CUET PG Agri-Business Management Question Paper 2024 will be available here for download. NTA conducted CUET PG Agri-Business Management paper 2024 on from March 28 in Shift 3. CUET PG Question Paper 2024 is based on objective-type questions (MCQs). According to latest exam pattern, candidates get 105 minutes to solve 75 MCQs in CUET PG 2024 Agri-Business Management question paper.
Related Links:
- Download CUET PG Previous Year Question Papers PDF with Solutions
- Download CUET PG 2025 Question Paper for all Subjects
CUET PG Agri-Business Management Question Paper 2024 PDF Download
| CUET PG Agri-Business Management Question Paper 2024 with Answer Key | Check Solutions |

Agri Business Management Questions with Solutions
Question 1:
When E-evaporation, T-transpiration, B-water needs for building up of plant body, CU-consumptive use, ET-evapotranspiration, WR-water requirement, GW-ground water, and ER-effective rainfall, then irrigation requirement (IR) of an individual crop at field head is given by the equation:
View Solution
The irrigation requirement (IR) includes the sum of evaporation, transpiration, water needs for plant body buildup, and special needs. This equation ensures optimal water supply for the crop.
Efficient irrigation management helps reduce water waste and ensures the health of crops, especially in water-scarce regions.
Question 2:
Species of wheat that has gone practically out of cultivation in India because of its low productivity and disease susceptibility is:
View Solution
Triticum sphaerococcum has gone out of cultivation due to its low productivity and susceptibility to diseases compared to other wheat species.
Focusing on high-yield and resilient wheat varieties has been crucial for improving productivity and combating food insecurity.
Question 3:
In view of storage of the world's water resources, the share of groundwater in total water in the hydrosphere is:
View Solution
Groundwater constitutes approximately 3.84% of the total water in the hydrosphere, making it a significant freshwater resource.
Groundwater management is essential for addressing the increasing demand for water in agriculture, industry, and domestic use.
Question 4:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Crops) | List-II (Varieties) |
|---|---|
| (A) Wheat | (I) Pusa Sugandh 5 |
| (B) Rice | (II) HD 2932 |
| (C) Barley | (III) Pusa Composite 383 |
| (D) Pearl millet | (IV) DWR 28 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The matching of crops with their respective varieties reflects their common classifications in Indian agriculture.
Familiarity with crop varieties is essential for improving agricultural practices and crop management.
Question 5:
The critical stage(s) for irrigation in wheat is/are:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
All the mentioned stages are critical for wheat irrigation to ensure proper crop development and high yield.
Critical stages like Crown Root Initiation and Dough stage demand precise water management for optimal wheat yield.
Question 6:
Arrange the following millet crops in increasing order of acreage under each:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The acreage under millet crops varies, with little millet having the smallest acreage, followed by kodo millet, finger millet, and pearl millet.
Millets are an important group of crops, and knowing their acreage helps prioritize crop research and extension services.
Question 7:
The allelochemical allyl isothiocyanate is found in the plant:
View Solution
Allyl isothiocyanate is an allelochemical commonly found in mustard plants and is known for its toxic effects on other plants.
Understanding allelochemicals helps in weed management and natural plant interactions in agriculture.
Question 8:
The phenomenon of one plant having a detrimental effect on another through the production and release of toxic chemicals is termed as:
View Solution
Allelopathy refers to the production of toxic chemicals by plants that inhibit the growth of nearby plants.
This mechanism helps plants reduce competition and create a favorable environment for growth.
Question 9:
The herbicide Metsulfuron methyl belongs to the group:
View Solution
Metsulfuron methyl is a selective herbicide that belongs to the sulfonylureas group, commonly used for broadleaf weed control.
Sulfonylurea herbicides are effective at low doses and are integral to integrated weed management strategies.
Question 10:
Which of the statement(s) is/are correct?
(A) Urea herbicides inhibit photolysis in photosynthesis
(B) Triazines inhibit the growth of emerging seedlings
(C) Sulfonyl ureas first affect the meristematic tissues resulting into chlorosis and necrosis
(D) Paraquat is a systemic herbicide
View Solution
Urea herbicides inhibit photolysis, triazines inhibit seedling growth, and sulfonylureas affect meristematic tissues. Paraquat, however, is a contact herbicide, not systemic.
Identifying herbicide mechanisms helps in targeted and effective weed management.
