Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Ruthenium was discovered in 1844 by Karl Klaus at Kazan State University. The official symbol of this element is ‘Ru’. Ruthenium has an atomic mass of 101.1 g.mol -1. The atomic number of this element is 44. Ruthenium is a rare transition d block element and belongs to the group of platinum in the periodic table.
Also Read: Electronegativity Chart of Elements
Ruthenium
- Ruthenium is a d block element of the periodic table with an atomic number 44.
- Ruthenium is the 74th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust.
- It is a rare transition metal.
- It has a silvery and shiny appearance.
- It is found as a free metal and can be easily detected in platinum ores.
- It is found in the Ural Mountains in North and South America.
- A small amount of ruthenium is also found in pentlandite mines in Ontario, Sudbury, Canada, and a few deposits in pyroxenite mines in South Africa.
The video below explains this:
Ruthenium Detailed Video Explanation:

Ruthenium
Chemical properties of Ruthenium
- Ruthenium belongs to group 8 and period 5.
- The density of this element is 12.1.
- Its melting point is 2250oC whereas its point of ruthenium is 4150oC.
- Ruthenium has a solid-state at 20oC.
- It belongs to block d.
- The atomic number of ruthenium is 44 and the relative atomic mass of this element is 101.07.
- The CAS number of ruthenium is 7440-18-8.
- The electronic configuration of ruthenium is [Kr] 4d75s1

Chemical Representation of Ruthenium
General Properties of Ruthenium
- Ruthenium is a member of the periodic table that falls under the platinum group.
- It is sometimes associated with nickel deposits.
- It is generally found as a free metal in the environment.
- It is occasionally found as a chemical combination with iridium, platinum, or osmium ores.
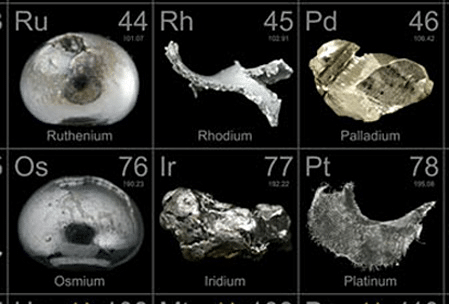
Uses of Ruthenium
- Ruthenium is used as an exotic material.
- It is used in the manufacturing of electronic devices.
- It is employed in olefin metathesis.
- It is used as a catalyst in Fischer Tropsch synthesis.
- It is also used during the manufacture of solar cells.
Ruthenium in Electronic Devices
Things to Remember Based on Ruthenium
- Ruthenium is a d block element of the periodic table.
- The official symbol of ruthenium is ‘Ru’.
- The CAS number of ruthenium is 7440-18-8.
- The electronic configuration of ruthenium is [Kr] 4d75s1
- It is a rare transition metal found in the Ural Mountains in North and South America.
- Ruthenium is silvery and shiny in appearance and is frequently found in platinum ores.
- Ruthenium belongs to group 8 and period 5 and its relative atomic mass is 101.07.
- The melting point of this element is 2250oC and the boiling point is 4150oC.
- Ruthenium is generally found as a free metal in the environment. It is occasionally found as a chemical combination with iridium, platinum, or osmium ores. It is sometimes associated with nickel deposits.
Important Questions Based on Ruthenium
Ques: Which of the following is not a d block element: (1 Mark)
- Cerium
- Ruthenium
- Scandium
- Zinc
Ans: a) Cerium
Ques: Which d block element shows the largest number of oxidation states? (1 Mark)
Ans: Manganese exhibits the largest number of oxidation states.
Ques: Where is Ruthenium found? (2 Marks)
Ans: Ruthenium is found as a free metal in platinum ores. It is found in the Ural Mountains in North and South America. Small amounts of ruthenium are also found in pentlandite mines in Ontario, Sudbury, Canada, and a few deposits in pyroxenite mines in South Africa.
Ques: Mention some applications of Ruthenium. (2 Marks)
Ans: Applications of Ruthenium:
- Ruthenium is used in electrical contacts to achieve durability.
- Ruthenium is also employed in thick-film chip resistors.
- It is used as a catalyst in Fischer Tropsch synthesis.
- It is used as an alloy with palladium and platinum.
Ques: Write a note on Ruthenium. (3 Marks)
Ans: Ruthenium is a d block element in the periodic table with atomic number 44. The official symbol of this element is ‘Ru’. The melting point of this element is 2250 ?C and the boiling point of ruthenium is 4150?C. The period of ruthenium is 5. The electronic configuration of ruthenium is [Kr] 4d75s1. Ruthenium falls under the platinum group and it has multiple uses. It is used as an exotic material. It is employed in olefin metathesis and Fischer Tropsch synthesis.
Ques: What are D Block Elements? (3 Marks)
Ans: D block elements are elements that have 1 to 10 electrons in the d-orbital of the penultimate energy level and 1 to 2 electrons in the s-orbital. D block elements exhibit metallic properties.
There are four series under the d block elements:
- 3d series, also called the first transition
- 4d series, also called the second transition
- 5d series, also called the third transition
- 6d series, also called the fourth transition
Ques: What are F Block Elements? (3 Marks)
Ans: F block elements are elements that have anywhere between 1 to 14 electrons in the f orbital and 0 or 1 electron in the d orbital. F block elements are a subset of the 6th and 7th periods. They are also called inner transition metals.
There are two series under f block elements:
- 4f series
- 5f series
Ques: Mention all the D Block Elements of the periodic table. (5 Marks)
Ans: D block elements:
- 3d series (first transition)
Scandium (Sc), Titanium (Ti), Vanadium (V), Chromium (Cr), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), Nickel (Ni), Copper (Cu), and Zinc (Zn).
- 4d series (second transition)
Yttrium (Y), Zirconium (Zr), Niobium (Nb), Molybdenum (Mo), Technetium (Tc), Ruthenium (Ru), Rhodium (Rh), Palladium (Pd), Silver (Ag), and Cadmium (Cd).
- 5d series (third transition)
Lanthanum (La), Hafnium (Hf), Tantalum (Ta), Tungsten (W), Rhenium (Re), Osmium (Os), Iridium (Ir), Platinum (Pt), Gold (Au), and Mercury (Hg).
- 6d series (fourth transition)
Actinium (Ac), Rutherfordium (Rf), Hahnium (Ha), Seaborgium (Sg), Bohrium (Bh), Hassium (Hs) and Meitnerium (Mt). This series is still considered to be incomplete.
Ques: Mention the F Block Elements in the periodic table. (5 Marks)
Ans: F block elements:
- 4f series (Lanthanides)
Lanthanum (La), Cerium (Ce), Praseodymium (Pr), Neodymium (Nd), Promethium (Pm), Samarium (Sm), Europium (Eu), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysprosium (Dy), Holmium (Ho), Erbium (Er), Thulium (Tm), Ytterbium (Yb), and Lutetium (Lu).
- 5f series (Actinides)
Actinium (Ac), Thorium (Th), Protactinium (Pa), Uranium (U), Neptunium (Np), Plutonium (Pu), Americium (Am), Curium (Cm), Berkelium (Bk), Californium (Cf), Einsteinium (Es), Fermium (Fr), Mendelevium (Md), Nobelium (No), and Lawrencium (Lw).



Comments