The CUET PG Data Science 2025 exam was conducted between 13th May and 3rd June. After the test, NTA will release the question paper, answer key, and solutions PDF for all sets. The paper checks the candidate’s competency in statistics, machine learning, data analytics, programming (Python/R), data visualization, databases, and core concepts in data modeling.
The format is 75 MCQs in 60 minutes, with a total of 300 marks and +4/-1 marking scheme.
CUET PG Data Science 2025 Question Paper with Answer Key PDF
| CUET PG Data Science Question Paper with Solutions PDF | Download PDF | Check Solutions |
CUET PG Data Science 2025 Question Paper with Solutions
Consider the following relation \( R = \{(4,5), (5,4), (7,6), (6,7)\} \) on set \( I = \{4,5,6,7\} \). Which of the following properties relation \( R \) does not have?
(A) Reflexive property
(B) Symmetric property
(C) Transitive property
(D) Antisymmetric property
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If an algebraic system \( (M, *) \) where \( M \) is the set of all non-zero real numbers and \( * \) is a binary operator defined by \( x * y = \frac{x y}{4} \), which of the following properties are satisfied by \( M \)?
(A) Closure Property
(B) Associative Property
(C) Inverse Property
(D) Commutative Property
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Step 1: Closure Property.
For closure, the result of \( x * y \) must belong to the set \( M \). Since \( x * y = \frac{x y}{4} \), and the product of two non-zero real numbers divided by 4 will always yield a non-zero real number, the set is closed under \( * \). Thus, the closure property is satisfied.
Step 2: Associative Property.
The associative property states that for all \( x, y, z \in M \), \( (x * y) * z = x * (y * z) \). We can verify that: \[ (x * y) * z = \left( \frac{x y}{4} \right) * z = \frac{\left( \frac{x y}{4} \right) z}{4} = \frac{x y z}{16} \]
and \[ x * (y * z) = x * \left( \frac{y z}{4} \right) = \frac{x \left( \frac{y z}{4} \right)}{4} = \frac{x y z}{16} \]
Since both are equal, the associative property is satisfied.
Step 3: Inverse Property.
The inverse property states that for every \( x \in M \), there exists an element \( y \in M \) such that \( x * y = e \), where \( e \) is the identity element. Here, the identity element \( e \) for the operation \( * \) is 4, since \( x * 4 = x \). Therefore, for any \( x \), the inverse is given by \( y = \frac{4}{x} \). Thus, the inverse property is satisfied.
Step 4: Commutative Property.
The commutative property states that for all \( x, y \in M \), \( x * y = y * x \). Since: \[ x * y = \frac{x y}{4} \quad and \quad y * x = \frac{y x}{4} \]
and \( \frac{x y}{4} = \frac{y x}{4} \), the commutative property is satisfied.
Step 5: Conclusion.
The closure, associative, and inverse properties are satisfied by \( M \), so the correct answer is (1) A, B, and C only.
Quick Tip: When verifying properties of algebraic systems, always check closure, associativity, inverse, and commutativity to ensure the system follows the necessary rules.
