The CUET PG Material Science and Technology exam in 2025 will be conducted between 13th May and 3rd June, and candidates will be able to download the question paper, answer key, and solution PDF after the exam. The test assesses a candidate’s knowledge in material structures, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanical behavior of materials, nanotechnology, and current advancements in material sciences.
Students must attempt 75 questions in 60 minutes, with a total of 300 marks. Each correct answer is awarded 4 marks, while 1 mark is deducted for every incorrect response.
CUET PG Material Science and Technology 2025 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| CUET PG Material Science and Technology Question Paper with Solutions PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |

CUET PG Material Science and Technology 2025 Question Paper with Solutions
The number of atoms per unit cell of SCC are:
Which of the following statements are correct:
A. In SC structure a = 2r
B. In SC structure a = r/2
C. In BCC structure a = \( 4r/\sqrt{3} \)
D. In FCC structure a = \( 2\sqrt{2} r \)
Where a is a lattice parameter and r is the atomic radius.
Which statements are correct for edge dislocation?
A. An edge dislocation moves in the direction of the Burger vector.
B. An edge dislocation involves an extra row of atoms above the slip plane.
C. An edge of the atomic plane is formed internal of the crystal.
D. The Burger vector of an edge dislocation is parallel to the dislocation line.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
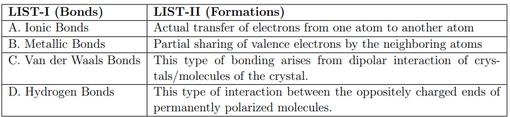
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following relations are correct for the cubic crystal:
A. a = b \( \neq \) c
B. a = b = c
C. \( \alpha = \beta = \gamma = 90^\circ \)
D. \( \alpha \neq \beta = \gamma = 90^\circ \)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following symmetry does not exist:
Copper has FCC structure with a lattice constant 3.61 Å. The radius of the copper atom is:
The surface defects are two-dimensional defects, which have:
A. Grain boundaries
B. Tilt boundaries
C. Twin boundaries
D. Stacking boundaries
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Vacancies of the crystal may arise due to:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The energies involved in the process of domain growth are:
A. Exchange energy
B. Anisotropic energy
C. Domain Wall energy
D. Magnetostrictive energy
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The potential energy of a system of two atoms is given by the expression \( U = -A/r^2 + B/r^{10} \). A stable molecule is formed with the release of 8.0 eV of energy, when the interatomic distance is 2.8 Å. The values of A and B are:
The steps involved in determining the Miller indices are:
A. Take the reciprocal of these intercepts.
B. Simplify the fraction.
C. Enclose the obtained numbers into parentheses.
D. Find the intercepts of the plane on the crystallographic axes.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The correct statements about SC lattice are:
A. The number of atoms per unit cell is 1
B. Its packing factor is 0.52
C. Iron is an example of SC lattice
D. Its Coordination Number is 6
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Diamond exhibits which type of structures:
The vector form of Bragg's law is used in the construction of:
In Laue's technique of X-ray diffraction, a single crystal is held stationary and the beam of white radiation of wavelength \(\lambda\) is inclined at which condition with glancing angle (\(\theta\)):
The shortest wavelength, present in X-rays produced by an accelerating potential of 50kV, is:
The number of distinct space groups possible in 3-dimensions is:
The coordination number and volume of unit cell of hexagonal closed packed structure are respectively:
Which type of liquid crystal has its structure twisted about the helical axis lying perpendicular to the orientation of molecules?
The magnitude of the reciprocal lattice vector is related to interplaner spacing \(d_{hkl}\):
Inter-planer spacing for a (034) plane in a simple cubic, whose lattice constant is \(4.5 \times 10^{-10}\) m, is:
The reciprocal lattice for a body centered cubic crystal is:
The value of specific heat at constant volume (\(C_V\)) for diatomic molecules is:
According to the Entropy hypothesis, which one of the following statements is correct:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
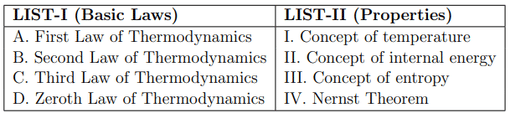
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
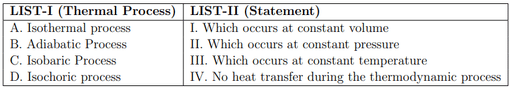
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following are the correct statements about laws of thermodynamics:
A. The first law does not indicate the direction in which the change can occur.
B. The first law indicates the direction in which the change can occur.
C. The second law does not indicate the direction in which the change occurs.
D. The second law indicates the direction in which the change can occur.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Select the correct sequence:
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
B. First law of thermodynamics
C. Second law of thermodynamics
D. Third law of thermodynamics
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
How does the gas constant R is related to the universal gas constant \(\bar{R}\) and molecular mass M?
Choose the correct sequence of operations in the Carnot cycle.
A. Isothermal expansion of gas.
B. Isothermal compression of gas.
C. Adiabatic compression of gas.
D. Adiabatic expansion of gas.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The speed of sound in a fluid is the velocity at which a weak pressure wave propagates in the medium.
