CUET PG Home Science Question Paper 2024 is available here for download. NTA conducted CUET PG Home Science paper 2024 on from March 23 in Shift 1. CUET PG Question Paper 2024 is based on objective-type questions (MCQs). According to latest exam pattern, candidates get 105 minutes to solve 75 MCQs in CUET PG 2024 Home Science question paper.
CUET PG Home Science Question Paper 2024 PDF Download
| CUET PG Home Science Question Paper 2024 with Answer Key | Check Solutions |
Home Science 2024 Questions with Solutions
Question 1:
Name the moist heating method in which cooking is carried out in the minimum amount of liquid at a temperature of 80°C-85°C.
View Solution
Solution: Poaching is a moist-heat cooking method that involves cooking food gently in a small amount of liquid at a temperature range of 80°C to 85°C. This method is ideal for delicate foods like eggs, fish, and fruits, ensuring they retain their shape and texture while being cooked. The low temperature prevents overcooking or breaking apart of the food.
Quick Tip: Poaching involves cooking food gently in a small amount of liquid, maintaining the temperature between 80°C and 85°C, which is ideal for delicate foods like eggs or fish.
Question 2:
Which way of coating food implies passing a food through a fine dry or powdery substance in order to coat it?
View Solution
Solution: Dredging is a cooking technique in which food is coated by passing it through a fine dry or powdery substance such as flour, breadcrumbs, or cornmeal. This is commonly done to prepare foods for frying or sautéing, ensuring a crisp and even outer layer.
Quick Tip: Dredging is a technique where food is coated in a fine dry substance, such as flour or breadcrumbs, to prepare it for frying or baking.
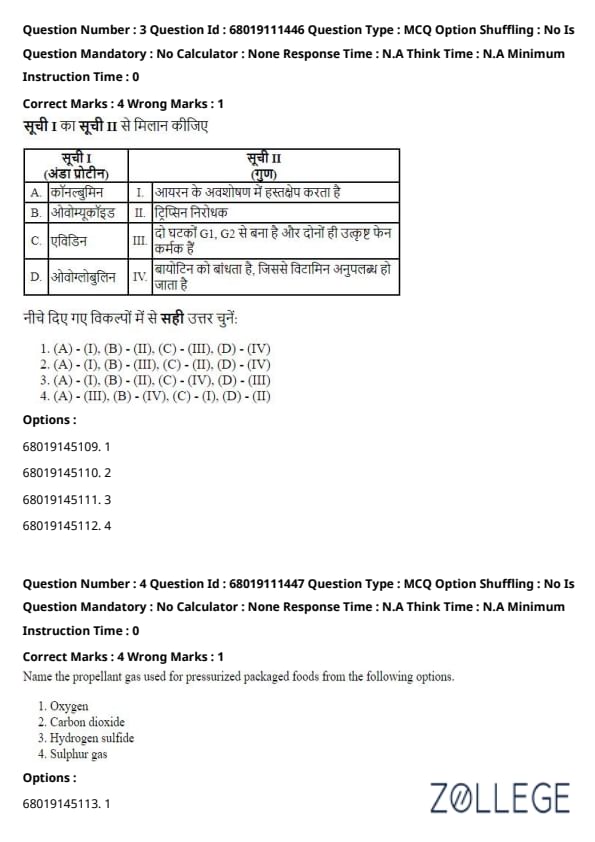
Question 3:
Match List I with List II:
List I (Egg proteins)
List II (Properties)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
A. Conalbumin interferes with the absorption of iron. (I)
B. Ovomucoid acts as a trypsin inhibitor. (II)
C. Avidin binds biotin, making the vitamin unavailable. (IV)
D. Ovoglobulin consists of two components, G1 and G2; both are excellent foaming agents. (III)
Quick Tip: Each egg protein has a specific function: Conalbumin (A) is a foaming agent; Ovomucoid (B) binds biotin, Avidin (C) interferes with iron absorption, and Ovoglobulin (D) inhibits trypsin.
Question 4:
Name the propellant gas used for pressurized packaged foods from the following options.
View Solution
Solution: Carbon dioxide is commonly used as a propellant gas in pressurized packaged foods due to its non-toxic nature and ability to preserve freshness. Other gases like hydrogen sulfide and sulfur gas are not safe for food use.
Quick Tip: The type of gas used in packaging to ensure food safety and freshness.
Question 5:
Freezer burn is produced due to which of the following reasons?
View Solution
Solution: Freezer burn occurs when water molecules evaporate from the frozen food surface due to sublimation, leading to a dehydrated and dry texture. This can affect the taste and quality of the food.
Quick Tip: Use airtight containers or freezer bags to prevent freezer burn.
Question 6:
The image given below is the structural formula of which amino acid?

View Solution
Solution: Methionine is an essential amino acid characterized by a sulfur-containing side chain. Its structure includes a methyl group attached to the sulfur atom, distinguishing it from other amino acids like alanine, leucine, and isoleucine.
Quick Tip: Methionine plays a critical role in protein synthesis and acts as a precursor for important molecules like S-adenosylmethionine.
Question 7:
Which of the following types of chemical reactions does not occur in the TCA cycle?
View Solution
Solution: The TCA (Tricarboxylic Acid) cycle involves decarboxylation, hydrolysis, and phosphorylation reactions, but not dephosphorylation reactions. Phosphorylation occurs in the substrate-level phosphorylation step.
Quick Tip: Focus on the core steps of the TCA cycle: oxidation, decarboxylation, and substrate-level phosphorylation. Dephosphorylation is not part of the cycle.
Question 8:
Site for fatty acid biosynthesis within the cell is
View Solution
Solution: Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytoplasm where acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA are involved in the enzymatic synthesis. Mitochondria, in contrast, are the site for fatty acid oxidation.
Quick Tip: Biosynthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, while breakdown (oxidation) occurs in the mitochondria.
Question 9:
Which of the following options is CORRECT with respect to allosteric inhibitor of an enzyme?
