Arpita Srivastava Content Writer
Content Writer
A specific gravity formula indicates the ratio of the density of a given substance to the density of water (H2O). This is a special case of relative density, which gives information about the properties of fluids in terms of their density or weight.
- Specific gravity is a dimensionless quantity that depends upon the mass of an object and the density of the fluid.
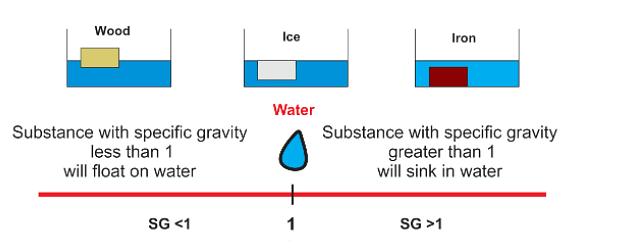
- If you are wondering why an object sinks or floats in water, specific gravity is one reason.
- In case the value of specific gravity is less than one then the object will float.
- On the other hand, if the specific gravity is greater than one, then the object will sink.
- Mathematically, it can be represented as:
Specific Gravity Formula : \(RD= \frac{\rho_{substance}}{\rho_{reference}}\)
- where RD = relative density, \(\rho_{substance}\) = density of the substance being measured, \(\rho_{reference}\) = density of the reference.
Key Terms: Gravity, Specific Gravity, Density, Mass, Weight, Volume, Relative Density, Pressure, Temperature, Specific Gravity Formula
What is Specific Gravity?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Specific gravity may also be defined as the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of the water at a specified temperature. It is mainly used to determine the properties of the fluid in relation to the concerned objects.
- Science represents specific gravity with the symbol ‘S’.
- It is the most important topic in Physics, where the concept of specific density is implied to calculate whether any object or body placed in water, taken as fluid, will sink or float in it.
- The specific gravity of the fluid takes into account the density, mass or weight of the object and the fluid.
However, there are multiple factors affecting the tendency of the object or body to sink or float, such as,
- Weight/ mass of the object
- Volume of water
- Buoyant Force
- Density of water
- Substance placed in it
Specific Gravity
Check out:
Specific Gravity Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In general, specific gravity formula (S) is calculated in terms of the density, mass and weight of the concerned object or body in relation with the given fluid or say water.
- The temperature for calculating the specific gravity remains approximately 4o Celsius.
- We can have three different formulas for calculating the specific gravity as mentioned below:
Specific Gravity = Mass of unit volume of the substance / Mass of unit volume of water
Specific Gravity = Weight of the substance / Weight of the equal amount of water
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
- Here, all the three formulas have used different elements for calculating specific gravity, which states that the specific gravity is not a confined concept, rather, it depends upon multiple factors, such as, mass, density and weight of both water and the object, as already mentioned above.
Solved Example of Specific Gravity FormulaExample: A liquid has a mass of 36 grams and the volume of the water (reference material) is 3 mL. Find the specific gravity of the object? Specify if the object will sink or float in the water. The density of the water is 1 g/mL. Solution: Density of the object = \((\frac{m}{v})\) = \(\frac{36 g}{3 mL}\) = 12 g/mL Now, we know the density of both the elements that is the object and water. So, put the values in the specific gravity equation to know the answer. Specific Gravity = \(\frac{\rho_{object}}{\rho H_{2}O}\) = \(\frac{12 g/mL}{1 g/mL}\) = 12 So the density of the object is 12 g/mL and the specific gravity is 12. Hence, the specific gravity is greater than 1 so the object will sink in the water. |
Derivation of Specific Gravity Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
We know that, Density = Mass (m) / Volume (v)
- Here, m = mass of the object
- v = volume of the object,
- Therefore, with the above formula of density, it can be analyzed that the density and mass of an object are directly proportional.
- So, the specific gravity can be calculated by dividing the mass of the object with that of water, such as,
Specific Gravity = Mass of the substance / Mass of unit volume of water
SG = Mobject / MWater
- Now, it can also be seen that the weight of the object and the water are affecting the density, such as,
Specific Gravity = Weight of the substance / Weight of the equal amount of water
SG = Wobject / WWater
- However, in all the formulas, the units of different elements shall remain the same, so that they cancel each other because specific gravity is a unitless concept.
Note: We generally consider the density of water at a temperature 4 degree C as a reference point because water at this point of temperature has the highest density of 1000 kg/m3.
Specific Gravity of Gas
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The ratio of the density of gas to that of the density of air at a specific temperature and pressure resembles the specific gravity of the gas. Therefore, it can be said that the specific gravity of gas is mainly understood in terms of the air.
- However, the air is recognized in its constant terms. Mathematically, the specific gravity could be represented as,
SG = ρgas / ρair
Specific Gravity of Different Elements
The specific gravity of different materials or substances are mentioned below for better understanding.
- SG of water = 1
- SG of mercury = 13. 6
- SG of aluminium = 2.72
- SG of gold = 19.3
Check out:
Things to Remember
- Specific gravity mainly determines if the object will sink or float after being placed in the fluid,.
- The density of air at room temperature, that is, 1.20 kg /m3 , also impacts the calculations of the specific gravity, mainly of gas.
- It has been found that the density of water is 1000 kilogram / cubic meters.
- For the same density, the specific gravity of the water always remains one.
- Specific gravity is of extreme importance for multiple industries.
- The specific gravity formula can be utilized either to test the purity levels in the gems or to identify the amount of solvent in urine concentration.