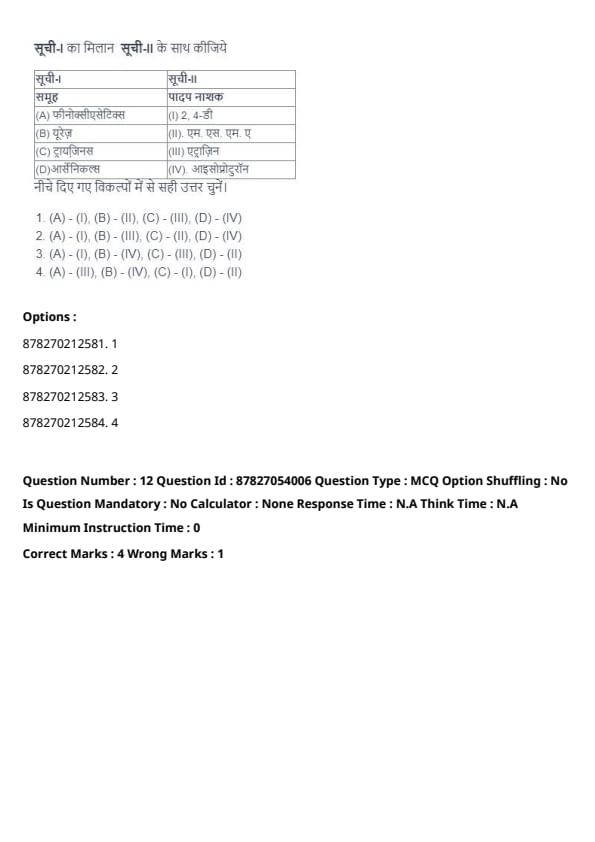
Question 11:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Group) | List-II (Herbicide) |
|---|---|
| (A) Phenoxyacetics | (1) 2,4-D |
| (B) Ureas | (II) MSMA |
| (C) Triazines | (III) Atrazine |
| (D) Arsenicals | (IV) Isoproturon |
View Solution
Each group of herbicides is matched with the appropriate chemical commonly used for weed control.
Knowing the herbicide classification enhances strategic application in weed management.
Question 12:
Some herbicides control weeds by inhibiting photosynthesis. The sequence of reactions involved in the process is:
(A) Production of lipid radical and initiation of chain of lipid peroxidation
(B) Extraction of hydrogen from unsaturated lipids by triplet chlorophyll and singlet oxygen
(C) Oxidation of lipids and proteins
(D) Loss of chlorophyll and carotenoids
View Solution
The inhibition of photosynthesis involves extraction of hydrogen by singlet oxygen, production of lipid radicals, oxidation of lipids and proteins, and subsequent loss of chlorophyll and carotenoids.
Understanding the mechanism of herbicides helps in identifying their action on plants.
Question 13:
Which is not true about organic agriculture?
View Solution
Weed control and fertilization are major challenges in organic agriculture due to restrictions on synthetic chemicals.
Organic farming focuses on sustainable practices but faces challenges in managing weeds and maintaining soil fertility.
Question 14:
Allowed inputs for organic production are:
View Solution
Organic agriculture allows natural inputs like manure, compost, elemental sulfur, and rock phosphate but prohibits synthetic chemicals like glyphosate and imidachloprid.
Organic farming inputs must comply with natural and eco-friendly standards.
Question 15:
Which statement is correct about organic agriculture?
View Solution
Organic farming relies on diverse crop rotations and nonsynthetic insecticides to manage pests sustainably.
Organic agriculture emphasizes biodiversity and ecological practices over synthetic inputs.
Question 16:
Which of the following statements is/are correct about cropping systems?
View Solution
These practices improve soil health, optimize resource use, and enhance productivity in cropping systems.
Integrating legumes and green manure crops in cropping systems enhances soil fertility and sustainability.
Question 17:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (System) | List-II (Description) |
| Agroforestry | A type of system where trees or shrubs are grown for harvest alongside other crops |
| Alley Cropping | A type of agroforestry where trees are grown in rows with annual or perennial crops between the trees |
| Strip Cropping | A polyculture strategy that involves growing crops in adjacent strips within a field |
| Mixed Cropping | A type of polyculture where two or more crops are grown together at random |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Each system is correctly matched with its description, highlighting different cropping strategies used in agriculture.
Understanding cropping systems helps in choosing the right method for specific ecological and economic goals.
Question 18:
Given below are the activities performed while cultivating a crop, arrange them from first to last:
- Ploughing
- Thinning
- Seeding
- Harvesting
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct sequence of activities is ploughing, seeding, thinning, and harvesting, reflecting the logical flow of crop cultivation.
