KCET 2023 Chemistry Question Paper B2 is available for download. KCET 2023 Question Paper May 21 Shift 2 2:30 PM to 3:50 PM will be conducted for Chemistry Paper. KCET 2023 Question Paper consists of 60 MCQ-based questions in total. Each candidate is awarded +1 for correct answers, however, there will be no negative marking for incorrect responses. Students got 80 minutes to attempt KCET 2023 Chemistry Question Paper.
KCET 2023 Chemistry Question Paper with Answer Key PDF B2
| KCET 2024 Chemistry Question Paper with Answer Key | Check Solutions |

KCET 2023 Chemistry Questions with Solutions
A pair of compounds having the same boiling points are:
(A) cis but-2-ene and trans but-2-ene
(B) n-hexane and neo-hexane
(C) benzene and naphthalene
(D) (+) butan-2-ol and (-) butan-2-ol
Identify A, B, and C in the sequence:
![]()
(A) CH₃CH₂CN, CH₃CH₂CH₂NH₂, CH₃CH₂OH
(B) CH₃CH₂NC, CH₃CH₂OH, CH₃CH₂NH₂
(C) CH₃CH₂NC, CH₃CH₂OH, C₆H₅N₂C1
(D) CH₃CH₂NC, CH₃CH₂NH₂, C₂H₅OH
![]()
Hybridisation change involved at C-1 in the above reaction is:
(A) sp³ to sp
(B) sp³ to sp²
(C) sp² to sp³
(D) sp to sp²
If a didentate ligand ethane -1, 2-diamine is progressively added in the molar ratio en : Ni :: 1 : 1, 2 : 1,3 : 1 to [Ni(H₂O)₆]²⁺ aq solution, following co-ordination entities are formed:
I. [Ni(H₂O)₄(en)₂]²⁺ (aq) - pale blue
II. [Ni(H₂O)₂(en)₂]²⁺ (aq) - blue/purple
III. [Ni(en)₃]²⁺ (aq) - violet
The wavelength in nm of light absorbed in case of I and III are respectively:
(A) 475 nm and 310 nm
(B) 300 nm and 475 nm
(C) 310 nm and 500 nm
(D) 600 nm and 535 nm
Which of the following is an organometallic compound?
(A) CH₃COONa
(B) CH₃CH₂MgBr
(C) (CH₃COO)₂Ca
(D) CH₃ONa
A better reagent to oxidize primary alcohols into aldehydes is:
(A) PCC
(B) Alkaline KMnO₄
(C) Acidified K₂Cr₂O₇
(D) CrO₃
In the reaction:
![]()
Formation of X, formation of Y and Z are known by:
(A) Rosenmund reduction, Cannizzaro reaction
(B) Clemensen reduction, Sandmeyer reaction
(C) Wolff-Kishner reduction, Wurtz reaction
(D) Stephen reaction, Cannizzaro reaction
Compounds P and R in the following reaction are:
CH₃CHO ---> P ---> R
(A) Position isomers
(B) Functional isomers
(C) Metamers
(D) Identical
Aniline does not undergo:
(A) Nitration
(B) Sulphonation
(C) Friedel-Craft reaction
(D) Bromination
The heating of phenyl methyl ether with HI produces an aromatic compound A which on treatment with conc. HNO gives B. A and B respectively are:
(A) Methanol, Ethanoic acid
(B) Picric acid, Phenol
(C) Iodobenzene, 1-Iodo-4-nitrobenzene
(D) Phenol, Picric acid
Y in the below reaction is:
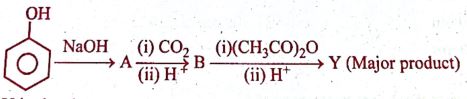
(A) Salicylaldehyde
(B) Aspirin
(C) Cumene
(D) Picric acid
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but after hydrolysis the mixture shows laevorotation, this is because of:
(A) Laevorotation of glucose is more than dextrorotation of fructose.
(B) Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
(C) Racemic mixture is formed.
