Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Ammonium Nitrate is an artificially synthesized compound which is widely known in agricultural production. The chemical formula of Ammonium Nitrate is NH4NO3 which consists of NH4+(ammonium ion) & NO3+(nitrate ion). It is not found in nature due to ammonium nitrate’s high solubility in water. Since Ammonium nitrate is one of the vastly used nitrogen compounds out there. Let’s have a descriptive look at it in this article.
What is Ammonium Nitrate?
Ammonium Nitrate is an acidic salt. The grains of ammonium nitrate are of a solid crystalline structure. It consists of Nitrogen(2), hydrogen(4) & oxygen(3) atoms. There is an ionic bond between NH4+ (ammonium ion) and NO3+ (nitrate ion).

Ammonium Nitrate
Read More:
Chemical Structure of Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium Nitrate has an ionic bond between NH4+and NO3+. This ionic bond is formed by NH?? because there is delocalization of π-bond due to the ability of resonance of nitrate NO3+.
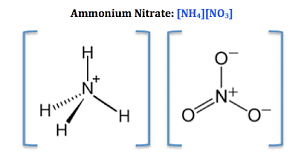
Ammonium Nitrate Structure
Chemical Properties of Ammonium Nitrate
- Ammonium Nitrate is a weak acidic salt. It has a pH of 5.4 (<7)
- The molar weight or mass of ammonium nitrate is 80.044 g/mol.
- It is an inorganic compound.
- When in solid state, ammonium nitrate is a hygroscopic compound. It has a natural tendency to absorb or attract water on its surface.
Ammonium nitrate structure
- Ammonium Nitrate is not flammable. So, it is not reactive on its own, but in the contact of any combustible compound with a temperature of more than 210?, it gets combustible.
- It works as an accelerator. As a result, some toxic nitrogen oxides and water get produced.
- Ammonium nitrate produces by-products such as H2O, N2, O2 at a specific temperature.
- The heat of formation of ammonium nitrate is -365.6 Kj/mol at room temperature(25oC).
Read More:
Physical Properties Of Ammonium Nitrate
- Ammonium Nitrate is mostly colourless or white crystalline salt in solid state but the colour varies from grey to brown sometimes.
- The melting point of ammonium nitrate is 337.8oC.
- Ammonium Nitrate has a boiling point of 200 - 260oC, where it gets decomposed.
- At room temperature, 213 grams of ammonium nitrate is soluble in 100 grams of water.
- Ammonium nitrate is fully soluble in alcohol, acetone, alkalies and ammonia.

Brown Ammonium Nitrate
- It is insoluble in ether & half soluble in methanol (which is 17.1g per 100 cc).
- The density of ammonium nitrate at room temperature is approx 1.7g/cm3.
- In water, the vapour pressure is 2.3 KPa(20oC).
- Ammonium nitrate is a strong electrolyte and therefore it has high conductivity due to its easily solvable ions.
- It has an endothermic (positive) enthalpy of fusion and the enthalpy of solution is exothermic (Negative).
- The heat capacity of ammonium nitrate is 139.3 j/ moloC at 25oC.
Read More:
Preparation methods of Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium nitrate can be prepared by various processes as follows.
Industrial Process: The industrial process follows the simple acid-base reaction to form the acidic salt, Ammonium Nitrate.
HNO3 + NH3 → NH4NO3
The water-free ammonia NH3 is produced by a Haber-Boss process. With the anhydrous ammonia & nitric acid, ammonium Nitrate is formed. When the reaction is 80% completed, the remaining water gets evaporated and 99% ammonium nitrate is formed.
Through Metathesis reactions: The metathesis process is where the participating chemical compounds undergo an exchange in the chemical bonds resulting in the formation of identical or similar bond affiliations.
(NH4)2 SO4 + Ba(NO3)2 → 2NH4NO3 + BaSO4
NH4Cl + AgNO3 → NH4NO3 + AgCl
Through Nitrophosphate process: It is the process by which N2 fertilizers are produced.
Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + 2NH3 + H2O → 2NH4NO3 + CaCO3
Read More:
Chemical reactions of Ammonium Nitrate
- Ammonium Nitrate reacts with itself where it gets self-decomposed at higher temperature and produces 2 molecules of Nitrogen, 1 molecule of oxygen atom and 4 molecules of water.
2NH4NO3 →2 N2 + O2 + 4H2O
- Below 300oC, ammonium nitrate produces nitrous oxide and two molecules of water.
NH4NO3 → N2O + 2H2O
- With metal hydroxides, it produces ammonia & metal nitrate with excess water as a byproduct.
NH4NO3 + XOH → NH3 + H2O + XNO3
Where, X is a metal.
Uses of Ammonium Nitrate
Agricultural production: As a fertilizer, liquid Ammonium Nitrate is used in agricultural productions. The nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium ratio is nitrogen centered (which is approx 34%). An advantage of ammonium nitrate is that it doesn’t lose nitrogen easily in the air. Since it is highly soluble in water, plants get proper nutrition through it and increase the production rate.

