KCET 2025 was conducted for Physics on 16 April from 10:30am to 11:50am. KCET 2025 Physics Question paper with solutions pdf is available here for download. In KCET 2025, students are required to attempt 60 questions for 60 marks in 80 minutes. KCET has a marking scheme of +1 mark for correct answers and no negative marking for incorrect answers.
KCET 2025 Physics 16 April Question Paper PDF Download
| KCET 2025 Physics Question Paper With Answer Key | Download | Check Solution |

KCET 2025 Physics Questions with Solutions
Question 1:
The variations of resistivity \( \rho \) with absolute temperature \( T \) for three different materials X, Y, and Z are shown in the graph below. Identify the materials X, Y, and Z.
View Solution
Given, a current carrying wire of non-uniform cross-section, which of the following is constant throughout the length of the wire?
View Solution
The graph between variation of resistance of a wire as a function of its diameter keeping other parameters like length and temperature constant is
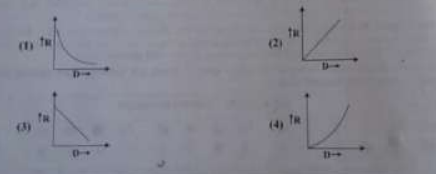
View Solution
Two thin long parallel wires separated by a distance \( r \) from each other in vacuum carry a current of 1 ampere in opposite directions. Then, they will
View Solution
A solenoid is 1 m long and 4 cm in diameter. It has five layers of windings of 1000 turns each and carries a current of 7 A. The magnetic field at the centre of the solenoid is
View Solution
Two similar galvanometers are converted into an ammeter and a millammeter. The shunt resistance of ammeter as compared to the shunt resistance of millammeter will be
View Solution
Which of the following statements is true in respect of diamagnetic substances?
View Solution
Identify the correct statement:
View Solution
Which of the following graphs represent the variation of magnetic field \( B \) with perpendicular distance \( r \) from an infinitely long, straight conductor carrying current?
View Solution
If we consider an electron and a photon with the same de-Broglie wavelength, then they will have the same
View Solution
The anode voltage of a photocell is kept fixed. The frequency of the light falling on the cathode is gradually increased. Then the correct graph which shows the variation of photo current \( I \) with the frequency \( f \) of incident light is
View Solution
When a bar magnet is pushed towards the coil, along its axis, as shown in the figure, the galvanometer pointer deflects towards X. When this magnet is pulled away from the coil, the galvanometer pointer
View Solution
A square loop of side 2 m lies in the Y-Z plane in a region having a magnetic field \( \mathbf{B} = (5 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k}) \, T \). The magnitude of magnetic flux through the square loop is
View Solution
In domestic electric mains supply, the voltage and the current are
View Solution
A sinusoidal voltage produced by an AC generator at any instant \( t \) is given by an equation \( V = 311 \sin (314t) \). The rms value of voltage and frequency are respectively
View Solution
A series LCR circuit containing an AC source of 100V has an inductor and a capacitor of reactances 24\(\Omega\) and 16\(\Omega\) respectively. If a resistance of 6\(\Omega\) is connected in series, then the potential difference across the series combination of inductor and capacitor will be
View Solution
Match the following types of waves with their wavelength ranges
View Solution
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index \( n \). If the angle of incidence is twice the angle of refraction, then the angle of incidence in terms of refractive index \( n \) is
View Solution
A convex lens has power \( P \). It is cut into two halves along its principal axis. Further, one piece (out of two halves) is cut into two halves perpendicular to the principal axis as shown in the figure. Choose the incorrect option for the reported lens pieces.

View Solution
The image formed by an objective lens of a compound microscope is
View Solution
If \( r \) and \( r' \) denote the angles inside the prism having angle of prism \( 50^\circ \), considering that during the interval of time from \( t = 0 \) to \( t = T \), \( r \) varies with time as \( r = 10^\circ + t^2 \). During this time \( r' \) will vary with time as
View Solution
If AB is incident plane wave front, then refracted wave front is (n\(_1\) → n\(_2\))

View Solution
The total energy carried by the light wave when it travels from a rarer to a non-reflecting and non-absorbing medium
View Solution
If the radius of the first Bohr orbit is \( r \), then the radius of the second Bohr orbit will be
View Solution
Match the following types of nuclei with examples shown:

