Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Mass and weight are two terms that are often used interchangeably, however, they have significant differences between them. Mass is the measurement of the amount of matter in a body. Weight is the measurement of the amount of force acting on a mass as a result of acceleration due to gravity. The difference between mass and weight is that mass is the amount of matter in a material and weight is a measure of how the force of gravity acts upon the mass.
- Mass is the amount of matter in a body and is denoted by the symbol m (or M).
- Weight is the gravitational force of attraction on an object, caused by the presence of a massive second object.
Key Terms: Mass and weight difference, mass, weight, gravity, vector quantity, matter, SI Unit
What is Mass?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Mass is the quantity of matter contained in a body. For example, the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an item can also be termed the measure of the mass.
- Mass, therefore, refers to both the property of a physical body and the measure of the resistance of the object to acceleration when a net force is applied.
- Mass is the quantitative measure of inertia.
- The greater the mass of a body, the smaller will be the change when we apply force.
- The common units to measure mass are kilograms and grams.
What is Weight?
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Weight is defined as the measurement of the gravitational force acting on an object.
- Newton (N) is the SI Unit of Weight.
- It directly depends on the gravitational force.
- The weight of an object is directly related to its mass.
W = M*g
- where M = mass and g = acceleration due to gravity
- Therefore, with an increase in mass, the weight will increase too.
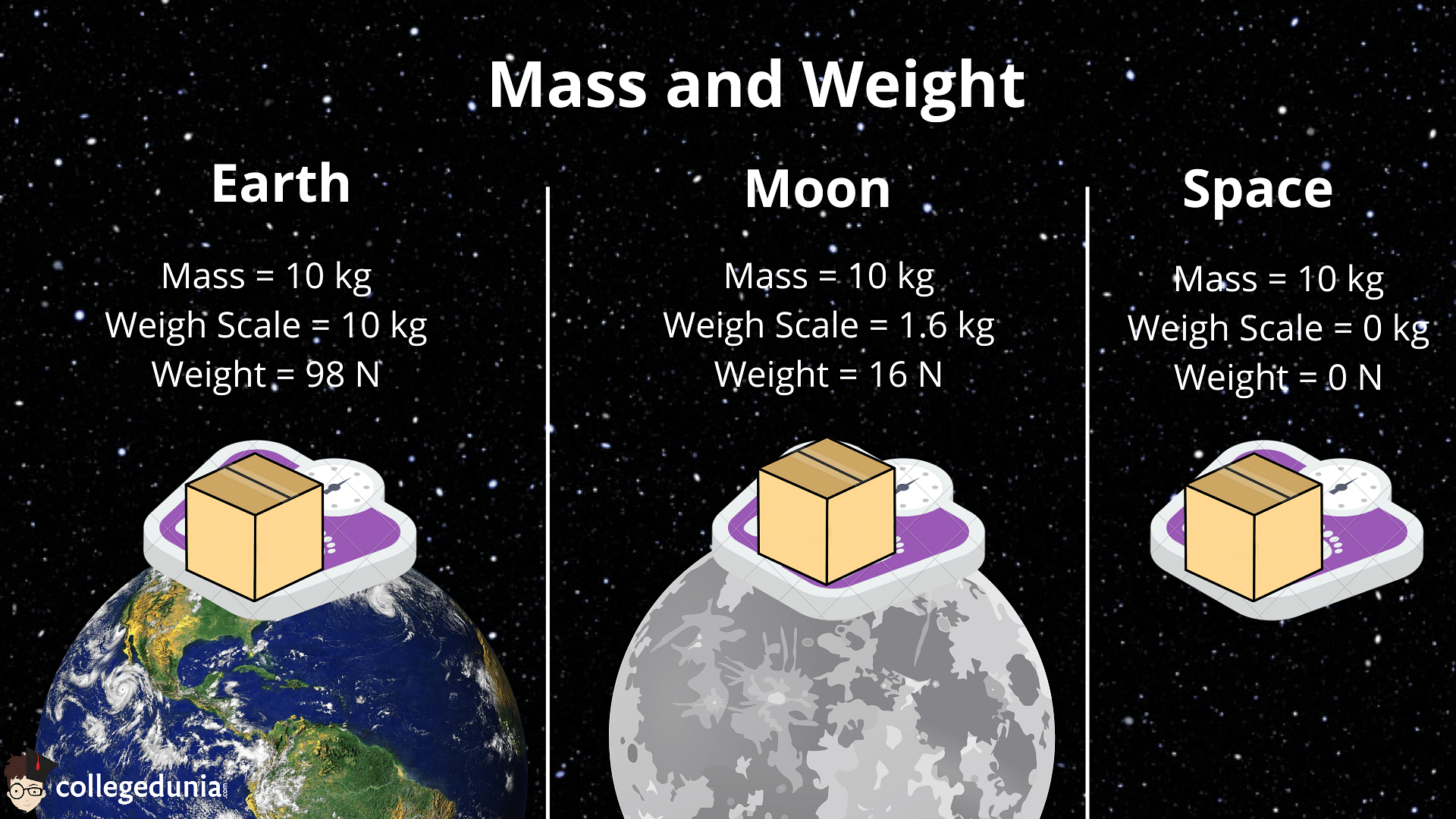
Difference Between Mass and Weight
Difference between Mass and Weight
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The mass and weight differences are tabulated below –
| Mass | Weight |
|---|---|
| Mass is the amount of matter contained in a body. | Weight is the measurement of gravitational force acting on an object. |
| Mass is always constant at any place at any time and does not depend on gravity. | Weight depends on gravity in the place, therefore it differs from one place to another. |
| Mass is a Scalar quantity. It has magnitude. | Weight is a vector quantity. It has magnitude and is directed towards the centre of the earth. |
| Mass is expressed in grams (g), kilogram(kg), and milligrams (mg). The SI unit of mass is Kilogram (Kg) | The SI unit of weight to measure weight is Newton (N) |
| Mass can never be Zero. | Weight can be Zero if no gravity acts upon an object as in space. |
| It is measured using pan balance, triple beam balance, lever balance, or electronic balance. | Spring balance is used as a tool for measurement. |
