Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
An ecosystem is a group of living organisms that live in cooperation with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. The ecosystem is the functional and structural unit of ecology in which the living organisms interact with each other surrounded by the environment. In other words, the ecosystem is a series of interactions between organisms and their environment. The term “Ecosystem” was first invented by A. G. Tansley, an English botanist, in 1935.
Also Read:- Class 10 Our Environment
Related Links
- Appearing for NEET, Download NEET PYQ for all subjects
- Appearing for CUET, Download CUET PYQ for all subjects
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Ecosystem, Components of Ecosystem, Biotic, Abiotic
Define Ecosystem
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
All organisms such as plants, animals, human beings, and microorganisms physically interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting plants and animals in an area, together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Thus, an ecosystem consists of abiotic components comprising physical factors like soil, minerals temperature, rainfall, wind, etc., and biotic components comprising living organisms.

Ecosystem
Ecosystem is the base for ecology. The ecosystem works as the structural and functional unit of ecology. An ecosystem can be large or small depending upon the availability of abiotic components in the Environment. If we compare the North and South pole, it does not have as much flora and fauna (plants and animals) as the tropical climate like forests, due to different climates. Overall, we can say that ecosystems combined make up the biosphere.
The easiest definition of the ecosystem is “an ecosystem is a group of living organisms that live and interact with each other in a specific or particular environment.”
Also Read: Food Chains and Webs
Components for Ecosystem
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
According to Ecology, Eco-system is a physically defined environment that comprises of two inseparable components:
- Biotic or biocenosis
- Abiotic or biotope
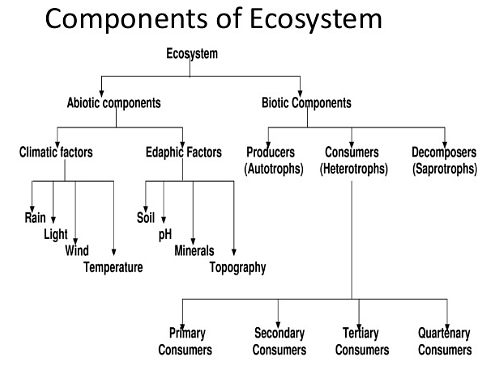
Components for Ecosystem
Biotic Components
Biotic components comprise all living organisms in an ecosystem. Biotic components are also known as ‘biocenosis’ or biotic factors. Biotic components describe a living component of an ecosystem, for example, organisms, such as plants and animals. Biotic Components also include human impact, disease outbreaks, and pathogens. Each biotic factor needs a proper level of energy and nutrition to function properly and healthy. As per the Nutritional requirements, biotic components can be categorized into autotrophs(organisms that produce their own food), heterotrophs(depending on other organisms), and saprotrophs (decomposers - organisms that feed on nonliving organic matter).
- Producers: It includes all autotrophic organisms such as plants. They can produce food through the process of photosynthesis that's why they are known as producers. All other organisms higher up on the food chain depend on producers for food.
Producers
- Consumers: They’re also known as heterotrophs. They’re organisms that depend on other organisms for food as they take nutrition from the food that is made by the Producers. They’re further classified into primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers:
- Primary Consumers: Primary consumers are herbivores and vegetarians in nature as they rely on producers for food.
- Secondary Consumers: They depend upon the primary consumers for food, they can be either Carnivores or omnivores in nature.
- Tertiary Consumers: Tertiary consumers depend upon secondary consumers for food.
- Quaternary consumers: Humans are quaternary consumers, Quaternary consumers are at the top of the food chain, and they prey on the tertiary consumers.
Also Read:- Biotic Factors
Consumers
- Decomposers: These are the Organisms that feed on the nonliving organic matter called detritus. They are also known as saprotrophic organisms and include saprophytes such as fungi and bacteria. They consume the dead and decaying matters. They recycle the nutrients so they can be used by plants in the ecosystem. Many Scientists say and believe that the earliest extensive form of life on Earth was cyanobacteria. These cells which made food and organic substances from sunlight played a huge vital role in creating all of Earth’s modern ecosystems. Ecologists also gave warnings that man-made climate change is moving towards dangerous insect-borne diseases, which used to be restricted. As the most dominant species humans are causing various threats to the environment. This needs to be stopped via spreading more awareness about the environment and ecosystem.
Decomposers
Abiotic Components
Abiotic components or biotope or Abiotic factors are the nonliving components of an ecosystem. This basically involves inorganic or non-living minerals, phosphorus, and iron. It includes wind, altitude, turbidity, air, water, soil, minerals, sunlight, temperature, nutrients, etc. Abiotic factors refer to non-living chemical and physical elements which ease the creation of an ecosystem. Abiotic resources are usually obtained from the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. Abiotic components affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce.Abiotic components affect individuals, populations, communities, ecosystems, biome, biosphere. Humans can change abiotic factors in the environment. Occasionally, fertilizers can affect the habitat of a snail, and greenhouse gases that humans utilize can decline or change the marine pH levels.

