Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Moon is the natural satellite of our Earth and the nearest celestial body that we can observe every day in the sky during nighttime. It is an astronomical body that moves around the Earth in an orbit. It is the fifth-largest celestial body existing in our solar system. It is composed of loose dirt and rocks and also has craters on its surface that exist as a result of the impact of the collision of meteorites. As the moon does not have an atmosphere, the meteorites don’t get burnt up before reaching the surface and hitting it. There is also an absence of life on the moon as the air is not present there. The American astronaut, Neil Armstrong was the first person to land on the moon in 1969. In this article, we will learn more about the moon and its multiple features.
Read More: Some Natural Phenomena due to Sunlight
| Table of Contents |
Key Terms: Moon, Earth, Solar System, Lunar Phases, Eclipse, Tides, Full Moon, New Moon, Celestial Body, Gravitational Force
What is Moon?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Moon appears the largest in the sky as it is the closest celestial body to us. The stars appear much smaller in comparison to the moon as they are very far away from us than the moon, our celestial neighbor. Even as the moon revolves around the Earth, the gravitational forces of attraction that exist between the Earth and the moon hold the same in its orbit. Moon keeps changing its shapes every night in the form of 4 phases.

Moon
Read More:
Movement of Moon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The moon is always in synchronous motion to the motion of the Earth. Therefore, we can see only one side of the moon from the Earth at a time. The orbital distance of the moon is 384,402 km or 1.28 light seconds. The gravitational effect of moon also influences the ocean bodies leading to tides.

Movement of Moon
Read Also: Why do stars twinkle?
Phases of Moon
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The appearance of the moon over a month is known as the phases of moon. As the moon revolves around the Earth, half the side of the moon is lit up by the light from the sun. Each phase of the moon repeats after every 29.5 days. The 8 main phases of the moon or the lunar phases are as follows:
-
New Moon
A new moon occurs when the moon is not visible to us. We see the half-unlit portion of the moon at this time. It begins when moon exists right in the middle of sun and Earth. A solar eclipse only happens at a new moon.
-
Waxing Crescent Moon
When the moon looks similar to a crescent in appearance, it is known as the waxing crescent moon. The moon increases the “waxes” in size each day. Usually, this phase is only visible in the west.
-
First Quarter Moon
Also known as the half-moon, the first quarter phase of moon appears only when half of the portion of the moon that is lit is visible to us. This comes after the waxing crescent phase, usually after one week of the new moon.
-
Waxing Gibbous Moon
A waxing gibbous moon is observed when more than half of the area of moon that is lit is visible. The shape of the moon increases in this phase from one day to the next. The waxing gibbous phase occurs between the first quarter phase and the full moon.
-
Full Moon
When all of the lit area of the moon is visible to us from Earth, we are observing a full moon. This happens when the moon is located between the opposite of Earth from the sun.
-
Waning Gibbous Moon
This lunar phase only occurs when more than half of the area of the moon lit by the sun is visible. From one day to another, the shape of the moon continues to decrease at this point. This phase exists in the midst of the full moon and the third quarter phase of the moon.
-
Last Quarter Moon
Half of the moon is visible to us after the waning gibbous lunar phase in the last quarter moon phase.
-
Waning Crescent Moon
Here, in this phase, the moon resembles a crescent which decreases in size every day.
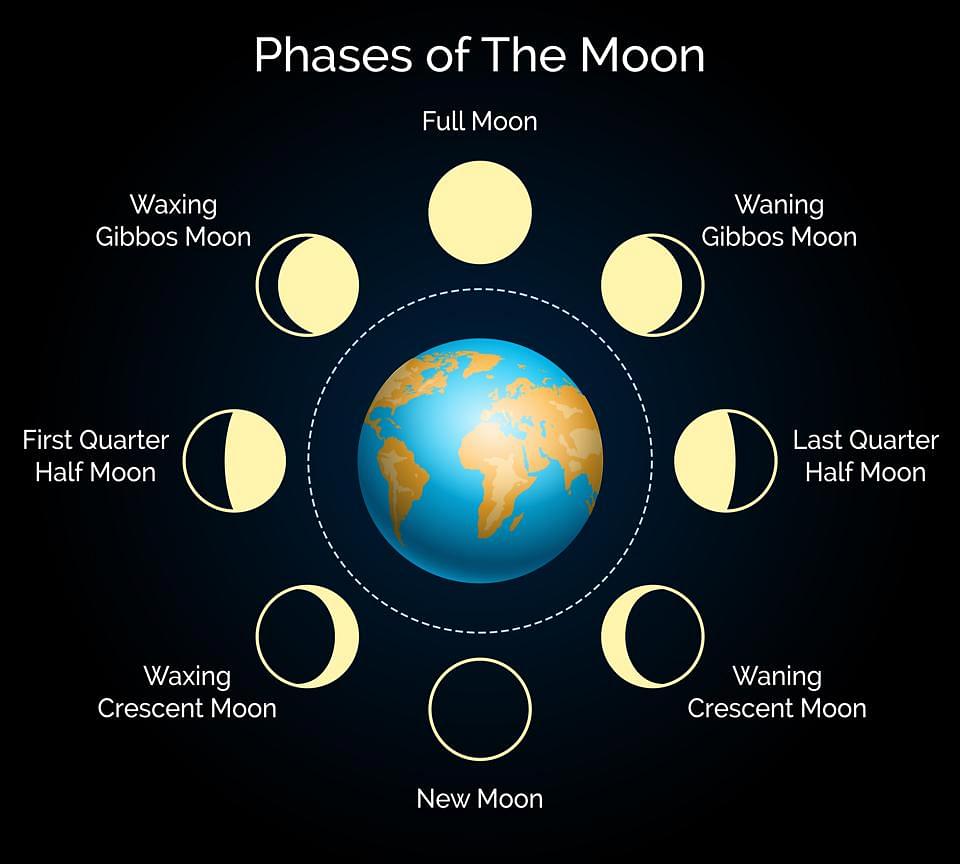
Phases of Moon
Read More: Difference Between Stars and Planets
