Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Ions refer to atoms or molecules that have either gained or lost electrons and thus gained an electric charge. They possess an equal number of protons while the number of electrons varies in an ion. An atom on the other hand has an equal number of electrons and protons, thus they have a neutral or zero charge in nature. Ions either possess a positive charge as in Na+, NH4+ or have a negative charge as in O2- and OH-. Anions refer to an ion with a negative charge while ions with a positive charge are known as cations. Since they both have opposite charges, they attract each other to form an ionic bond. In this article, we will explore the differences between anions and cations.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Ions, Atoms, Electric charge, Anion, cation, Ionic Bond, Protons, Electrons, Metals, Non-metals
Read Also: Ionisation Enthalpy
What are anions?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Anions are the ions that possess a negative charge in nature. They are formed when an atom gains more electrons in order to become more stable, gaining a negative charge in the process. This charge is due to the addition and increase in the number of electrons than the number of protons in an atom. Examples of anions are Iodide (I-), Hydroxide (OH-), Chloride (Cl-), etc.
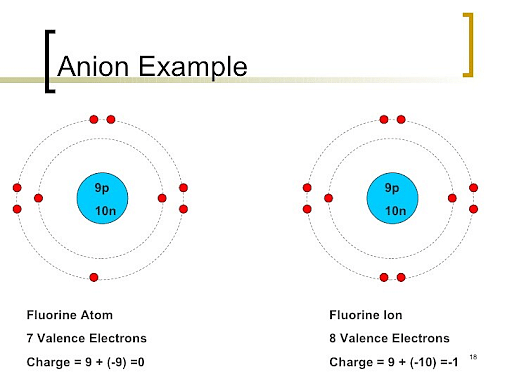
Example of an Anion: Fluorine atom gains an electron to form a Fluorine Ion
Read More:
| Important Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Clemmensen Reduction Reaction | Williamson Ether Synthesis | Tollen’s Test |
| Ruthenium | Rubidium | Lutetium |
| Periodic Acid Formula | Technetium | Strontium |
| Seaborgium | Rutherfordium | Scandium |
What are cations?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Cations are ions that possess a positive charge in nature. They are formed when an atom loses more electrons in order to become more stable, gaining a positive charge in the process. This charge is due to the removal and decrease in the number of electrons than the number of protons in an atom. Examples of cations are Hydrogen (H+), Calcium (Ca+2), Potassium (K+), etc.

Sodium loses an electron to form Sodium ion - cation
A group of atoms or elements which are bonded to each other through covalent bonds but carry a positive or a negative charge are known as polyatomic ions. Examples of these types of ions are CO32-, NH4+, OH-, CN-, etc.
Ions that have just one element that carries either a positive charge or a negative charge are known as monoatomic ions. Examples of these types of ions are O2-, Al+3, Ce+3, Na+, etc.
Read more: Electron Gain Enthalpy
Difference Between Anions and Cations
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
| Anions | Cations |
|---|---|
| A charged particle or an ion having a negative charge in nature is known as an anion. | A charged particle or an ion having a positive charge in nature is known as a cation. |
| Anions have more electrons than protons. | Cations have fewer electrons than protons. |
| Anions transform into neutral molecules or atoms by losing electrons. | Cations transform into neutral molecules or atoms by gaining electrons. |
| Anions are generally formed from non-metals. | Cations are generally formed from metals. |
| Anions form ionic or electrostatic bonds with the cations in order to yield ionic compounds. | Cations form ionic or electrostatic bonds with the anions to form ionic compounds. |
| Anions are attracted towards the electrode that is positively charged during the process of electrolysis. | Cations are attracted towards the electrode that is negatively charged during the process of electrolysis. |
| Compared to the cations, anions are larger in size generally. | Cations are smaller as compared to the size of anions. |
| Some examples of anions are Cl-, Br-, and O2-. | Some examples of cations are Na+, Fe+3, Ca+2, and Mg+2. |
The formation of Cation and Anion from a neutral atom by losing or gaining electrons
Na+ is an example of a sodium cation. It depicts that sodium has one electron less than the number of protons in the sodium atom. This uneven distribution in the protons and electrons leads to sodium gaining a positive charge. Similarly, in the case of Chloride ions, Cl-, has one more electron as compared to the protons in the Chlorine atom. This uneven distribution leads to the Chloride ion gaining a negative charge.
Anions and cations both are types of ions having a polar opposite charge. Due to their opposite charge, they are attracted towards each other while anions repel other anions due to the same charge as cations repel other cations.
Read More:
Things to Remember
- Ions refer to atoms or molecules that have either gained or lost electrons and thus gained an electric charge.
- Anions are the ions that possess a negative charge in nature.
- Anions have an increased number of electrons than the number of protons in an atom.
- Some examples of anions are Cl-, Br-, and O2-.
- Cations are ions that possess a positive charge in nature.
- Cations have an increased number of protons than the number of electrons in an atom.
