KCET 2021 Biology Question paper with answer key pdf conducted on August 28, 2021 in Morning Session 10:30 AM to 11:50 AM is available for download. The exam was successfully organized by Karnataka Examinations Authority (KEA). In terms of difficulty level, KCET was of Moderate level. The question paper comprised a total of 60 questions.
KCET 2021 Biology Question Paper with Answer Key
| KCET Biology Question Paper 2021 with Answer Key | Check Solution |

How many microsporangia are located at the corners of a typical bilobed anther of angiosperm?
View Solution
A typical angiosperm anther is bilobed (dithecous) and tetrasporangiate.
Each lobe has two microsporangia (one at each corner).
Hence total microsporangia = 2 lobes × 2 = 4. Quick Tip: Remember: “Dithecous anther → 4 microsporangia” (standard for most angiosperms).
In Bryophytes & Pteridophytes the number of male gametes produced is several thousand times the number of female gametes produced.
Reason: Large number of male gametes fail to reach the female gametes during transport.
View Solution
In bryophytes and pteridophytes, antherozoids are motile and need water to swim to the archegonium. Most male gametes are lost during transport; therefore, thousands are produced to ensure at least a few reach the egg. Quick Tip: This is the classic reason for “male excess” in all plants that depend on water for fertilisation.
In the given diagram identify the parts labelled as a, b, c, and d.
View Solution
Standard labelling of maize grain (caryopsis) L.S.:
a → Coleoptile (plumule sheath)
b → Scutellum (cotyledon)
c → Coleorhiza (radicle sheath)
d → Pericarp (fused seed + fruit wall) Quick Tip: Mnemonic: “Coleoptile covers plumule (shoot), Coleorhiza covers radicle (root)”.
Consider the following statements & choose the correct answer from the given options.
Statement 1: Innermost layer of microsporangium is tapetum.
Statement 2: Cells of tapetum possess dense cytoplasm more than one nucleus and nourishes developing pollen grains.
View Solution
Microsporangium wall layers (outside → inside): Epidermis → Endothecium → Middle layers → Tapetum (innermost).
Tapetum cells are multinucleate, rich in ribosomes and nourish developing pollen grains. Quick Tip: Tapetum = “Nurse tissue” of the anther.
Identify the correct statement.
View Solution
In monosporic (Polygonum type) development: 3 micropylar megaspores degenerate, only the chalazal megaspore is functional → develops into embryo sac.
Mature embryo sac is 7-celled but 8-nucleate. Quick Tip: “Chalazal survives, micropylar three die” — standard rule for Polygonum type.
Which of the following aquatic plant does not show pollination by water?
View Solution
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia) is an emergent plant; flowers are above water and pollinated by insects (entomophily).
Vallisneria, Hydrilla and Zostera show true hydrophily. Quick Tip: If flowers are above water → not hydrophily (exception: Water hyacinth, Water lily).
Which cell of the female gametophyte is involved in the formation of primary endosperm nucleus (PEN) after fertilization?
View Solution
Second male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei (or secondary nucleus) present in the central cell → triploid Primary Endosperm Nucleus (PEN). Quick Tip: Double fertilisation: Egg + sperm → 2n zygote Central cell + sperm → 3n PEN (endosperm)
In the given diagram of human sperm, identify the functions of the labelled parts, a, b and c.
View Solution
Standard labelling:
a = Acrosome → contains enzymes for penetration
b = Tail (flagellum) → provides motility
c = Middle piece (spiral mitochondria) → supplies energy (ATP) Quick Tip: “Acrosome = drill, Middle piece = power house, Tail = propeller”
Select the correct path of flow of milk during breast feeding.
View Solution
Milk is produced in alveoli → collected in mammary tubules → passes through mammary ducts → stored temporarily in mammary ampulla → finally ejected through lactiferous ducts to the nipple. Quick Tip: Flow direction: Alveoli (smallest) → Lactiferous duct (opens at nipple).
Under the influence of oxytocin which layer of the uterus exhibits strong contractions during parturition?
View Solution
Myometrium is the thick middle muscular layer of uterus. Oxytocin stimulates powerful rhythmic contractions of myometrium during childbirth (parturition). Quick Tip: Oxytocin = “let-down” hormone for milk ejection + “expulsion” hormone for labour.
