Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Hexane, or n-hexane, is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane having six carbon atoms.
- The molecular formula of hexane is C6H14.
- It is a colorless, odorless liquid with a boiling point of around 69 °C (156 °F).
- It is widely used as a low-cost, reasonably safe, mostly unreactive, easily evaporated non-polar solvent, with modern gasoline blends containing around 3% hexane.
- Hexanes are a mixture that contains more than 60% n-hexane, various amounts of the isomeric compounds 2-methylpentane and 3-methylpentane, and possibly a smaller amount of nonisomeric C5, C6, and C7 (cyclo) alkanes.
- These "hexane" mixtures are less expensive than pure hexane.
- They are commonly used in large-scale processes that do not need a single isomer (such as cleaning solvent or chromatography).
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Hexane, Chemical formula, Isomeric compounds, Alkanes, Polar solvent, Carbon, Hydrogen, Density, Solubility, Organic compounds
What is Hexane?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
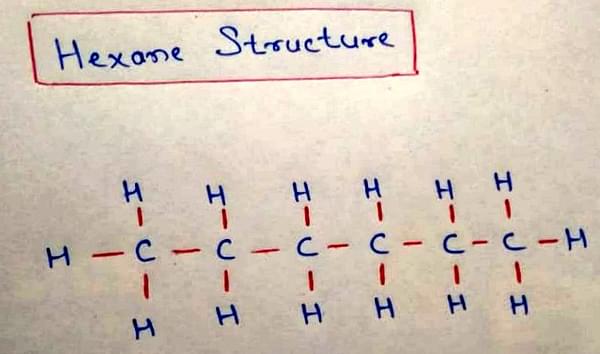
Hexane is a straight-chain hydrocarbon having 6 Carbon and 14 hydrogen atoms bonded together with single bonds.
- It is a colorless, odorless, largely unreactive, volatile, non-polar solvent.
- The other names of hexane are- Amyl Carbinol, 1-hexanol, 1- Hydroxyhexane, and hexyl alcohol.
- Hexane has isomers that are formed on the basis of different arrangements of carbon as 2-methyl pentane, 3-methyl pentane, 2-2 dimethyl butane, etc.
Some details about hexane are given in the table
| Hexane | |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H14 |
| Density | 655 kg/m³ |
| Types of Hydrocarbon | Saturated hydrocarbon |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 86.18 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 68.5 to 69.1 °C |
| Melting Point | −96 to −94 °C |
Also check:
| Related Concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Isomerism in Coordination Compounds | Werners Theory of Coordination Compounds | Aliphatic Hydrocarbons |
| Coordination Compounds | Elements and Compounds | Classification of Organic Compounds |
Hexane Structure
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The structure of Hexane (C6H14) is shown below
Properties of Hexane
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Hexane shows different physical properties a detailed description is given in tabulated form
| Physical properties of Hexane | |
|---|---|
| Odor | Gasoline-like odor |
| Appearance | Colorless volatile liquid |
| Complexity | 12 |
| Vapor Pressure | 17.60 kPa (at 20.0 °C) |
| Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.9 (LogP) |
| Viscosity | 3.26 x 10-4 Pa-s at 20 °C |
| Solubility | 9.5 mg L−1 at 25 °C |
Chemical Properties of Hexane
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Hexane is a non-polar, highly volatile compound consisting of weak intermolecular forces.
- The heat of combustion of hexane is 4163.2 kJ/mol and it undergoes a combustion reaction to release carbon dioxide and water.
2C6H14 + 19O2 → 12CO2 + 14H2O
- Hexane is used in petroleum products as it undergoes thermal cracking to decompose higher hydrocarbons into more than one simpler hydrocarbon-
C6H14 (on thermal cracking) → C4H10(butane) + C2H4(ethene)
Hexane decomposes to emit fumes and acrid smoke as the heat of evaporation of hexane is 31.56 kJ/mol at 25 °C.
Uses of Hexane
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Hexane is one of the most useful organic compounds that have certain uses in our daily lives such as
- It is used in the extraction of edible oils from seed and vegetable crops( soybeans, peanuts, corn) and used as a solvent for glues, varnishes, and inks.
- Hexane is also used as a cleansing agent in the printing industry and used as a liquid in low-temperature thermometers.
- One of the most common solvents for lipase-based synthetic processes.
- Used to make biodiesel.
- Hexane in commercial grades is used as a solvent for varnishes, inks, and adhesives.
- Hexane azeotropes have been used to enhance the flavor and odor of hexane-extracted meals by secondary extracting leftover lipids from them.
Health Hazard of Hexane
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The following are the health hazards of hexane
The hazardous effect of Hexane
- Short-term exposure to high-level hexane in humans causes dizziness, nausea, headache, giddiness, and mild central nervous system effects.
- It may cause dermatitis and irritation of the eyes and throat in humans.
- Long-term exposure to hexane in the air causes muscular weakness, headache, blurred vision, fatigue, and polyneuropathy in humans.
Harmful effects of Hexane in mice
- Long exposure to hexane in mice causes neurotoxic effects.
- It affects the olfactory and respiratory epithelium of the nasal cavity of the mice.
