The CUET PG Library and Information Science 2025 exam was conducted on 24th March 2025 during Shift 1 (2). Candidates can access the question paper, answer key, and PDF solutions post-exam. This paper evaluates understanding of library management, classification systems, information retrieval, digital libraries, knowledge organization, and emerging technologies in library sciences.
The exam includes 75 questions to be attempted in 60 minutes, with a total score of 300 marks. Each correct answer yields 4 marks, and each incorrect response incurs a 1-mark penalty.
CUET PG Library and Information Science 2025 Question Paper with Solutions PDF
Question 1:
According to C.W. Hanson "encyclopaedia article on a subject" would be counted as _____________.
- (A) Primary Document
- (B) Secondary Document
- (C) Non-Conventional Document
- (D) Tertiary Document
Question 2:
"The nature of information sought in such a situation is very specific and a quick answer is expected" comes under:
- (A) Current Approach
- (B) Everyday Approach
- (C) Exhaustive Approach
- (D) Brushing-up Approach
Question 3:
Who first gave us the concept of SDI ?
- (A) S.R. Ranganathan
- (B) H.P. Luhn
- (C) G. Bhattacharya
- (D) A.M. Howatson
Question 4:
The National Translation Centre (Formely known as the SLA Translation Centre) is located at
- (A) Delft
- (B) Chicago
- (C) Boston Spa
- (D) London
Question 5:
"LUCI" stand for
- (A) Logical Union Cyclic Index
- (B) Logical Unit-based Cyclic Index
- (C) Logical unit wise Cyclic Index
- (D) Logical Unit Compound Index
Question 6:
The International Standardization Association (ISA) was established in __.
- (A) 1928
- (B) 1935
- (C) 1955
- (D) 1984
Question 7:
INSDOC was setup in__.
- (A) 1952
- (B) 1956
- (C) 1978
- (D) 1979
Question 8:
"Fair Dealing" associated with
- (A) Patent
- (B) Standard
- (C) Copyright
- (D) Author
Question 9:
The Universal Copyright Convention (UCC) was adopted in __.
- (A) 1911
- (B) 1952
- (C) 1978
- (D) 1986
Question 10:
Which university started a one-year diploma course in 1945 ?
- (A) Punjab University
- (B) Banaras Hindu University
- (C) University of Calcutta
- (D) Madras University
Question 11:
Indian Library Science Abstract (ILSA) associated with
- (A) IFLA
- (B) IASLIC
- (C) ASLIB
- (D) UGC
Question 12:
Which of the following is not a documentation list?
- (A) Keesing's Record of world event
- (B) Science Citation Index
- (C) Fodor's Guide to India
- (D) Annual Review of Psychology
Question 13:
Which one of the following canons is not related to the verbal plane?
- (A) Canon of Currency
- (B) Canon of Context
- (C) Canon of Enumeration
- (D) Canon of Array
Question 14:
Schedules of CC were constructed during
- (A) 1925-1932
- (B) 1924-1931
- (C) 1933-1934
- (D) 1919-1934
Question 15:
IAB is the following
- (A) International Advance Board
- (B) Internet Architecture Board
- (C) Internet Administrative Bodies
- (D) Internet Application Body
Question 16:
OSI is the following:
- (A) Organization for International Standards
- (B) Open System Intercollections
- (C) Open System Internet
- (D) Open System Interconnection
Question 17:
Data rate is :
- (A) Interfaces
- (B) Media Representation
- (C) Transmission rate
- (D) Devices
Question 18:
FTAM is the following:
- (A) File Transfer and Application Menu
- (B) File Transfer Application Management
- (C) File Transmission, Access and Management
- (D) File Transfer, Access and Management
Question 19:
Machine Readable Cataloguing is the following :
- (A) Representation Bibliographic Information
- (B) Communication for Internet
- (C) Feature twenty-six vignettes
- (D) Eithical and regulatory issues
Question 20:
Fayol's principles are the following :
- (A) General Principle of Administrative
- (B) Commercial Activities and Elements
- (C) Optimum Security and Accounting
- (D) Managerial Activities and Principles
Question 21:
Theory of Bureaucracy was given by
- (A) L.D. White
- (B) Fayol
- (C) Max Weber
- (D) Robert Merton
Question 22:
e-GRANTHALAYA is associated with
- (A) NIC
- (B) NCI
- (C) TMH
- (D) CUI
Question 23:
Enhanced service in a library is
- (A) Circulation
- (B) Standard Reports
- (C) Multilingual Support
- (D) Data Exchange
Question 24:
KOHA features include
- (A) Multilingual cataloguing
- (B) System Builders
- (C) OASIS
- (D) Traditional Library Materials
Question 25:
The following summary includes class number 611.