Following the correct sequence in crop cultivation ensures efficient and effective farming operations.
Question 19:
Di-ammonium phosphate contains:
View Solution
Di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) is a widely used fertilizer containing 18% nitrogen and 46% phosphorus, which are essential for plant growth.
DAP is highly effective for early plant growth due to its high phosphorus content.
Question 20:
In a market economy, resources are allocated by:
View Solution
In a market economy, prices serve as the primary mechanism for resource allocation, reflecting supply and demand dynamics.
Understanding price mechanisms helps in analyzing market-driven economies.
Question 21:
If the marginal cost is greater than average cost, it means:
View Solution
When marginal cost (MC) is greater than average cost (AC), it pulls the average cost upward, meaning the average total cost is increasing.
Marginal cost directly affects the average cost curve, and their relationship determines the direction of AC change.
Question 22:
The production possibilities frontier shows:
View Solution
The production possibilities frontier (PPF) shows the maximum possible combinations of two goods that can be produced using a fixed set of resources efficiently.
PPF illustrates trade-offs and opportunity costs in production decisions.
Question 23:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Schemes/Events) | List-II (Year) |
|---|---|
| (A) Lead Bank Scheme | (IV) 1969 |
| (B) All India Rural Credit Survey Committee | (I) 1954 |
| (C) Regional Rural Banks | (II) 1975 |
| (D) Service Area Approach | (III) 1989 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Each scheme or event is matched with its respective year of establishment based on historical records.
Understanding the timeline of financial schemes helps in analyzing their historical impact.
Question 24:
Borrowing funds by the farmers for paying tax to the government is known as:
View Solution
Loans taken by farmers for specific purposes such as paying taxes or investing in productive activities are classified as productive loans.
Understanding loan classifications aids in financial planning and effective use of credit.
Question 25:
Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPG) model of development was introduced by:
View Solution
Dr. Manmohan Singh introduced the LPG model of economic reforms in India in 1991, which aimed at liberalizing the economy, encouraging privatization, and promoting globalization.
The LPG model marked a significant turning point in India's economic history.
Question 26:
The third amendment in the Indian Patent Act was introduced during:
View Solution
The third amendment to the Indian Patent Act was introduced in 2004 to align Indian laws with international standards under TRIPS (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights).
Understanding amendments in the Patent Act is crucial for intellectual property rights.
Question 27:
Consumers' ability to identify the brand under different conditions, as reflected by their brand or recall performance is known as:
View Solution
Brand awareness refers to the extent to which consumers can recognize or recall a brand under various conditions.
Strong brand awareness is vital for creating customer loyalty and market success.
Question 28:
Financial requirements of the farmers can be classified on the basis of time period:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Farmers' financial needs can be categorized as short-term (e.g., for seeds), medium-term (e.g., for machinery), and long-term (e.g., for land development). Very long-term needs are not a common classification.
Proper classification helps in addressing farmers' financial needs effectively.
Question 29:
RBI set up a high-level committee on agricultural credit chaired by Mr. R.V. Gupta, and he recommended:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The committee's recommendations covered multiple areas to improve agricultural credit systems in India.
Understanding recommendations helps in analyzing credit policies for agriculture.
Question 30:
If the data is classified by attributes and if two or more characters are to be compared within each attribute, we use the statistical tool as:
View Solution
A multiple bar diagram is used when comparing two or more variables for each attribute.
Multiple bar diagrams provide a clear visual representation for comparative analysis.
Question 31:
The deviation of individual values from their average is called as:
View Solution
Mean deviation measures the average of absolute deviations of individual data points from their mean. It gives a sense of how spread out the data is around the central value.
Mean deviation is a simple measure of dispersion and is easier to calculate compared to standard deviation.
Question 32:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Rural Development Programmes) | List-II (Year of Starting) |
|---|---|
| (A) Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana | (IV) 2006 |
| (B) Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act | (I) 1999 |
| (C) Swarnajayanti Gram Swarojgar Yojana | (II) 1989 |
| (D) Integrated Watershed Development Programme | (III) 15th August 1993 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The years of initiation for the given rural development programmes are matched as follows:
- (A) Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana started in 2006 (IV).
- (B) Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act started in 1999 (I).
- (C) Swarnajayanti Gram Swarojgar Yojana started in 1989 (II).
- (D) Integrated Watershed Development Programme started on 15th August 1993 (III).
Review rural development programmes by their starting years to understand their historical context and impact.
