Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
On a dark moonless night, while gazing at the thousands of stars above, we often try to find patterns in them. We observe a shape forming in the sky above as we connect the dots in our minds. Some groups of a few bright stars make patterns in the sky that are easy to recognize by everyone. These groups of stars form constellations. The constellations or the group of stars were given their name by ancients according to the animals or the objects they resembled. To remember these names of the constellations easily, they also built stories around the patterns. For instance, the constellations Cetus, Perseus, Andromeda, Cassiopeia, and Pegasus are all related to Greek mythology. Some constellation names are common or similar across various cultures as in Greek the constellation Pisces is known as Meena in Sanskrit which also means fish.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Orion, Big Dipper, Little Dipper, Cassiopeia, Taurus, Gemini, Cetus, Perseus, Andromeda, Cassiopeia, Pegasus, Pisces
Read Also: Why do Stars Twinkle?
What are Constellations?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The constellations are the patterns in the night sky that are formed of stars and that can be easily recognized. The name constellation was derived from the Latin word constellatus which refers to a set of stars. Hence, a constellation is a grouping of numerous stars. The stars in a constellation are not generally as close to each other in space as they appear to be from the Earth.
In the sky, all these constellations appear to be in a movement from west to east. This motion is because the Earth undergoes rotation from the West to the East. Because the Earth is round, some constellations do not appear in our line of sight. Hence, all the constellations in the Northern Hemisphere are not visible in the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa. A person standing on the equator however can almost see all the constellations that exist in our sky.
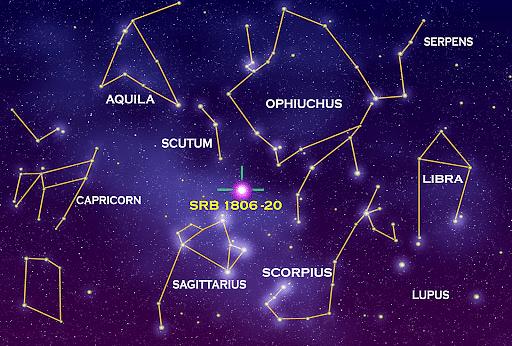
Constellations in the night sky
Presently, 88 constellations in the night sky are officially recognized and named. These constellations cover the entire sky across the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres. At present, these Constellations represent 19 land animals along with 14 men and women. It also represents 10 water creatures, 2 insects, 9 birds, 2 centaurs, 1 head of hair, and 29 objects which are inanimate. Out of these 88 constellations, only a distinct of 60 constellations are visible completely at one time of the year or another.
Check Important Notes for Motion of Celestial Bodies in Space
Uses of Constellations
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Constellations were identified for a wide variety of reasons by the common people such as
- Constellations helped in determining the change of seasons in agriculture before the advent of the new calendars.
- Explorers and navigators found it easy to travel and find their way through tracking the location of the famous constellations. Celestial navigation has been of widespread use.
- The celestial objects in the universe can be explained using the constellations in the sky. Many nebulae, stars, and various other objects for example are named after the constellations that they are observed in.
For example, the Orionids meteor shower that occurs every year in the month of October appears to emerge from the same direction of the Orion Constellation, which is also known as the Hunter.
Also Read:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Uses of Solar Panel | Magnetic Declination | Earth's Magnetic Field |
| Gravitation | Neptune | Forest conservation |
Zodiac Constellations
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The ecliptic plane holds certain constellations through which the sun appears to pass throughout the year. There exist 12 astrological zodiac constellations however astronomically there are 13 zodiac Constellations which are Aquarius, Capricornus, Pisces, Taurus, Aries, Cancer, Gemini, Virgo, Leo, Scorpius, Libra, Saggitarius, and Ophiuchus.
Majorly there are 12 constellations astrologically that exist in the sky lining up along the path of the sun, known as the ecliptic. The 12 zodiac constellations are:
- Aries (Mesha)
- Taurus (Vrushabha)
- Gemini (Mithuna)
- Cancer/Crab (Karka)
- Leo (Simha)
- Virgo (Kanya)
- Libra (Tula)
- Scorpion (Vruschika)
- Sagittarius (Dhanusha)
- Capricorn (Makara)
- Aquarius (Kumba)
- Pisces (Meena)
These major constellations were often used to track time through the location of these constellations and by the movement of the sun in ancient times.
