Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Difference between molds and yeasts is that mold grows in multicellular filaments and yeast grows as a single cell. In kingdom Fungi, both yeast and molds belong to eukaryotes with cell nuclei as well as membrane-bound organelles. There are over 1500 different types of yeast that are used for baking, additives, alcohol production, and food beverages in the industry. There are approximately 400,000 types of molds found, which are also used for cheese making and other processes in the industry.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Mold and yeast, Yeast and mold reproduction, Yeast fungus, Types of mold
Also Read: Fungus Life Cycle
What are Yeasts?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Yeast is a microscopic fungus that is made up of a single oval cell and has a one-celled organism. Yeast is oval-shaped as well as colourless or we can say white in appearance. The asexual reproductive process of yeast is its most notable trait. As a bud, It creates a daughter cell & this mechanism of asexual reproduction is known as budding. Yeast can only get its nourishment from organic things.
They secrete enzymes into external food sources, which they digest to acquire simple nutrient forms. As a result, It can be utilised to make ethanol through fermentation & also utilised to make the dough rise in the banking sector. It is quite common and it can be found in a variety of areas, including fruits, vegetables, and the skin of mammals.
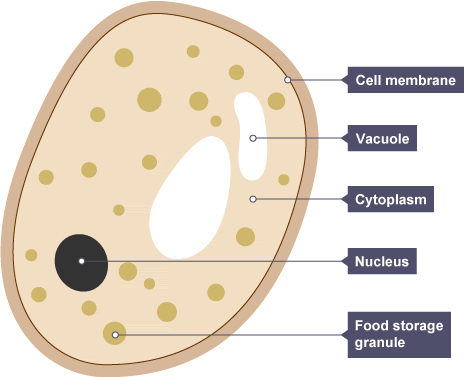
Yeasts Labelled Diagram
Also Read: Explanation on Budding in Yeast Cells
What are Molds?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Mold is a type of fungus that arises in the form of hyphae, which are multicellular threads & colonies that can be seen with the naked eye. The vegetative reproduction of fungi is how they multiply. Tubular hyphae can have a high number of nuclei that have the same genetic makeup. It thrives in the presence of organic substances & produces spores that are both sexual and asexual. Molds, like yeast, get their nourishment from the enzymatic digestion of organic materials.
They take up nutrients via their cell walls. They are also employed in the manufacturing of cheese, tempeh, and soy sauce. Molds, on the other hand, might be dangerous since they can cause respiratory illnesses and allergies. It thrives in moist, dark, & especially in steamy environments.
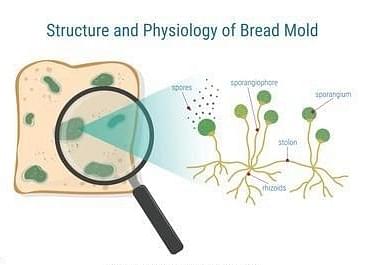
Molds in Bread Diagram
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Difference Between Molds and Yeasts
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The differences between molds and yeast are represented in the table below.
| S. No. | Character | Molds | Yeasts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Definition | It is a multicellular organism and threadlike fungus. | It is a unicellular organism and budding fungus. |
| 2. | Form | The growth of molds in form of multiple tubular branches. | The growth of yeasts in form of large single cells |
| 3. | Habitat | Found in humid areas, damp areas, dark areas, etc. | Found on fruits, in stomachs of mammals, on the skin, etc. |
| 4. | Cell type | Its cell type is multicellular. | Its cell type is unicellular. |
| 5. | Sporing fungi | Yes | No |
| 6. | Colony Morphology | They are soft, opaque & cream-coloured. | They are filamentous types. |
| 7. | Hyphae | have microscopic filaments. | They do not have true hyphae. |
| 8. | Appearance | It has a fuzzy appearance & can be found in several shapes. | Oval in shape. |
| 9. | Incubation Temperature | Room temperature | It has also been used at room temperature but sometimes it can be used at above room temperature. |
| 10. | Color | It may be orange, green, pink, brown, purple, etc | It is colourless as compared to moulds. |
| 11. | Cultivation time | It takes more time than yeasts to grow. | It takes approx 25 to 35 hours to grow. |
| 12. | Aerobic/Anaerobic | It grows only in Aerobic conditions. | It grows Both in Aerobic and Anaerobic conditions. |
| 13. | pH range for growth | Unlike yeasts, it can grow in a wider range of pH levels. | pH Range 4.0 to 4.5 |
| 14. | Reproduction | Sexual or Asexual | Asexual |
| 15. | Asexual Spores | Sporangiospores & Conidia | Blastospore |
| 16. | Diagnosis/Identification | Most clinical molds may be identified by looking at the ontogeny and morphology of their asexual spores under a microscope. | Physiologic testing and a few important morphologic features are used to identify the species. |
| 17. | Sexual Spores | Zygospores, Ascospores, and Basidiospores are all types of sexual spores. | No sexual spores. |
| 18. | Energy Production | Secrete hydrolytic enzymes that break down polymers like starch, cellulose, and lignin into more absorbable forms. | In anaerobic fermentation, convert carbohydrates to alcohol and carbon dioxide. However, Carbon can also be obtained from hexose sugars. |
| 19. | Health risks | Reactions to allergens and respiratory issues | infection in those with weakened immune systems. |
| 20. | Uses | Food Production etc | Ethanol production, Vitamin supplements etc |
| 21. | Species type | Approx 4,00,000 | Approx 1,500 |
| 22. | Examples | Alternaria, Aspergillus, Fusarium, Mucor, Penicillium, Rhizopus, etc. | Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cryptococcus neoformans, and other yeasts are examples. |
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
Similarities Between Yeasts and Molds
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The following are the similarities in mold and yeast.