Question 33:
A process which aims at improving the well-being and self-realization of people living outside the urbanized area through collective processes is known as:
View Solution
Rural development is focused on improving the quality of life and economic well-being in rural areas through community-based initiatives and resource development.
Rural development is essential for bridging the gap between urban and rural communities.
Question 34:
Community Development Programme was launched by the Government of India on:
View Solution
The Community Development Programme was launched on 2 October 1952 to enhance rural socio-economic infrastructure, focusing on education, health, and agriculture.
This program laid the foundation for rural development initiatives in India.
Question 35:
When too much of an input is used, and output decreases, the production process results in:
View Solution
Decreasing returns occur when additional units of input lead to a reduction in total output, indicating inefficiency in resource usage.
Negative returns signify that optimal input levels have been surpassed, causing production inefficiencies.
Question 36:
Arrange the following Rural Development Programmes in chronological order:
- (A) Marthandam
- (B) Gurgaon
- (C) Sarvoday
- (D) Etwah Pilot Project
View Solution
The correct chronological order of Rural Development Programmes is as follows:
- (B) Gurgaon
- (A) Marthandam
- (D) Etwah Pilot Project
- (C) Sarvoday
Chronological order helps in understanding the historical development and implementation sequence of programmes.
Question 37:
A measure of revenue and expenses during a specified accounting period is known as:
View Solution
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, measures revenue and expenses over a specific accounting period, providing a summary of the company's financial performance.
Use the income statement to analyze a business's profitability over time.
Question 38:
India's Share in total World's Buffalo population is:
View Solution
India contributes approximately 53% of the world's buffalo population, making it a significant contributor to the global livestock sector.
India's buffalo population supports its dairy and meat production industries.
Question 39:
The equation, S = (cl, b, r, p, t...) was first formulated by:
View Solution
Hans Jenny formulated the equation \( S = f(cl, o, r, p, t...) \), which describes soil formation as a function of climate (\(cl\)), organisms (\(o\)), relief (\(r\)), parent material (\(p\)), and time (\(t\)).
The soil formation equation highlights the factors influencing soil development.
Question 40:
Which one of the following minerals is a boron mineral in soils?
View Solution
Colemanite is a boron-containing mineral commonly found in soils, which serves as a source of boron for plant nutrition.
Boron is essential for plant growth, especially in cell wall formation and development.
Question 41:
Which of the following statement is/are correct with reference to bulk density?
View Solution
Bulk density depends on soil properties such as texture, structure, and organic matter. Adding organic matter reduces bulk density, while compaction increases it. Fine-textured soils have lower bulk density compared to coarse-textured soils.
Understanding bulk density is important for assessing soil health and root penetration.
Question 42:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Soil Forming Process) | List-II (Description) |
|---|---|
| (A) Laterization | (II) Accumulation of Sesquioxide |
| (B) Podsolization | (IV) Eluviation of Sesquioxide |
| (C) Pedoturbation | (I) Mixing of Soil |
| (D) Gleization | (III) Hydromorphic |
View Solution
Laterization involves accumulation of sesquioxides. Podsolization is characterized by the eluviation of sesquioxides. Pedoturbation involves mixing of soil. Gleization is a hydromorphic process.
Soil forming processes are essential for understanding soil classification and fertility.
Question 43:
A soil, which has pH more than 8.5, ESP more than 15, and EC less than 4 ds/m is called:
View Solution
Alkali soils have a high pH (>8.5), high exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP >15), and low electrical conductivity (EC <4 ds/m), which make them unsuitable for most crops.
Reclamation of alkali soils involves gypsum application and proper drainage systems.
Question 44:
Which one of the following is NOT considered as a chemical weathering?
View Solution
Calcification is a pedogenic process rather than a chemical weathering process. Other options like hydrolysis, carbonation, and reduction are chemical weathering processes.
Chemical weathering alters the mineral composition of rocks and soils.
Question 45:
Arrange the sequence in terms of the increasing order of soil loss from the field due to water erosions:
View Solution
The increasing order of soil loss due to water erosion is:
- Splash erosion (C)
- Sheet erosion (D)
- Rill erosion (B)
- Gully erosion (A)
Proper soil conservation techniques can mitigate water erosion and prevent land degradation.
Question 46:
Size range of soil particles in saltation type of wind erosion is:
View Solution
Saltation is a process in wind erosion where soil particles of size 0.05 to 0.5 mm are lifted by the wind and moved in a series of short jumps. These particles are too heavy to be carried in suspension and too light to remain stationary, causing them to bounce along the surface.