- Some examples of cations are Na+, Fe+3, Ca+2, and Mg+2.
Previous Year Questions
- Identify the wrong statement in the following… [NEET 2012]
- Among the elements Ca,Mg,P and Cl, the order of increasing atomic radii is… [NEET 2010]
- Among the following which one has the highest cation to anion size ratio?… [NEET 2010]
- Which one of the following ions will be smallest in size?… [NEET 1996]
- The decreasing order of basic character of K2O,BaO,CaO and MgO is… [JIPMER 2015]
- Which one of the following arrangements represents the correct order of electron gain enthalpy… [NEET 2005]
- One of the characteristic properties of non-metals is that they… [NEET 1993]
- Which electronic configuration of an element has abnormally high difference between second and third ionisation energy?… [NEET 1993]
- Which of the following does not have valence electron in 3d-subshell? [BITSAT 2012]
- Electronic configuration of S2− ion is? [JIPMER 1998]
- Which of the following has magic number of protons and neutrons? [AP EAPCET 1997]
- The outer electronic structure of 3s23p5 is possessed by? [KCET]
- The number of unpaired electrons in a paramagnetic diatomic molecule of an element with atomic number 16 is? [NEET 2006]
- Which one of the following orders is not in accordance with the property stated against it?… [NEET 2006]
- The first ionisation potential (in eV) of Be and B, respectively are… [NEET 1998]
Sample Questions
Ques. What are anions? (2 marks)
Ans. Anions are the ions that possess a negative charge in nature. They are formed when an atom gains more electrons in order to become more stable, gaining a negative charge in the process. Examples of anions are Iodide (I-), Hydroxide (OH-), Chloride (Cl-), etc.
Ques. What are cations? (2 marks)
Ans. Cations are ions that possess a positive charge in nature. They are formed when an atom loses more electrons in order to become more stable, gaining a positive charge in the process. Examples of cations are Hydrogen (H+), Calcium (Ca+2), Potassium (K+), etc.
Ques. State whether oxygen is an anion or a cation. (3 marks)
Ans. As oxygen has no charge, it is neither an anion nor a cation. Oxygen which constitutes about 20% of the air around us, is a gas that is highly reactive in nature. Hence, it forms compounds with other elements in addition to the pure oxygen that is dissolved in water and in the air. These compounds or molecules often break down to form ions.
Ques. What is a Zwitterion? (2 marks)
Ans. Molecules that have both negative and positive charge regions are known as Zwitterion. The charged atoms in these molecules are bonded together with the help of one or more covalent bonds.
Ques. What do you understand by ionic radius? (1 mark)
Ans. In an ionic crystal, the distance between the anions and cations is known as the ionic radius.
Ques. What is the basic difference between anions and cations? (2 marks)
Ans. Anions are the ions that possess a negative charge due to an increase in the number of electrons as compared to protons of an element.
Cations are ions that possess a positive charge in nature due to an increase in the number of protons as compared to electrons.
Ques. Anions are larger in radius and cations are smaller than their respective parent atoms. Give reason. (3 marks)
Ans. As a cation has fewer electrons than its parent atom despite having the same nuclear charge, it is smaller in size. Anions are larger than their parent atom as they gain electrons leading to an increase in the repulsion forces that exists between the electrons and a decrease in the nuclear charge of the atom.
Ques. What happens to anions and cations in an electrochemical cell reaction? (2 marks)
Ans. When an electrochemical cell undergoes a reaction, the anions are attracted towards the positive end of the electrode which is known as an anode, and the anions get deposited there. Whereas the cations on the other hand are deposited on the negative end of the electrode which is known as the cathode.
Ques. Give examples of anions and cations. (2 marks)
Ans. Some examples of anions and cations are as follows:
Anions: Chloride ion (Cl-), Bromide ion (Br-), and Oxide ion (O2-).
Cations: Sodium ion (Na+), Ferric ion (Fe+3), Calcium ion (Ca+2), and Magnesium ion (Mg+2).
Ques. How the position of an element in the periodic table affects its ability to form ions? (5 marks)
Ans. The electron configuration of an element helps in determining its ability to form an anion. For instance, the elements present in group 17 of the periodic table, which are also readily known as halogens have seven valence electrons in their outermost shell. These elements can readily form anions because it is easier for these elements in the periodic table to gain an electron rather than losing one due to the attraction of these elements to the nucleus. Hence, they gain one electron instead of losing any to form an anion that possesses a negative charge. Various other non-metals like oxygen, sulphur, and carbon also form anions. Out of these, sulphur and oxygen are of Group 16 of the periodic table while carbon belongs to Group 12.
Hence, we can conclude that as we move from left to right in a periodic table, an elements’ tendency to form anions increases due to the increasing number of electrons present in the valence shell of these elements. With the increasing number of electrons, the electron shielding effect also increases, and due to the increase in attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons of an element, the atomic size of the ion formed decreases.
Also check:



Comments