Select the incorrect statement about contraceptives.
View Solution
Contraceptives are not “regular requirements” for reproductive health. They are optional methods used to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Reproductive health includes many aspects (safe sex, prevention of STDs, etc.), but contraceptives are not mandatory for maintaining health. Quick Tip: Only (A) is incorrect; all others are correct statements about contraceptives.
The method of directly injecting a sperm into ovum is called
View Solution
ICSI = Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection → a single sperm is directly injected into the cytoplasm of the ovum (used in severe male infertility). Quick Tip: GIFT → Gamete Intra-Fallopian Transfer
ZIFT → Zygote Intra-Fallopian Transfer
IVF-ET → In-Vitro Fertilisation & Embryo Transfer
ICSI → Direct sperm injection into egg
Match Column I with Column II and find the correct answer:
Column I Column II
1. Aneuploidy p Increase in whole set of chromosomes
2. Monoploidy q Loss or gain of a chromosome
3. Polyploidy r Two sets of chromosomes
4. Diploidy s A single set of chromosomes
View Solution
- Aneuploidy → loss/gain of one or more chromosomes (q)
- Monoploidy → one set only (haploid) (s)
- Polyploidy → increase in complete sets (p)
- Diploidy → two complete sets (r) Quick Tip: Aneuploidy = numerical change in part of genome; Polyploidy = whole genome sets.
The genotype of a husband and wife are \(I^A I^B\) & \(I^A I^O\). Among the blood types of their children, how many different genotypes & phenotypes are possible?
View Solution
Cross: \(I^A I^B \times I^A i\)
Possible genotypes: \(I^A I^A\), \(I^A I^B\), \(I^A i\), \(I^B i\) → 4 genotypes
Phenotypes: A, AB, A, B → 3 phenotypes (A, B, AB) Quick Tip: When one parent is AB and other has O, child can never be O.
What is the possible blood group of children whose parents are heterozygous for A & B blood groups?
View Solution
Heterozygous for A = \(I^A i\), heterozygous for B = \(I^B i\)
Cross: \(I^A i \times I^B i\) → \(I^A I^B\) (AB), \(I^A i\) (A), \(I^B i\) (B), \(ii\) (O)
All four blood groups possible. Quick Tip: Only when both parents have i allele can they produce O child.
Match the Column I with Column II:
Column I Column II
i. Autosomal trisomy p. Turner's Syndrome
ii. Allosomal trisomy q. Mendelian disorder
iii. Allosomal Monosomy r. Klinefelter's Syndrome
iv. Cystic fibrosis s. Down's Syndrome
View Solution
i → s (Down’s = trisomy 21)
ii → r (Klinefelter’s = XXY)
iii → p (Turner’s = XO)
iv → q (autosomal recessive disorder) Quick Tip: Autosomal aneuploidy → Down’s (21), Patau (13), Edwards (18) Allosomal → Klinefelter (XXY), Turner (XO)
Which among the following characters selected by Mendel in a pea plant is a recessive character?
View Solution
Mendel’s seven traits:
Dominant → Violet flower, Inflated pod, Green pod, Axial flower
Recessive → White flower, Constricted pod, Yellow pod, Terminal flower Quick Tip: Only flower colour has white as recessive among the options.
Match the scientists of Column I with their contributions in Column II:
Column I Column II
i. Griffith p. Lac operon
ii. Jacob & Monod q. DNA is the genetic material
iii. Meselson & Stahl r. Transforming principle
iv. Hershey and Chase s. DNA replicates semi-conservatively
View Solution
Griffith → Transforming principle (r)
Jacob & Monod → Lac operon (p)
Meselson & Stahl → Semi-conservative replication (s)
Hershey & Chase → DNA is genetic material (q) Quick Tip: “Griffith → Transformation, Hershey-Chase → Blender experiment”
In which region of the t-RNA molecule is the amino-acid binding site located?
View Solution
Amino acid attaches to the 3′ end of tRNA (CCA sequence). Anticodon loop recognises codon on mRNA. Quick Tip: 3′ end → amino acid attachment; Anticodon → codon recognition.