- (A) Hierarcy Summary
- (B) Third Summary
- (C) Arts Summary
- (D) Second Summary
Question 26:
Who formulated a set of normative principles to provide scientific basis for bibliographic description?
- (A) Antony Panizzi
- (B) Charles Ami Cutter
- (C) S.R. Ranganathan
- (D) IFLA
Question 27:
Theory X and Y are associated with the following :
- (A) Quest for high performance
- (B) Economic of Surplus value
- (C) Exploitative Instruments
- (D) Poverty of Phylosophy
Question 28:
Dublin Core Metadata Schema was developed in
- (A) 1990
- (B) 1995
- (C) 1997
- (D) 2000
Question 29:
UKOLN's Analytical Model of Collection and their Catalogues has been developed in __
- (A) 1998
- (B) 2000
- (C) 2001
- (D) 2002
Question 30:
Relative index includes the following :
- (A) Organization of knowledge
- (B) Numbers in square brackates
- (C) Alphabetical list
- (D) Up to date information
Question 31:
The following is not the value-Addedd service in a library
- (A) Stock verification through RFID
- (B) Barcode Generation
- (C) On call support
- (D) Serials Control
Question 32:
The following is related to Bradford's Law
- (A) Productivity of authors
- (B) Patterns of growth of literature
- (C) Frequency of occurrence of word
- (D) Scattering and seepage of article
Question 33:
'Shodh Chakra' is an initiative of:
- (A) ICMR
- (B) NIC
- (C) INFLIBNET
- (D) ICAR
Question 34:
ISO-2709 is related with the following:
- (A) DC metadata encoding
- (B) Thesaurus development
- (C) Exchange of circular data
- (D) Exchange of bibliographic data
Question 35:
Division of labor or specialization expresses
- (A) Elaborating function of staff experts.
- (B) Each individual should perform a single function.
- (C) Public administrative review policy
- (D) Nature of Management under capital income
Question 36:
Which section of IT Act 2000 deals with the provision of 'Display of licence' ?
- (A) Section 28
- (B) Section 29
- (C) Section 30
- (D) Section 32
Question 37:
Following is a freeware :
- (A) DLT System
- (B) LAMP
- (C) NCIP
- (D) IRC
Question 38:
'Sugamaya Pustakalaya' is:
- (A) Online platform for visual disabilities.
- (B) Books for Divyangjans
- (C) Available in single language
- (D) Dictionary
Question 39:
Web-OPAC is related with
- (A) Reports
- (B) Information Retrieval
- (C) MIS
- (D) Maintanance
Question 40:
'BibExcel' is developed by?
- (A) Eugen Garfield
- (B) Olle Persson
- (C) Peter Ingewersen
- (D) Mike Thelwall
Question 41:
896 class number of DDC is related with:
- (A) Spanish Poetry
- (B) African Literatures
- (C) French Drama
- (D) English Speeches
Question 42:
'Bandwith' is related with:
- (A) Electronic path which determines how many cycles.
- (B) Methods of digital transmission
- (C) Define the number of bits.
- (D) Frequency modulation
Question 43:
'Multiplexing' is a
- (A) Conventional voice telephone technology
- (B) Improve transmission quality and reduce noise.
- (C) Introduce noise and interface into the transmission
- (D) Message travels in one direction
Question 44:
A series of instructions that performs a particular task is called _
- (A) Application Software
- (B) System Software
- (C) Program
- (D) Operating System
Question 45:
The following is not a component of library automation software.