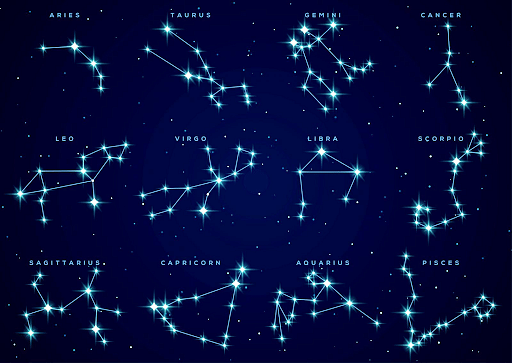
Zodiac Constellations
The 12 zodiac signs of the horoscope determine the movement of the Earth through the heavens. The constellations carve out the path of the sun. As Earth revolves around the sun, the movement of the Earth appears to be such that the sun passes through various constellations. As the position of the moon appears to change each night, the sun's position also moves towards the East relative to the stars that are distant. However, the sun doesn't actually change its position or move. The appearance of the movement seems to be due to the motion of the Earth as it moves around the sun.
Checkout Important Notes for Gravity
Big Dipper
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Also known as Saptarishi in India, the big dipper constellation is formed of seven stars and is visible in the Northern Hemisphere in the sky. It is also known as Ursa Major.
It is generally observed during the summer in the early part of the season.
- The pattern is in the form of a big ladle that comprises 7 major stars out of which 3 exist in the handle while 3 are in the bowl.
- The shape of the constellation is like a wheelbarrow or like a big ladle.
- The constellation is a part of the bigger constellation known as Ursa Major, also called The Great Bear.
- Two of the stars of the big dipper constellation appear to be pointing towards the Pole Star, also called Dhruva or the Polaris.
- This Pole Star is the only star that does not move from East to West in the night sky, instead it appears to be fixed.
- This fixed appearance of the Pole Star is because the star is placed directly above the axis of the Earth.
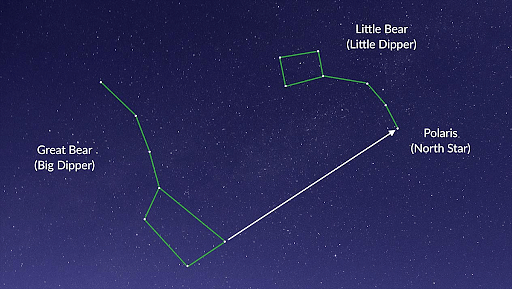
Big Dipper and Little Dipper pointing towards Polaris
Little Dipper
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The constellation Little Dipper can be identified in the night sky through the Big Dipper. It is also known as Ursa Minor, or "The Little Bear". Observing the right part of the constellation that is in the form of a cup and following a straight line in the North direction can lead us to the North Star, also known as Polaris. This is located towards the end of the handle of the Little Dipper which forms the cup of the little bear and the tail of the stars forms a part of the side of the bear.
Read More: Difference between Stars and Planets
Orion
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The constellation Orion is also known as 'the hunter'. In India, it is called Mriga. The Orion constellation is composed of numerous bright stars. The 'belt' of the hunter is made up of three bright stars that are in a straight line. These straight-lined stars point towards the brightest star that exists in our night sky i.e. Sirius. It can be observed in the winter season during the evening time
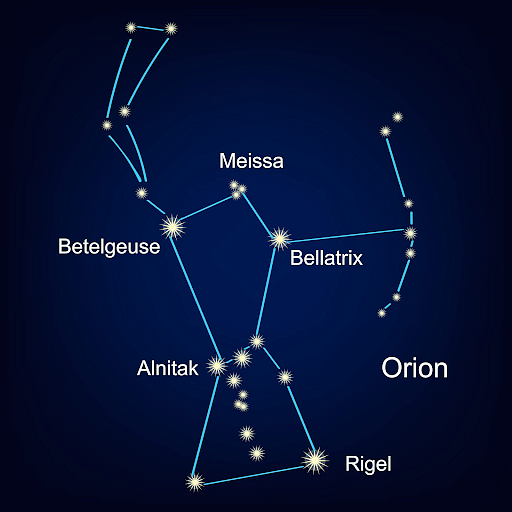
Orion constellation
Taurus
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The Taurus constellation, also known as "The Bull" exists above the Orion constellation and is much easier to locate in the night sky. The Taurus constellation can be easily located through Aldebaran, which is a large red star. The bottom of the horn of the formation is a part of the Crab Nebula. These clusters of stars can easily be located through the naked eyes.

Taurus Constellation
Gemini
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The Gemini constellation is also known as "The Twins". This constellation can easily be located through Orion. It can be identified above a side of the raised arm of the hunter. The constellation looks like two stick figure twins touching with outstretched arms. Both of these twins have torsos, heads, and legs which can be easily identified once the two brightest stars of the twins are located.

