Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Dark side of the moon is the lunar surface that always faces away from the earth. This side is never visible from the earth’s surface. From the earth, only one side of the moon can be seen. The other side being hidden always is named as ‘dark side of the moon.’ Before its discovery, no one knew the fact that there is one more side of the moon that looks different from the side we have always observed. Moon is an earth satellite that revolves around the earth in its orbit.
Also Read: Value of g on moon
Key Takeaways: Far Side of the Moon, Tidal Locking, Libration, Orbit, Lunar Hemispheres, Phases of the Moon
Dark Side of the Moon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
It is a generally known fact that the moon shape is almost, not exactly, spherical. In its spherical shape, it revolves around the earth in its orbit. However, at any time, from anywhere on the earth only the same side of the moon is visible. This side is called ‘the near side of the moon.’ This is the side that faces towards the earth.
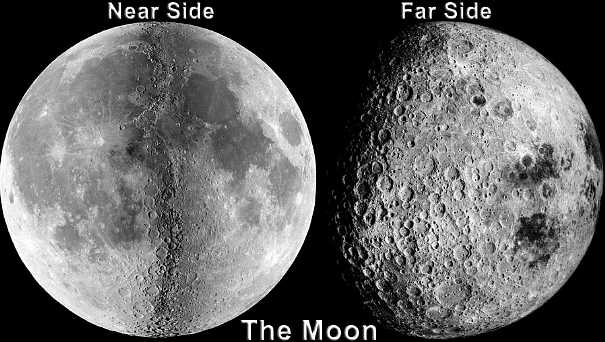
The near side and the far side of the moon
On the contrary, the other side that is away from the earth and is never visible from the earth is called ‘the dark side of the moon’. More appropriately, it should be called ‘the far side of the moon’ rather than the dark side since it is not dark at all. Both the near and far sides of the moon receive almost equal amounts of light.
The reason behind the concept of the far side of the moon is a phenomenon called ‘Tidal Locking’. The speed of rotation of the moon on its axis is the same as that of its revolution around the earth in its orbit. Due to this, the same side always faces towards the earth and the other side remains away. This is called the tidal locking of the moon and the earth. In other words, the rotation and revolution of the moon around the earth occur synchronously, thus only one side of the moon is visible from the earth.

Tidal Locking of Moon
However, it is not only the 50% of the lunar surface that we see from the earth. Since the orbit of the moon is not exactly circular, thus sometimes little portions of the far side of the moon can also be observed in the shape of crescent edges. This occurs due to libration.
Libration is the wagging or wavering of the moon in its orbit due to external forces. This allows us to see different hemispheres of the moon at different times. So, in total 59% of the lunar surface is visible from the earth.
Read More:
Phases of the Moon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Due to its motion, different shapes of the moon are visible from the earth on different days. These are called ‘Phases of the Moon’ which are determined by its position with respect to the earth and the sun. The 8 phases of the moon are:
- New Moon - In this phase, the moon is not visible since it is positioned between the earth and the sun.
- Waxing Crescent Moon - This phase follows the new moon and occurs a few days after the new moon. A crescent-shaped moon is seen.
- First-Quarter Moon - It is the third phase in which the half-moon is visible from the earth.

