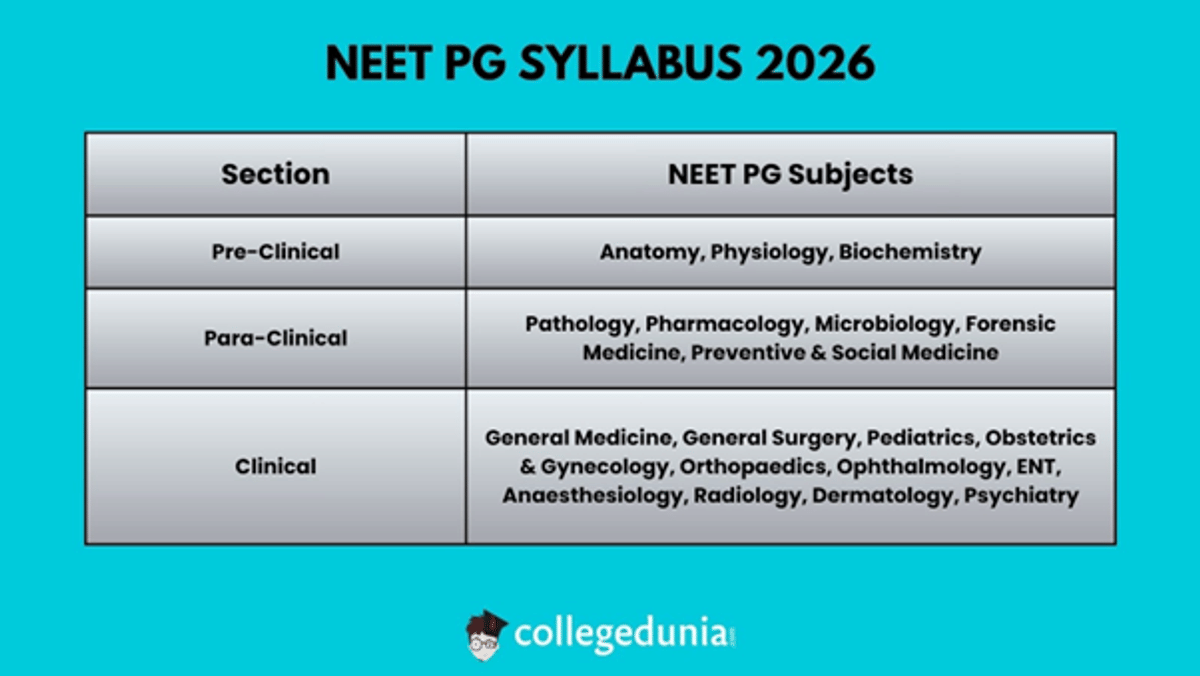
NEET PG syllabus 2026 is yet to be released by NBEMS on the official website. However, the syllabus for NEET PG is likely to be the same as last year’s NEET PG syllabus. NEET PG syllabus is based on 19 subjects across 3 sections: Pre Clinical, Para Clinical and Clinical subjects.
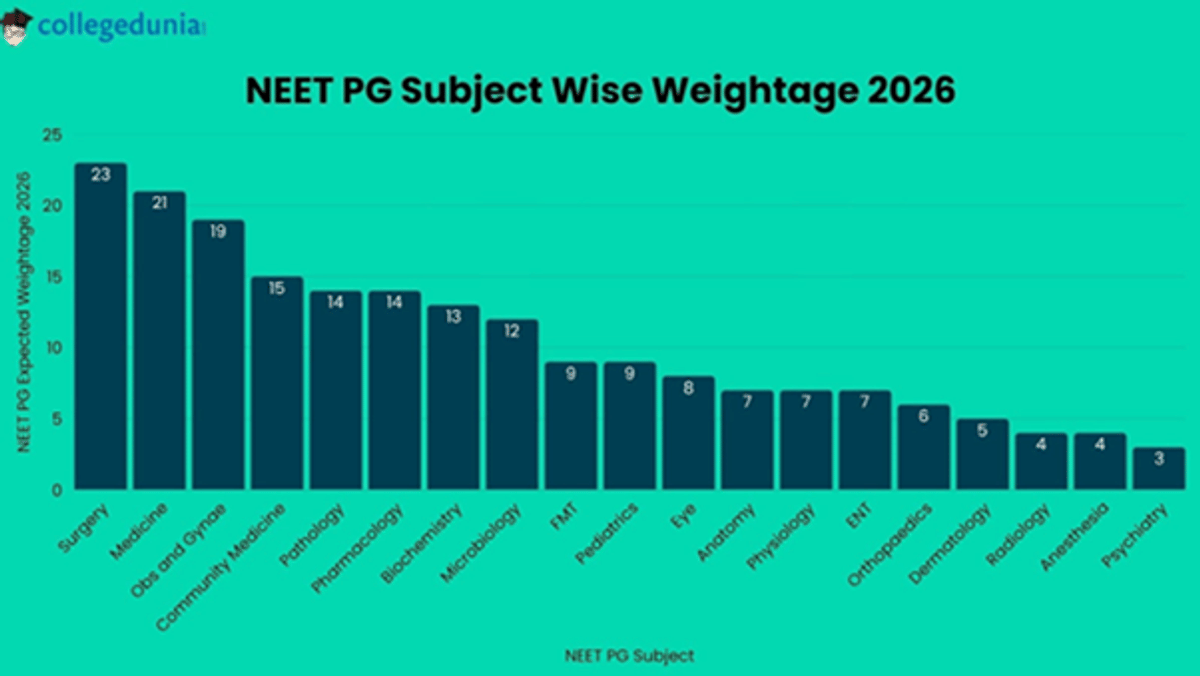
Surgery is considered to be the high weightage topic in NEET PG syllabus, carrying around 23 questions. Other high weightage topics in the syllabus for NEET PG include Medicine (21 questions), Obs and Gynae (19 questions), Community Medicine (15 questions), Pathology (14 questions), Pharmacology (14 questions), and so on.
From NEET PG syllabus, there will be a total of 200 questions asked in NEET PG question paper. Students are required to solve NEET PG question paper in 3 hours and 30 minutes. With +4 marks for each correct answer, and -1 mark for each incorrect answer, you can score a maximum of 800 marks according to latest NEET PG marking scheme.
NEET PG exam date for 2026 is yet to be announced and is likely to be conducted on 2 August 2026 based on the NEET exam date 2025. You must be prepared even before the NEET PG dates are released to ensure you clear the examination. For that purpose, we have discussed the detailed NEET PG syllabus 2026 to help you prepare for the examination.
| NEET PG Syllabus PDF |
|---|
| Download PDF Here |
Related Articles:

Key Summary
- NEET PG syllabus is prescribed by NBEMS every year.
- NEET PG syllabus includes 3 sections: Pre Clinical, Para Clinical and Clinical subjects.
- Syllabus for NEET PG will be based on a total of 19 subjects including Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Pathology, Pharmacology, Microbiology, Forensic Medicine, Preventive & Social Medicine, General Medicine, General Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Anaesthesiology, Radiology, Dermatology, and Psychiatry.