(D) Laevorotation of fructose is more than dextrorotation of glucose.
The correct order of match between column X and column Y is:
| X | Y | ||
| I. | Vitamin A | i. | Muscular weakness |
| II. | Vitamin D | ii. | Increased blood clotting time |
| III. | Vitamin E | iii. | Night-blindness |
| IV. | Vitamin K | iv. | Osteomalacia |
(A) I - iv, II - iii, III - ii, IV - i
(B) I - ii, II - i, III - iii, IV - iv
(C) I - iii, II - ii, III - iv, IV - i
(D) I - iii, II - iv, III - i, IV - ii
In the reaction:
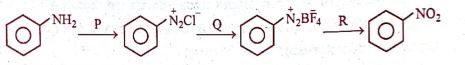
P, Q, and R respectively are:
(A) NaNO₂ + dil. HCl, HBF₄, Cu + NaNO₂
(B) NaNO₂ + conc.HCl, F₂, Cu + NaNO₃
(C) NaNO₂ + dil.HCl, BF₃, Cu + NaNO₃
(D) NaNO₂ + dil. HCl, F₂, Cu + NaNO₃
Thyroxine produced in the thyroid gland is an iodinated derivative of:
(A) Threonine
(B) Lysine
(C) Tyrosine
(D) Tryptophan
Which one of the following is a non-narcotic analgesic?
(A) Heroin
(B) Codeine
(C) Aspirin
(D) Morphine
Receptors are proteins and crucial to body communication process. These receptors are embedded in:
(A) Cell membrane
(B) Protein
(C) Endocrine gland
(D) Chromosomes
Which of the following monomers form biodegradable polymers?
(A) Ethylene glycol and phthalic acid
(B) Caprolactum and 1,3-butadiene
(C) Phenol and formaldehyde
(D) 3-hydroxybutanoic acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid
Match the List-I with List-II in the following:

(A) 1-c, 2-d, 3-a, 4-b
(B) 1-a, 2-d, 3-c, 4-b
(C) 1-d, 2-c, 3-a, 4-b
(D) 1-c, 2-c, 3-b, 4-a
The correct order of first ionisation enthalpy of given elements is:
(A) Li < B < Be < C
(B) Be < Li
(D) Li < Be
Which of the following statement is INCORRECT?
(A) Bond length of O₂ > Bond length of O₂⁺
(B) Bond order of O₂ > Bond order of O₂⁺
(C) Bond length of O₂ > Bond length of O₂⁻
(D) Bond order of O₂ > Bond order of O₂⁻
A gas at a pressure of 2 atm is heated from 25°C to 323°C and simultaneously compressed to ⅓ of its original volume. Then the final pressure is:
(A) 1.33 atm
(B) 6 atm
(C) 2 atm
(D) 4 atm
Lattice enthalpy for NaCl is +788 kJ/mol and ∆Hhyd = -784kJ/mol. Enthalpy of solution of NaCl is:
(A) +572 kJ/mol
(B) +4 kJ/mol
(C) -572 kJ/mol
(D) -4 kJ/mol
At 500 K, for a reversible reaction A₂(g) + B₂(g) ⇌ 2AB(g) in a closed container, Kc = 2 × 10⁻⁵. In the presence of catalyst, the equilibrium is attaining 10 times faster. The equilibrium constant Kc in the presence of catalyst at the same temperature is:
(A) 2 × 10⁻⁴
(B) 2 × 10⁻⁶
(C) 2 × 10⁻¹⁰
(D) 2 × 10⁻⁵
A weak acid with pKa 5.9 and weak base with pKb 5.8 are mixed in equal proportions. pH of the resulting solution is:
