Arpita Srivastava Content Writer
Content Writer
Nitrogen Dioxide is a highly reactive gas in the nitrogen oxides category. It is formed by the combination of nitrogen and oxygen.
- Nitrogen Dioxide gas is created by natural sources, motor vehicles, and other fuel combustion processes.
- The formula of the compound is NO2.
- It is an odourless, acidic, and extremely corrosive gas and can harm our health and the environment.
- Nitrogen Dioxide is also used as a catalyst in rocket fuels.
- It completely turns into a reddish-brown gas at high temperatures.
- The colour of the compound changes into a yellow-brown liquid when the compound is compressed.
- The compound is paramagnetic in nature.
- It is used in the production of fertilizers and the synthesis of nitric acid.
Read More: Class 12 Dinitrogen
Key Terms: Nitrogen Dioxide, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Molecule, Atom, Carbon, Element, Compound, Nitric Acid, Paramagnetic
What is Nitrogen Dioxide?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Nitrogen dioxide is a nitrogen and oxygen-based chemical compound. It is one of a group of nitrogen oxides.
- It is also known as Nitrogen oxide or Deutoxide of Nitrogen.
- NO2 is a byproduct of the industrial synthesis of nitric acid.
- It is used to produce millions of tonnes of fertiliser, which is used in the manufacturing industries.
- Nitrogen Dioxide can be used in the production of dyes and lacquers.
- The compound is part of the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants.
- If inhaled in significant amounts, it can be dangerous.
Read More: Class 12 Group 15 Elements
Formula of Nitrogen Dioxide
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Any compound's chemical formula can be either empirical or molecular. A molecular formula describes the number of atoms of each element in one molecule, whereas an empirical formula specifies the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound.
- In nitrogen dioxide, the simplest whole number ratio of nitrogen vs oxygen is 1:2.
- So, the empirical and chemical formula of nitrogen dioxide is NO2.
- In this, one nitrogen atom combines with two oxygen atoms to form a covalent compound.
- It involves the sharing of electrons between oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
- The boiling point of nitrogen dioxide is 21.15 °C.
- The melting point of nitrogen dioxide is −9.3 °C.
| Category | Data |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 46.006 g/mol |
| Bond Angle | 134.4 Degree Celsius |
| Melting Point | −9.3 °C |
| Boiling Point | 21.15 °C |
| Density | 1.880 g/dm3 |
Read More: Electron Gain Enthalpy
Nitrogen Dioxide Structure
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The electrical structure of nitrogen dioxide is known to be O=N-O. Because nitrogen dioxide possesses an unpaired electron, it behaves like any other odd molecule.
- The monomer NO2 has an angular structure, with angle = 134 degrees and distance = 1.18 Ao.
- The distance between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms is 119.7 Pico meters.
- At low quantities of nitrogen dioxide, it is a negligibly slow process.
- When combined with dinitrogen tetroxide gas, it tends to exist in an equilibrium state.
- The chemical equation involved in the process is as follows: 2NO2 ----→ N2O4.
- Since nitrogen has one unpaired electron, it's ground electronic state is doublet.
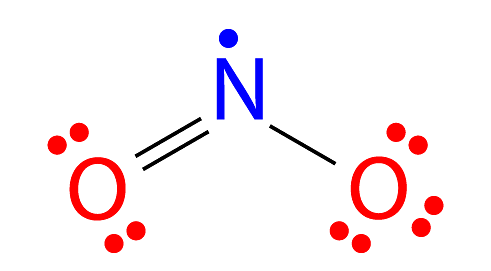
Structure of Nitrogen Dioxide
Also Read:
Preparation of Nitrogen Dioxide
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Nitrogen dioxide can be prepared by a variety of methods. The following are some of the methods for producing nitrogen dioxide.
- Nitrogen dioxide is usually created when nitric oxide in the air is oxidised by oxygen.
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
- Nitrogen dioxide is produced by most combustion processes that use air as an oxidant. At high temperatures, nitrogen reacts with oxygen to generate nitric oxide.
O2 + N2 → 2NO
2NO + N2 → 2NO
- Some metal nitrates, such as lead nitrate, break thermally and produce nitrites.
2Pb(NO3)2 → 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
- The action of strong nitric acid on copper turnings produces nitrogen dioxide in the laboratory.
4HNO3 + Cu → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
- In the laboratory, nitrogen dioxide is made by dehydrating nitric acid to form dinitrogen pentoxide, which is then thermally destroyed to produce nitrogen dioxide.
2HNO3 → N2O5 + H2O
2N2O5 → 4NO2 + O2
Read More: Types of solutions
Sources of Nitrogen Dioxide
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Nitrogen dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere directly. Nitrogen oxide (NO) and other nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the air interact with other chemicals to generate nitrogen dioxide.
- The largest source of nitrogen dioxide is the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, gas, and oil), particularly gasoline used in automobiles.
- It is also formed during the creation of nitric acid, welding and using explosives, refining fuel and metals, commercial manufacturing, and food processing.
- Natural sources of nitrogen oxides include volcanoes and microbes.
- Buses, cars and trucks are the largest sources of nitrogen dioxide.
Read More: Critical temperature
Nitrogen Dioxide Uses
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The various uses of Nitrogen Dioxide are as follows:
- Nitrogen dioxide is used as an intermediary in the production of nitric acid.
- It is used to make oxidized cellulose molecules.
- It is used as a catalyst in many reactions.
- The compound is used as an oxidizer for rocket fuels.