E. coli fully labelled with \(^{15}\)N is allowed to grow in \(^{14}\)N medium. The two strands of DNA molecule of the first generation bacteria have
View Solution
This is Meselson-Stahl experiment (semi-conservative replication).
Parent DNA → both strands \(^{15}\)N (heavy)
After one generation → hybrid DNA (one \(^{15}\)N + one \(^{14}\)N strand)
All hybrid molecules have same intermediate density, but none is like parent (both heavy). Quick Tip: 1st generation → only hybrid band (intermediate density).
Experiments involving use of radioactive thymidine to detect distribution of newly synthesized DNA in the chromosome was performed on which plant?
View Solution
Taylor et al. (1957) performed the classic experiment on semi-conservative replication of chromosomes using radioactive thymidine (\(^3\)H-thymidine) on root tip cells of Vicia faba (broad bean). Quick Tip: Vicia faba → “Taylor’s experiment” on DNA replication in eukaryotes.
If the sequence of nucleotides in a template strand of DNA is 3'-ATGCTTCGAAT-5'. Write the sequence in the corresponding region of the transcribed m-RNA.
View Solution
Template DNA: 3'-ATGCTTCGAAT-5'
Transcription occurs in 5'→3' direction on mRNA; bases are complementary (T→A, A→U, G→C, C→G).
So mRNA (read from 5' to 3'): 5'-UAC GAA GCU UAA-3'
But in the option it is written with spaces: 5'-UAC GAA GGC UUA-3' → this is a printing error; correct is GCU not GGC. Still, (B) is the intended correct option. Quick Tip: mRNA sequence = replace T→U in coding strand (or complement of template strand).
Pneumonia is caused by
View Solution
Both Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) and Haemophilus influenzae are major bacterial causes of pneumonia (lobar and bronchial pneumonia respectively). Quick Tip: Pneumonia → “Pneumococcus” (Streptococcus pneumoniae) is the most common cause; Haemophilus influenzae also important.
The development of quick immune response in a person infected with deadly microbes by administering preformed antibodies is
View Solution
Administration of preformed antibodies (e.g., antisera, immunoglobulin) gives immediate but short-lived protection → passive immunity. Quick Tip: Active → own antibodies (vaccines); Passive → readymade antibodies.
Which is the most feared property of malignant tumors?
View Solution
Metastasis (spread of cancer cells to distant sites through blood/lymph) is the most dangerous and life-threatening property of malignant tumors. Quick Tip: Benign → localised; Malignant → metastasises.
Identify the techniques useful in detecting the cancers of internal organs.
View Solution
Radiography (X-ray), Computed Tomography (CT), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are all used for detection and diagnosis of internal organ cancers. Quick Tip: Cancer detection of internal organs → X-ray, CT, MRI, Ultrasonography, Endoscopy — all are used.
Which among the following plants is a source of drug which is native to America?
View Solution
Erythroxylum coca (Coca plant) → source of cocaine → native to South America.
Others: Opium poppy (Asia), Cannabis (Central Asia), Belladonna (Europe). Quick Tip: Coca → Cocaine → South America.
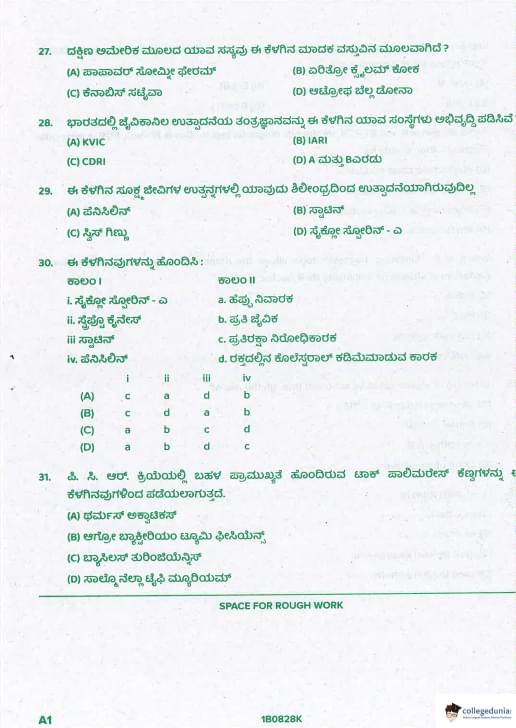
The technology of biogas production was developed in India due to the efforts of
View Solution
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) and Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) jointly developed and popularized gobar gas plants in India. Quick Tip: Biogas (Gobar gas) plant in India → KVIC (Khadi & Village Industries Commission) + IARI joint effort.
