Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Light Energy is a type of kinetic energy that allows different types of lights to be visible to human vision. Light is electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by heated things such as lasers, bulbs, and sunlight. The Sun emits several different types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all conceivable radiation frequencies. It depicts electromagnetic radiations like ultraviolet and X-rays, rising from the sun.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Electromagnetic radiation, Ultraviolet rays, X rays, Frequency, Kinetic Energy, Wavelength
Read about: Photon Energy
What is Light Energy?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Photons are little energy packets produced by light. Creation of photons occurs when an object's atoms are heated. Heat excites the electrons, causing them to produce more energy. This energy is released in the form of a photon, and as the material heats up, more photons are emitted.
As it moves, light energy takes the form of a wave. Whatever the case may be, it can move light energy. This is why light energy may travel across space without needing to pass through air, whereas sound waves must pass through solids, liquids, or gases. Light energy is extremely rapid and moves faster than any other form of energy. 186,282 miles per second is the speed of light.
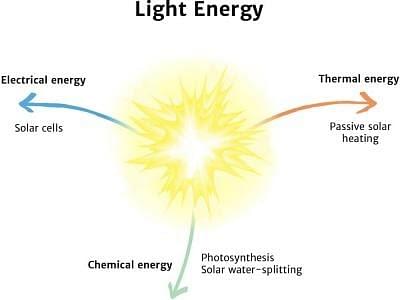
Light Energy
Read More: Types of Energy
Types of Light Energy
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Following are types of Light Energy:
Infrared Light
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation that has wavelengths longer than visible light wavelength. It is, therefore, invisible to human eyes. Infrared encompasses wavelengths from 1 millimeter to nominal red edge of visible spectrum, i.e., around 700 nanometers.

Infrared Light
Also check: Potential Energy
Visible Light
Visible lights are electromagnetic radiations that can only be seen with the naked eye. These waves can be visualized as the colors of the rainbow, with each color containing a different wavelength. Wavelength of red is the longest, whereas that of violet is the shortest. When all of the waves are observed at the same time, white light is formed. When white light passes through the prism, it is split down into the visible light spectrum's colors.
Also check:
X-rays and Ultraviolet Light
Doctors utilize these brief light waves to take images within our bodies and detect fractures in our bones. X-rays are often used by dentists to monitor the amount of tooth decay. Wavelength, frequency, and quantum energy are all variations between ultraviolet light and x-rays.
Read More: Light
Properties of Light Energy
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- The rate at which the source discharges light energy is referred to as light intensity. A watt is its power unit. It's also known as brightness, which is defined as the rate of light generation in a surface unit or energy per unit time per unit area.
- The number of crests that pass across a certain spot in a second is known as light frequency.
- The space between two successive crests or troughs is known as the wavelength of light. Light waves travel at the same speed through the vacuum. Because wavelength and frequency are nearly identical, the shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency.
- It's a specific point in the cyclic waveform's time frame. When the waves are in phase, the intensity of light energy is increased.
- Unpolarized light undergoes polarization as a result of a mechanism called polarisation. There are multiple planes on which light waves vibrate. As a result, they're called unpolarized light.