Saltation is a key contributor to soil erosion in arid and semi-arid regions.
Question 47:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I | List-II |
|---|---|
| Chepil and Milne (1941) | Mechanics of soil movement by wind |
| Surface creep | Coarse soil particles |
| Vegetative residue | Protection of soil surface from wind action |
| Strip cropping | Alternate arrangement of erosion susceptibility and erosion-resistant crops |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Chepil and Milne (1941) studied the mechanics of soil movement by wind.
Surface creep involves the movement of coarse soil particles.
Vegetative residues protect the soil surface from wind erosion.
Strip cropping alternates erosion-prone and erosion-resistant crops to prevent soil loss.
Combining vegetative residues and strip cropping enhances soil conservation.
Question 48:
In Universal Soil Loss Equation, A = RKLSCP, K denotes:
View Solution
In the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE):
A refers to average annual soil loss.
R represents rainfall-runoff erosivity factor.
K indicates the soil erodibility factor, which shows the susceptibility of soil to erosion.
L is the slope length factor.
S is the slope steepness factor.
C denotes the crop management factor.
P reflects erosion control practices.
Soil erodibility (K) depends on soil texture, structure, permeability, and organic matter.
Question 49:
The practice of conducting all field operations such as ploughing, planting, and cultivating land across the slope is called:
View Solution
Contour farming involves ploughing, planting, and cultivating land along the contour lines of a slope. This practice reduces water runoff and minimizes soil erosion by creating natural barriers to water flow.
Contour farming is especially effective in hilly and sloped agricultural areas, preventing nutrient loss and soil degradation.
Question 50:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Plant Diseases/Famine) | List-II (Year) |
|---|---|
| Irish Famine | 1845 |
| Bengal Famine | 1943 |
| Coffee Rust | 1870 |
| Downy Mildew of Tobacco | 1950 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Irish Famine occurred in 1845 due to potato blight.
Bengal Famine happened in 1943 due to food shortages.
Coffee rust was identified in 1870.
Downy mildew of tobacco emerged in 1950.
Understanding the history of plant diseases aids in planning better disease prevention and management strategies.
Question 51:
Bordeaux mixture is a mixture of:
View Solution
Bordeaux mixture is a classic fungicide and bactericide made by combining copper sulphate with hydrated lime. It is widely used in agriculture to prevent fungal diseases in crops.
Prepare Bordeaux mixture fresh before use to maximize its effectiveness in disease control.
Question 52:
Who reported that fire blight of pear was caused by a bacterium?
View Solution
T.J. Burrill was the first to identify that the fire blight disease of pear is caused by a bacterium, marking a significant milestone in plant pathology.
Fire blight is caused by Erwinia amylovora, a bacterial pathogen affecting fruit trees.
Question 53:
Arrange the sequence of spore production in Puccinia:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct sequence of spore production in Puccinia is:
- Aeciospores: Produced on the alternate host and spread to the primary host.
- Urediospores: Produced repeatedly during the growing season, allowing infection to spread.
- Teleutospores: Thick-walled spores formed for overwintering.
- Basidiospores: Formed after germination of teleutospores in spring, restarting the infection cycle.
Puccinia species exhibit a heteroecious life cycle, requiring two different hosts to complete their spore stages.
Question 54:
Viroids are discovered by:
View Solution
The discovery of viroids was made by T.O. Diener, who described them as small, circular RNA molecules that cause plant diseases.
Viroids differ from viruses as they lack a protein coat and replicate autonomously within host cells.
Question 55:
Ratoon stunting disease of sugarcane is caused by:
View Solution
Ratoon stunting disease of sugarcane is caused by the bacterium Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli. It reduces cane yield significantly and is spread through infected planting material or mechanical means.
Use clean planting material and sterilized tools to manage ratoon stunting disease effectively.
Question 56:
Arrange the correct sequence of events in a disease cycle:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
- Inoculation: The pathogen comes in contact with the host.
- Penetration: The pathogen enters the host tissue.
- Infection: The pathogen establishes itself and begins multiplying.
- Colonization: The pathogen spreads within the host.
Understanding the disease cycle helps in developing effective disease management strategies.
Question 57:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Cattle Breeds) | List-II (Crossing Breeds) |
|---|---|
| (A) Karan Swiss | (II) Brown Swiss with Sahiwal |
| (B) Karan Fries | (III) Holstein-Friesian with Tharparkar |
| (C) Frieswal | (IV) Holstein-Friesian with Sahiwal |
| (D) Sunandini | (I) Brown Swiss with Red Sindhi |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
- Karan Swiss: Cross of Brown Swiss and Sahiwal.