The ideal gas, which is a model for gas used in constant volume gas thermometers, for which P = \(\rho\)RT. This equation illustrates that there are only ___________ independent intensive thermodynamic properties for a simple fluid.
The breaking stress of a wire depends on:
Under the elastic limit, Poisson's ratio is:
The elastic energy density of a stretched wire is given by:
Which of the following option is correct related to the application of elastic hysteresis?
Which statements are true for total internal reflection?
A. The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
B. light goes from an optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium.
C. light goes from an optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium.
D. The critical angle depends on the refractive index of both media.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
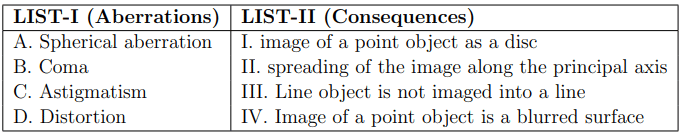
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which statements are true about wave propagation through a medium:
A. Frequency changes in a non-linear medium but remains constant in a linear medium.
B. Frequency changes in a linear medium but remains constant in a non-linear medium.
C. R + T = 1, where R is the reflection coefficient and T is the transmission coefficient
D. R + T \(>\) 1, where R is the reflection coefficient and T is the transmission coefficient
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Paramagnetic materials behaves as diamagnetic materials :
What is the effect of temperature on magnetic susceptibility of ferromagnetic materials?
Domain theory explains:
Antiferromagnetic materials have magnetic susceptibility in the range:
Which of the following is true for hard magnetic materials:
The density of zinc is \(7.13 \times 10^3\) kg/m\(^3\) and its atomic weight is 65.4. The fermi energy of Zinc is:
(Given that the effective mass of the electron in zinc is \(0.85m_e\))
In 3-dimensional system, the mean energy of an electron in electron gas at absolute zero is _____________ of fermi energy, \(E_f(0)\) at absolute zero.
Which of the following statements are correct for the Sommerfeld model:
A. The free electrons are valence electrons of the composing atoms.
B. The potential energy of an electron at rest inside the metal is assumed to be higher than that of an electron outside the metal.
C. In this model, the mutual repulsion between the electrons is neglected.
D. The potential energy for an electron is periodic.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and other one labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): In the absence of an electric field, the electron gas is in an equilibrium state described by equilibrium distribution functions, viz the fermi-Dirac distribution function for a degenerate electron gas and Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution function for a non-degenerate electron gas.
Reason (R): In a conductor, the number of electrons moving in opposite directions is always the same, their average velocity in any direction is zero and consequently, the distribution functions are symmetric about the axis of ordinates.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
According to Weidemann-Franz-Lorentz Law, the theoretical value of Lorentz number (L) for metals is:
The effective density of states of electrons (\(N_c\)) at the conduction band edge of the intrinsic semiconductor varies with temperature, as:
Which current does not contribute to a uniformly doped semiconductor:
For temperature greater than 0 K, the fermi level is the level where the probability of occupation of electrons is:
According to the Bloch theorem, which of the following equations is the correct form for Bloch functions:
In the Kronig penny Model, the energy of the lowest band at wave vector k = 0 is given by \( E = \frac{h^2 P}{4\pi^2 m a^2} \). This value of energy holds for which condition of Kronig penny potential (P):
Choose the correct statement for the first Brillouin zone in two dimensions:
A. The region in k space that the electrons can occupy without being diffracted is called the First Brillouin zone.
B. For k < \(\pi\)/a electrons can not move freely in any direction inside the square without being diffracted.
C. For k = \(\pi\)/a electrons are prevented from moving in the x or y directions due to diffraction.
D. For k > \(\pi\)/a electrons can move perpendicularly inside the square.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
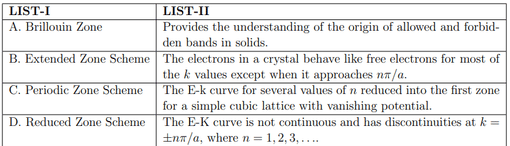
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The effective mass of an electron is _______________ in the lower part of the band and _______________ near the zone boundary (k\(\sim\)\(\pi\)/a).
In which type of metals, there is overlapping of valence band with the conduction band?
The electronic contribution of specific heat of copper at 300K is:
(Given that the fermi energy of copper is 7.05eV, and it is assumed to be temperature independent)
The characteristic length of nano-materials is:
Surface area to volume ratio of materials:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
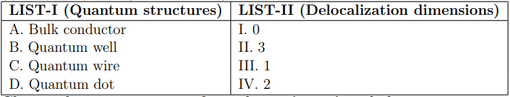
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Electronic magic numbers of atoms are:
A. 2
B. 15
C. 10
D. 18
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
As the particle size reduces, the optical absorption spectra shifts towards:
Carbon nanotube shows magneto-resistive effects:
Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
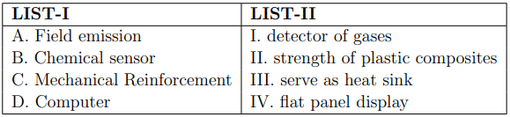
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Lithography is:
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy is based on:
Which statement is true for Scanning Tunneling Microscopy:
Atomic Force Microscopy is a modified version of:
Atomic Force Microscopy monitors:



Comments