(1) A - iii, B - ii, C - i
View Solution
Which of the following statements is incorrect with reference to 'Nuclear force'?
View Solution
The range of electrical conductivity \( \sigma \) and resistivity \( \rho \) for metals, among the following, is:
View Solution
Which of the following statements is correct for an n-type semiconductor?
View Solution
The circuit shown in the figure contains two ideal diodes \( D_1 \) and \( D_2 \). If a cell of emf 3V and negligible internal resistance is connected as shown, then the current through \( 70 \, \Omega \) resistance (in amperes) is:
View Solution
In determining the refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope, the following readings are tabulated:
(a) Reading of travelling microscope for ink = 8.123 cm
(b) Reading of travelling microscope for ink through glass slab = 6.123 cm
(c) Reading of travelling microscope for chalk dust on glass slab = 8.123 cm
From the data, the refractive index of a glass slab is:
View Solution
In an experiment to determine the figure of merit of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a student constructed the following circuit. He applied a resistance of \( 520 \, \Omega \) in \( R \). When \( K_1 \) is closed and \( K_2 \) is open, the deflection observed in the galvanometer is 20 div. When \( K_1 \) is also closed and a resistance of \( 90 \, \Omega \) is removed in \( S \), the deflection becomes 13 div. The resistance of galvanometer is nearly:
View Solution
While determining the coefficient of viscosity of the given liquid, a spherical steel ball sinks by a distance \( x = 0.8 \, m \). The radius of the ball is \( 2.5 \times 10^{-3} \, m \). The time taken by the ball to sink in three trials are tabulated as shown:

View Solution
Which of the following expressions can be deduced on the basis of dimensional analysis? (All symbols have their usual meanings)
View Solution
Two stones begin to fall from rest from the same height, with the second stone starting to fall \( t_1 \) seconds after the first falls from rest. The distance of separation between the two stones becomes \( H \) after the first stone starts its motion. Then \( t_1 \) is equal to:
View Solution
In the projectile motion of a particle on a level ground, which of the following remains constant with reference to time and position?
View Solution
A particle is in uniform circular motion. The equation of its trajectory is given by \( x = 2t^2 - 3t + 5 \), where \( x \) and \( y \) are in meters. The speed of the particle is 2 m/s. When the particle attains the lowest \( y \)-coordinate, the acceleration of the particle is (in \( m/s^2 \)):
View Solution
A wooden block of mass M lies on a rough floor. Another wooden block of the same mass is hanging from the point O through strings as shown in the figure. To achieve equilibrium, the coefficient of static friction between the block on the floor and the floor itself is

View Solution
A block of certain mass is placed on a rough floor. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the block and the floor are 0.4 and 0.25 respectively. A constant horizontal force \( F = 20 \, N \) acts on it so that the velocity of the block varies with time according to the following graph. The mass of the block is nearly (Take \( g = 10 \, m/s^2 \)):

View Solution
A body of mass 0.25 kg travels along a straight line from \( x = 0 \) to \( x = 2 \, m \) with a speed \( v = k x^2 \) where \( k = 2 \, m^{-1} \). The work done by the net force during this displacement is
View Solution
During an elastic collision between two bodies, which of the following statements are correct?
View Solution
Three particles of mass 1 kg, 2 kg, and 3 kg are placed at the vertices A, B and C respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. The centre of mass of the system from vertices A (located at origin) is
View Solution
Two flywheels are connected by a non-slipping belt as shown in the figure. \(m_1 = 4 \, kg\), \(r_1 = 20 \, cm\), \(m_2 = 20 \, kg\), \(r_2 = 30 \, cm\). A torque of 10 Nm is applied on the smaller wheel. Then match the entries of column I with appropriate entries of column II.

View Solution
If \( r_1, v_1, L_1 \) and \( r_2, v_2, L_2 \) are radii, velocities, and angular momenta of a planet at perihelion and aphelion of its elliptical orbit around the Sun respectively, then
View Solution
The total energy of a satellite in a circular orbit at a distance \( (R + h) \) from the center of the Earth varies as
View Solution
Two wires A and B are made of the same material. Their diameters are in the ratio 1:2 and lengths are in the ratio 1:3. If they are stretched by the same force, then increase in their lengths will be in the ratio of
View Solution
A horizontal pipe carries water in a streamlined flow. At a point along the pipe, where the cross-sectional area is \( 10 \, cm^2 \), the velocity of water is 1 m/s and the pressure is 2000 Pa. What is the pressure of water at another point where the cross-sectional area is \( 5 \, cm^2 \)? [Density of water = 1000 kg/m³]
View Solution
Three metal rods of the same material and identical in all respects are joined as shown in the figure. The temperatures at the ends of these rods are maintained as indicated. Assuming no heat energy loss occurs through the curved surfaces of the rods, the temperature at the junction is