- (A) Circulation Control
- (B) Bibliographic Control
- (C) Staff related documents
- (D) Public Access Catalogue
Question 46:
Arrange the following Library Act in increasing order
(A) Karnataka Public Library Act
(B) Haryana Public Library Act
(C) West Bengal Public Library Act
(D) Tamil Nadu Public Library Act
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (D), (B), (C), (A)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (D), (A), (C), (B)
Question 47:
Arrange the following according to DDC main classes
(A) Metaphysics
(B) Law
(C) The Bible
(D) Statistics
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (A), (C), (D), (B)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (B), (D), (A)
Question 48:
Arrange the following according to their establishment
(A) Imperial Library
(B) National Library of India
(C) Delivery of Books Act (Public Libraries Act)
(D) NAPLIS
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (A), (C), (B), (D)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (B), (D), (A)
Question 49:
Sequence the following in the ascending order
(A) IFLA-UAP
(B) IFLA-UBC
(C) IFLA-PDG
(D) ISBD (M)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (A), (C), (B), (D)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (B), (A), (D)
Question 50:
Arrange the following in increasing order:
(A) ISBD (CR)
(B) ISBD (ER)
(C) ISBD (NBM)
(D) ISBD (A)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (A), (C), (B), (D)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (D), (B), (A)
Question 51:
Arrange the following in increasing order:
(A) PHP
(B) Visual Basic
(C) C++
(D) Fortran
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (B), (A), (C), (D)
- (3) (D), (C), (B), (A)
- (4) (C), (B), (D), (A)
Question 52:
Arrange the correct sequence of the following citation index:
(A) Science Citation Index
(B) Indian Citation Index
(C) Social Science Citation Index
(D) Art and Humanities Citation Index
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (A), (C), (D), (B)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (B), (D), (A)
Question 53:
Arrange the following Information Centres in order of their establishment:
(A) DESIDOC
(B) DRTC
(C) NASSDOC
(D) INSDOC
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (D), (B), (A), (C)
- (2) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (D), (A), (B), (C)
Question 54:
Arrange the following on the basis of their evolution:
(A) Resource Sharing
(B) Consortia
(C) Library Cooperation
(D) Networking
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (2) (A), (C), (B), (D)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (A), (D), (B)
Question 55:
Arrange the correct sequence of the Facets in main class 'O' literature in CC (6th ed.):
(A) Language
(B) Form
(C) Work
(D) Author
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B), (D), (C)
- (2) (A), (B), (C), (D)
- (3) (B), (A), (D), (C)
- (4) (C), (B), (D), (A)
Question 56:
Control Information, Number and Codes have the following :
(A) Field Number
(B) ISBN
(C) ISSN
(D) DDC
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B) and (D) only
- (2) (A), (C) and (D) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 57:
The following Software are developed by commercial vendors:
(A) LIBSUITE
(B) LIBSYS
(C) GRANTHALAYA
(D) LMS
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) and (B) only
- (2) (B) and (D) only
- (3) (A), (B), and (C) only
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 58:
The OPAC module has the following combinations:
(A) Catalogue Database
(B) Dublin Core
(C) Inter-Library Loan
(D) Subscriptions
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B) and (D) only
- (2) (A), (B) and (C) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 59:
Control fields in MARC-21 have the following :
(A) Fixed length Data Elements
(B) Control Number Identifier
(C) Data Content
(D) Physical Description Fixed Field
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B) and (D) only
- (2) (A), (C) and (D) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 60:
To access the global internet, the following are required :
(A) Electronic Mail Protocol
(B) Order Protocol
(C) File Transfer Protocol
(D) Segment Protocol
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) and (B) only
- (2) (A) and (C) only
- (3) (B) and (D) only
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 61:
Network Virtual Terminal is associated with the following:
(A) Software Version
(B) Remote Host
(C) Encryption
(D) Translation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) and (B) only
- (2) (B) and (C) only
- (3) (A), (B), and (D) only
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 62:
Layer-3 in OSI is composed of the following:
(A) Physical Topology
(B) Framing
(C) Physical Addressing
(D) Synchronization of bits
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) and (D) only
- (2) (B) and (C) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) None of the above. The correct answer is Logical Addressing and Routing.
Question 63:
Network support layers of OSI are:
(A) Network Layer
(B) Physical Layer
(C) Presentation Layer
(D) Data Link Layer
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B) and (D) only
- (2) (A), (C) and (D) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 64:
The National Knowledge Commission recommended for the overall development of LIS education in the country. These are:
(A) All departments of LIS should set up computer center and well-equipped departmental libraries.
(B) Established a well-equipped institute for advanced training and research in LIS
(C) Revamp LIS education, training and research facilities.
(D) There should be 1:10 teacher-students ratio.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B) and (D) only
- (2) (A), (C) and (D) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
Question 65:
The purpose and scope of the ISBD as follows:
(A) It is designed as an instrument for the international communication of bibliographical information.