- Exposure to hexane by inhalation causes testicular damage in male rats.
Also check:
| Relevant Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lewis acids | Schottky Defect | Carboxylic Acids |
| Gatterman reaction | Reimer Tiemann reaction | Combined Gas Law |
Things to Remember
- Hexane is a straight-chain hydrocarbon having 6 Carbon and 14 hydrogen atoms bonded together with single bonds.
- It is a colorless, odorless, largely unreactive, volatile, non-polar solvent.
- The molecular formula of hexane is C6H14.
- The other names of hexane are- Amyl Carbinol, 1-hexanol, 1- Hydroxyhexane, and hexyl alcohol.
- Hexane has isomers that are formed on the basis of different arrangements of carbon as 2-methyl pentane, 3-methyl pentane, 2-2 dimethyl butane, etc.
- It is used in the extraction of edible oils from seed and vegetable crops( soybeans, peanuts, corn) and used as a solvent for glues, varnishes, and inks.
- Short-term exposure to high-level hexane in humans causes dizziness, nausea, headache, giddiness, and mild central nervous system effects.
- It may cause dermatitis and irritation of the eyes and throat in humans.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is hexane used for? (3 Marks)
Ans. Hexane is used as a solvent, cleansing agent, and for extracting oils from seeds like peanuts, corn, etc.
Hexane is one of the most useful organic compounds that have certain uses in our daily lives such as
- It is used in the extraction of edible oils from seed and vegetable crops( soybeans, peanuts, corn) and used as a solvent for glues, varnishes, and inks.
- Hexane is also used as a cleansing agent in the printing industry and used as a liquid in low-temperature thermometers.
Ques. Is hexane harmful to humans? (3 Marks)
Ans. Yes, harmful effects are different in acute and chronic exposure, It may cause nausea, dizziness, headache, unconsciousness, etc.
- Short-term exposure to high-level hexane in humans causes dizziness, nausea, headache, giddiness, and mild central nervous system effects. It may cause dermatitis and irritation of the eyes and throat in humans.
- Long-term exposure to hexane in the air causes muscular weakness, headache, blurred vision, fatigue, and polyneuropathy in humans.
Ques. Does hexane have a double bond? Elaborate. (5 Marks)
Ans. Hexane is a saturated compound that contains single bonds of C-C and C-H bonds, unsaturated compounds have double or triple bonds.
Apart from this, the Hexane molecular formula is C6H14 which consists of 6 Carbon atoms and 14 Hydrogen atoms-
Hexane is categorized on the basis of its structure, their structure varies as the arrangement of carbon atoms-
The structural isomers of hexane are given below-
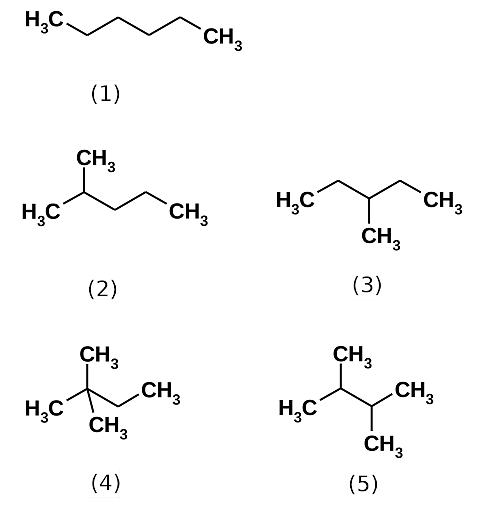
Hexanes are obtained from crude oil refining; it is also prepared by various methods such as the reaction of propane with Na/dry ether forms hexane, and hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes also produces hexane.
Ques. Is hexane polar or nonpolar? (1 Mark)
Ans. Hexane is a nonpolar solvent as it has a symmetrical structure and zero dipole moment.
Ques. What happens when hexane is mixed with water? (1 Mark)
Ans. Hexane will float on top of the water with no mixing because both water and hexane have different natures and possess different kinds of intermolecular forces.
Ques. Is hexane a base or an acid? (1 Mark)
Ans. Hexane is neither acidic nor basic in nature, it can be said that it is amphoteric in nature.
Ques. What is the difference between hexane and n-hexane? (2 Marks)
Ans. The main difference between hexane and n-hexane is that hexane has 5 structural isomers that may be branched or unbranched whereas n-hexane is an unbranched structure.
Ques. Is hexane denser than water? (1 Mark)
Ans. As we know hexane is insoluble in water which means it is less dense than water.
Ques. Is hexane a good solvent? (2 Marks)
Ans. Hexane is a strong solvent for dissolving nonpolar compounds; nevertheless, it would be poor for dissolving polar compounds. Water is a safer alternative than hexane when dealing with a polar compound since it is polar and can interact with it more easily.
Ques. Why hexane is flammable? (2 Marks)
Ans. N-hexane is a crude oil-producing compound. Pure n-hexane is a liquid with a slightly unpleasant odor. It is very flammable and can produce explosive vapors. The main use for n-Hexane-containing solvents is to extract vegetable oils from crops like soybeans.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Also Read:



Comments