View Solution
Solution: Allosteric inhibitors bind to the enzyme at a site other than the active site and are involved in feedback regulation, altering enzyme activity. This mechanism often plays a key role in feedback regulation to maintain metabolic balance.
Quick Tip: Feedback inhibition by allosteric regulators ensures that metabolic pathways are tightly controlled and not overactive.
Question 10:
According to ICMR NIN, what is the Estimated Average Requirement (2024) of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) for a lactating woman?
View Solution
Solution: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) recommend an average of 95 mg/day of vitamin C for lactating women to meet the increased nutritional requirements during lactation.
Quick Tip: Vitamin C is essential for lactating women to support both maternal and infant health. Remember the updated value of 95 mg/d as per the 2024 recommendation.
Question 11:
Which component of protein contributes to the maximum percentage of total plasma protein?
View Solution
Solution: Albumin is the most abundant protein in plasma, contributing around 60 percent of the total plasma protein. It is essential for maintaining oncotic pressure and transporting various molecules.
Quick Tip: Albumin is the primary protein for maintaining blood volume and pressure, making it the highest contributor to plasma protein.
Question 12:
Ms. X complains of passing clay-colored, bulky, greasy, and foul-smelling stools for the last 2-3 days. Most likely she is having
View Solution
Solution: Clay-colored stools are indicative of bile duct obstruction, which prevents bile from reaching the intestine. Bile is essential for fat digestion, and its absence causes bulky, greasy stools.
Quick Tip: Clay-colored stools are a hallmark of bile duct obstruction. Look for accompanying symptoms like jaundice for confirmation.
Question 13:
Arrange the steps of the nutritional care process in the correct sequence.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The nutritional care process starts with assessing nutritional status, followed by identifying problems, planning nutritional care, evaluating the outcomes, and finally implementing nutritional interventions. This sequence ensures an effective and comprehensive approach to nutritional management.
Quick Tip: Use the sequence: Assess → Identify → Plan → Evaluate → Implement (AIPEI) for easier recall of the steps in nutritional care.
Question 14:
Arrange the steps for growth monitoring in the correct sequence.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Growth monitoring starts with determining the child's correct age, followed by measuring the correct weight, plotting the weight against age on a growth chart, and finally interpreting the growth curve to assess if the child is growing properly.
Quick Tip: Use the sequence: Age → Weight → Plot → Interpret (AWPI) for remembering the steps in growth monitoring.
Question 15:
Which of the following statements are CORRECT with respect to parenteral nutrition?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Parenteral nutrition bypasses the gastrointestinal tract entirely. Nutrients are delivered intravenously, typically to patients with severe GI dysfunction or those who cannot consume food orally. Statement (A) is incorrect as it describes enteral feeding, which involves accessing the gastrointestinal tract.
Quick Tip: Parenteral nutrition = IV delivery of nutrients. It's for patients unable to use their GI tract.
Question 16:
Identify the deficiency symptoms of niacin (vitamin B3).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Niacin deficiency leads to pellagra, which is characterized by the symptoms Casal's necklace, dementia, diarrhoea, and sometimes delirium. These symptoms are associated with severe niacin deficiency, affecting the skin, nervous system, and gastrointestinal tract.
Quick Tip: The symptoms of niacin deficiency are often summarized as the "4 Ds": Dermatitis, Dementia, Diarrhea, and Delirium.
Question 17:
Identify among the following, which is NOT a common adulterant in coffee.
View Solution
Solution: Common adulterants in coffee include chicory, starch, and tamarind or date-seed powder, which are used to add bulk or alter flavor. Cassia bark is not a typical coffee adulterant.
Quick Tip: Coffee adulterants often aim to mimic color or increase volume, but cassia bark is not used for such purposes.
Question 18:
Which of the following stain removal methods needs to be adopted for lipstick stain?
View Solution
Solution: Lipstick stains are best removed by sponging the stained area with mentholated spirit. Other methods like salt water, ammonia, or soap are not as effective in breaking down the oils and pigments in lipstick.
Quick Tip: For stubborn lipstick stains, always use mentholated spirit to effectively dissolve the oil-based residue.
Question 19:
Identify the characteristic features of disperse dyes.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Disperse dyes are water-insoluble, low molecular weight dyes that dye synthetic fibers such as polyester, acetate, and nylon. They are non-ionic and dissolve in organic solvents to form a dye bath, which is critical for dyeing synthetic fibers.
Quick Tip: Disperse dyes dissolve in organic solvents and are primarily used for synthetic fibers like polyester and acetate.
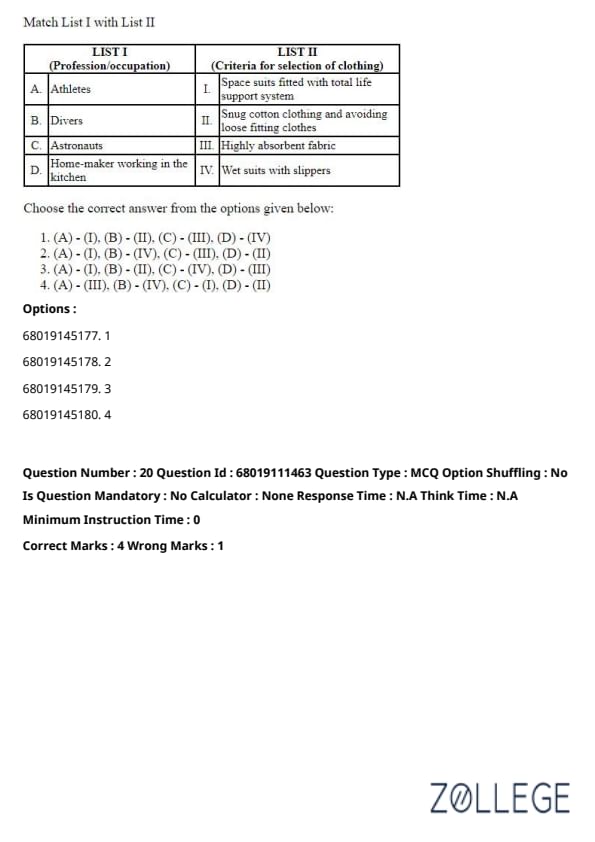
Question 20:
Match List I with List II and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
List I (Profession/occupation)
List II (Criteria for selection of clothing)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
Athletes: Space suits fitted with a total life support system ensure survival in high-performance environments. Matches with I.