View Solution
A gas is taken from state A to state B along two different paths 1 and 2. The heat absorbed and work done by the system along these two paths are \( Q_1 \) and \( W_1 \), and \( Q_2 \) and \( W_2 \), respectively. Then
View Solution
At 27°C temperature, the mean kinetic energy of the atoms of an ideal gas is \( E_1 \). If the temperature is increased to 327°C, then the mean kinetic energy of the atoms will be
View Solution
The variations of kinetic energy \( K \), potential energy \( U \), and total energy \( E \) as a function of displacement of a particle in SHM is shown in the figure. The value of \( x_3 \) is
View Solution
The angle between the particle velocity and wave velocity in a transverse wave is (except when the particle passes through the mean position)
View Solution
A metallic sphere of radius \( R \) carrying a charge \( q \) is kept at a certain distance from another metallic sphere of radius \( R_4 \) carrying a charge \( Q \). What is the electric flux at any point inside the metallic sphere of radius \( R \) due to the sphere of radius \( R_4 \)?
View Solution
You are given a dipole of charge \( +q \) and \( -q \) separated by a distance \( 2l \). A sphere 'A' of radius \( R \) passes through the centre of the dipole as shown below and another sphere 'B' of radius \( 2R \) passes through the charge \( +q \). Then the electric flux through the sphere A is
View Solution
A potential at a point A is 3 V and that at another point B is 5 V. What is the work done in carrying a charge of 5 mC from B to A?
View Solution
Charges are uniformly spread on the surface of a conducting sphere. The electric field from the center of the sphere in a point outside the sphere varies with distance \( r \) from the center as

View Solution
Match Column-I with Column-II related to an electric dipole of dipole moment \( \vec{p} \) that is placed in a uniform electric field \( \vec{E} \):

View Solution
Which of the following statements is not true?
View Solution
Which of the following is a correct statement?
View Solution
In the following circuit, the terminal voltage across the cell is
View Solution
Two cells of emf \( E_1 \) and \( E_2 \), and internal resistances \( r_1 \) and \( r_2 \), respectively, are connected in parallel as shown in the figure. The equivalent emf of the combination is \( E_{eq} \). Then

View Solution





















Also Check:
- KCET 2025 April 16 Chemistry Question Paper
- KCET 2025 April 17 Biology Question Paper
- KCET 2025 April 17 Mathematics Question Paper
KCET 2025 Physics: Expected Difficulty Level
The KCET 2025 Physics paper was held on April 16 between 10:30 AM and 11:50 AM.
As per the previous year's trends, the KCET 2025 Physics exam is expected to be moderate to difficult, with more conceptual questions than direct ones.
Approximately 60–70% of the paper can be application-based or numerical questions, particularly from subjects such as Electrodynamics, Mechanics, and Modern Physics.
Section-wise Expected Difficulty Level – KCET 2025 Physics
| Physics Section | Expected Difficulty Level | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanics | Moderate to High | Core formulas and conceptual clarity are required |
| Thermodynamics | Moderate | Requires conceptual understanding and formula recall |
| Electrodynamics | High | Involves trickier numerical problems; often 15–20% of paper |
| Modern Physics | Moderate | Frequently asked, often application-based |
| Optics | Moderate | Ray and wave optics questions, usually balanced |
| Waves & Oscillations | Easy to Moderate | Scoring section if basics are clear |
| Properties of Matter | Easy | Mostly direct theory-based questions |
| Units & Dimensions | Easy | Simple questions; usually 1–2 in number |
| Kinematics | Moderate | Graph-based or concept questions expected |
KCET 2025 Safe Score: Minimum Marks for Top Ranks
KCET 2025 Physics: Expected Section-Wise Weightage
The KCET Physics paper generally adheres to a well-balanced pattern across all the key topics of the 1st and 2nd PUC syllabus. From the analysis of the past year's papers, Mechanics, Electrodynamics, and Modern Physics collectively account for more than 50% of the questions.
| Section | Expected No. of Questions | Weightage (%) |
| Mechanics | 12–14 | 20–23% |
| Electrodynamics | 10–12 | 18–20% |
| Modern Physics | 7–8 | 12–14% |
| Thermodynamics & Heat | 5–6 | 8–10% |
| Optics | 5–6 | 8–10% |
| Waves & Oscillations | 3–4 | 5–7% |
| Properties of Matter | 3–4 | 5–7% |
| Kinematics & Units | 3–4 | 5–6% |
Also Check:







Comments