When moon, a heavenly body, is located behind the Earth and the sun, we are able to observe all of the illuminated portions of the moon. This is the full moon phase (Poornima). When moon is located between the sun and the Earth, we can only observe the dark potion of the earth and a new moon occurs (Amavasya). In between these two extreme phases, there are intermediate phases of the moon such as crescent and half moon.
This celestial body takes almost 27 days to continue its motion and revolve around the Earth. However, between the two full moons, a time gap of 29.5 days exists. This is because the Earth is also traveling through space covering its own distance at that time, revolving around the sun. Therefore, moon has to cover some extra distance if it has to come exactly behind the Earth and sun one more time. This extra distance takes about 2 days more.
Only one side of moon is visible to us, the other side is known as the far side or the dark side as it does not face the Earth at any time. The reason behind this is that the moon takes almost the same time to revolve around the Earth as it takes to rotate around its own axis. This occurs due to a known phenomenon that is referred to as Tidal Locking. We had not been able to observe the dark side of the moon until the year 1959 when a picture of it was taken by the Soviet space probe - Luna 3.
Read More:
Things to Remember
- Moon is the natural satellite of our Earth and the nearest celestial body that we can observe every day in the sky during nighttime.
- The gravitational forces of attraction that exist between the Earth and the moon keeps the same in its orbit as it revolves around the Earth.
- The moon reflects the light it receives from the Sun as it does not have any light of its own.
- Due to this, the shape and appearance of moon change every day.
- When moon is located between the Earth and the sun, the entire portion of the moon that is lit up is visible to us. This is the full moon phase of the moon.
- When the moon exists between the sun and Earth, it is not visible to us and this is the new moon phase of the moon.
- Moon revolves around the Earth in 27 days.
- A time period of 29.5 days exists between any two full moons.
- Moon takes almost the same time to revolve around the Earth as it takes to rotate around its own axis. This phenomenon is referred to as Tidal Locking.
Sample Questions
Ques. State some properties of moon. (5 Marks)
Ans. Some of the properties of the moon are as stated below:
- The average distance of the moon from Earth is 384,400 kilometers.
- The moon rotates in its orbit and has an orbital period of 27.32 Earth days.
- The mass of the moon is about a bit more than 1 percent of the Earth.
- The gravity of moon is 0.166 of the Earth’s gravity.
- The temperature of the moon ranges from -248 to 123 degrees Celsius.
Ques. What is the lunar terrain? (3 Marks)
Ans. The light areas existing on the moon are referred to as the highlands while the dark portions are known as maria, which is the Latin word for seas. The dark features of the moon are the impact basins that were filled up with lava about 4.2 and 1.2 billion years ago. These light and dark areas of the moon are formed from rocks that have different compositions and different ages. The craters of the moon have been preserved for about billions of years. They also act as evidence for the impact of history and collisions on the moon and other celestial bodies of our solar system.
Ques. Explain the relation between the moon and tides. (5 Marks)
Ans. The gravitational pull of the moon on Earth is mainly responsible for the formation of tides in oceans. As the gravity of the moon tugs at Earth, the mass of the Earth is shifted which distorts its shape slightly as the equator gets elongated and the poles get shortened. The gravitational pull of the moon acts on all the points of the Earth. While the strongest of the pull occurs at the point that is closest to the location of the moon, the weakest pull is at the locations that lie farther away from the moon.