Phases of the Moon
- Waxing Gibbous Moon - In the fourth phase, named waxing gibbous, the moon seems like a growing shape. More than half of the moon is visible.
- Full Moon - In this phase, the position of the earth is between the sun and the moon. The shape of the moon is visible almost like a complete circle.
- Waning Gibbous Moon - After the full moon, the shape of the moon starts decreasing from the complete circle towards the half-moon shape.
- Third-Quarter Moon - In this phase, the half-moon is seen and 3/4th of the lunar cycle is completed.
- Waning Crescent Moon - This is the last phase in which a crescent-shaped moon is seen. When this phase ends, a new lunar cycle starts repeating all the above-mentioned phases.
Read More:
Things to Remember
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- The dark side of the moon is the side that faces away from the earth. It is also called the far side of the moon.
- The dark side of the moon is not visible from the earth due to the tidal locking of the earth and the moon.
- Some of the portions of the far side are seen as crescent edges due to libration.
- In total, 59% of the total lunar surface is visible from the earth.
- The first photographs of the far side were taken by the Soviet probe Luna 3.
- In a lunar cycle, 8 different shapes of the moon are observed which are called ‘phases of the moon.’
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques: Define ‘Dark side of the moon.’(2 marks)
Ans. Dark side of the moon is the one which we are never able to see from the earth.
Ques. What is Tidal Locking? (3 marks)
Ans. Tidal Locking is the phenomenon in which the rotational speed and orbital speed of an object are the same in space. Tidal Locking is observed between the earth and the moon due to which only one side of the moon always faces the earth. This happens because the earth and the moon both exert force upon each other. This force is also responsible for the tides on earth. Due to this force, the motion of the moon slows down to the speed at which its revolution around the earth and its rotation on its axis becomes the same. Tidal locking can be observed between any two bodies in space that have the same rotational and orbital motion.
Ques. What is Libration? (2 marks)
Ans. Libration is the oscillating movement of a planet while revolving in its orbit. Because the axis of the moon is slightly tilted and its orbit is not exactly circular, it shows libration. Due to libration some of the portions of the far side of the moon becomes visible from the earth even though it always shows only the near side to the earth. Due to libration, 59% of the total lunar surface is visible from the earth.
Ques. How does the moon affect the ocean tides? (3 marks)
Ans. Tides are the periodic rise and fall observed in the sea level. Tides are caused as a result of the gravitational force exerted by the moon on the earth. The moon revolves around the earth in its orbit and both earth and the moon exerts a pulling force on each other. The gravitational force of the moon on the earth causes water to rise up as mounds. When the mound reaches its maximum height, it is called a high tide.
The flat surface of the seawater between two high tides is called low tide. High tides are also caused due to the centrifugal force resulting due to earth’s rotation. If the sun, moon, and earth are positioned in a straight line, unusually high and low tides occur. The extent of these tides depends upon the position of the sun, moon, and earth.
Ques. List the different phases of the moon. (3 marks)
Ans. There are 8 different phases of the moon which are listed below:
- New Moon
- Waxing crescent moon
- First-quarter moon
- Waxing gibbous moon
- Full moon
- Waning Gibbous moon
- Third Quarter moon
- Waning Crescent moon
Ques. What is an Asteroid? (3 marks)
Ans. Asteroids are small objects made up of rocks and orbit the sun in the solar system. They are much smaller as compared to planets. Between Mars and Jupiter, an asteroid belt is present. It is believed that the solar system was formed as a result of a collision between a big cloud of gas and dust. Due to this, most of the material reached the centre of the cloud and formed the sun. The dust condensed and formed the planets. The remaining objects that were not included in the planets became asteroids. Some of their features are:
- They are rocky and have irregular shapes.
- Their size can be big or very small. However, they are not as big as planets.
- In some asteroids, clays and metals like nickel and iron are also found.
Ques. What is a Lunar Eclipse? What are its types? (5 marks)
Ans. A lunar eclipse is a natural phenomenon that occurs when the sun, moon, and earth are aligned closely in a position that earth comes in between the sun and moon. The moon is shadowed by the earth and is either partially or slightly visible. A lunar eclipse may last for several hours. The different types of lunar eclipse are as follows:
- Total Lunar Eclipse: In this, the moon completely moves into the shadow of the earth and appears red. This moon is also called the blood moon due to its reddish appearance.
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: In this, the moon passes partially through the earth’s shadow and is not much affected. It almost appears the same except it becomes a little dark.
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: In this, some part of the moon moves into the shadow of the earth and the remaining part is visible. This occurs when the sun, moon, and earth are not exactly aligned.
Ques. What is the difference between the far side and the near side of the moon? (3 marks)
Ans. The far side and near side of the moon differ greatly in appearances and features. The far side of the moon is characterised by the presence of craters. Only 1% of the surface of the far side is covered by maria which is very much low as compared to the near side (31.2%). This may be due to the high concentration of heat-producing elements on the near-side hemisphere.
The far side of the moon is shielded from radio transmissions emitted from the earth, thus it can also be used for placing radio telescopes. The maria on the far side are expected to have a very high concentration of helium-3 because the near side is only partly shielded from the earth’s solar wind.
Read More:








Comments