- There will be a total of 200 questions asked in NEET PG 2026 question paper.
- Highest weightage is given to topics like Surgery, Medicine, Obs and Gynae, Community Medicine, Pathology, Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Microbiology.
- Maximum score that students can get in NEET PG 2026 is 800 marks with +4 marks allocated for each question.
What is NEET PG Syllabus?
NEET PG syllabus is designed to test the knowledge of students that they have studied during their MBBS course. Syllabus for NEET PG includes sections like Pre Clinical Subjects, Para Clinical Subjects, and Clinical Subjects as listed below.
- Pre Clinical Subjects: Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry
- Para Clinical Subjects: Pathology, Pharmacology, Microbiology, Forensic Medicine, Preventive & Social Medicine
- Clinical Subjects: General Medicine, General Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Anaesthesiology, Radiology, Dermatology, Psychiatry.
NEET PG syllabus is based on a total of 19 subjects. Subjects with high weightage in NEET PG syllabus include Surgery, Medicine, Obs and Gynae, Community Medicine, Pathology, Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Microbiology.
NEET PG Syllabus: Chapter Wise Weightage
NEET PG syllabus weightage is different for different subjects. Surgery has the highest weightage and is expected to carry around 23 questions in NEET 2026.
- Medicine subject is likely to carry around 21 questions in NEET PG 2026 question paper.
- OBS & Gynae has a weightage of around 19 questions as per the analysis from previous years.