(A) 7.005
(B) 7.5
(C) 7
(D) 7.05
Temperature of 25°C in Fahrenheit and Kelvin scale respectively are:
(A) 77°F and 298.15 K
(B) 17°F and 298.15 K
(C) 45°F and 260.15 K
(D) 47°F and 312.15 K
The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in the ion ³²S²⁻ are respectively:
(A) 16, 16, 18
(B) 16, 18, 16
(C) 18, 16, 16
(D) 16, 16, 16
A pair of amphoteric oxides is:
(A) Al₂O₃, Li₂O
(B) BeO, B₂O₃
(C) BeO, MgO
(D) BeO, ZnO
The composition of water gas is:
(A) CO₂(g) + N₂(g)
(B) CH₄(g)
(C) CO(g) + H₂O(g)
(D) CO(g) + H₂(g)
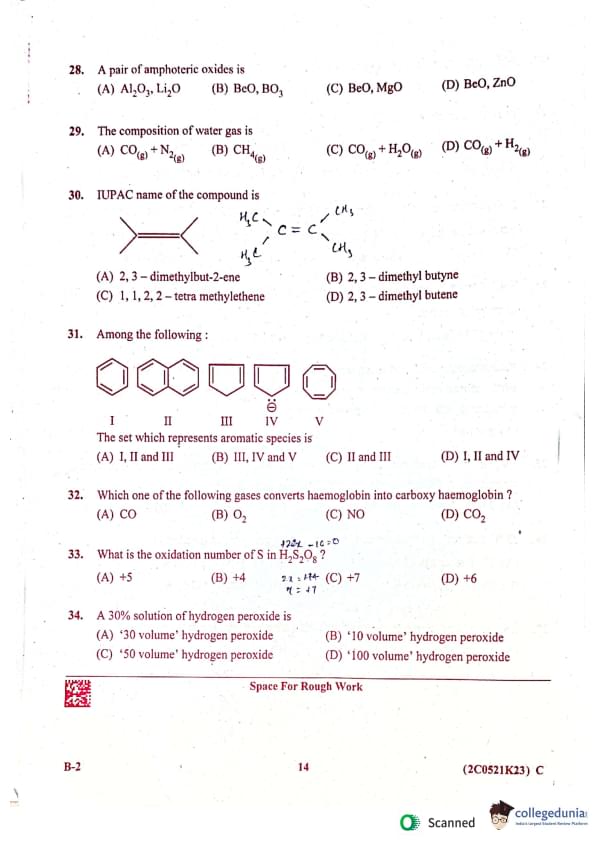
IUPAC name of the compound is:
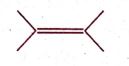
(A) 2, 3 - dimethylbut-2-ene
(B) 2, 3 - dimethylbutyne
(C) 1, 1, 2, 2 - tetramethylene
(D) 2, 3 - dimethylbutene
Among the following:
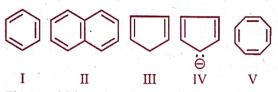
The set which represents aromatic species is:
(A) I, II and III
(B) III, IV and V
(C) II and III
(D) I, II and IV
Which one of the following gases converts haemoglobin into carboxy haemoglobin?
(A) CO
(B) O₂
(C) NO
(D) CO₂
A 30% solution of hydrogen peroxide is:
(A) '30 volume' hydrogen peroxide
(B) '10 volume' hydrogen peroxide
(C) '50 volume' hydrogen peroxide
(D) ‘100 volume' hydrogen peroxide
If 'a' stands for the edge length of the cubic systems, the ratio of radii in simple cubic, body-centered cubic and face-centered cubic unit cells is:
(A) ½a : (√3/4)a : (1/√2)a
(B) ½a : (√3/2)a : (½)a
(C) ½a : (√3/2)a : (1/√2)a
(D) (½)a : (½)a : (½)a
Dimerisation of solute molecules in low dielectric constant solvent is due to:
(A) Hydrogen bond
(B) Covalent bond
(C) Co-ordinate bond
(D) Ionic bond
The swelling in feet and ankles of an aged person due to sitting continuously for long hours during travel, is reduced by soaking the feet in warm salt water. This is because of:
(A) Reverse Osmosis
(B) Osmosis
(C) Edema
(D) Diffusion
A sample of water is found to contain 5.85% (w/w) of AB (molecular mass 58.5) and 9.50% (w/w) XY₂ (molecular mass 95). Assuming 80% ionisation of AB and 60% ionisation of XY₂, the freezing point of water sample is [Given: Kƒ for water is 1.86 K kg mol⁻¹, Freezing point of pure water is 273 K and A, B and Y are monovalent ions]:
(A) 264.25 K
(B) 265.56 K
(C) 280.44 K
(D) 281.75 K
Match the column A (type of crystalline solid) with the column B (example for each type):
| A | B | ||
| P. | Molecular Solid | i. | SiC |
| Q. | Ionic Solid | ii. | Mg |
| R. | Metallic Solid | iii. | H2O |
| S. | Network Solid | iv. | MgO |
(A) P-iii, Q-ii, R-ii, S-iv
(B) P-iii, Q-i, R-ii, S-i
(C) P-ii, Q-i, R-iii, S-i