Gemini Constellation
Read More: The Role of Atmosphere in Climate Control
Cassiopeia
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Cassiopeia is another constellation that can be observed in the winter sky during the early night. The shape of the pattern resembles a W or an M.
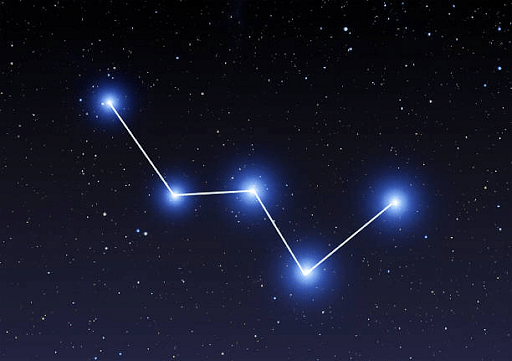
Cassiopeia Constellation
These constellations can be easily spotted even in cities as they are bright enough. So, the next time you gaze towards the night sky, try to identify the constellations in the sky above.
Things to Remember
- The constellations are the patterns in the night sky that are formed of stars and that can be easily recognized.
- In the sky, all these constellations appear to be in a movement from west to east. This motion is because the Earth undergoes rotation from the West to the East.
- Constellations helped in determining the change of seasons in agriculture before the advent of the new calendars.
- The celestial objects in the universe can be explained using the constellations in the sky.
- The constellation Orion is also known as 'the hunter' and is composed of numerous bright stars.
- The Gemini constellation is also known as "The Twins". This constellation can easily be located through Orion.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. What are constellations? (5 marks)
Ans. Constellations are a group of stars that resemble an imaginary pattern or shape in the night sky. These are also known as nakshatras. They are given their names after people, mythological characters, inanimate objects, and animals they resemble. So far, 88 constellations have been recognized. Some of them are:
- Ursa Major or the Great Bear: This is a well-known and the third largest constellation. It resembles a big dipper in shape and is easily visible in the northern hemisphere in the sky. It is composed of 7 bright stars.
- Ursa Minor or the Little Bear: It resembles a ladle shape similar to the Ursa Major. It has 7 stars. Pole star can be located near the tail of the Little Bear.
- Orion or the Hunter: Orion is composed of 7 major stars. The three stars in the middle are organized in a straight line which resembles the hunter's belt. The other four stars take the formation of a quadrilateral.
- Cassiopeia: Cassiopeia is a northern sky constellation that resembles a distorted M or W. It can be located easily in the winter sky in the early hours of the night.
- Leo: The Constellation Leo is made up of numerous bright stars and therefore it can be easily recognized in the night sky. It can be seen from both the Northern and the Southern Hemisphere.
Ques. How are zodiac signs related to Constellations in the night sky? (5 marks)
Ans. When Earth revolves around the sun, it appears that the sun is moving around in a circular path. This circular path defines a plane which is known as the plane of the ecliptic. This plane holds certain constellations through which the sun appears to pass throughout the year. There exist 12 astrological zodiac constellations however astronomically there are 13 zodiac Constellations which are Aquarius, Capricornus, Pisces, Taurus, Aries, Cancer, Gemini, Virgo, Leo, Scorpius, Libra, Saggitarius, and Ophiuchus. Astrologically, the 12 Constellations along with dates are as follows:
- Capricorn: December 22 - January 19
- Aquarius: January 20 - February 18
- Pisces: February 19 - March 20
- Aries: March 19 - April 19
- Taurus: April 20 - May 20
- Gemini: May 21 - June 20
- Cancer: June 21 - July 22
- Leo: July 23 - August 22
- Virgo: August 23 - September 22
- Libra: September 23 - October 22
- Scorpio: October 23 - November 21
- Sagittarius: November 22 - December 21
Zodiac refers to the region that resembles a belt of a celestial sphere across the sun's ecliptic path over the year while constellations refer to the patterns of stars in the night sky. There are 88 constellations that are officially recognized and named.
Ques. Name the largest constellation. (2 marks)
Ans. Out of the 88 recognized constellations, the largest constellation is Hydra which is a slender, winding, and extended star region. It is stretched across the Northern Hemisphere and is named after the sea serpent Hercules associated with Greek mythology.
strong>Ques. What is Orion? (2 marks)
Ans. Orion is a constellation that resembles the shape of a man. It is made up of 7 prominent stars. It has three stars located in a straight line which represents the belt of the hunter.
Ques. What are stars? Why do different stars show different colors? (3 marks)
Ans. Stars are basically clusters of dust and gas which emit light and heat. The color of the star indicates how much heat a star emits:
- Red stars are the coolest stars
- Yellow stars emit medium-range heat such as sun
- Blue and white stars are the hottest stars.