- Karan Fries: Cross of Holstein-Friesian and Tharparkar.
- Frieswal: Cross of Holstein-Friesian and Sahiwal.
- Sunandini: Cross of Brown Swiss and Red Sindhi.
Cattle breeding enhances milk production and adapts breeds to local environmental conditions.
Question 58:
In open pollinated variety of maize, how much minimum isolation distance is required to produce foundation seed:
View Solution
For open pollinated maize varieties, a minimum isolation distance of 400 meters is required to ensure genetic purity while producing foundation seed. Isolation distances prevent cross-pollination with other maize varieties.
Maintaining isolation distances is critical in seed production to maintain genetic integrity.
Question 59:
Which of the following statements is TRUE about T cytoplasm?
View Solution
T cytoplasm in maize is known to induce male sterility, which is utilized in hybrid seed production. This cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) eliminates the need for manual emasculation in hybrid seed production.
Cytoplasmic male sterility is a tool for producing hybrid seeds in crops like maize.
Question 60:
What was the title of the paper written by Gregor Johann Mendel and published in 1866?
View Solution
Gregor Johann Mendel's paper, "Experiments on Plant Hybridization," published in 1866, laid the foundation for the field of genetics. His experiments on pea plants established the basic laws of inheritance.
Mendel's work went unrecognized during his lifetime but became the cornerstone of modern genetics.
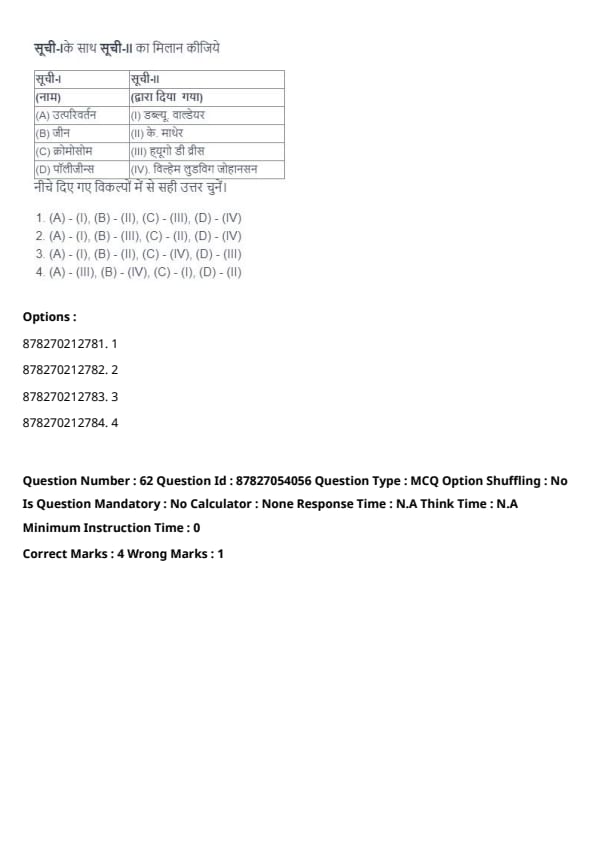
Question 61:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Term) | List-II (Coined by) |
|---|---|
| (A) Mutation | (III) Hugo de Vries |
| (B) Gene | (IV) Wilhelm Ludvig Johannsen |
| (C) Chromosome | (I) W. Waldeyer |
| (D) Polygenes | (II) K. Mather |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The terms and their respective coining are as follows:
Mutation: Hugo de Vries.
Gene: Wilhelm Ludvig Johannsen.
Chromosome: W. Waldeyer.
Polygenes: K. Mather.
Knowing the history of genetic terms helps in understanding the development of genetics as a science.
Question 62:
Arrange the following sub-stages of prophase I in meiotic cell division in the correct sequence:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The correct sequence of sub-stages in prophase I of meiosis:
1. Leptotene: Chromosomes start condensing.
2. Zygotene: Synapsis begins as homologous chromosomes pair.
3. Pachytene: Crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes.
4. Diplotene: Homologous chromosomes start separating, but chiasmata remain visible.
Understanding prophase I is crucial for studying genetic variation mechanisms.
Question 63:
Which of the following statements are correct?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Statement (B): Correct. Polytene chromosomes are large chromosomes formed by repeated DNA replication without cell division.
Statement (C): Correct. Mutation serves as the primary source of genetic variation.