What will be the output after minimizing the following expression with the help of a K-map? \[ F(X,Y) = X Y + X Y' + X Y \]
Find the least upper bound and greatest lower bound of \( S = \{X, Y, Z\} \) if they exist, of the poset whose Hasse diagram is shown below:
For a Non-deterministic Finite Automaton (NDFA) with \( N \) number of states, the equivalent Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA) has \( D \) number of states. Then, possible number of states in DFA can be defined as:
Suppose \( D_1 = (S_1, \Sigma, q_1, F_1, \delta_1) \) and \( D_2 = (S_2, \Sigma, q_2, F_2, \delta_2) \) are finite automata accepting languages \( L_1 \) and \( L_2 \), respectively. Then, which of the following languages will also be accepted by the finite automata:
(A) \( L_1 \cup L_2 \)
(B) \( L_1 \cap L_2 \)
(C) \( L_1 - L_2 \)
(D) \( L_2 - L_1 \)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
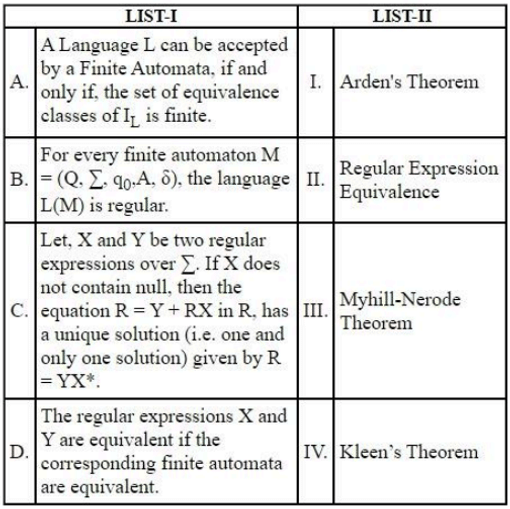
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If \( L_i \) is the set of languages of type \( i \) for \( i = 0, 1, 2 \) or 3. Then, as per Chomsky hierarchy, arrange the given set of four languages in order from subset to superset, from left to right.
(A) \( L_3 \)
(B) \( L_2 \)
(C) \( L_1 \)
(D) \( L_0 \)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
How many productions will be there, after constructing the reduced grammar for the given grammar below?
\[1. X \rightarrow aYa \] \[2. Y \rightarrow Xb \] \[3. Y \rightarrow bCC \] \[4. C \rightarrow ab \] \[5. E \rightarrow aC \] \[6. Z \rightarrow aZY\]
In a standard Turing Machine \( T \), the transition function \( \delta (q, a) \) for \( q \in Q \) and \( a \in \Gamma \) is defined:
What will be the output, if we compute the 9’s complement of the decimal number 782.54?
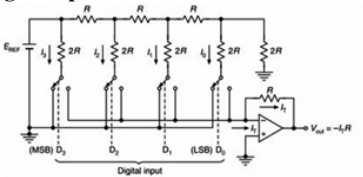
The given diagram is of a 4-bit switched current-source Digital to Analog Converter (DAC), where \( E_{REF} = 10V \) and \( R = 5 \, k\Omega \). What will be the output voltage \( V_{out} \) for the digital input 1101?
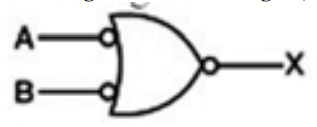
For the gate shown in the figure, the output will be HIGH
The Prime Implicant (PI) whose each 1 is covered by a minimum of one Essential Prime Implicant (EPI) is known as:
A parallel adder in which the carry-out of each full-adder is the carry-in to the next significant digit adder is known as:
Which flip-flop is not widely available for commercial purposes?
The expression \( X = (A+B) \times (C+D) \) has been evaluated using two address instructions method. The following is the set of instructions used.
(A) MOV R1, A
(B) MUL R1, R2
(C) MOV R2, C
(D) ADD R2, D
(E) MOV X, R1
Choose the correct sequence of instruction execution from the options given below:
Which of the following instruction format is used by stack-organised computer?
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
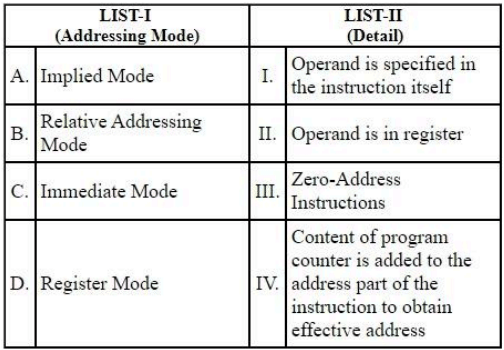
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider a pipeline system. Let the time it takes to process a sub operation in each segment be equal to \( t_p = 20 \, ns \). Assume that the pipeline has \( k = 4 \) segments and executes \( n = 100 \) tasks in sequence. Consider a non-pipeline system, assume that \( t_n = k t_p \) (a non-pipeline system to perform the operation takes a time equal to \( t_n \) to complete each task), where \( t_p = 20 \, ns \), \( k = 4 \). Find the speedup of a pipeline processing over an equivalent non-pipeline processing to execute 100 tasks.