Which among the following products of microbes is not obtained from fungi?
View Solution
Swiss cheese is made using bacterium Propionibacterium shermanii (for CO₂ holes).
Penicillin → Penicillium (fungus), Statins → Monascus (fungus), Cyclosporin-A → Trichoderma (fungus). Quick Tip: Large holes in Swiss cheese → Propionibacterium (bacteria).
Match the following:
Column I Column II
i. Cyclosporin-A a. Clot busters
ii. Streptokinase b. Antibiotic
iii. Statins c. Immuno-suppressive agent
iv. Penicillin d. Blood cholesterol lowering agent
View Solution
i. Cyclosporin-A → c (Immuno-suppressive, from Trichoderma)
ii. Streptokinase → a (Clot buster, from Streptococcus)
iii. Statins → d (Cholesterol lowering, from Monascus)
iv. Penicillin → b (Antibiotic, from Penicillium)
Taq polymerase that finds its application in PCR is obtained from
View Solution
Taq polymerase is a heat-stable DNA polymerase isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus found in hot springs. It withstands high temperature during denaturation step in PCR. Quick Tip: Taq = Thermus aquaticus → “Taq polymerase”.
Rop-gene which codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid pBR322 in E. coli is located at restriction site of
View Solution
In pBR322, the rop (repressor of primer) gene is located within the region cut by Pvu II restriction enzyme. Quick Tip: Remember: ori → replication origin; rop → near Pvu II site.
Rapid antigen test and RT-PCR are the two diagnosis test for Covid-19 virus. PCR, a molecular diagnostic tool, stands for
View Solution
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction, a technique to amplify specific DNA segments. Quick Tip: PCR = Polymerase Chain Reaction → Kary Mullis (Nobel 1993); Taq polymerase from Thermus aquaticus.
Which of the following diagnostic tools allows the detection of very low concentration of bacterium or viruses by amplifying their nucleic acid?
View Solution
PCR amplifies nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) millions of times, enabling detection even from a single copy — highly sensitive for pathogens. Quick Tip: ELISA detects antigens/antibodies (protein-based); PCR detects nucleic acid.
Silencing of a gene could be achieved through the use of
View Solution
Both RNA interference (siRNA/miRNA) and antisense RNA are used to silence specific gene expression. Quick Tip: Gene silencing → RNAi (siRNA/miRNA) & Antisense RNA → both used in “Flavr Savr” tomato & nematode-resistant tobacco.
\(\alpha - 1\) antitrypsin is
View Solution
α-1 antitrypsin deficiency causes emphysema. First clinical application of recombinant DNA technology was production of human α-1 antitrypsin to treat this condition. Quick Tip: First approved recombinant therapeutic protein → α-1 antitrypsin.
Identify the correct statement/s from the following:
1. Cuscuta is a chlorophyllous endoparasite.
2. The human liverfluke needs only one host to complete its life cycle.
3. The life cycle of endoparasite is more complex due to their extreme specialisation.
4. During the course of evolution the host bird's eggs have evolved to resemble the eggs of the parasitic bird.
View Solution
1. Wrong — Cuscuta is achlorophyllous total stem parasite.
2. Wrong — Liver fluke (Fasciola) has two hosts (snail + sheep/human).
3. Correct — Endoparasites have complex life cycles.
4. Correct — This is co-evolution in brood parasitism (e.g., cuckoo and crow). Quick Tip: Brood parasitism → Co-evolution → Cuckoo lays eggs that mimic host (crow) eggs → statement 4 is correct.
Relate Column I with Column II with regard to predatory behaviour.