Abiotic components
Abiotic components include a physical state and non-living resources that affect living organisms in terms of reproduction, growth, and maintenance. Abiotic factors or abiotic components are the organisms that contribute to the earth in many different ways for setting it up. Degradation of a substance occurs by chemical or physical processes (I.e., hydrolysis). All the non-living components of an ecosystem, such as atmospheric conditions and water resources, are called abiotic components. For example temperature, humidity, light, radiation, atmosphere, acidity, and soil, water. These are some of the examples of abiotic factors.
Also Read:- Abiotic Factors
Abiotic and biotic factors work together to create a precious unique ecosystem. Biotic factors and non-living abiotic factors or components such as temperature, sunlight, geography, and chemistry, both together determine the shape of ecosystems and how it looks like and what ecological niches are available.
Sample Questions
Ques: What is an ecosystem? (1 mark)
Ans. An ecosystem is a group of living organisms that live and interact with each other in a specific or particular environment.
Ques: What are the two components of the ecosystem? (1 mark)
Ans. Biotic and abiotic factors
Ques: What are biotic components? (1 mark)
Ans. Biotic components comprise all living organisms in an ecosystem. Biotic components describe a living component of an ecosystem, for example, organisms, such as plants and animals.
Eg - plants and animals
Ques: What are abiotic components? (1 mark)
Ans. Abiotic components are the nonliving components of an ecosystem. This basically involves inorganic or non-living minerals. Eg- trees, rivers, phosphorus, iron, etc.
Ques: Who are producers? (1 mark)
Ans. All autotrophic organisms such as plants can produce food through the process of photosynthesis that's why they are known as producers. All other organisms higher up on the food chain depend on producers for food.
Ques: Differentiate between a detritivore and a decomposer giving an example of each. (1 mark)
Ans. The difference between a detritivore and a decomposer is,
| Detritivore | Decomposer |
|---|---|
| The organisms that break down the detritus into smaller particles are the detritivore. For example, earthworms. | The organisms which do enzymatic degradation of detritus into simpler inorganic substances are the decomposers. For example, some bacteria and fungi. |
Ques: Why decomposition occurs at a faster rate in the tropic regions? (1 mark)
Ans. Decomposition occurs due to climatic factors, therefore favourable humidity and temperature in the tropics make possible the activities of decomposers along with the soil rich in dead remain supporting the rapid rate of decomposition.
Ques: Why is the rate of decomposition affected by the abiotic factors such as pH of the soil, availability of the oxygen, temperature and so on? (1 mark)
Ans. The abiotic factor such as pH of the soil affects the structure of basophilic and acidophilic microbes. In the presence of oxygen, aerobic processes take place causing complete degradation of the substance, while anaerobic processes take place in the absence of the oxygen. This results in the incomplete degradation of the substance. At higher temperatures, microbes are unable to grow to their fullest, while at low or high temperatures, stress-tolerant organisms flourish.
Ques: Define producers, composers and decomposers. (2 marks)
Ans. Producers: It includes all autotrophic organisms such as plants. They can produce food through the process of photosynthesis that's why they are known as Autotrophic organisms. Hence, all other organisms higher up on the food chain depend on producers for food.
Consumers: It is also known as heterotrophs. heterotrophs are organisms that depend on other organisms for food as they take nutrition from the food that is made by the Producers. Consumers or heterotrophs are further classified into primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers.
Decomposers: These are the Organisms that feed on the nonliving organic matter called detritus. They are also known as saprotrophic organisms and include saprophytes such as fungi and bacteria. They consume the dead and decaying matters. Recycling the nutrients and to be used by plants in ecosystem ‘decomposers’ is necessary for that. Decomposers are the organisms that carry out the process of decomposition, which all living organisms undergo after death.
Ques: Explain the structure of the ecosystem with the help of flowchart. (1 mark)
Ans. The structure of the ecosystem involves the living organisms along with e physical features of the environment that include the distribution of nutrients in a particular habitat. Moreover, it also provides information regarding climatic conditions of that particular area.
Check-Out:



Comments