Divers: Snug cotton clothing and avoiding loose-fitting clothes provide comfort and safety during underwater activities. Matches with II.
Astronauts: Wet suits with slippers retain heat and provide protection in space. Matches with IV.
Home-maker working in the kitchen: Highly absorbent fabric is ideal for absorbing spills and ensuring comfort. Matches with III.
Quick Tip: Matching criteria for clothing:
- Athletes: Require full support in rigorous environments.
- Divers: Safety and snug clothing for mobility in water.
- Astronauts: Space-related protection like wetsuits.
- Home-makers: Practical absorbent materials for daily tasks.
Question 21:
Identify the unfavorable properties of silk fiber.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The unfavorable properties of silk include its sensitivity to heat, poor resistance to prolonged sunlight exposure (leading to weakening of the fiber), and vulnerability to alkalis. It is, however, resistant to acids.
Quick Tip: Silk is sensitive to heat, sunlight, and alkalis. Handle with care to preserve its luster and integrity.
Question 22:
Which type of novelty yarns resemble caterpillars, as tufts of fibers are inserted uniformly in the yarn twist, perpendicular to the yarn?
View Solution
Solution: Chenille yarns are characterized by their caterpillar-like appearance, created by uniformly inserting tufts of fibers perpendicular to the yarn. This gives them a soft, fuzzy texture.
Quick Tip: "Chenille" means "caterpillar" in French, making it easy to remember their characteristic fuzzy structure.
Question 23:
Which among the following is NOT a primary operation in the motions of the loom?
View Solution
Solution: The primary operations in the motions of the loom are shedding, picking, and beating. "Let off" is a secondary motion that involves unwinding the warp during weaving.
Quick Tip: The three primary loom motions: Shedding, Picking, and Beating (SPB). Let off is secondary.
Question 24:
Which type of knit fabric resembles a miniature honeycomb pattern and is usually seen in sportswear?
View Solution
Solution: Pique knit fabric features a distinctive honeycomb pattern, offering breathability and durability, making it ideal for sportswear like polo shirts.
Quick Tip: Think "Pique for Polo" to remember its honeycomb pattern and use in sportswear.
Question 25:
Arrange commonly employed steps in printing the fabrics in order of their implementation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The correct order of steps is:
(B) Preparation of fabric and print paste
(E) Printing of fabric
(A) Drying
(D) Fixing of dyestuff
(C) Washing off and soaping treatment
This sequence ensures that the fabric is prepared, printed, and finished effectively.
Quick Tip: Use the mnemonic "Prepare → Print → Dry → Fix → Wash" to recall the steps in fabric printing. Note: Drying usually precedes fixing.
Question 26:
Identify the type of finish in which fabric is pressed by a roller which has fine diagonal lines etched out on the surface producing smooth fabrics with a soft luster.
View Solution
Solution: Schreinering is a finishing process where the fabric is pressed with rollers etched with fine diagonal lines, giving it a smooth texture and soft luster. This process enhances the appearance and feel of the fabric.
Quick Tip: Schreinering = "Shiny and smooth" fabric. Think of the etched roller lines as enhancing luster.
Question 27:
Which of the following type of weave is used to prepare brocade, damask, and brocatelle fabrics?
View Solution
Solution: Jacquard weave is a technique used to create intricate patterns such as brocade, damask, and brocatelle. It involves a loom that controls individual warp threads, allowing complex designs.
Quick Tip: Jacquard = Intricate patterns. Think of brocade and damask as luxurious examples of this weave.
Question 28:
Arrange the steps involved in production of wool fiber in correct sequence.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The correct sequence is:
(A) Shearing, grading, and sorting
(E) Scouring
(D) Carbonisation
(C) Carding
(B) Combing
This ensures the wool fiber is cleaned, processed, and prepared for further use.
Quick Tip: Think: Shear → Scour → Carbonise → Card → Comb for the sequence of wool production.
Question 29:
Identify the characteristic features indicating chemical composition of silk.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The chemical composition of silk includes reactive carboxyl (COOH) and amino (NH2) groups, very few cross-links between fibroin protein chains, and Van der Waal's forces that play a significant role in maintaining structural integrity. While hydrogen bonds exist, they are less significant in determining crystallinity compared to other fibers.
Quick Tip: Silk composition relies on COOH and NH2 groups, fibroin protein chains, and Van der Waal's forces for its unique properties.
Question 30:
Which among the following specialty hair fiber is obtained from rabbit?
View Solution
Solution: Angora fiber is derived from Angora rabbits. It is known for its silky texture and warmth, making it a valued material in the textile industry.
Quick Tip: Angora = Rabbits. Alpaca, Cashmere, and Mohair come from other animals like alpacas and goats.
Question 31:
Name the decorative strip worn in the Post-Vedic Period (600-323 BCE) and Maurya and Sunga period (321-72 BCE) by women that was tucked at the center front of the waist over the antariya.
View Solution
Solution: Patka was a decorative strip worn by women during the Post-Vedic and Maurya periods. It was tucked at the center front of the waist over the antariya and often embellished for decorative purposes.
Quick Tip: Patka = Waist decoration. Remember it as a traditional Indian accessory.