(D) P-iii, Q-iv, R-ii, S-i
A metal crystallises in a body-centered cubic lattice with the metallic radius √3Å. The volume of the unit cell in m³ is:
(A) 64 × 10⁻²⁹ m³
(B) 4 × 10⁻²⁹ m³
(C) 6.4 × 10⁻²⁹ m³
(D) 4 × 10⁻¹⁰ m³
The resistance of 0.1 M weak acid HA in a conductivity cell is 2 x 10³ Ohm. The cell constant of the cell is 0.78 C cm⁻¹ and Ʌm of acid HA is 390 S cm² mol⁻¹. The pH of the solution is:
(A) 3.3
(B) 4.2
(C) 5
(D) 3
In which one of the following reactions, rate constant has the unit mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹ ?
(A) Acid catalysed hydrolysis of CH₃COOCH₃
(B) CHCl₃ + Cl₂ → CCl₄ + HCl
(C) 2NO(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g)
(D) Decomposition of HI on the surface of Gold
For a reaction, the value of rate constant at 300 K is 6.0 x 10⁵ s⁻¹. The value of Arrhenius factor A at infinitely high temperature is:
(A) 6 × 10⁵ × e^(-Ea/300R)
(B) e^(-Ea/300R)
(C) 6 × 10⁵
(D) 6 × 10⁵ × e^(-Ea/300R)
The rate constants k₁ and k₂ for two different reactions are 10¹⁶ x e⁻²⁰⁰⁰/T and 10¹⁵ x e⁻¹⁰⁰⁰/T respectively. The temperature at which k₁ = k₂ is:
(A) 2000 K
(B) 2000 K
(C) 1000 K
(D) 1000 K
During the electrolysis of brine, by using inert electrodes,
(A) O₂ liberates at anode
(B) H₂ liberates at anode
(C) Na deposits on cathode
(D) Cl₂ liberates at anode
Consider the following 4 electrodes:
A: Ag⁺ (0.0001 M) / Ag(s)
B: Ag⁺ (0.1 M) / Ag(s)
C: Ag⁺ (0.01 M) / Ag(s)
D: Ag⁺ (0.001 M) / Ag(s); E°Ag⁺/Ag = +0.80 V
Then reduction potential in volts of the electrodes in the order:
(A) B > C > D > A
(B) C > D > A > B
(C) A > D > C > B
(D) A > B > C > D
Okay, continuing from question number 47:
When FeCl₃ is added to excess of hot water gives a sol 'X'. When FeCl₃ is added to NaOH(aq) solution, gives sol 'Y'.
X and Y formed in the above processes respectively are:
(A) Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / OH⁻ and Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / Fe³⁺
(B) Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / H⁺ and Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / Na⁺
(C) Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / Cl⁻ and Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / OH⁻
(D) Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / Fe³⁺ and Fe₂O₃ · xH₂O / OH⁻
The reducing agent in the given equations:
4 Ag⁺(aq) + 8 CN⁻(aq) + 2 H₂O → 4[Ag(CN)₂ ]aq + 4 OH⁻
2[Ag(CN)₂]⁻aq + Zn(s) → [Zn(CN)₄]²⁻aq + 2 Ag(s)
(A) Zn
(B) O₂
(C) H₂O
(D) CN⁻
For the formation of which compound in Ellingham diagram, ∆G° becomes more and more negative with increase in temperature?