- Other subjects with high weightage in NEET PG syllabus include Community Medicine (15 questions), Pathology (14 questions), Pharmacology (14 questions), and so on.
| NEET PG Subject | NEET PG Expected Weightage 2026 |
|---|---|
| Surgery | 23 |
| Medicine | 21 |
| Obs and Gynae | 19 |
| Community Medicine | 15 |
| Pathology | 14 |
| Pharmacology | 14 |
| Biochemistry | 13 |
| Microbiology | 12 |
| FMT | 9 |
| Pediatrics | 9 |
| Eye | 8 |
| Anatomy | 7 |
| Physiology | 7 |
| ENT | 7 |
| Orthopaedics | 6 |
| Dermatology | 5 |
| Radiology | 4 |
| Anesthesia | 4 |
| Psychiatry | 3 |
NEET PG Syllabus 2026: Subject Wise
NEET PG syllabus is based on 19 subjects across 3 sections, including Pre-Clinical Subjects, Para-Clinical Subjects, and Clinical Subjects. Subjects included in each section of NEET PG syllabus are tabulated below.
| Section | NEET PG Subjects |
|---|---|
| Pre-Clinical | Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry |
| Para-Clinical | Pathology, Pharmacology, Microbiology, Forensic Medicine, Preventive & Social Medicine |
| Clinical | General Medicine, General Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Anaesthesiology, Radiology, Dermatology, Psychiatry |
NEET PG Syllabus 2026: Pre Clinical Subjects
NEET PG Pre-clinical syllabus is based on subjects including:
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Biochemistry
NEET PG Syllabus for Anatomy
| NEET PG Syllabus for Anatomy | |
|---|---|
| Anatomical terminology | Head & neck Joints, Histology, Development, Radiography & Surface marking |
| General features of bones & Joints | Anterior abdominal wall |
| General features of Muscle | Posterior abdominal wall |
| General features of skin and fascia | Male external genitalia |
| General features of the cardiovascular system | Abdominal cavity |
| General Features of Lymphatic System | Pelvic wall and viscera |
| Introduction to the nervous system | Perineum |
| Features of individual bones (Upper Limb) | Vertebral column |
| Pectoral region | Sectional Anatomy |
| Axilla, Shoulder and Scapular region | Histology & Embryology |
| Arm & Cubital fossa | Osteology |
| Forearm & hand (General Features, Joints, radiographs & surface marking) | Radiodiagnosis |
| Features of individual bones (Lower Limb) | Surface marking |
| Front & Medial side of thigh | Meninges & CSF |
| Gluteal region & back of thigh | Spinal Cord |
| Hip Joint | Medulla Oblongata |
| Knee joint, Anterolateral compartment of leg & dorsum of foot | Pons |
| Back of Leg & Sole (General Features, Joints, radiographs & surface marking) | Cerebellum |
| Thoracic cage | Midbrain |
| Heart & Pericardium | Cranial nerve nuclei & Cerebral hemispheres |
| Mediastinum | Ventricular System |
| Lungs & Trachea | Epithelium histology |
| Thorax | Connective tissue histology |
| Skull osteology | Muscle histology |
| Scalp | Nervous tissue histology |
| Face & parotid region | Blood Vessels |
| Posterior triangle of neck | Glands & Lymphoid tissue |
| Cranial cavity | Bone & Cartilage |
| Orbit | Integumentary System |
| Anterior Triangle | Chromosomes |
| Temporal and Infratemporal regions | Patterns of Inheritance |
| Submandibular region | Principle of Genetics, Chromosomal Aberrations & Clinical Genetics |
| Deep structures in the neck | Introduction to embryology |
| Mouth, Pharynx & Palate | Gametogenesis and fertilization |
| Cavity of Nose | Second week of development |
| Larynx | 3rd to 8th week of development |
| Tongue | Fetal membranes |
| Organs of hearing and equilibrium | Prenatal Diagnosis |
| Eyeball | Ethics in Anatomy |
| Back Region | - |
NEET PG Syllabus for Physiology
| NEET PG Syllabus for Physiology |
|---|
| General Physiology |
| Haematology |
| Nerve and Muscle Physiology |
| Gastro-intestinal Physiology |
| Cardiovascular Physiology (CVS) |
| Respiratory Physiology |
| Renal Physiology |
| Endocrine Physiology |
| Reproductive Physiology |
| Neurophysiology |
| Integrated Physiology |
NEET PG Syllabus for Biochemistry
| NEET PG Syllabus for Biochemistry |
|---|
| Basic Biochemistry |
| Enzyme |
| Chemistry and Metabolism of Carbohydrates |
| Chemistry and Metabolism of Lipids |
| Chemistry and Metabolism of Proteins |
| Metabolism and homeostasis |
| Molecular biology |
| Nutrition |
| Extracellular Matrix |
| Oncogenesis and immunity |
| Biochemical Laboratory Tests |
NEET PG Syllabus: Important for Pre Clinical Subjects
| Subject | Book Name | Author/Publisher |
|---|---|---|
| Anatomy | Self Assessment and Review of Anatomy | Rajesh Kaushal |
| Anatomy | BD Chaurasia’s Human Anatomy (Vol I–III) | B.D. Chaurasia |
| Anatomy | Gray’s Anatomy Review | Richard L. Drake et al.; Elsevier |
| Physiology | Review of Physiology | Dr. Soumen Manna; Dr. Krishna Kumar |
| Physiology | Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology | John E. Hall; Elsevier |
| Physiology | Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology | Kim E. Barrett et al.; McGraw Hill |
| Biochemistry | Self Assessment and Review of Biochemistry | Rebecca James |
| Biochemistry | Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry | Victor W. Rodwell et al.; McGraw Hill |
| Biochemistry | Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry | Pamela C. Champe et al.; Lippincott |
NEET PG Syllabus Para Clinical Subjects
Subjects included in NEET PG Para Clinical syllabus are listed below.