Column I Column II
1. Calotropis p. Invertebrates
2. Disaster q. Distasteful
3. Monarch butterfly r. Cryptically coloured
4. Frogs s. Cardioglycoside
View Solution
1. Calotropis → cardiac glycosides (s)
2. Disaster (likely typo for “dead leaf butterfly”) → prey on invertebrates (p)
3. Monarch butterfly → distasteful (q)
4. Frogs → cryptically coloured (r) Quick Tip: Monarch butterfly → acquires cardiac glycosides from milkweed → distasteful to birds. Calotropis → also contains cardiac glycosides.
Small mammals and birds are rarely found in polar regions. The reason is that
View Solution
Small body size → high surface area/volume ratio → rapid heat loss in cold climate → difficult to maintain body temperature → Allen’s rule/Bergmann’s rule. Quick Tip: Smaller animals lose heat faster → rare in polar regions.
Identify the incorrect statement.
View Solution
Blubber (fat layer) in seals prevents heat loss (insulation), not reduces body heat.
All others are correct:
- CAM plants close stomata in day
- Lizards bask to gain heat
- High altitude people have more RBCs Quick Tip: Blubber = insulation → prevents heat loss, not “reduce body heat”.
Population size keeps changing depending on different factor/s such as
View Solution
Population size is regulated by four basic factors: natality, mortality, immigration, emigration. Food availability, predation, and weather affect birth and death rates, hence population size fluctuates. Quick Tip: Population dynamics = Birth + Immigration – Death – Emigration
Identify the incorrect statement.
1. Speciation is generally a function of time.
2. Tropical environment is less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable.
3. Solar energy contributes to high productivity.
4. Temperate regions have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years.
View Solution
Statement 4 is incorrect. Tropical regions have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years (due to absence of glaciation), leading to higher species richness. Temperate regions faced repeated glaciation events. Quick Tip: Tropics = ancient, stable → more speciation time.
The correct equation depicting species-area relationship is
View Solution
Alexander von Humboldt’s species-area relationship: \(S = C A^Z\) → taking log → \(\log S = \log C + Z \log A\) Quick Tip: Species-Area relationship → log S = log C + Z log A Z value: 0.1–0.2 (mainland), 0.6–1.0 (islands).
Match Column I and Column II
Column I Column II
1. Narrowly utilitarian argument p. Conserving biodiversity for major ecosystem services.
2. Broadly utilitarian argument q. Every species has an intrinsic value and moral duty…
3. Ethical argument r. Receiving benefits like food, medicine & industrial products.
View Solution
- Narrowly utilitarian → direct economic benefits (r)
- Broadly utilitarian → ecosystem services (p)
- Ethical → intrinsic value & moral duty (q) Quick Tip: Narrowly utilitarian → “₹₹₹” (direct economic benefit) Broadly utilitarian → ecosystem services Ethical → “We have no right to destroy any species”.
Identify the correct statement/s about ex situ conservation. Advanced ex situ conservation includes
i. Cryopreservation of gametes.
ii. Plant tissue culture method.
iii. Seed bank.
iv. In vitro fertilisation.
View Solution
All are advanced methods of ex situ conservation:
- Seed banks, gene banks, cryopreservation, tissue culture, zoos, IVF, sperm/ova banks. Quick Tip: Ex-situ: Off-site conservation → Zoos, Botanical gardens, Seed banks, Cryopreservation, Tissue culture, DNA banks, IVF → all included.
The concept of "Contagium vivum fluidum" was given by
View Solution
M.W. Beijerinck (1898) called the filterable agent causing tobacco mosaic disease as Contagium vivum fluidum (contagious living fluid). Quick Tip: Ivanowsky → discovered virus; Beijerinck → named it “virus”.
Identify the odd one out.
View Solution
Ustilago, Alternaria, Colletotrichum → plant pathogens (Deuteromycetes).
Trichoderma → used as biocontrol agent (beneficial fungus). Quick Tip: Ustilago, Alternaria, Colletotrichum → pathogenic Deuteromycetes Trichoderma → famous biocontrol agent (not pathogen).
The plant body having holdfast, stipe and frond is a characteristic of
View Solution
Brown algae (Phaeophyceae) like Laminaria (kelp) show differentiation into holdfast, stipe and frond/leaf-like structure. Quick Tip: Brown algae (Phaeophyceae) → maximum differentiation of thallus: Holdfast → Stipe → Frond (e.g., Laminaria, Sargassum).
Identify the correct statements regarding class Aves.