The major difficulties that cause the instruction pipeline to deviate from its normal operation are:
(A) Resource conflicts
(B) Stack operation
(C) Data dependency
(D) Branch difficulties
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which among the following statement(s) is/are true in the context of a page replacement policy?
(A) The goal of a page replacement policy is to try to remove the page most likely to be referenced in the immediate future.
(B) First in First Out (FIFO) and Least Recently Used (LRU) are the two most common page replacement algorithms.
(C) The FIFO algorithm selects for replacement the page that has been in memory the longest time.
(D) LRU algorithm is based on the assumption that the least recently loaded page is a better candidate for removal than the least recently used page.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
\(128 \times 8 \)RAM represents:
A conditional branch instruction in Microprocessor-
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
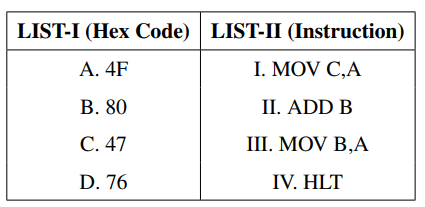
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The time required to complete one operation of accessing memory, I/O, or acknowledging an external request by a microprocessor, is known as:
Arrange these interrupt call locations in order of priority (from highest to lowest priority) of the interrupts with whom they are associated with:
A. 003CH
B. 0024H
C. 0034H
D. 002CH
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements are applicable to 8237 DMA controller for working in the Master Mode:
(A) The signals Input Output Read and Input Output Write are kept in tri-state.
(B) The signals Memory Read and Memory Write are kept in tri-state.
(C) The signals Input Output Read, Input Output Write, Memory Read and Memory Write may all be used as per the data transfer requirement.
(D) The data transfer can be terminated by sending low End of Process (EOP) from outside, also.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
What will be the foldback memory address range of the following memory chip while interfacing with 8085 microprocessor?

____________ refers to a set of data values and associated operations that are specified accurately, independent of any particular implementation.
Arrange the following data types available in C language according to their size (smallest to largest):
A. signed long int
B. long double
C. unsigned char
D. unsigned int
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the following code blocks.
A. for (i=0; i < 1000; i++)
statement block;
B. for (i=0; i < 100; i+=2)
statement block;
C. for (i=1; i < 1000; i*=2)
statement block;
D. for (i=0; i < 10; i++)
for (j=0; j < 10; j++)
statement block;
Match LIST-I with LIST-II

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the following statements about arrays. Which of the following are TRUE?
A. The index specifies an offset from the beginning of the array to the element being referenced.
B. Declaring an array means specifying three parameters; data type, name, and its size.
C. The length of an array is given by the number of elements stored in it.
D. The name of an array is a symbolic reference to the address of the first byte of the array.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Consider the binary tree given below. What will be the corresponding infix expression to this?
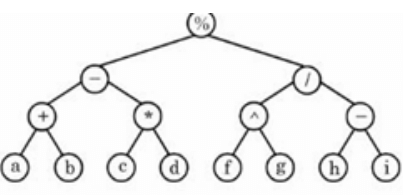
Loop invariant allows us to understand and prove the correctness of an algorithm. Which of the following options is NOT to be proven, when we prove the correctness of any algorithm using loop invariant?
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
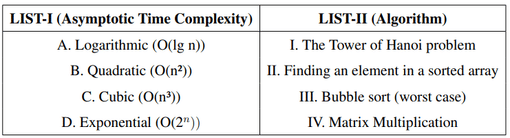
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is not the application of Divide and Conquer technique?
In C language, mat[i][j] is equivalent to:
(where mat[i][j] is a two-dimensional array)
Suppose a minimum spanning tree is to be generated for a graph whose edge weights are given below. Identify the graph which represents a valid minimum spanning tree?