Ammonium Nitrate in agriculture
Rocket Propellant: Due to the property of working as an accelerator with combustion compounds, ammonium nitrate is used as an oxidizer in rocket propellants. This oxidizer is produced by mixing it with nitric acid. The mixture is called Cavea-B.

Rocket Propellant
Freezing agent: It is used for instant packaging of frozen products.
Explosives: Solid ammonium nitrate is used as an explosive compound. Though it isn’t flammable, the prills or grains work as an accelerator. 6% of fuel oil and 94% of ammonium nitrate are used as an explosive in mineral mining and stone quarrying.
Fertilizer: Ammonium nitrate is used as a nutrient fertilizer of antibiotics & eatable microbes such as yeast.
Absorber: It is also an absorber of Nitric oxides.
Also Read:
Abuses of Ammonium Nitrate
- While ammonium nitrate has quite impressive uses, its explosive nature is inevitable. It is used by terrorists for illegal purposes such as bombing & blasting government properties.

Ammonium nitrate explosions
- A little amount of LD50 contains 2217 mg/kg of Ammonium nitrate which is lethal for the human population.
Things to Remember
- Ammonium Nitrate is a weak acidic salt. It has a pH of 5.4(<7)
- It is a hydrogenic compound. It has a natural tendency to absorb or attract water on its surface.
- At room temperature, 213 grams of ammonium nitrate is soluble in 100 grams of water.
- The industrial process follows the simple acid-base reaction to form the acidic salt, Ammonium Nitrate.
- As a fertilizer, liquid Ammonium Nitrate is used in agricultural productions.
- Ammonium Nitrate is mostly colourless or white crystalline salt but the colour varies from grey to brown sometimes.
- Ammonium nitrate is a strong electrolyte and therefore it has high conductivity due to its easily solvable ions
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. What is NH4NO3? Identify if it is a base or acid? (3 marks)
Ans: NH4NO3 is a chemical compound made of NH4+ (ammonium ion) & NO3-(nitrate ion) . It consists of colourless crystalline structured grains or prills (granules). It can be found in both forms of liquid and solid. The structure of NH4NO3 is formed of ionic bonds. Ammonium Nitrate is a strong electrolyte. NH4NO3 is an acidic salt with pH 5.4.
Ques. Write down the Industrial process of preparing NH4NO3? (3 marks)
Ans: The industrial process follows the simple acid-base reaction to form the acidic salt, Ammonium Nitrate.
HNO3+NH3NH4NO3
The water-free ammonia(NH3) is produced by a Haber-Boss process that is a compound of nitrogen & hydrogen. With the anhydrous ammonia & nitric acid, ammonium Nitrate is formed.
When the reaction is 80% completed, the remaining water gets evaporated and 99% NH4NO3 is formed.
Ques. Why ammonium nitrate is preferred over urea in agriculture? (3 marks)
Ans: As a fertilizer, liquid Ammonium Nitrate is used in agricultural productions. The nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium ratio is nitrogen centered( which is approx 34%).An advantage of