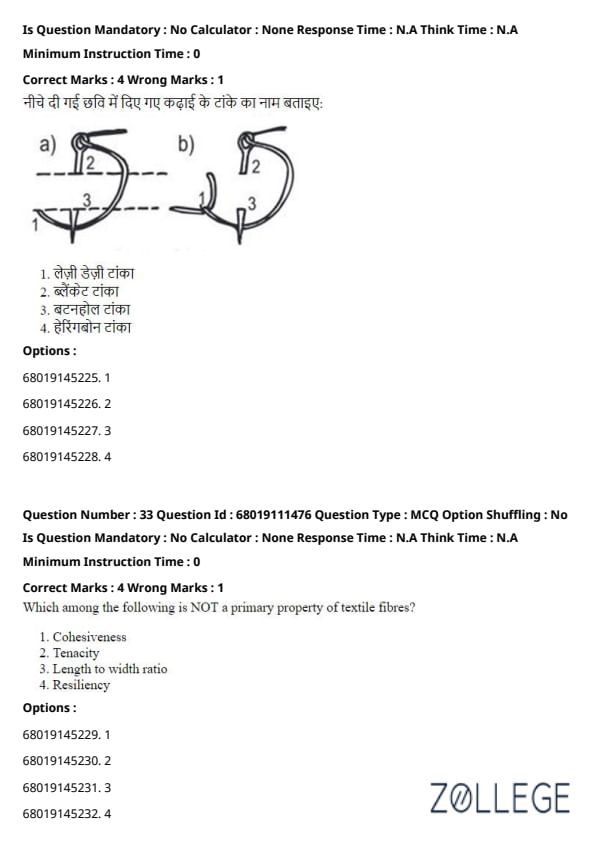
Question 32:
Name the embroidery stitch given in the image below:
(Image placeholder - replace with actual image)
View Solution
Solution: The blanket stitch is shown in the image. It is used to finish the edges of fabric to prevent fraying and provides a decorative effect.
Quick Tip: Blanket stitch is used for edging blankets or fabrics. Recognize it by its characteristic looping edge.
Question 33:
Which among the following is NOT a primary property of textile fibers?
View Solution
Solution: Resiliency, which refers to the ability to recover shape after deformation, is considered a secondary property. Primary properties include cohesiveness, tenacity, and length-to-width ratio, which are fundamental for textile fiber usability.
Quick Tip: Primary fiber properties: Cohesiveness, tenacity, and aspect ratio. Resiliency is secondary.
Question 34:
Put the following steps of the decision-making process in sequential order.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The correct sequence for decision-making is:
(B) Identify the problem
(D) Identify the alternatives
(A) Evaluate the alternatives
(E) Make a decision
(C) Evaluate the decision
Quick Tip: Decision-making steps: Identify the problem → Identify alternatives → Evaluate alternatives → Decide → Evaluate decision.
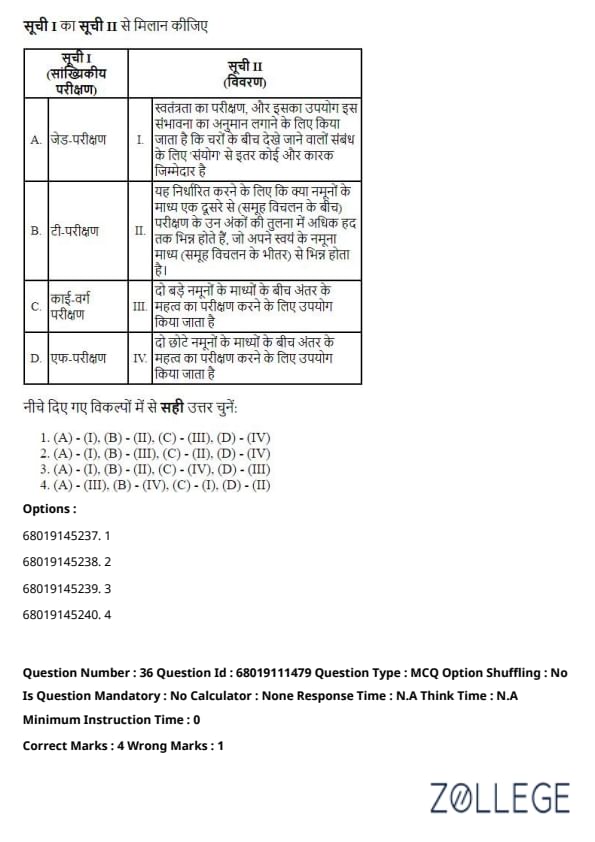
Question 35:
Match List I with List II and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
List I (Statistical test)
List II (Description)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
F-test: Used for testing the significance of the difference between the means of two large samples. Matches with III.
Chi-square test: Used for testing the significance of the difference between the means of two small samples. Matches with IV.
t-test: A test of independence used to estimate the likelihood that some factor other than chance accounts for the observed relationship. Matches with I.
Z-test: To determine whether the sample means differ significantly, considering between-group and within-group variances. Matches with II.
Quick Tip: For statistical tests:
- Z-test: Focuses on comparing group variances.
- t-test: Tests independence and associations between factors.
- Chi-square: Suitable for small sample mean comparisons.
- F-test: Works well for testing variances in large samples.
Understanding the purpose of these tests can help you match them quickly.
Question 36:
Match List I with List II and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
List I (Principle given by Henry Fayol)
List II (Description)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
Esprit de corps: Implies 'in union there is strength'; it stresses the need for team spirit, cordial relations, and cooperation among personnel. Matches with III.
Centralisation: Implies authority relationships from the top to the lowest echelons of an organization. Matches with IV.
Unity of direction: A set of activities having the same objective should be under the direction of a single manager. Matches with I.
Scalar chain of command: Relative concentration of much authority in a manager at any managerial level, but especially at the top managerial level. Matches with II.
Quick Tip: When matching principles of management:
- Esprit de corps: Think of team spirit and unity.
- Scalar chain: Concentration of authority at managerial levels.
- Unity of direction: Alignment of activities under one manager.
- Centralisation: Represents hierarchical authority relationships.
Use these associations to match quickly.
Question 37:
Identify the different aspects that contribute to the family's hidden income.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Hidden income includes benefits like community facilities, employee benefits (e.g., gratuity and bonuses), and consumer savings through buying at wholesale prices. Capital gains income is taxable and not hidden.
