Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Chemistry is one of the three major sub-disciplines of science. Chemistry is the study of matter present in the universe, the properties of matter, how substances are able to transform and evolve to form new substances. Chemistry is considered a central science as it plays a foundational role in the understanding of scientific disciplines (basic and applied) at fundamental levels. ![Chemical Formula]()
![Chemical Reactions]()
The list of all chemistry articles is given below. Click on a category to acess all articles.

Chemical Formula
Check Also: CBSE Class 12 Chemistry: Question Bank Aspects of Chemistry
- Periodic Table is the tabular presentation of all Chemical Elements known to mankind. It contains information about the elements such as atomic mass, weight, and chemical symbol. Elements are organized in rows (called periods) and columns (called groups) in increasing atomic number. The first version of the Periodic Table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1896.

Periodic Table
- Chemical Reaction is a process where one or more substances (reactants), are converted to different substances (products) via breakage and formation of chemical bonds. Chemical Equation is used to describe a chemical reaction. The Chemical Equation are a symbolic representation of the identities and quantites of the substances involved in the chemical reaction.
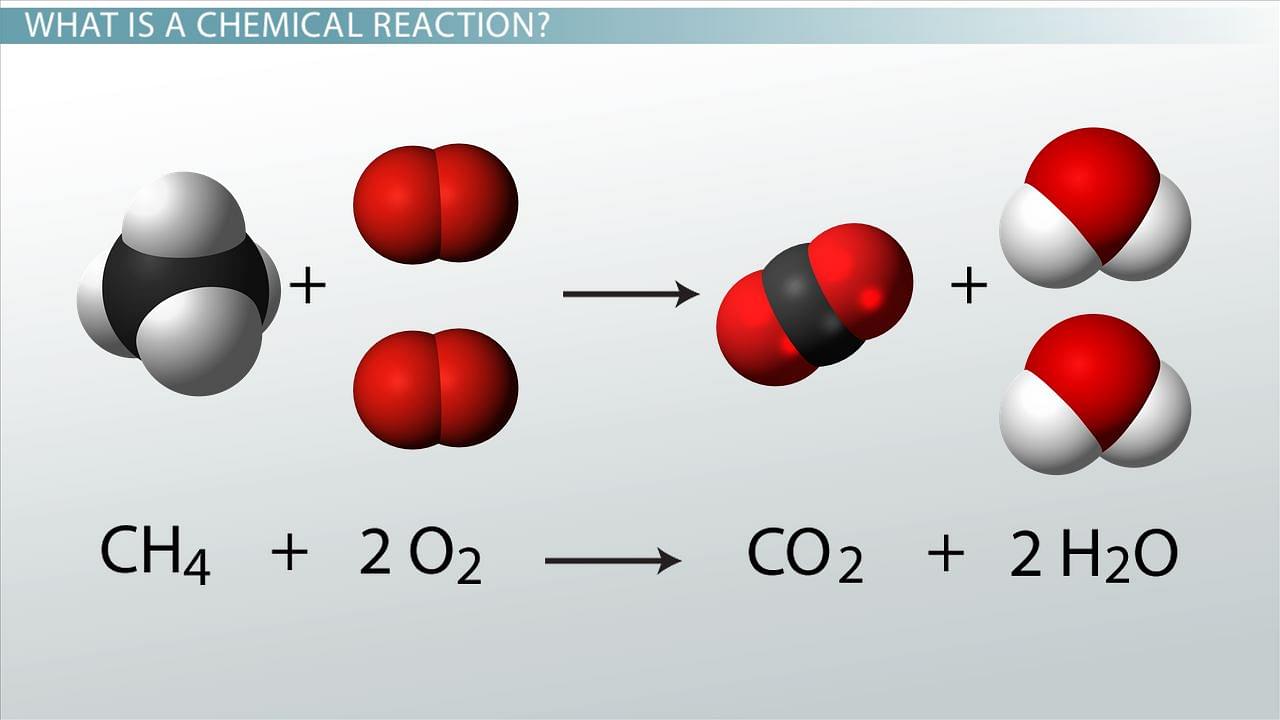
Chemical Reactions
- Atoms and Molecules are the foundational blocks of all creation. Atoms are known as the “basic building blocks of matter”. Molecules are formed when multiple atoms join and form a bond together. The study of atoms and molecules is essential to the study of the universe. It allows scientists a deeper understanding of how all matter functions and what properties are exhibited by various substances.
- Chemistry is an integral part of life and can be found everywhere from the functioning of the human body to the formation of stars in distant universes. The presence of chemistry and chemical reactions are everywhere. As students, you are introduced to the study of chemistry from the primary level itself and are required to study until at least Grade 12. Given below are a number of Study Guides essential to Chemistry at all levels of education.
List of Articles
Chemical Compounds
Difference Between Articles
Chemical Formulas
Biomolecules
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxyllic Acids
Chemical Reactions and Equations
Periodic Classification of Elements
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Chemistry Important Topics
CBSE Class 11 & 12 Study Guides




Comments