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic Medicine
- Preventive & Social Medicine
NEET PG Syllabus for Pathology
| NEET PG Syllabus for Pathology |
|---|
| Introduction to Pathology |
| Cell Injury and Adaptation |
| Amyloidosis |
| Inflammation |
| Healing and repair |
| Hemodynamic disorders |
| Neoplastic disorders |
| Basic diagnostic cytology |
| Immunopathology and AIDS |
| Infections and Infestations |
| Genetic and paediatric diseases |
| Environmental and nutritional diseases |
| Introduction to haematology |
| Microcytic anemia |
| Macrocytic anemia |
| Hemolytic anemia |
| Aplastic anemia |
| Leukocyte disorders |
| Lymph node and spleen |
| Plasma cell disorders |
| Hemorrhagic disorders |
| Blood banking and transfusion |
| Clinical Pathology (Tumors)Gastrointestinal tractHepatobiliary systemRespiratory systemCardiovascular systemUrinary TractMale Genital TractFemale Genital TractBreastEndocrine systemBone and soft tissueSkinCentral Nervous SystemEye |
NEET PG Syllabus for Pharmacology
| NEET PG Syllabus for Pharmacology |
|---|
| Basic Principles of Pharmacology |
| Clinical Pharmacy |
| Clinical Pharmacology |
| Experimental Pharmacology |
| Communication |
NEET PG Syllabus for Microbiology
| NEET PG Syllabus for Microbiology |
|---|
| General Microbiology and Immunity |
| CVS and Blood |
| Gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary system |
| Musculoskeletal system, skin, and soft tissue infections |
| Central Nervous System Infections |
| Respiratory tract infections |
| Genitourinary & Sexually transmitted infections |
| Zoonotic diseases and miscellaneous |
NEET PG Syllabus for Forensic Medicine
| NEET PG Syllabus for Forensic Medicine |
|---|
| General Information |
| Forensic Pathology |
| Clinical Forensic Medicine |
| Medical Jurisprudence (Medical Law and Ethics) |
| Forensic Psychiatry |
| Forensic Laboratory investigation in medical legal practice |
| Emerging Technologies in Forensic Medicine |
| General Toxicology |
| Chemical Toxicology |
| Pharmaceutical Toxicology |
| Biotoxicology |
| Sociomedical Toxicology |
| Environmental Toxicology |
| Skills in Forensic Medicine & Toxicology |
NEET PG Syllabus for Preventive & Social Medicine
| NEET PG Syllabus for Preventive & Social Medicine |
|---|
| Concept of Health and Disease |
| Relationship of social and behavioural to health and disease |
| Environmental Health Problems |
| Principles of health promotion and education |
| Nutrition |
| Basic statistics and its applications |
| Epidemiology |
| Epidemiology of communicable and non-communicable diseases |
| Demography and vital statistics |
| Reproductive, maternal, and child health |
| Occupational Health |
| Geriatric services |
| Disaster Management |
| Hospital waste management |
| Mental Health |
| Health planning and management |
| Health care of the community |
| International Health |
| Essential Medicine |
| Recent advances in Community Medicine |
NEET PG Syllabus: Important Books for Para Clinical Subjects
| Subject | Book Name | Author/Publisher |
|---|---|---|
| Pathology | Review of Pathology and Genetics | Sparsh Gupta; Devesh Mishra (editions) |
| Pathology | Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease | Vinay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, Jon C. Aster; Elsevier |
| Pathology | Robbins Basic Pathology | Vinay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, Jon C. Aster; Elsevier |
| Pharmacology | Review of Pharmacology | Gobind Rai Garg; Sparsh Gupta; Ranjan Patel |
| Pharmacology | Essentials of Medical Pharmacology | K.D. Tripathi; Jaypee |
| Pharmacology | Katzung’s Basic & Clinical Pharmacology | Bertram G. Katzung; McGraw Hill |
| Microbiology | Review of Microbiology and Immunology | Rachna Chaurasia / Apurba Sastry |
| Microbiology | Jawetz, Melnick & Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology | Karen C. Carroll et al.; McGraw Hill |
| Forensic Medicine | Self Assessment and Review of Basic Anatomy and Forensic Medicine | Arvind Arora |
| Forensic Medicine | The Essentials of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology | K.S. Narayan Reddy |
| PSM | Community Medicine (PSM) | Vivek Jain |
| PSM | Park’s Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine | K. Park; Banarsidas Bhanot |
NEET PG Syllabus Clinical Subjects
NEET PG syllabus 2026 for Clinical section is based on subjects listed below.