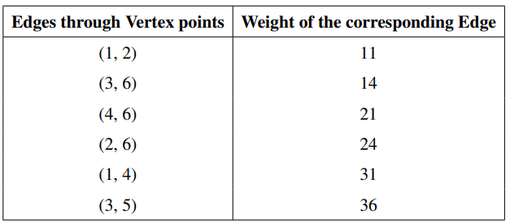
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
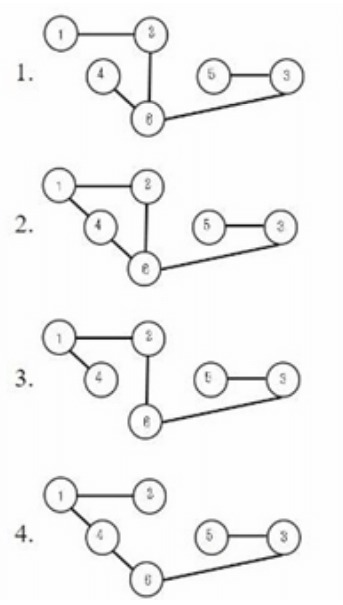
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The time complexity in order to build a heap of ‘n’ elements is ..............
The operating system is not responsible for:
Process control block in operating system is defined as:
In the context of process creation, arrange the following statements in sequential order of their occurrence:
A. One of the two processes typically uses the exec() system call to replace the process’s memory space with a new program.
B. A new process is created by the fork() system call.
C. The parent can then create more children; or, can issue a wait() system call to move itself off the ready queue.
D. The exec() system call loads a binary file into memory (destroying the memory image of the program containing the exec() system call) and starts its execution.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A solution to the critical-section problem must satisfy:
Consider the following set of processes, assumed to have arrived at time 0 in the order P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5, with the given length of the CPU burst (in milliseconds) and their priority:
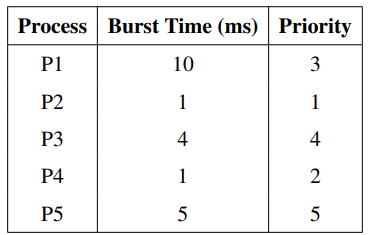
Using priority scheduling (where priority 1 denotes the highest priority and priority 5 denotes the lowest priority), find the average waiting time.
In a system with multiple instances of resources, the resource allocation graph for deadlock avoidance does NOT contain the following edge:
Consider a paging system in which the hit ratio is 80%, TLB (Translation Look Ahead Buffer) access time is 100 nanoseconds, and main memory access time is 100 nanoseconds. Find Effective Access Time (EAT), assuming page-table lookup takes only one memory access.
A device which connects dissimilar LANs of different topologies, using different sets of communication protocols, is called:
Match LIST-I with LIST-II:
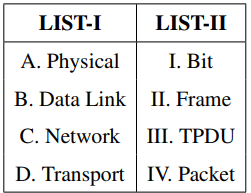
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following functionality is to be implemented by the transport layer?
Match LIST-I with LIST-II:
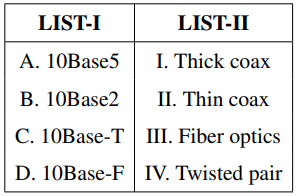
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The data link layer has a number of specific functions it can carry out. These functions include:
(A) Providing a well-defined interface to the network layer
(B) Dealing with transmission errors
(C) Regulating the flow of data so that slow receivers are not swamped by fast senders
(D) Routing packets from the source machine to the destination machine
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
What will be the number of cross points needed for a full duplex 8-line cross point switch with no self connections?
Which of the following IP address can be used as a loop-back address?
Arrange the following steps in order in which they take place, while solving problems using State Space Approach.
(A) Identify the set of rules (all possible actions).
(B) Describe the states.
(C) Identify the initial state followed by the goal state.
(D) Find the solution path in the state space.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
With respect to Artificial Intelligence, find the correct properties of an agent.
(A) An agent’s choice of action at any given instant does not depend on its built-in knowledge.
(B) Agents do not interact with the environment.
(C) Agents interact with the environment through sensors and actuators.