Quick Tip: Hidden income = Savings or benefits that are indirect or untaxed, like bonuses, wholesale savings, or public facilities.
Question 38:
The process of combining two or more activities at the same time is known as:
View Solution
Solution: Dovetailing refers to combining two or more activities simultaneously to save time and improve efficiency. For example, listening to an audiobook while exercising.
Quick Tip: Dovetailing = Multitasking effectively. Think of the efficiency of interlocking tasks like dovetail joints.
Question 39:
Which among the following is NOT a feature of a typical work curve?
View Solution
Solution: A typical work curve does not show acceleration in the last hour. Instead, it demonstrates a slow start, a peak, a dip mid-way, and a final spurt near the end of the work session.
Quick Tip: Work curve = Slow start → Peak performance → Midway dip → Final spurt. No last-hour acceleration!
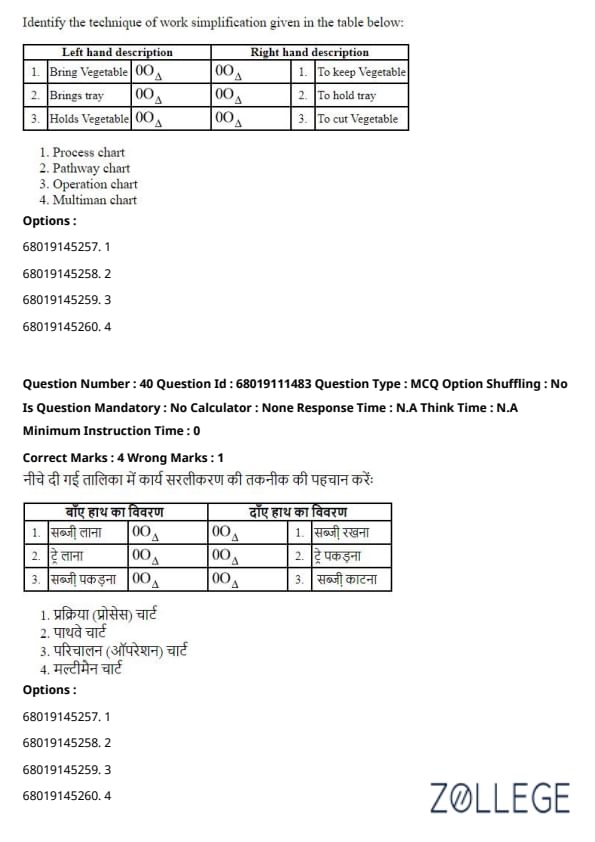
Question 40:
Identify the technique of work simplification given in the table below:
Work Simplification Table
| Left hand description | Right hand description |
|---|---|
| Brings Vegetable | To keep Vegetable |
| Brings tray | To hold tray |
| Holds Vegetable | To cut Vegetable |
View Solution
Solution: The operation chart is a work simplification technique that records the actions of both hands in detail. It helps analyze and improve efficiency in tasks by showing how each hand is utilized during a process.
Quick Tip: Operation charts focus on hand movements to streamline tasks and enhance productivity.
Question 41:
Which of the following is NOT a salient feature of Sukanya Samriddhi Account (SSA) scheme?
View Solution
Solution: Under the Sukanya Samriddhi Account scheme, the minimum deposit is INR 250/- and not INR 500/-, and the maximum deposit is INR 1,50,000/- per year. The rest of the features are correct.
Quick Tip: For SSA, remember: INR 250/- minimum deposit, INR 1,50,000/- maximum deposit per year.
Question 42:
Components like social class, lifestyle, and personality fall under which type of market segmentation?
View Solution
Solution: Psychographic segmentation focuses on consumer lifestyles, social class, and personality traits to understand their preferences and behaviors.
Quick Tip: Psychographic = Lifestyle + Personality. Think of "psyche" for understanding deeper consumer motivations.
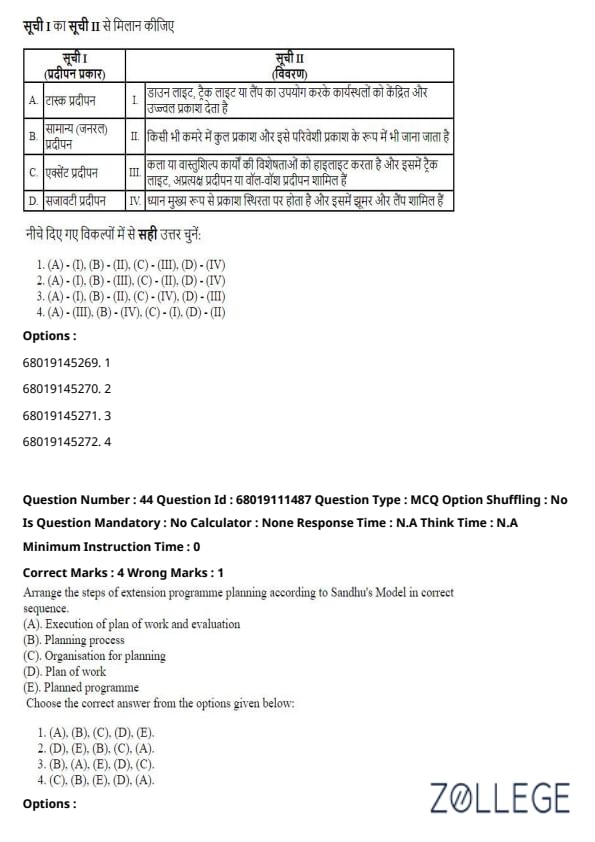
Question 43:
Match List I with List II and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
List I (Type of lighting)
List II (Description)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
- Task lighting: Provides focused lighting for workspaces using tools like down lights, track lights, or lamps. Matches with I.
- General lighting: Refers to total light in a room, also called ambient lighting. Matches with II.
- Accent lighting: Highlights works of art or architectural features, including track lights, indirect lighting, or wall-wash lighting. Matches with III.