NH4NO3 is that it doesn’t lose nitrogen easily in the air. But urea loses nitrogen while being in the soil.
And though the concentration of Ammonium Nitrate is less, still its high solubility in water helps plants to get proper nutrition through it and increase the production rate. Hence, ammonium nitrate is more preferred than urea.
Ques. Write down the reaction of ammonium nitrate when it reacts with (3 marks)
i) NaOH, ii)KOH
Write the name of by-products of the reactions.
Ans: i)NH4NO3+NaOHNH3+H2O+NaNO3
The byproducts are ammonia and sodium nitrate
ii)NH4NO3+KOHNH3+H2O+KNO3
The byproducts are ammonia and potassium nitrate.
Ques. What is the occurrence of NH4NO3? (3 marks)
Ans: NH4NO3 doesn’t get found in nature. It is due to ammonium nitrate’s high solubility in water. First, it was artificially synthesized by German chemist Johann Rudolf Glauber in 1659.
But, there is a natural mineral named nitrimmite(gwihabaite) found in the desert in Chile. From this mineral ammonium nitrate used to be produced until the synthetic process was developed.
Read More:
Ques. Why ammonium nitrate is explosive? (3 marks)
Ans: Solid NH4NO3 is used as an explosive compound. Though,NH4NO3 isn’t flammable. So, it isn’t reactive on its own, but in the contact of any combustible compound with a temperature of more than 210oCIt works as an accelerator. As a result, some toxic nitrogen oxides and water get produced.
Ques. Write down some uses of ammonium nitrate? (3 marks)
Ans: Some uses of NH4NO3 are-
- Liquid ammonium Nitrate is used in agricultural productions as a fertilizer.
- As a freezing agent, it is used for instant packaging of frozen products.
- Solid NH4NO3 is used as an explosive compound.
- NH4NO3 used as a nutrient fertilizer of antibiotics & edible microbes such as yeast.
- It is also a good absorber of Nitric oxides.
Ques. Calculate the molecular weight of NH4NO3(3 marks)
Ans:NH4NO3 have Nitrogen(2), hydrogen(4) & oxygen(3) atoms.
∴Molecular weight of NH4NO3=2x(Molecular weight of Nitrogen)+3x(Molecular weight of oxygen)+4x(Molecular weight of hydrogen)
=2x(14.0067)+3x(15.999)+4x(1.00784)
=80.04176 g/mol
Read More:
Ques. Write down 2 physical & 2 chemical properties of NH4NO3(3 marks)
Ans: 2 physical properties are-
- Ammonium Nitrate is mostly colourless or white crystalline salt but the colour varies from grey to brown sometimes.
- The suitable temperature of its decompose is (>)170oC.
2 chemical properties are-
- Ammonium Nitrate is a weak acidic salt. It has the pH of 5.4(<7)
- When in solid state, NH4NO3 is a hygroscopic compound. It has a natural tendency to absorb or attract water on its surface
Ques. Briefly describe & draw the lewis dot structure of NH4NO3. (3 marks)
Ans: NH4NO3 have an ionic bond between NH4+ and NO3-.This ionic bond is formed by NH4+ because there is a delocalization π-bond due to the ability of resonance of nitrate NO3-.
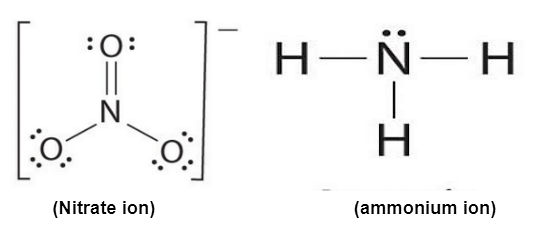
Read More:



Comments