- It also helps recognize the mineral contents in rocks, which are majorly used by geologists.
- One of its major uses is in the medical sector, where urinalysis is an important part of usual treatments.
Sample Questions
Ques. The density of an iron is given as 7850 kg / m3. Calculate its specific gravity? (3 marks)
Ans. Given,
Density of iron = 7850 Kg / m3
Density of water = 1000 Kg / m3
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
S = 7850 / 1000
S = 7. 85
Hence, the specific gravity of iron is 7. 85.
Ques. The density of granite is given as 174.8 lbs / ft3. If the density of water is 62.4 lb / ft3. Calculate the specific gravity? (3 marks)
Ans. Given,
Density of granite = 174. 8 lbs / ft3
Density of water = 62. 4 lbs / ft3
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
S = 174. 8 / 62. 4
S = 2. 8
Hence, the specific gravity is 2. 8.
Ques. Find the specific gravity of the object and illustrate if the object will sink or float in the water if the volume of the water is given as 3 ml and the mass of the same is 36 grams. The density of the water is given as 1 gram / ml? (4 marks)
Ans. Given,
Mass of the water = 36g
Volume of water = 3ml
Density of water = 1 g / ml
So,
The density of the object = mass / volume = 36g / 3mL = 12 g / mL
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
S = 12 / 1
S = 12
Hence, the specific gravity is 12 which is more than 1, specifying that the object will sink in water.
Ques. Find the specific gravity if a cylinder is 100 mm long and has a diameter of 50 mm. Also specify whether the cylinder would float or sink in water if it has a mass of 1 kg? (5 marks)
Ans. Given,
Diameter = 50 mm
So, radius (R) = 50 / 2 = 25mm = 2.5cm
Now,
Area (A) = pi X R^2
A = 3. 1415926535 X (2. 5 cm) ^ 2
A = 3. 1415926535 X 6. 25 sq cm
A = 19. 635 sq cm
Volume = Area X length
V = 19. 635 X 100
V = 196. 25
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Mass of unit volume of the substance / Mass of unit volume of water
S = 1000 X 196. 25
S = 5. 09
Hence, the specific gravity is 5. 09 which is more than 1, specifying that the object will sink in water.
Ques. Calculate the mass if a bar measures 12 mm x 20 mm x 1 m. The specific gravity is given as 2. 78? (4 marks)
Ans. Given,
Specific gravity = 2. 78
Bar measurement = 12 mm x 20 mm x 1 m
Therefore, the volume = 12 mm x 20 mm x 1 m
= 1. 2 cm x 2 cm x 100 cm = 240 cm
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Mass of unit volume of the substance / Mass of unit volume of water
Mass = Specific Gravity X Mass of unit volume of water
M = 2. 78 X 240
M = 667. 2 g
Hence, the mass is 667. 2 g.
Ques. The Specific Gravity of granite is given as 2. 8. If the density of water is 62.4 lb / ft3. Calculate the density of an object? (3 marks)
Ans. Given is,
Specific Gravity of granite = 2. 8
Density of water = 62. 4 lbs / ft3
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
Density of substance = 2. 8 X 62. 4
Density of substance = 174. 8 lbs / ft3
Hence, the density is 174. 8 lbs / ft3.
Ques. The density of an aluminium bar is given as 785 kg / m3. Calculate its specific gravity? (3 marks)
Ans. Given,
Density of aluminium bar = 785 Kg / m3
Density of water = 1000 Kg / m3
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
S = 785 / 1000
S = 0. 785
Hence, the specific gravity of the aluminium bar is 0. 785.
Ques. The density of marble is given as 174.8 lbs / ft3. If the density of water is 62.4 lb/ft3. Calculate the specific gravity? (3 Marks)
Ans.Given is,
Density of marble = 174 lbs / ft3
Density of water = 62 lbs / ft3
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
S = 174 / 62
S = 2. 80
Hence, the specific gravity is 2. 80.
Ques. The density of a metal tool is given as 7856 kg / m3. Calculate its specific gravity? (3 Marks)
Ans. Given is,
Density of metal tool = 7856 Kg / m3
Density of water = 1000 Kg / m3
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Density of substance / Density of equal amount of water
S = 7856 / 1000
S = 7. 856
Hence, the specific gravity of the metal tool is 7. 856.
Ques. Calculate the mass if a table measures 11 mm x 25 mm x 4 m. The specific gravity is given as 2. 78? (3 Marks)
Ans. Given:
Specific gravity = 2. 78
Bar measurement = 11 mm x 25 mm x 4 m
Therefore, the volume = 11 mm x 25 mm x 4 m = 110 cm
Therefore,
Specific Gravity = Mass of unit volume of the substance / Mass of unit volume of water
Mass = Specific Gravity X Mass of unit volume of water
M = 2. 78 X 110
M = 305. 8 g
Hence, the mass is 305. 8 g.
Ques. What are the factors affecting specific gravity? (3 marks)
Ans. By seeing the above–mentioned formulas for specific gravity, it could be analyzed that the multiple elements like density, mass, weight, etc. affect the specific gravity of any object, however, the impact may be direct or inverse. The density of an object completely impacts the specific gravity and further this density also varies on the basis of the dynamism in the rate of pressure and temperature. Hence, specific gravity is mainly calculated under the controlled situation, otherwise, tends to vary as per the various factors.
Also check:





Comments