When the gravitational pull of the moon acts on the water present in the water bodies, it just pushes and squeezes it around the globe. As a result of both this pull and some other forces, the water rises on the side and bulges closest to the moon and the one that is farther. These bulges are known as the high tides.
Ques. What is a supermoon? When does it occur? (5 Marks)
Ans. When a full moon coincides with the closest approach of the moon to Earth in its elliptical-shaped orbit, which is a point also known as perigee. During its 27 day orbit around the Earth, the moon travels through both its perigee, which is located about 363,300 km from Earth, and its apogee which is its farthest point, which is located about 405,500 km from Earth.
“Supermoon” typically refers to a full moon that comes within atleast 90% of the perigee. The phenomenon of a supermoon happens just three to four times a year. When it is at its closest point, the moon is about 17% bigger and 30% brighter than the faint moon of the year. When the moon is at its closest approach, it can cause higher tides than usual.
Ques. What are lunar eclipses? What are its various types? (5 Marks)
Ans. Lunar eclipses generally occur at the phase of the full moon. When Earth is located in between the moon and the sun, the shadow of the Earth fall upon the moon’s surface. This dims the moon and at some times, turns the surface of the moon striking red for a few hours. There are three different types of lunar eclipses:
- Total Lunar Eclipse: During the total lunar eclipse, the moon moves in the innermost part of the shadow of the Earth or the umbra. Some of the sunlight that passes through the atmosphere of the Earth reaches the surface of the moon which also makes it dimmer. The colors with longer wavelengths i.e. red and orange pass through the atmosphere of the Earth while the shorter wavelengths i.e. violets and blues get scattered. This is why the moon appears to be reddish or orangish during the time of a lunar eclipse. The more clouds and more dust is present in the atmosphere, the redder the moon will appear.
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: An imperfect alignment of moon, earth, and sun result in the passing of moon through only a certain part of the umbra of the Earth. The shadow of the moon then grows and recedes without covering the moon entirely at any point in time.
- Penumbral eclipse: During a penumbral eclipse, the moon passes through the penumbra of the Earth. It also refers to the faint outermost part of its shadow. The moon dims slightly as a result of this. It is really hard to notice this eclipse.
Ques. Describe the motion of moon around the Earth. (3 Marks)
Ans. The moon takes about 27.3 Earth days to complete its motion in the orbit around the Earth. However, it takes 29.5 days to change from one new moon to the next.
As the moon is revolving around the Earth, the Earth is also moving in its orbit. Due to this motion and this change in the position of the Earth, the light from the sun hits the moon at a bit different angle on the 27th day than it did at the starting of the cycle. Thus, it takes additionally a little more than two days for sunlight to reach and hit the moon the same way it did on the zeroeth day. It is due to this reason that Earth takes 27.3 days to revolve around the Earth while it takes 29.5 days from one new moon to the next.
Ques. Why is only a part of the moon visible to us? (3 Marks)
Ans. Except at the time of a lunar eclipse, the moon is always half-lit by the light from the sun. The side of the moon that faces the sun appears to be bright due to the sunlight that is reflected off its surface. Whereas, the side of the moon that faces away from the sunlight appears dark to us. When the side of the moon that is closest to us is fully lit, we observe a full moon.
Whereas when the side of the moon closest to us is dark while the lit side is farther away, we observe a new moon. When we are looking at the other phases of the moon, we are typically looking at the division that exists between the dark part, known as the lunar night, and the bright part i.e. the day.
Ques. What is moon? Describe the various types of moon existing in our solar system. (5 Marks)
Ans. Moon refers to the natural satellites that move around the planet and asteroids in the solar system. More than 200 moons exist in our solar system. Moons have various shapes, types, and sizes. Most of the planetary moons are mostly formed from the gas discs and the dust which circulates in our solar system around the planets. Whereas some moons are formed as “captured objects” that were formed somewhere else but fell into the orbits around the planets in the solar system.
The different types of moons existing in our solar system are
- Earth’s moon: The only satellite of the Earth, our moon acts as a stabilizing force that makes our planet ideal for life. Earth has only one moon
- Mars moons: The red planet, Mars, is orbited by two tiny moons. One of the moons, named Phobos is slowly being torn apart as a result of the gravitational force of mars.
- Jupiter moons: This giant planet is swarmed with moons that orbit around it. There are 53 confirmed moons of Jupiter while 26 are awaiting official names.
- Saturn moons: With fifty-three confirmed moons and 29 awaiting confirmation, Saturn has a total of 82 moons.
- Uranus moons: Uranus has 27 moons that are named after Shakespearean characters.
- Neptune moons: Scientists have discovered 14 moons that orbit this giant distant planet.
- Pluto moons: Pluto has 5 small moons.
Check-Out:








Comments