- Decorative lighting: Focuses on the light fixture itself, such as chandeliers and lamps. Matches with IV.
Quick Tip:
- Task lighting: Functional lighting for workspaces.
- General lighting: Basic lighting in a room (ambient).
- Accent lighting: Highlights objects or features.
- Decorative lighting: Focuses on the aesthetics of fixtures.
Question 44:
Arrange the steps of extension programme planning according to Sandhu's Model in correct sequence.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The correct sequence is:
(C) Organisation for planning
(B) Planning process
(E) Planned programme
(D) Plan of work
(A) Execution of plan of work and evaluation
Quick Tip: Remember Sandhu's model: Organize → Plan → Programme → Work → Execute.
Question 45:
Arrange the steps in making time plans in correct sequence.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: The correct sequence for making time plans is:
(A) Listing and grouping items under flexible and nonflexible
(E) Setting time required for each item of work
(C) Balancing time with the total time available
(B) Determining time sequence and order of work
(D) Writing out the plan
Quick Tip: Time planning steps: List → Set time → Balance time → Sequence → Write plan.
Question 46:
Which of the following standardisation mark aims to make common standards of products and services at the international level for facilitating foreign trade and can be applicable on hospital, insurance, etc.?
View Solution
Solution: ISO (International Organization for Standardization) sets common international standards for products and services to facilitate trade and ensure quality, safety, and efficiency. It is applicable in diverse fields like hospitals and insurance.
Quick Tip: ISO = International standards for global trade facilitation and quality assurance.
Question 47:
Which among the following antibodies can easily cross the placenta?
View Solution
Solution: IgG is the only antibody that can cross the placenta, providing passive immunity to the fetus. Other antibodies, like IgA, IgM, and IgE, do not cross the placental barrier.
Quick Tip: IgG = Placental transfer antibody, essential for fetal immunity.
Question 48:
Rh-negative individuals are those:
View Solution
Solution: Rh-negative individuals lack the Rh antigen (antigen D) on their RBC membranes and do not naturally have Rh antibodies unless exposed to Rh-positive blood.
Quick Tip: Rh-negative = No Rh antigen. Anti-D antibodies are only produced upon exposure to Rh-positive blood.
Question 49:
Name the diagram given below showing disease transmission routes and how the routes can be blocked. (Diagram Placeholder - Please insert image)
View Solution
Solution: The F-diagram illustrates the routes of disease transmission, focusing on six pathways: Fluids, Fingers, Flies, Fomites, Food, and Fields. It also highlights hygiene measures to block transmission.
Quick Tip: F-diagram = Focuses on Fluids, Fingers, Flies, Food, Fields, and Fomites for understanding transmission.
Question 50:
The Scheme of Continuing Education was launched in which year?
View Solution
Solution: The Scheme of Continuing Education was launched in 1995 to support adult learning, improve literacy rates, and provide opportunities for lifelong education, with a focus on bridging educational gaps.
Quick Tip: 1995 = Launch of Continuing Education Scheme to enhance adult education and literacy.
Question 51:
What was the core focus of the Constitution's Seventy Third Amendment Act, 1992?
View Solution
Solution: The 73rd Amendment Act, 1992, introduced Panchayati Raj Institutions, empowering local self-governments and ensuring democratic decentralization at the village level.
Quick Tip: 73rd Amendment = Panchayati Raj Institutions for grassroots governance.
Question 52:
Which of the following schemes aims at providing financial support for pregnant and lactating mothers to improve the health and nutrition for mother and child as well as compensation for wage loss?
View Solution
Solution: PMMVY provides cash incentives to pregnant and lactating mothers to improve nutrition and health, ensuring compensation for wage loss during maternity.
Quick Tip: PMMVY = Nutrition and wage support for pregnant and lactating mothers.
Question 53:
If the size of the audience is small and geographically concentrated, the preferable extension method would be:
View Solution
Solution: The individual contact method is suitable for small, localized audiences as it allows for personalized communication and effective engagement.
Quick Tip: Individual contact = Best for small, concentrated audiences with tailored communication.
Question 54:
What type of evaluation is carried out at the initial stage of the programme?
View Solution
Solution: Formative evaluation is conducted at the beginning of a program to assess its design, feasibility, and potential improvements before implementation.
Quick Tip: Formative = Initial evaluation to refine program design and objectives.
Question 55:
The specialization of functions of two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex is called as:
View Solution
Solution: Psychological organization (or lateralization) refers to the specialization and division of functions between the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
Quick Tip: Psychological organization = Functional specialization of brain hemispheres. Also consider: Lateralization = Division of functions between brain hemispheres.
Question 56:
Put Sigmund Freud's five stages of psychosexual development in correct sequence.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Freud's psychosexual development stages are: Oral stage, Anal stage, Phallic stage, Latency stage, and Genital stage. These stages correspond to different aspects of personality and sexual development.
Quick Tip: Mnemonic: OAPLG (Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital) for Freud's psychosexual stages.