Energy Waves
Read More: Wave Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation
Uses of Light Energy
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- It is only because of light that we can receive sustenance from plants. Photosynthesis is aided by the presence of light. Plants use the light they receive to prepare food for themselves and us.
- Vitamin D is well-known for its health benefits. As a result, the Sun is the best source of this vitamin for obtaining it for free.
- The light energy that we receive from the sun can be used for residential purposes, such as powering solar cookers. We also come across solar water heaters that utilize sunshine.
- Because of light, the human eye can discern between 6,000 different shades of a single color. Light has a variety of electromagnetic spectrums, each of which contains seven colors (VIBGYOR): Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red
- Spectroscopy analyzes numerous chemicals quantitatively and qualitatively; yet, all of this is made possible by light. Spectroscopy comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the wavelength of light used.
- Light's UV component is a powerful sterilizing agent. UV lamps are the most effective sterilizers, as you may have noticed in supermarkets and hospitals.
- UV rays eliminate microorganisms in the air, making the supermarket or hospital area sterile. As a result, UV light is called a dry sterilization procedure. Sunlight is one of the most efficient sterilizing agents available, helping to eliminate all microorganisms found in hospital blankets and mattresses.
Read More: Refraction of Light
Things to Remember
- Light is a form of energy
- There are two types of sources: natural and man-made. Natural sources include the sun, while man-made sources include bulbs, candles, and lights.
- The amount of energy contained in photons determines the intensity of light.
- Because light can only be seen when it bounces off an object, space is dark because there is no object to bounce the energy back.
- Because each color has a particular wavelength, we see multiple colors of light.
- Light energy is always moving and can therefore not be stored.
- Although humans are unable to see UV light, some insects are able to do so.
Read More:
Sample Questions
Ques. Why is light a particle? (2 marks)
Ans. Light mostly behaves as a wave, but it may also be thought of as a collection of microscopic energy bundles known as photons. Photons have no bulk but convey a constant quantity of energy. They also discovered that raising the intensity of the light increased the number of electrons emitted but not the speed with which they were ejected.
Ques. How Does Light Produce Energy? (2 marks)
Ans. Photons are little energy packets produced by light. The creation of photons occurs when an object's atoms are heated. The heat excites the electrons, causing them to produce more energy. This energy is released in the form of a photon, and as the material heats up, more photons are emitted.
Ques. Is Light Energy Kinetic Energy? (2 marks)
Ans. Light energy is a wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the naked eye. It is a kinetic energy kind. Kinetic energy is energy that causes anything to move. It is potential energy if it lifts things. However, it is the same energy that is expressing its many consequences. Light is referred to be kinetic energy since it is simply energy in motion.
Ques. What is the significance of light energy? (2 marks)
Ans. The uses and value of light energy are incalculable. The sun supplies the light that plants need to photosynthesize, making food available to all species. Visible lights allow us to see the items that surround us. The temperature of the water is affected by light energy, as is the connection between predators and prey. As a result, light regulates the ecosystem's growth and development.
Ques. What is the artificial form of light energy? (2 marks)
Ans. Aside from the Sun, which is a natural source of light energy, other artificial light sources include bulbs, lanterns, and LEDs, which emit light when it is naturally dark. India's primary source of artificial light is fossil fuels; nevertheless, this type of light energy pollutes and disrupts the natural ecology. As a result, we concentrate on protecting and harnessing natural light.
Ques. Is light a wave or particle? (3 marks)
Ans. Both a wave and a particle, light can be characterized. The dual nature of light has been demonstrated in two tests in particular. When we think of light as a collection of particles, we refer to them as "photons." Photons are massless particles that carry a certain quantity of energy.
Light has a dual nature as "both a particle and a wave". Thus, the fundamental theory of light has progressed from electromagnetics to quantum mechanics. Light is a particle (photon), and the passage of photons is a wave, according to Einstein.
Ques. Can light be controlled in natural conditions? (3 marks)
Ans. Light does not always flow in the same direction. Various factors influence the amount of light that enters a natural habitat. Topography, for example, has an impact on light insolation. Ice has a high albedo, which means it reflects more light than white snow.
Hard and dark topography, on the other hand, attracts more light examples, such as black soil. Similarly, additional elements such as vegetation, cloudiness, seasonal patterns, and day-night variations influence the amount of light that reaches the Earth. In the paper and video courses, the factors are examined in depth.
Ques. What are the challenges caused by artificial light energy? (4 marks)
Ans. The sort of light energy generated by humans is known as artificial light energy. These light energies are primarily generated using fossil fuels. It has the following negative consequences:
- Light pollution disrupts the natural ecology, resulting in biodiversity loss.
- As a result of the release of dangerous greenhouse gases during the process of light generation, it pollutes the air.
- Global warming and climate change have a greater impact.
Because of these negative consequences, India is primarily focused on encouraging the use of natural light energy. As a result, the National Solar Mission is being promoted.
Read about: Quantum Theory of Light



Comments