(D) An agent’s choice of action at any given instant can depend on its built-in knowledge and on the entire percept sequence observed to date, but not on anything it hasn’t perceived.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
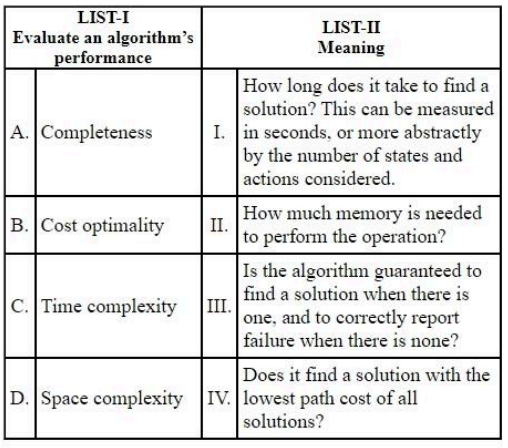
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Match LIST-I with LIST-II
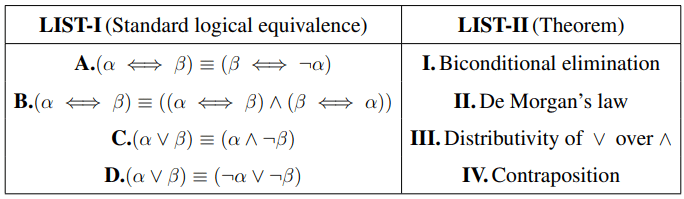
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Convert the following statement into First Order Logic:
"For every \(s\), if \(s\) is a student, then \(s\) is a player"
Consider the following arguments and determine whether they are valid.
A. Either I will get good marks or I will not graduate. If I did not graduate I will go to America. I got good marks. Thus, I would not go to America.
B. Either I will pass the examination or I will not graduate. If I do not graduate I will go to America. I failed. Thus, I will go to America.
C. If I study then I will pass examination. If I do not go to shopping then I will study. But I failed examination. Therefore, I went to shopping.
D. If the mall is free then there is no inflation. If there is no inflation then there are price controls. Since there are price controls, therefore, the mall is free.
Choose the correct valid arguments from the options given below:
If we encrypt the following plain text using rail fence technique with depth 2, what will be the encrypted message?
Plain Text = DIFFICULTWAYLEADSTODESTINATION
In Playfair cipher what happens when two identical letters appear in the same pair?
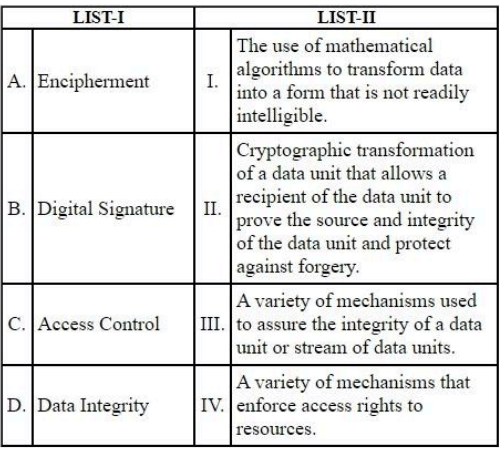
Which of the following is not included in the CIA triad?
If a cryptanalyst only knows the encryption algorithm and ciphertext, then which type of attack can be performed by him?
If it is known that a given ciphertext is Caesar Cipher, then a brute-force cryptanalysis requires _____ keys to try.
The agent observes input-output pairs and learns a function that this learning maps from input to output. For example, the inputs could be camera images, each one accompanied by an output saying “bus” or “pedestrian,” etc. This type of learning is known as:
____ is the process of computing the distribution over past states given evidence up to the present.
When the output is one of a finite set of values (such as sunny/cloudy/rainy or true/false), the learning problem is known as:
Which model is represented by the following graph?

The term "Residual" is defined as:
Which among the following is not a valid distance specifying criterion between the clusters, in the context of hierarchical clustering?
In k-means algorithm, if there are n data points, then what is the minimum value of k and the maximum value of k?





Comments