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Pediatrics
- Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Orthopaedics
- Ophthalmology
- ENT
- Anaesthesiology
- Radiology
- Dermatology
- Psychiatry
NEET PG Syllabus for General Medicine
| NEET PG syllabus for Medicine |
|---|
| Heart Failure |
| Acute Myocardial Infarction/IHD |
| Pneumonia |
| Fever and febrile syndromes |
| Liver disease |
| HIV |
| Rheumatologic problems |
| Hypertension |
| Anemia |
| Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Renal Failure |
| Diabetes Mellitus |
| Thyroid dysfunction |
| Common malignancies |
| Obesity |
| GI bleeding |
| Diarrheal disorders |
| Headache |
| Cerebrovascular accident |
| Movement disorders |
| Envenomation |
| Poisoning |
| Mineral, Fluid Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders |
| Nutritional and Vitamin Deficiencies |
| Geriatrics |
| Miscellaneous infections (e.g., Leptospirosis, Rabies, Tetanus) |
| The role of the physician in the community |
NEET PG Syllabus for General Surgery
| NEET PG Syllabus for General Surgery |
|---|
| Metabolic response to injury |
| Shock |
| Blood and blood components |
| Burns |
| Wound healing and wound care |
| Surgical infections |
| Surgical Audit and Research |
| Ethics |
| Investigation of surgical patient |
| Pre, intra, and post-operative management |
| Anaesthesia and pain management |
| Nutrition and fluid therapy |
| Transplantation |
| Basic Surgical Skills |
| Bichazard disposal |
| Minimally invasive General Surgery |
| Trauma |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue |
| Developmental anomalies of face, mouth, and jaws |
| Oropharyngeal cancer |
| Disorders of salivary glands |
| Endocrine General SurgeryThyroid and parathyroidAdrenal GlandsPancreas |
| Breast |
| Cardio-thoracic General Surgery- Chest - Heart and Lungs |
| Vascular disease |
| Abdomen |
| Urinary System |
| Penis, Testis, and Scrotum |
NEET PG Syllabus for Pediatrics
| NEET PG syllabus for Paediatrics |
|---|
| Normal Growth and Development |
| Common problems related to Growth |
| Common problems related to Development - 1 (Developmental delay, Cerebral palsy) |
| Common problems related to Development-2 (Scholastic backwardness, Learning Disabilities, Autism, ADHD) |
| Common problems related to behavior |
| Adolescent Health & Common Problems Related to Adolescent Health |
| To promote and support optimal breastfeeding for infants |
| Complementary Feeding |
| Normal nutrition, assessment, and monitoring |
| Provide nutritional support, assessment, and monitoring for common nutritional problems |
| Obesity in children |
| Micronutrients in Health and Disease-1 (Vitamins ADEK, B Complex and C) |
| Micronutrients in Health and Disease-2: Iron, Iodine, Calcium, Magnesium |
| Toxic elements and free radicals, and oxygen toxicity |
| Fluid and electrolyte balance |
| Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illnesses (IMNCI) Guideline |
| The National Health programs: NHM |
| The National Health Programs: RCH |
| National Programs, RCH - Universal Immunizations program |
| Care of the Normal Newborn and High-risk Newborn |
| Genito-Urinary system |
| Approach to and recognition of a child with a possible Rheumatologic problem |
| Cardiovascular system- Heart Diseases |
| Diarrhoea diseases and Dehydration |
| Malabsorption |
| Acute and chronic liver disorders |
| Pediatric Emergencies - Common Pediatric Emergencies |
| Respiratory system |
| Anemia and other Hemato-oncologic disorders in children |
| Systemic Pediatrics-Central Nervous System |
| Allergic Rhinitis, Atopic Dermatitis, Bronchial Asthma, Urticaria, Angioedema |
| Chromosomal Abnormalities |
| Endocrinology |
| Vaccine-preventable Diseases - Tuberculosis |
NEET PG Syllabus for Obstetrics & Gynecology
| NEET PG syllabus for Obstetrics & Gynaecology |
|---|
| Demographic and Vital Statistics |
| Anatomy of the female reproductive tract (Basic anatomy and embryology) |
| Physiology of conception |
| Development of the fetus and the placenta |
| Preconception counselling |
| Diagnosis of pregnancy |
| Maternal Changes in Pregnancy |
| Antenatal Care |
| Complications in early pregnancy |
| Antepartum haemorrhage |
| Multiple pregnancies |
| Medical Disorders in Pregnancy |
| Labour |
| Abnormal Lie and Presentation; Maternal Pelvis |
| Operative obstetrics |
| Complications of the third stage |
| Lactation |