Question 57:
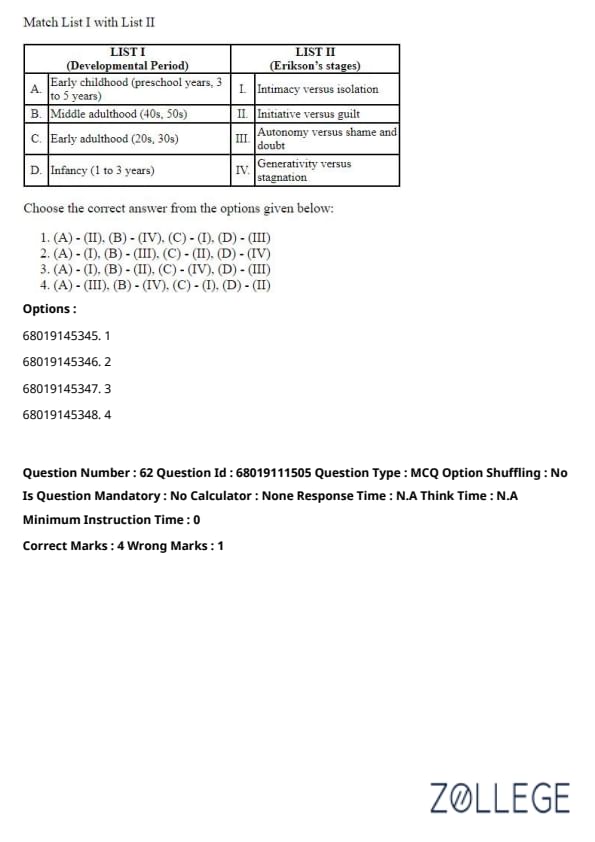
The ecological system theory defines which of the following systems influencing child development?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory outlines five environmental systems influencing child development. The Chronosystem relates to changes over time, the Exosystem involves external influences, and the Mesosystem deals with interconnections among the microsystems.
Quick Tip: Bronfenbrenner's systems: Chronosystem, Microsystem, Mesosystem, Exosystem, Macrosystem.
Question 58:
According to E. Mavis Hetherington's, which of the following common pathways are adopted by men and women for exiting divorce?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Hetherington's pathways for navigating divorce include "The Defeated," "The Not-Good-Enoughs," and "The Enhancers." These groups represent distinct outcomes, with the enhancers being the most resilient and adaptive.
Quick Tip: Key Hetherington pathways: Defeated, Not-Good-Enoughs, and Enhancers – focusing on resilience and adaptability.
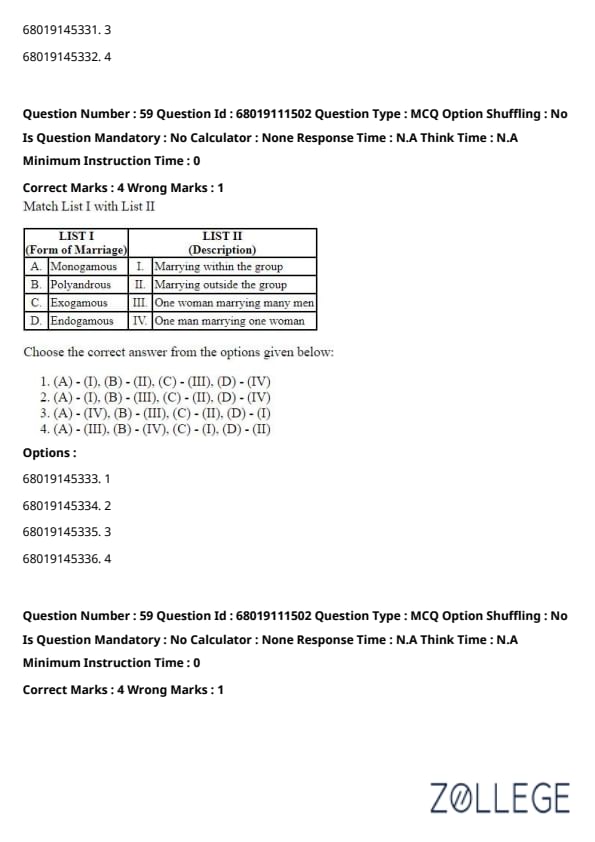
Question 59:
Match List I with List II and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
List I (Form of Marriage)
List II (Description)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
Monogamous: One man marrying one woman. Matches with IV.
Polyandrous: One woman marrying many men. Matches with III.
Exogamous: Marrying outside the group. Matches with II.
Endogamous: Marrying within the group. Matches with I.
Quick Tip: To match forms of marriage:
- Monogamous: Mono means "one" (one man, one woman).
- Polyandrous/Polygamous: Poly means "many"; androus refers to "men," -gamous refers to marriage.
- Exogamous: Exo means "outside" (marrying outside the group).
- Endogamous: Endo means "within" (marrying within the group).
These definitions make matching easier.
Question 63:
A pre-term infant has a gestational age of less than
View Solution
Solution: Pre-term infants are defined as those born before completing 37 weeks of gestation. This classification helps in identifying babies who may need additional care and monitoring.
Quick Tip: Remember: A full-term pregnancy ranges from 37 to 42 weeks.
Question 64:
Which of the following is NOT a reflex?
View Solution
Solution: Reflexes such as Moro, Grasping, and Babinski are involuntary actions seen in infants. Blinking of eyes, however, is a voluntary action rather than a reflex.
Quick Tip: Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli, commonly observed in newborns, such as the Moro and Grasping reflexes.
Question 65:
Extension education is primarily considered as
View Solution
Solution: Extension education refers to the process of imparting knowledge and skills outside of formal education systems. It is designed to meet the specific learning needs of individuals or groups.
Quick Tip: Non-formal education often emphasizes flexibility and practical applications, tailored to learners' needs.
Question 66:
Which of the following is the largest school feeding programme in India?
View Solution
Solution: The PM Poshan (formerly known as the Mid-Day Meal Scheme) is the largest school feeding program in India, aimed at improving nutritional levels among school children.
Quick Tip: PM Poshan focuses on enhancing education and nutrition for children, promoting school attendance and performance.
Question 67:
Match the programme given in List-I with the issue dealt by it in List-II.
List-I (Programme/Scheme)
List-II (Objective)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
NHM (National Health Mission): Provides elementary education including life skills. Matches with I.
ICDS (Integrated Child Development Scheme): Improves the nutritional and health status of children in the age group of 0-6 years. Matches with II.
MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act): Provides not less than 100 days of unskilled manual work as guaranteed employment in rural areas. Matches with III.
SSA (Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan): Universal access to equitable, affordable, and quality health services. Matches with IV.
Quick Tip: To match schemes with objectives:
- NHM: Think of education and life skills.
- ICDS: Child nutrition and health.
- MGNREGA: Guarantees rural employment.
- SSA: Focuses on health services.