- Nitrogen Dioxide is used as a nitrating agent and an oxidizing agent.
- It is used as an intermediate in the production of sulphuric acid.
- The compound is used in the preparation of explosives.
- It is used in the bleach flour.
- Nitrogen Dioxide is used in the manufacturing of cellulose compounds.
Chemical Properties of Nitrogen Dioxide
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The chemical properties of Nitrogen Dioxide are as follows:
- As an oxidizer: Nitrogen Dioxide is a powerful oxidant because of the weak N–O bond.
- Hydrolysis reaction: Nitrous acid and nitric acid are produced via the hydrolysis reaction.
2NO2 (N2O4) + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
- Nitrite formation: Alkyl and metal iodides produce similiar nitrites.
2 CH3I + 2NO2 → 2CH3NO2 + I2
TiI4 + 4NO2 → Ti(NO2)4 + 2I2
Read More: Colloids
Effect of Nitrogen Dioxide on Health
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Nitrogen dioxide has a number of negative consequences on the body. The following are the effects of Nitrogen Dioxide on Health:
- Nitrogen Dioxide increases airway inflammation
- It will worsen cough and sneeze
- Nitrogen Dioxide will decrease the capacity of the lungs.
- High inhalation of the compound will cause an allergic response.
- It will increase the probability of respiratory problems
- It will cause a burning sensation in the eyes and skin.
Also Check:
Things to Remember
- Nitrogen Dioxide is a highly reactive gas with molecular formula NO2 oxides.
- It is formed by the combination of nitrogen and oxygen.
- It is an odourless, acidic, and highly corrosive gas and can harm our health and the environment.
- It is the byproduct of the industrial synthesis of nitric acid.
- Nitrogen dioxide levels in the air have also been associated with an increase in respiratory illness mortality and hospitalizations.
- It is used as an oxidizing agent and as an intermediate in the manufacture of nitric acid and oxidized cellulose compounds.
Sample Questions
Ques: Is nitrogen dioxide ionic or covalent? (1 Mark)
Ans: Nitrogen dioxide is a covalent molecule in which one nitrogen atom is central and is coupled to two oxygen atoms, one of which is bonded by a single bond and the other by a double bond.
Ques: Is nitrogen dioxide a greenhouse gas? (1 Mark)
Ans: Nitrogen dioxide is vital in the process of creating tropospheric ozone. Neither nitric oxide nor nitrogen dioxide are greenhouse gases.
Ques: What is nitrogen dioxide? (2 Marks)
Ans: Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is a gaseous air pollutant made up of nitrogen and oxygen that belongs to the nitrogen oxides (NOx) family of gases. NO2 is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil, gas, or diesel are burned at high temperatures.
Ques: Where is nitrogen dioxide found? (2 Marks)
Ans: Vehicles, power plants, industrial emissions, and off-road sources such as construction, lawn, and gardening equipment all emit nitrogen dioxide. All of these sources rely on fossil fuels to operate.
Ques: Is nitrogen dioxide heavier than air? (2 Marks)
Ans: Nitric oxide is easily oxidized in the air to create nitrogen dioxide at high concentrations. Expositions. Because nitrogen dioxide is heavier than air, it can cause asphyxiation in inadequately ventilated, sealed, or low-lying spaces. Both nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide are gases that exist at ambient temperature.
Ques: Is nitrogen dioxide harmful to humans? (2 Marks)
Ans: Higher doses of nitrogen dioxide are known to be detrimental to people because it is a toxic gas. It can harm the respiratory system, particularly the lungs, as well as increase the risk of respiratory infections and asthma. Chronic lung illnesses can also be caused by long-term exposure to nitrogen dioxide gas.
Ques: What does nitrogen dioxide do? (2 Marks)
Ans: The main effect of breathing in high levels of nitrogen dioxide is an increased risk of respiratory problems. Nitrogen dioxide irritates the lining of the lungs, lowering immunity against lung infections. Wheezing, coughing, colds, pneumonia, and bronchitis are diseases caused by nitrogen dioxide.
Ques: What is nitrogen dioxide used for? (3 Marks)
Ans: The following are the uses of nitrogen dioxide:
- NO2 is used as a catalyst in various oxidation operations.
- It is used as an inhibitor to prevent acrylate polymerization during distillation.
- It is used as an organic compound nitrating agent.
- Used as an oxidizing agent
- Used as a rocket fuel.
- It is used as a flour-bleaching agent.
Ques. What is the molar mass of nitogen dioxide? (2 marks)
Ans. The molar mass of nitrogen dioxide is calculated as follows:
- Molar Mass = Atomic Mass of Nitrogen + 2 x Atomic Mass of Oxygen
- Molar Mass = 14.0067 + 2 × 15.999
- Molar Mass = 46.0055 gram per mole
Ques. Calculate the net charge on nitrogen dioxide? (3 marks)
Ans. The net charge on nitrogen dioxide is calculated as follows:
- Let us assume that the net charge on nitrogen is x.
- The valency of nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide is + 4.
- The charge on oxygen atom is – 2.
- x + 2 × (−2) = 0
- x = 4
So the net charge on nitrogen dioxide is 0
Ques. What are the main sources of nitrogen dioxide? (3 marks)
Ans. The main sources of nitrogen dioxide are as follows:
- It is produced from cars, buses and trucks.
- The main source of nitrogen dioxide includes the burning of fuels.
- It is caused by wielding and usage of explosives.
- Volcanoes and microbes are natural sources of nitrogen dioxide.
Check-Out:



Comments