| Care of the newborn |
| Normal and abnormal puerperium |
| Medical termination of pregnancy |
| Contraception |
| Vaginal discharge |
| Normal and abnormal puberty |
| Abnormal uterine bleeding |
| Amenorrhea |
| Genital injuries and fistulae |
| Genital infections |
| Infertility |
| Uterine fibroids |
| PCOS and hirsutism |
| Uterine prolapse |
| Menopause |
| Benign, Pre-malignant (CIN) and Malignant Lesions of the Cervix |
| Benign and malignant diseases of the uterus and the ovaries |
NEET PG Syllabus for Orthopaedics
| NEET PG syllabus for Orthopaedics |
|---|
| Skeletal Trauma, Poly trauma |
| Fractures |
| Musculoskeletal Infection |
| Skeletal Tuberculosis |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis and associated inflammatory disorders |
| Degenerative disorders |
| Metabolic bone disorders |
| Poliomyelitis |
| Cerebral Palsy |
| Bone Tumors |
| Peripheral nerve injuries |
| Congenital lesions |
| Procedural Skills |
| Counselling Skills |
NEET PG Syllabus for Ophthalmology
| NEET PG syllabus for Ophthalmology |
|---|
| Visual Acuity Assessment |
| Lids and Adnexa, Orbit |
| Conjunctiva |
| Cornea |
| Sclera |
| Iris and Anterior Chamber |
| Lens |
| Retina & Optic Nerve |
NEET PG Syllabus for ENT
| NEET PG Syllabus for ENT |
|---|
| Anatomy and Physiology of ear, nose, throat, head & neck |
| Clinical Skills |
| Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in ENT |
| Management of diseases of the ear, nose & throat |
NEET PG Syllabus for Anaesthesiology
| NEET PG syllabus for Anaesthesia |
|---|
| Anaesthesiology as a specialty |
| Cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| Preoperative evaluation and medication |
| General Anaesthesia |
| Regional anaesthesia |
| Post-anaesthesia recovery |
| Intensive Care Management |
| Pain and its management |
| Fluids |
| Patient safety |
NEET PG Syllabus for Radiology
| NEET PG syllabus for Radiology |
|---|
| Radiological investigations and Radiation safety |
NEET PG syllabus for Radiotherapy
| NEET PG syllabus for Radiotherapy |
|---|
| Principles of Radiation Oncology (Radiotherapy) |
| Radiation Protection |
| Radiobiology & Chemoradiation |
| Radiation Treatment Delivery & Outcome |
| Cancer Prevention & Registries |
NEET PG Syllabus for Dermatology
| NEET PG syllabus for Dermatology |
|---|
| Acne |
| Alopecia |
| Papulosquamous disorders |
| Lichen Planus |
| Scabies |
| Pediculosis |
| Fungal infections |
| Viral infections |
| Leprosy |
| Sexually Transmitted Diseases |
| HIV |
| Dermatitis and Eczema |
| Vesiculobullous Lesions |
| Urticaria and Angioedema |
| Pyoderma |
| Collagen Vascular disease |
| Nutritional Deficiencies and Skin |
| Systemic diseases and skin |
NEET PG Syllabus for Psychiatry
| NEET PG syllabus for Psychiatry |
|---|
| Doctor-patient relationship |
| Mental health |
| Introduction to psychiatry |
| Psychotic disorders (e.g. alcohol and substance abuse disorders, schizophrenia) |
| Depression |
| Bipolar disorders |
| Anxiety disorders |
| Stress-related disorders |
| Somatoform disorders |
| Personality disorders |
| Psychosomatic disorders |
| Psychosexual and gender identity disorders |
| Psychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence |
| Mental retardation |
| Psychiatric disorders in the elderly |
| Psychiatric emergencies |
| Therapeutics |
NEET PG Syllabus: Important Books for Clinical Subjects
| Subject | Book Name | Author/Publisher |
|---|---|---|
| Medicine | Complete Review of Medicine for NBE | Deepak Marwah |
| Medicine | Review of Medicine (MCQs) | Mudit Khanna |
| Surgery | Surgery Essence (SRB) | Pritesh Singh |
| Surgery | Bailey & Love’s Short Practice of Surgery | Norman S. Williams et al.; CRC Press |
| Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Self Assessment and Review of Obstetrics & Gynecology | Sakshi Arora |
| Pediatrics | Review of Pediatrics and Neonatology | Taruna Mehra |
| Pediatrics | Essential Pediatrics | O.P. Ghai; CBS Publishers |
| Orthopedics | Orthopedics Quick Review | Apurv Mehra |
| Ophthalmology | Comprehensive Ophthalmology | A.K. Khurana; with Ruchi Rai |
| ENT | ENT for Entrance Exam | Manisha Sinha; Sachin Budhiraja |
| Radiology | Review of Radiology | Rajat Jain |
| Dermatology | Review of Dermatology | Saurabh Jindal |
| Psychiatry | Review of Psychiatry | Praveen Tripathi |
| Anesthesia | PROAFS Anesthesia for NBE | Vivek Jain |
Ques. What syllabus comes in NEET PG?