Statement (D): Correct. Mendel's experiments on garden peas revealed traits as two opposing forms (dominant and recessive).
Statement (A): Incorrect. Co-dominance results in both parental traits being expressed, not an intermediate form.
Co-dominance and incomplete dominance are distinct phenomena in genetics.
Question 64:
Which of the following substances can be used to break the dormancy of buds?
View Solution
Gibberellic acid is a plant hormone that promotes growth and breaks bud dormancy by stimulating cell elongation and division.
Gibberellic acid is widely used in agriculture to enhance seed germination and bud growth.
Question 65:
What is a shared characteristic between vegetative reproduction and apomixis?
View Solution
Vegetative reproduction and apomixis both result in progeny that are genetically identical to the parent.
Vegetative reproduction involves parts like stems and roots, while apomixis involves seed formation without fertilization.
Both vegetative reproduction and apomixis help maintain the genetic uniformity of plants.
Question 66:
Which of the following statements are correct with regard to the position of emergence of flower buds in different fruits?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
(A) Mango: Fruit buds are terminal, producing inflorescence without leaves.
(C) Pears: Terminal buds produce leafy shoots that terminate into flower clusters.
(D) Jackfruit: Flower buds appear adventitiously on the old trunk or shoots.
(B) Apple: While buds are terminal and lateral, inflorescence is terminal.
Understanding the position of flower buds aids in proper pruning and cultural practices for fruit crops.
Question 67:
Which of the following systems follows the vertical row planting pattern system of layout?
View Solution
The rectangular system follows a vertical row planting pattern, where plants are aligned in straight rows and columns, ensuring easy access and management practices.
The rectangular system is the simplest and most commonly used planting method in orchards.
Question 68:
Consider the following statements/characteristics about the Gir breed of cattle and choose the correct one:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
The Gir breed is known for its curved horns ("half-moon" shape). It is disease-resistant and hardy, making it a preferred breed for dairy farming. Milk production ranges between 1200-1800 kgs per lactation. Statement (A) is incorrect as the breed originated in Gujarat, India, not Karachi or Hyderabad.
The Gir breed is extensively used in crossbreeding programs for improved milk production.
Question 69:
Climacteric fruits are:
View Solution
Climacteric fruits exhibit a rise in respiration and ethylene production during ripening. Examples include bananas, mangoes, apples, and tomatoes. Grapes, citrus, and peaches are non-climacteric fruits.
Climacteric fruits can be harvested before ripening and ripened during storage.
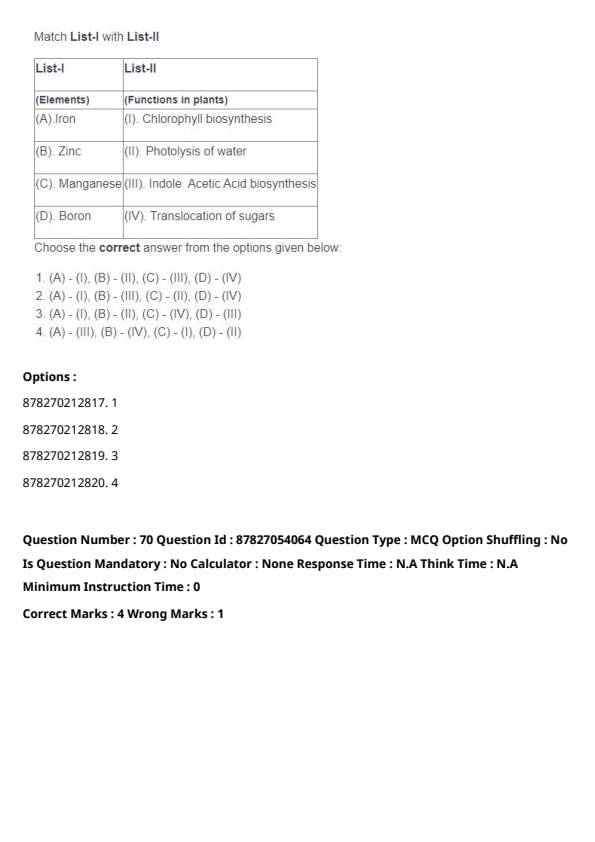
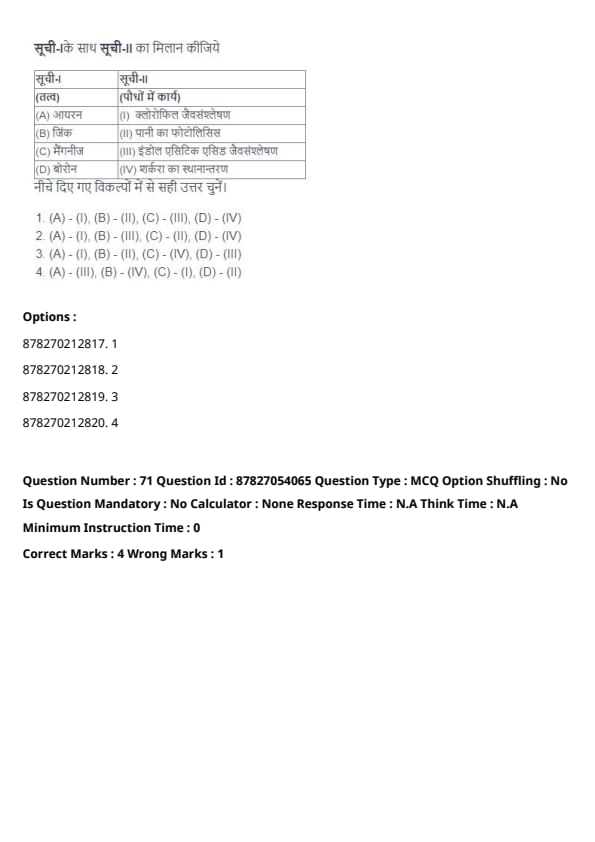
Question 70:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Elements) | List-II (Functions in Plants) |
|---|---|
| (A) Iron | (I) Chlorophyll biosynthesis |