- Fungi come in two forms: mold & yeast.
- A chitin cell wall is found in both mold & yeast.
- Mold and yeast are both saprophytes.
Also Read: Pollen Grains
Things to Remember
- Yeast is a colourless, filamentous, thread-like structure containing pseudohyphae but no spores. It may grow both aerobically and anaerobically.
- Yeast is a single-celled eukaryote that buddingly reproduces asexually.
- A few molds can be harmful to one's health, causing allergies, headaches, itching, and respiratory issues.
- Yeast is typically found in fruits, animal skin, vegetables, and other foods, and it has the ability to ferment carbohydrates into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Molds can cause allergies and other respiratory problems, while yeast can cause infection if your immune system is compromised.
- Molds and yeast are both eukaryotic microorganisms that belong to the kingdom fungi, however, yeast is a single-celled creature that reproduces asexually, whilst Molds are multicellular organisms that reproduce sexually or asexually.
Also Read: Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis
Sample Questions
Ques. What inhibits the growth of molds and yeast? (2 marks)
Ans. A variety of chemical preservatives are allowed in meals to prevent yeast and mould growth. Compounds including benzoic acid, sodium benzoate, propionic acid, sorbic acid, and sodium diacetate are on the list of safe substances.
Ques. Is yeast & mold harmful? (3 marks)
Ans. Food contamination by yeasts and molds can result in significant financial losses for the manufacturer, processor, and consumer. Because of their propensity to produce poisonous compounds known as mycotoxins, some foodborne molds and perhaps yeasts may be harmful to human and animal health.
Also Read: Difference between Fertilizers and Manure
Ques. In what conditions does mold grow? (3 marks)
Ans. Mold thrives in damp environments, such as around roof, window, or pipe leaks, or in areas where there has been flooding. Mold loves to grow on paper, cardboard, ceiling tiles, and wood goods. Dust, paints, wallpaper, insulation, drywall, carpet, fabric, and upholstery can all harbour mold.
Ques. How does yeast grow? (3 marks)
Ans. Budding is the most common way for yeast to reproduce asexually. On the mother cell, a tiny bud that will become the daughter cell forms and grows larger with ongoing growth. The mother cell multiplies and then segregates its DNA as the daughter cell grows. The daughter cell's nucleus splits and migrates into it.
Ques. Write uses of mold & yeast? (5 marks)
Ans. Molds are commonly employed in the manufacturing of soy sauce, sake, quorn, cheese, rennet, and salami, among other foods and beverages. Antibiotics like penicillin, cholesterol-lowering medications like Lovastatin, and immunosuppressants like cyclosporine all contain them. Yeasts are used to make ethanol for alcoholic beverages like beer, as baking leavening agents, and as a vegan nutritional supplement. Geneticists utilize them to investigate processes like the cell cycle, DNA replication, and recombination because of their simple cellular structure.
Ques. Explain the Health risk of mold & yeast? (5 marks)
Ans. In excessive numbers, certain species of mould can be harmful to human health, including allergic reactions and respiratory issues. Mycotoxins, which are produced by some molds, are dangerous to people and animals. Mold allergies can cause a variety of symptoms.
Watery, itchy eyes, persistent cough, headaches or migraines, difficulty breathing, exhaustion, rashes, sinus difficulties, nasal blockage, and frequent sneezing are all signs of a mold allergy. In persons with weakened immune systems, yeasts can cause illness. Cryptococcosis is a condition that affects 7-9 percent of AIDS patients in the United States. In humans, the yeast candida can cause candidiasis.
Also Read: Microbes in Human Welfare
Ques. Difference between yeast & molds according to energy production? (5 marks)
Ans. Molds release hydrolytic enzymes, which decompose polymers like starch, cellulose, and lignin into simpler molecules that may be absorbed, mainly from the hyphal tips. This contributes to the degradation of organic matter.
Yeasts can generate energy either aerobically (with oxygen) or anaerobically (without oxygen) (without oxygen). Yeasts use anaerobic respiration to produce energy by converting carbohydrates to carbon dioxide and alcohols. Hexose sugars are also a source of carbon for yeast.
Ques. Write 2 key differences between mold & yeast? (3 marks)
Ans. There are 1500 different varieties of yeast that may be found in fruits, vegetables, mammals' skin, and other places; there are 400,000 different species of molds that can be found in wet, dark, or steamy environments. Molds are used in the production of cheese, rannit, antibiotics (penicillin), and Lovastatin. Yeast is utilised in the production of food beverages, wine, and other products.
Also Read: Slash and Burn Agriculture



Comments