(B) It is specifying the elements which comprise a bibliographical description.
(C) It's prescribing the order in which they should be presented.
(D) To facilitate their interpretation across language barrier.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A), (B) and (C) only
- (2) (A), (B) and (D) only
- (3) (A), (B), (C) and (D)
- (4) (B), (C) and (D) only
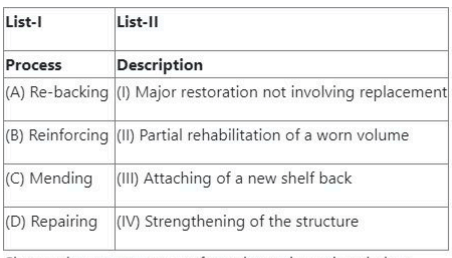
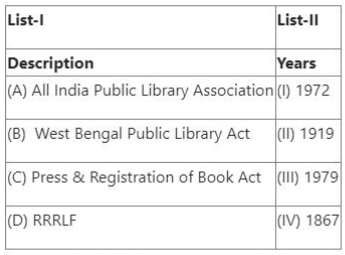
Question 66:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (3) (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
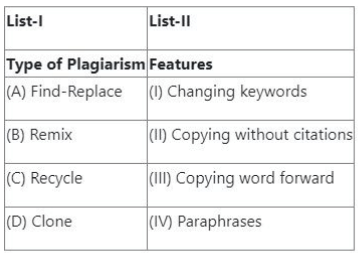
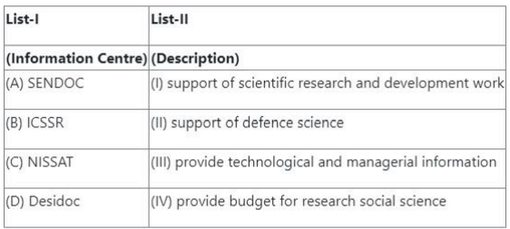
Question 67:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (IV)
- (3) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
- (4) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (II), (D) - (III)
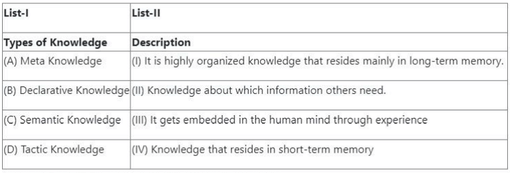
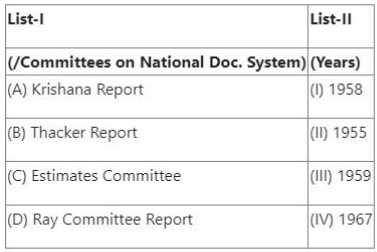
Question 68:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (II), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (III)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (3) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
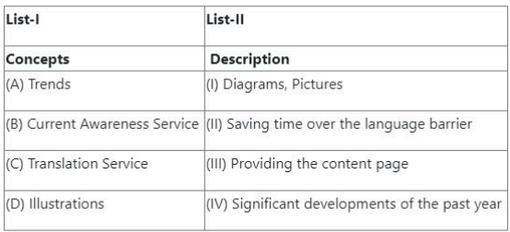
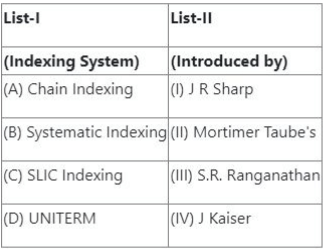
Question 69:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (III), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
- (3) (A) - (III), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
- (4) (A) - (IV), (B) - (III), (C) - (II), (D) - (I)
Question 70:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (IV), (D) - (I)
- (3) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
Question 71:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (III), (D) - (II)
- (3) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
Question 72:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (III), (D) - (II)
- (3) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
Question 73:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (II), (B) - (I), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (3) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
Question 74:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (III), (D) - (II)
- (3) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
- (4) (A) - (III), (B) - (IV), (C) - (I), (D) - (II)
Question 75:
Match List-I with List-II
![]()
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (1) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (III), (D) - (IV)
- (2) (A) - (I), (B) - (IV), (C) - (III), (D) - (II)
- (3) (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
- (4) (A) - (II), (B) - (III), (C) - (I), (D) - (IV)




























Comments