Ques. What are the various ways constellations are used? (3 marks)
Ans. Constellations, since earlier times, have been used for a variety of purposes which are as follows:
- As a reminder for farmers to harvest and plant crops according to changing seasons
- For the purpose of navigation through oceans and deserts
- They are also used for storytelling purposes.
Ques. What is the difference between galaxy and constellation? (3 marks)
Ans. The differences between constellation and galaxy are as follows:
| Galaxy | Constellation |
|---|---|
| Galaxy refers to a collection of billion stars. | Constellation refers to a collection of a few stars. |
| Galaxies don't resemble the shape of any animals or human beings. | Constellations however resemble the shapes of animals or humans or inanimate objects. |
| Our universe has billions of galaxies. | We have 88 recognized constellations up till now |
Ques. Are the stars in a constellation close to each other? (4 marks)
Ans. Though the stars in Constellations appear to be closer to each other from Earth, they are not necessarily near to each other in space. Each constellation is formed of a collection or a set of stars that are distributed in three dimensions in space as the stars are all at different distances from the Earth. As we are looking at the constellations from very far away, all of its stars appear to be in the same plane to us. However, stars differ greatly in terms of distance from Earth, their size, and their temperature. The stars which are dimmer might be smaller in size, cooler, and farther away than the brighter stars. Hence, the stars are not necessarily near each other as they appear to be for us.
Ques. How were constellations in the night sky named? (2 marks)
Ans. Most of the names of the constellations in our sky came from Greek, Middle Eastern, and Roman Cultures. Clusters of objects were identified as various objects, animals, gods, goddesses, and many mythological creatures.
Ques. Are all stars in the night sky part of one constellation or the other? (3 marks)
Ans. Our night sky is populated with a billion stars. However, just a fraction of these make up the patterns or shapes we easily recognize as constellations in the sky. The stars that are a part of one or other constellations are those that were easily visible in ancient times with the unaided eye. All the stars however can be identified within the boundaries of the 88 officially recognized constellations as with time when the astronomers studied the night sky with modern types of equipment, they identified stars in the darkest of spaces around the constellations that were not previously a part of the identified constellations.
Ques. Why do constellations and stars in the sky move? (5 marks)
Ans. Stars are at a great distance from Earth. With the exception of the sun, the nearest star to us is known as Proxima Centauri and it is more than four light-years away. As the Earth rotates on its own axis, we spin past the stars. Hence, the stars appear to move from the east to the west. Due to the same reason, the sun appears to set in the west and rise in the East to us.
Stars that are located near the celestial poles which are the imaginary points where the axis point of North and South meets in space have a smaller circle of spin. Hence, the pole star is observed to undergo very little movement in the night sky. The farther the stars are from Polaris, the wider the circle they will trace. Some stars make a full circle around the celestial pole. For instance, the Big and the Little Dipper exists in the Northern Hemisphere. These stars are known as circumpolar stars as they do not set.
Ques. Why all around the year, do we observe different constellations in the night sky? (2 marks)
Ans. The constellations in the sky appear to gradually shift towards the west. This shift is due to the movement of Earth around the Sun. Hence, as we are looking at different directions of space in summers and winters, we observe different constellations around the year.
Ques. Why don't the constellations match the astrological dates? (4 marks)
Ans. The astrological signs were defined and linked to the calendar about 2500 years ago. Since that time, the timing of the seasons of the Earth has shifted due to the fact that Earth wobbles a bit which is responsible for its axis shifting in different directions over time. This cycle of change continued for about 23000 years. Therefore, the direction of the axis of the rotation of the Earth helps in determining where at Earth's orbits, the seasons will change at a slightly different place with time. Hence, with time the seasons have changed while the background of the stars of the zodiac constellations has remained fixed. Hence, due to this change of over several thousand years, we observe that the Constellations don't line up with our astrological dates. For instance, over five thousand years ago, the sun passed through the Taurus constellation during the time of spring equinox. However, today it passes through Pisces towards the beginning of the spring season.
Ques. On what factors does the visibility of a particular constellation depend upon? (3 marks)
Ans. The constellations we see in the night sky depend on the time of the year as the Earth orbits the sun, therefore as we orbit our view of the space through the night sky undergoes a change. The stars appear to move towards the west due to this motion of the Earth.
Another factor that determines what constellations we can observe in the sky is our location on Earth. As the Northern hemisphere points in a different direction than the Southern Hemisphere. As a result of this, the stargazers of say, India will see a different view of the sky and different constellations than the stargazers of London.
Also Read:









Comments