Ans. NEET PG is conducted based on 3 sections including Pre Clinical, Para Clinical, and Clinical. Combined in all 3 sections, number of subjects that are asked in NEET PG are 19. The syllabus tests knowledge of candidates they have studied during MBBS program.
Ques. How many subjects are there in NEET PG?
Ans. There are a total of 19 subjects in NEET PG syllabus across 3 sections as listed below.
- Pre Clinical Subjects: Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry
- Para Clinical Subjects: Pathology, Pharmacology, Microbiology, Forensic Medicine, Preventive & Social Medicine
- Clinical Subjects: General Medicine, General Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Anaesthesiology, Radiology, Dermatology, Psychiatry.
Ques. What are the subjects in NEET PG pre clinical section?
Ans. Subjects included in NEET PG syllabus for pre clinical section include Anatomy, Physiology, and Biochemistry.
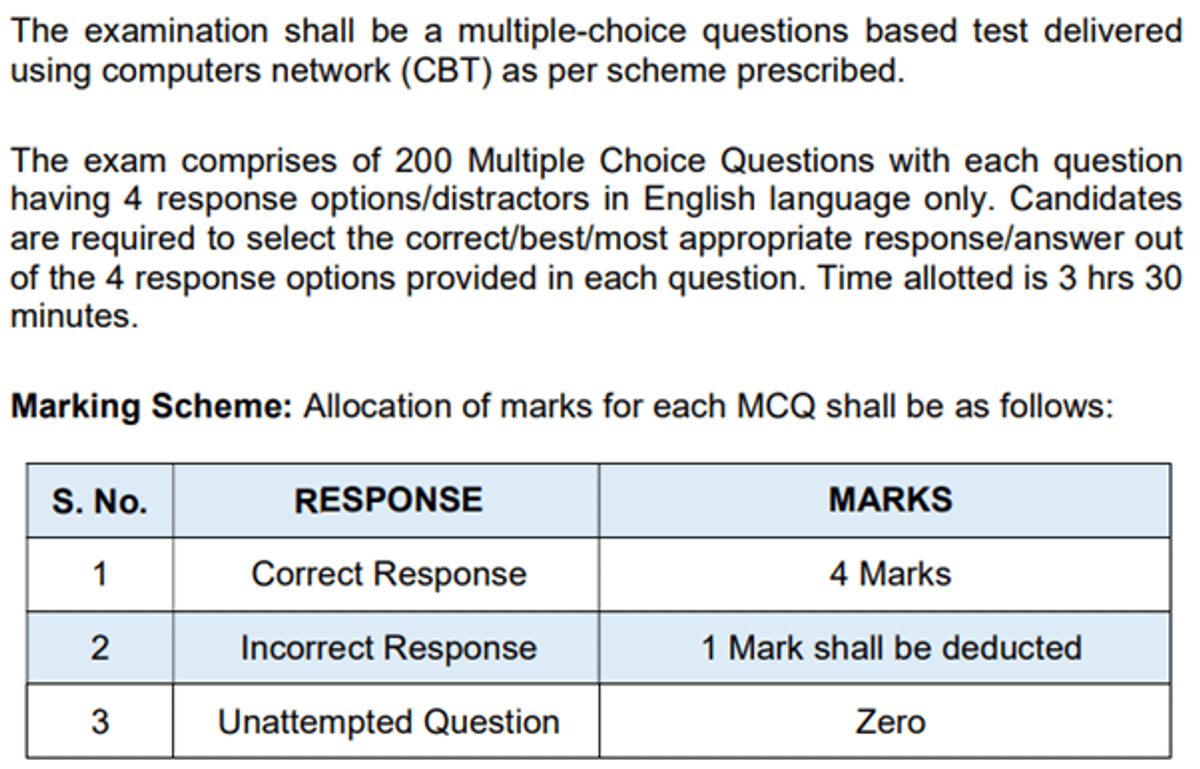
NEET PG Syllabus: Exam Pattern
NEET PG exam pattern is released by NBEMS on the official website at nbe.edu.in. According to the latest available NEET PG exam pattern, there are a total of 200 questions asked in NEET PG. You will be required to solve NEET PG question paper withing 3 hours and 30 minutes.