Use these associations for accurate matching.
Question 68:
Which of the following are the principles of adult learning given by Knowles?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Knowles' principles of adult learning emphasize that adults are relevancy-oriented, internally motivated, self-directed, goal-oriented, and practical in their approach to learning. They prefer learning that applies directly to their personal and professional lives, rather than rote memorization.
Quick Tip: Adult learning is most effective when it focuses on problem-solving, relevancy, and practical application.
Question 69:
Arrange the following learning experiences from bottom to top as per Edgar Dale's Cone of Experience.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Edgar Dale's Cone of Experience organizes learning experiences from the most concrete to the most abstract. The correct order from bottom to top is: Dramatized experiences (D), Field trips (B), Demonstrations (A), and Exhibits (C). This sequence reflects the transition from hands-on, direct experiences to abstract and symbolic representations.
Quick Tip: Dale's Cone emphasizes engaging learners through concrete experiences before introducing abstract concepts for better retention.
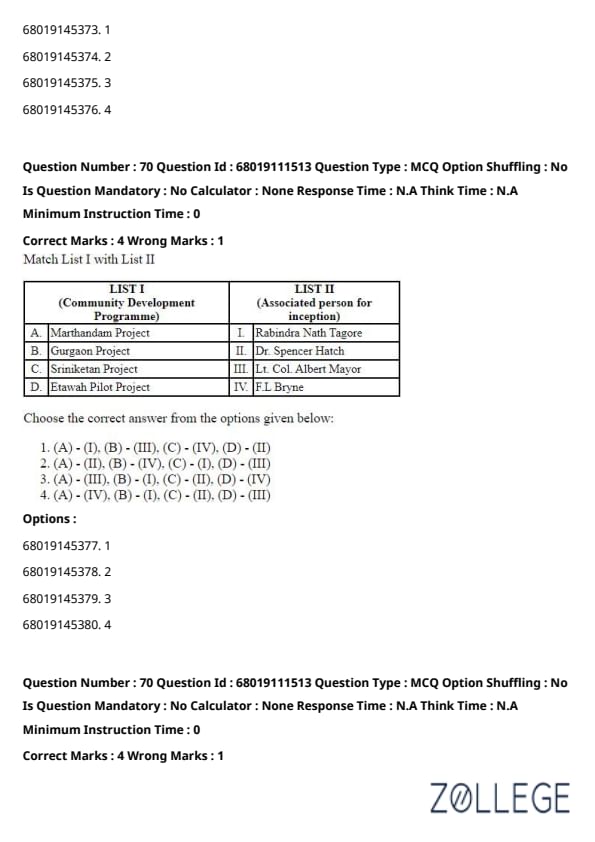
Question 70:
Match List I with List II and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
List I (Community Development Programme)
List II (Associated person for inception)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution:
Marthandam Project: Associated with Dr. Spencer Hatch. Matches with II.
Gurgaon Project: Associated with F. L. Byrne. Matches with IV.
Sriniketan Project: Associated with Rabindra Nath Tagore. Matches with I.
Etawah Pilot Project: Associated with Lt. Col. Albert Mayor. Matches with III.
Quick Tip: To remember community development projects:
- Marthandam Project: Focused on rural upliftment, linked with Dr. Spencer Hatch.
- Gurgaon Project: Linked with F. L. Byrne, emphasized community cooperation.
- Sriniketan Project: An initiative by Rabindra Nath Tagore for rural development.
- Etawah Pilot Project: Directed by Lt. Col. Albert Mayor for rural upliftment in India.
Memorizing key contributors helps to match projects accurately.
Question 71:
Which of the following are examples of fourth-generation media?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Fourth-generation media focus on interactive and digital platforms like mobile applications, Internet TV, and podcasts. These tools align with modern technology for communication and education. This evolution emphasizes user engagement, real-time content delivery, and personalized experiences, reshaping how information is consumed and shared in the digital age.
Quick Tip: Key fourth-generation media include digital platforms such as apps, Internet TV, and podcasts.
Question 72:
How many phases of Panchayati Raj were identified in Ashoka Mehta's (1978) Report of the Committee of Panchayati Raj Institutions?
View Solution
Solution: Ashoka Mehta's report categorized Panchayati Raj Institutions into two main phases to streamline decentralization and local governance systems. The report emphasized empowering these institutions with greater financial and administrative autonomy, ensuring grassroots participation in decision-making and developmental planning.
Quick Tip: Remember: Two phases in Ashoka Mehta's Panchayati Raj report focus on decentralization.
Question 73:
Which of the following methods depends on the 'Learning by Doing' principle?
View Solution
Solution: Method demonstrations emphasize active engagement and hands-on participation to enhance learning outcomes based on practical experience. This approach bridges the gap between theory and practice, enabling learners to acquire skills more effectively through observation, imitation, and direct involvement.
Quick Tip: "Learning by Doing" is central to method demonstration for practical skill acquisition.
Question 74:
Which of the following programmes provide micro-credit to poor women?
View Solution
Solution: Rashtriya Mahila Kosh aims to provide affordable micro-credit to underprivileged women, promoting financial independence and self-reliance. It supports income-generating activities through capacity-building programs and fosters entrepreneurship among women in rural and urban areas.
Quick Tip: Focus on micro-credit schemes: Rashtriya Mahila Kosh supports financial independence for women.
Question 75:
Which among the following are used for assessing reliability of a research tool?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Solution: Reliability testing ensures consistent results using methods like Test-retest, Parallel-form, and Split-half techniques. Concurrent validity checks are not applicable for reliability testing. Reliability focuses on the stability and precision of measurements, while validity assesses the accuracy and relevance of what the test intends to measure.
Quick Tip: Reliability testing focuses on consistency, using Test-retest, Parallel-form, and Split-half methods.

















































































Comments