 5f4 6d1 7s2 .
K – shell → 2 electrons
L – shell → 8 electrons
M – shell → 18 electrons
N – shell → 32 electrons
O – shell → 22 electrons
P – shell → 9 electrons
Q – shell → 2 electrons
Properties of Neptunium
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
| Element Classification | Metal |
|---|---|
| State at Room Temperature | Solid |
| Group Number | None |
| Group Name | Actinide |
| Period Number | 7 |
| Atomic Number | 93 |
| Atomic Mass | 237 g mol-1 |
| Pauling’s Electronegativity negativity | 1.3 |
| Density | 20.2 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Melting point | 644 °C or 917 K or 1191°F |
| Boiling point | 3902 °C or 4175 K or 7056°F |
| Van der Waals radius | unknown |
| Ionic radius | unknown |
| Isotopes | 8 |
| Discovered by | McMillan in 1940 |
Effects of Neptunium
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Bone cancer is seen as a possible health effect of this element.
- The bones store the majority of the neptunium that is kept in the body. Some of it is also held in the liver. Several investigations have shown "quite high amounts" of neptunium in laboratory animals' adrenal glands. The organs receiving a major dose of it is the gastrointestinal tract,
- In humans, no health effects unique to neptunium exposure "have been observed." A detailed assessment of experiments utilizing neptunium was undertaken by Roy C. Thompson of Battelle Pacific Northwest Laboratory in Richland's Biology Department. Russian studies indicated a rise in the number of bone tumors in animals given bone doses as low as a few rad, according to this analysis. "There can be little question," Thompson concluded, that neptunium can induce bone cancer.
- In 1984, a group of German scientists published early findings from an experiment with mice aimed at determining the combined effect of neptunium-239 depositing in bone and decaying into plutonium-239. These first findings revealed that the accumulation of plutonium-239 (as neptunium decayed) enhanced the number of bone cancers compared to what would be predicted from neptunium exposure alone.
- There have been no negative environmental consequences reported.
Applications of Neptunium
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Np (with a half-life of 2.14×106 years) is fissionable, which means it can be attacked with neutrons to produce more neutrons that can interact with adjacent material and be used in fast neutron reactors or nuclear weapons. In neutron detection instruments, 237Np is employed.
- Mainly used for research purposes. It is hardly used anywhere for commercial purposes.
- It is used to create Plutonium and its isotopes(Plutonium-238).
Points to Remember
- Neptunium, with an atomic number of 93, belongs to the Periodic Table's actinide series. Between uranium (92), the last of the natural elements, and plutonium (94), neptunium can be discovered.
- Neptunium is a synthetic element that is formed by the nuclear reaction of uranium. It is not found in nature in its pure elemental form. When exposed to wet air, it develops a green layer of its oxide.
- Neptunium is found in trace amounts in uranium ores and is found naturally on Earth. But, this amount is so low that it cannot be used for any purpose. Therefore, it is synthesized in chemical labs by bombarding with electrons and neutrons of heavier elements.
- Neptunium-237 can be blasted with neutrons to produce plutonium-238, which can subsequently be used to make nuclear batteries that can power satellites and spacecraft for extended periods.
- Although neptunium's applications are extremely limited, it does see some use in research, specifically for its potential use as fissile nuclear fuel.
Sample Questions
Ques: Where is neptunium in the periodic table? (1 mark)
Ans. Neptunium, with an atomic number of 93, belongs to the Periodic Table's actinide series. Between uranium (92), the last of the natural elements, and plutonium (94), neptunium can be discovered.
Ques: What are the applications of neptunium? (3 marks)
Ans. The applications of neptunium are:
- Neptunium can be used in fast neutron reactors or nuclear weapons. In neutron detection instruments, 237Np is employed.
- Mainly used for research purposes in chemical laboratories. It is hardly used anywhere for commercial purposes.
- It is used to create Plutonium and its isotopes(Plutonium-238).
Ques: Is Neptunium found in large quantities on the surface of the earth? How is the neptunium synthesized in the laboratory? (3 marks)
Ans. No, Neptunium is not found largely on the surface of the earth. Neptunium was previously thought to be only chemically created, however it has now been discovered in trace levels in uranium ores, where its presence can be attributed to decay. The majority of today's neptunium is a by-product of uranium neutron irradiation in nuclear power reactors, and much of the neptunium in the environment comes from nuclear explosions. Neptunium-239 is made by hitting uranium with neutrons from a cyclotron particle accelerator. It has a half-life of two and a half days.
Ques: Discuss about the properties of Neptunium. (5 marks)
Ans. Neptunium belongs to the actinide series of radioactive metals.
It was named after the planet Neptune. Neptunium is the next element in the periodic table after uranium similar to Neptune being the next planet after Uranus in the solar system. The melting point (640°C) and boiling point (estimated at 4174°C) of this silvery solid is regarded to be the widest of any element. Depending on the temperature, Neptunium can take on three different allotropes (structures). It has five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7, each of which exhibits a distinct color in solution, ranging from violet to yellow-green. There are no stable isotopes in it. Instead, it contains 20 radioisotopes with half-lives ranging from 225 to 244 and mass numbers ranging from 225 to 244. With a half-life of 2.14 million years, neptunium-237 is the isotope with the longest half-life. Neptunium is harmful not only because it is radioactive, but also because it is pyrophoric, meaning it can catch fire spontaneously at ambient temperature. The most common application for neptunium-237 is in high-energy neutron detectors.
Ques: Throw some light on the discovery of Neptunium. (4 marks)
Ans. Enrico Fermi of Italy claimed success in producing elements 93 and 94 by hitting uranium with neutrons in early 1934. Ida Tacke-Noddack questioned Fermi's claim, pointing out that he had neglected to conduct a thorough analysis and that all he had discovered were uranium fission products. (In fact, Fermi had discovered nuclear fission without realizing it.) Horia Hulubei and Yvette Cauchois claimed to have found element 93 in 1938, however, their claim was slammed because element 93 does not exist naturally. Edwin McMillan and Philip Abelson of Berkeley, California, were the first to create neptunium in 1940. It came from a uranium target that had been hit with slow neutrons and released strange beta-rays, indicating the presence of a novel isotope. Abelson demonstrated that a new element was present.
Ques: State the characteristics of Neptunium. (4 marks)
Ans. The characteristics are:
- Neptunium is a radioactive, ductile, silvery metal.
- Neptunium can be used to make a variety of chemical compounds.
- It is highly reactive chemically and is reactive with oxygen, steam, and acids, but not alkaline solutions.
- It can be found in a wide variety of oxidation states, ranging from neptunium (IV) to neptunium(VI).
Ques: Write a short note on neptunium. (3 marks)
Ans. Neptunium is a radioactive, ductile, silvery metal used in the making of a variety of chemical compounds. Neptunium is found between the elements uranium and plutonium on the periodic table. The nuclei of all three elements are massive enough to undergo nuclear fission, in which larger nuclei split into smaller and lighter nuclei. Neptunium is not as frequently used as uranium or plutonium because it was found much later. Neptunium is the first of the synthetically developed heavy elements. Synthetic elements do not naturally occur on the surface, they have to be created by bombarding with heavier elements so these are man-made. It is one of the by-products of radiating nuclear fuel, it is one of the actinides that are produced, it must be controlled within the Purex process. Among all the elements in the periodic table, it has the largest liquid range(from going from liquid phase to gas phase).
Also Read:





Comments