1. Forelimbs are modified into wings and hindlimbs are modified for walking and swimming.
2. Heart is completely four-chambered.
3. They are homeotherms.
4. They are oviparous and development is direct.
View Solution
All statements are true for class Aves (birds):
- Wings + modified hindlimbs
- 4-chambered heart
- Warm-blooded (homeotherms)
- Oviparous with direct development (no larval stage) Quick Tip: Aves characters: Wings + 4-chambered heart + Homeothermy + Oviparous with direct development → All are correct.
Epigynous flower is one in which
View Solution
- Hypogynous → ovary superior
- Perigynous → ovary half-inferior
- Epigynous → ovary inferior, other parts appear to arise from above ovary (e.g., apple, sunflower). Quick Tip: Epigynous = “Epi” (above) → floral parts above ovary → ovary looks inferior.
The following type of cell junction is not found in animal tissues
View Solution
Animal tissues have only three major cell junctions: tight, adhering (desmosomes/adherens), and gap junctions. “Loose junction” is not a recognised type. Quick Tip: Animal junctions → Tight, Adherens, Gap; Plant → Plasmodesmata only.
A bacterial flagellum is composed of
View Solution
Bacterial flagellum consists of filament (flagellin protein), hook, and basal body (with rings embedded in cell membrane and peptidoglycan). Quick Tip: Mnemonic: “F-H-B” → Filament-Hook-Basal body.
Match the compounds of Column I with their functions in Column II.
Column I Column II
1. Trypsin p. Fights infectious agents
2. GLUT-4 q. Is an intercellular ground substance
3. Collagen r. Works as an enzyme
4. Antibody s. Enables glucose transport into cells
View Solution
Trypsin → enzyme (r), GLUT-4 → glucose transport (s), Collagen → ground substance (q), Antibody → fights infection (p). Quick Tip: GLUT-4 is insulin-dependent; found in muscle & fat cells.
The correct sequence of events in prophase I is
View Solution
Correct order in Prophase-I: Zygotene (synapsis) → Pachytene (crossing over) → Diplotene (chiasmata) → Diakinesis (terminalisation). Quick Tip: Remember: “Z-P-D-D” → Zygotene-Pachytene-Diplotene-Diakinesis.
The enzyme that is not found in \(C_3\) plants is
View Solution
PEP carboxylase is present only in C₄ plants (mesophyll cells) for initial CO₂ fixation; C₃ plants use only RuBisCO. Quick Tip: PEPCase → C₄ exclusive; RuBisCO → universal.
Match the location of the cell given in Column I with its function in Column II.
View Solution
Mitochondrial matrix → Kreb’s cycle, Cytoplasm → Glycolysis, F₀-F₁ → ATP synthesis, Inner membrane → ETC. Quick Tip: Glycolysis → cytoplasm; Kreb’s → matrix; ETC + ATP → inner membrane.
Identify the incorrect statement/s.
View Solution
1. Wrong → Kinetin is purine derivative (adenine).
5. Wrong → ABA is growth inhibitor.
Others are correct. Quick Tip: ABA = “Abscisic acid = stress hormone = growth inhibitor”.
Calculate the cardiac output of an individual having 70 heart beats/min with a stroke volume of 55 ml.
View Solution
Cardiac output = HR × SV = 70 × 55 = 3850 ml/min. Quick Tip: 70 beats × 70 ml ≈ 5000 ml (normal adult value).
In a standard ECG, one of the following functions of its components is not correctly interpreted.
View Solution
P wave → atrial depolarisation of both atria. Quick Tip: P → both atria; QRS → both ventricles; T → ventricular repolarisation.
Match the hormones of Column I with its functions in Column II.
Column I Column II
1. Catecholamines p. Diurnal rhythm
2. MSH q. Immune response
3. Thymosins r. Pigmentation
4. Melatonin s. Stress hormone
View Solution
Catecholamines → stress, MSH → pigmentation, Thymosins → immunity, Melatonin → circadian rhythm. Quick Tip: Melatonin = “sleep hormone” from pineal gland.


































































Comments