(A) CO
(B) FeO
(C) ZnO
(D) Cu₂O
Which of the following compound does not give dinitrogen on heating?
(A) Ba(N₃)₂
(B) NH₄NO₂
(C) NH₄NO₃
(D) (NH₄)₂Cr₂O₇
Aqueous solution of raw sugar when passed over beds of animal charcoal, it becomes colourless. Pick the correct set of terminologies that can be used for the above example.
Adsorbent Adsorbate Process
Solution of Sugar Animal Charcoal Sorption
Animal Charcoal Solution of Sugar Absorption
Animal Charcoal Colouring substance Adsorption
Colouring Substance Animal Charcoal Adsorption
(A) Solution of Sugar, Animal Charcoal, Sorption
(B) Animal Charcoal, Solution of Sugar, Absorption
(C) Animal Charcoal, Colouring substance, Adsorption
(D) Colouring Substance, Animal Charcoal, Adsorption
For Freundlich adsorption isotherm, a graph of log (x/m) vs. log (P) gives a straight line. The slope of line and its Y-axis intercept respectively are:
(A) log(1/n), K
(B) 1/n, log K
(C) log (1/n), log K
(D) 1/n , K
In solid state, PCl₅ is a/an:
(A) Octahedral structure
(B) Ionic solid with [PCl₆]⁺ and [PCl₄]⁻
(C) Ionic solid with [PCl₄]⁺ and [PCl₆]⁻
(D) Covalent solid present in the form of P₂Cl₁₀
In which one of the following pairs, both the elements does not have (n-1)d¹⁰ns² configuration in its elementary state?
(A) Zn, Cd
(B) Cd, Hg
(C) Hg, Cn
(D) Cu, Zn
Which of the following is CORRECT with respect to melting point of a transition element?
(A) V > Cr
(B) Cr > Mn
(C) Mn > Fe
(D) Ti > V
aMnO₄⁻ + bS₂O₃²⁻ + H₂O → xMnO₂ + ySO₄²⁻ + zOH⁻
a and y respectively are:
(A) 8; 3
(B) 8; 6
(C) 3; 6
(D) 8; 8
Which formula and name combination is INCORRECT?
(A) K₃[Al(C₂O₄)₃] – Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
(B) [Pt(NH₃)₂Cl(NO₃)₂] – Diamminechloridonitrito – N – platinum (II)
(C) [CoCl₂(en)₂]Cl – Dichloridoethylenediammine cobalt (III) chloride
(D) [Co(NH₃)₄(H₂O)Cl]Cl₂ – Tetraamminaequachloridocobalt (III) chloride
Which of the following system in an octahedral complex has maximum unpaired electrons?
(A) d⁶ (high spin)
(B) d⁶ (low spin)
(C) d⁴ (low spin)
(D) d⁷ (high spin)
The correct decreasing order of basicity of hydrides of Group-15 elements is:
(A) SbH₃ > AsH₃ > PH₃ > NH₃
(B) PH₃ > AsH₃ > SbH₃ > NH₃
(C) AsH₃ > SbH₃ > NH₃ > PH₃
(D) NH₃ > PH₃ > AsH₃ > SbH₃
Which one of the following oxoacids of phosphorus can reduce AgNO₃ to metallic silver?
(A) H₃PO₄
(B) H₄P₂O₇
(C) H₄P₂O₆
(D) H₃PO₃










KCET 2023 Paper Analysis May 21
KCET 2023 paper analysis May 21 is available here. Candidates can check KCET 2023 paper analysis by clicking on the link provided below.
Also Check:
KCET Previous Year Question Paper
| KCET 2022 Question Paper | KCET 2021 Question Paper | KCET 2020 Question Paper |
| KCET 2019 Question Paper | KCET 2018 Question Paper | KCET 2017 Question Paper |




Comments