As per the NEET PG marking scheme, you will be awarded 4 marks for each correct answer,. However, for each incorrect answer, you will get -1 mark deducted from the overall score. You can score a maximum of 800 marks in NEET PG 2026.
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Mode of Examination | CBT (Computer-Based Test) |
| Medium of Examination | English |
| Type of Questions | MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) |
| Number of Questions | 200 |
| Exam Duration | 3 hours 30 minutes |
| Total Marks | 800 |
| Marking Scheme |
|
Source: @nbe.edu.in
Also Check:
Ques. What is the format of NEET PG exam?
Ans. As per the latest NEET PG exam pattern, NBEMS will conduct NEET PG 2026 in CBT mode. There will be MCQ type questions asked in NEET PG with a total of 200 MCQs.
Ques. How many total marks are in NEET PG?
Ans. In NEET PG, there are a total of 200 MCQs and for each MCQ 4 marks are allotted. Total marks in NEET PG are 800 as per the number of questions and marking scheme.
NEET PG Syllabus: Previous Years Question Papers
Aspirants must go through the previous years’ papers of NEET PG to understand the syllabus for NEET PG. You will also get to know the type of questions asked from NEET PG syllabus 2026.
| NEET PG Year | NEET PG Question papers |
|---|---|
| NEET PG 2025 | Check here |
| NEET PG 2022 | Check here |
Also Read:
NEET PG Syllabus: Mock Tests
NEET PG mock tests are also important in understanding the syllabus for NEET PG 2026. Students can attempt free NEET PG mock tests below.
NEET PG Syllabus FAQs
Ques. What are the subjects included in Para clinical section of NEET PG 2026?
Ans. In para clinical section, there are 5 subjects included as listed below.
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic Medicine
- Preventive & Social Medicine
Ques. What are the important books for NEET PG syllabus for pre clinical subjects?
Ans. For NEET PG Pre Clinical subjects, students can consider books as mentioned in the table below.
| Subject | Book Name | Author/Publisher |
|---|---|---|
| Anatomy | Self Assessment and Review of Anatomy | Rajesh Kaushal |
| Anatomy | BD Chaurasia’s Human Anatomy (Vol I–III) | B.D. Chaurasia |
| Anatomy | Gray’s Anatomy Review | Richard L. Drake et al.; Elsevier |
| Physiology | Review of Physiology | Dr. Soumen Manna; Dr. Krishna Kumar |
| Physiology | Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology | John E. Hall; Elsevier |
| Physiology | Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology | Kim E. Barrett et al.; McGraw Hill |
| Biochemistry | Self Assessment and Review of Biochemistry | Rebecca James |
| Biochemistry | Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry | Victor W. Rodwell et al.; McGraw Hill |
| Biochemistry | Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry | Pamela C. Champe et al.; Lippincott |
Ques. How many subjects are included in NEET Syllabus for Clinical section?
Ans. For clinical section of NEET PG syllabus, there are a total of 11 subjects and these include General Medicine, General Surgery, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Anaesthesiology, Radiology, Dermatology, Psychiatry.
Ques. How many questions will be asked from NEET PG syllabus?
Ans. From NEET PG syllabus, there will be a total of 200 MCQs asked in NEET PG question paper.
Ques. Which subjects have the highest weightage in NEET PG syllabus?
Ans. Subjects like Surgery, Medicine, OBS & Gynae, Community Medicine, Pathology, Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Microbiology carry the highest weightage in NEET PG syllabus. Students can check the table below to check the weightage of each subject.
| Surgery | 23 |
|---|---|
| Medicine | 21 |
| Obs and Gynae | 19 |
| Community Medicine | 15 |
| Pathology | 14 |
| Pharmacology | 14 |
| Biochemistry | 13 |
| Microbiology | 12 |







Comments