| (B) Zinc | (II) Photolysis of water |
| (C) Manganese | (III) Indole Acetic Acid biosynthesis |
| (D) Boron | (IV) Translocation of sugars |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Iron: Essential for chlorophyll biosynthesis.
Zinc: Plays a role in Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) biosynthesis.
Manganese: Involved in the photolysis of water during photosynthesis.
Boron: Helps in the translocation of sugars.
Balanced micronutrient supply enhances plant growth and productivity.
Question 71:
Arrange the following electron carriers in the correct sequence of electron flow during photosynthesis in the thylakoid membrane:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Plastoquinone accepts electrons from PS-II.
Cytochrome b6-f complex transfers electrons to plastocyanin.
Plastocyanin carries electrons to PS-I.
PS-I reduces NADP+ to NADPH.
Electron flow in the thylakoid membrane is vital for ATP and NADPH production during photosynthesis.
Question 72:
Consider the following statements about agrisilviculture and choose the correct statements:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Agrisilviculture integrates tree crops with agricultural crops to enhance productivity while maintaining soil health. However, it does not inherently involve fodder production, distinguishing it from agro-silvopastoral systems.
Agrisilviculture is effective in controlling soil erosion and providing long-term ecological benefits.
Question 73:
Match List-I with List-II:
| List-I (Pigment) | List-II (Associated with) |
|---|---|
| (A) Phytochrome | (I) Stimulation of flowering |
| (B) Leghaemoglobin | (II) Nitrogen fixation |
| (C) Chlorophyll a | (IV) All photosynthesizing plants except bacteria |
| (D) Chlorophyll d | (III) Red algae |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
Phytochrome: Controls flowering by responding to light quality and photoperiod.
Leghaemoglobin: Facilitates nitrogen fixation in legume nodules.
Chlorophyll a: Found in all photosynthesizing plants except bacteria.
Chlorophyll d: Present in red algae.
Chlorophyll pigments play distinct roles in photosynthesis across different plant groups.
Question 74:
Arrange the following steps involved in the Hatch and Slack cycle in correct sequence:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
View Solution
1. Carboxylation of Phosphoenol Pyruvate to form oxaloacetate.
2. Breakdown of Oxaloacetate into malate.
3. Splitting of Malate to release CO2 for the Calvin cycle.
4. Phosphorylation of Pyruvate to regenerate phosphoenol pyruvate.
The Hatch and Slack cycle is essential for efficient CO2 fixation in C4 plants.
Question 75:
Which nutrient element is involved in energy transformation in metabolic processes?
View Solution
Phosphorus plays a critical role in energy transformation as it is a key component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which acts as the energy currency in metabolic processes.
Adequate phosphorus availability is essential for energy metabolism and plant growth.












































































































Comments