| Mass is denoted by m or M | Weight is denoted by W = m.g |
| Mass is constant for a body and can be calculated by, Mass = volume x density | Weight can be calculated by Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity |

Read More:
| Difference between Mass and Weight – Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Archimedes Principle | Central Force | Global Positioning System |
| Gravitation | Escape Speed | Gravitational potential energy |
| Earth Satellites | Weightlessness | Neptune |
| Specific Gravity | Density of Air | Value of Gravitational Constant |
Things to Remember
- Mass and weight are seemingly similar terms but have different meanings.
- Mass is the quantity of matter contained in a body.
- Weight is the force experienced by a mass, applied due to the acceleration due to gravity.
- Mass and weight are sued as weight is the mass of a body multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity.
- A difference between mass and weight is that mass always remains the same while weight changes with a change in acceleration due to gravity.
Previous Year Questions
- There is a shell of mass M and the density of the shell is uniform… [BITSAT 2013]
- The time period of a satellite of earth is 5 hours… [BITSAT 2019]
- An artificial satellite is going around the earth assumed to be a uniform sphere… [JIPMER]
- Which of the following curves represents the variation of total energy… [AMUEEE 2014]
- A mass falls from a height 'h' and its time of fall ‘l’ is recorded… [NEET 2019]
- A synchronous relay satellite reflects TV signals and transmits… [BHU UET]
- The acceleration due to gravity at a height h above the earth's surface is… [AP EAPCET]
- Acceleration due to gravity is g on the surface of Earth… [JKCET 2004]
- If the earth shrinks such that its density becomes 8 times to… [AP EAPCET]
- A remote-sensing satellite of earth revolves in a circular orbit at a height… [NEET 2015]
- For a satellite, the escape velocity is 11 km/s. If the satellite is launched… [NEET 1989]
- A satellite A of mass m is at a distance of r from the surface of the earth… [NEET 1993]
- The escape velocity from Earth is 11.2 km/s. If a body is to be… [NEET 1993]
- The dependence of acceleration due to gravity g on the distance r… [NEET 2010]
- A body weighs 72 N on the surface of the earth… [NEET 2020]
Sample Questions
Ques. Mass is the measure of _________ in an object. (1 Mark)
1. Weight
2. Size
3. Capacity
4. Matter
Ans. Matter
Explanation: Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. The SI unit for mass is the kilogram (kg), but smaller masses can be measured in grams (g). To measure mass, a balance is used.
Ques. Weight is the measure of the force of _______ on an object. (1 Mark)
1. Density
2. Gravity
3. Velocity
4. Mass
Ans. Gravity
Explanation: Force is the vector product of mass and acceleration: F = ma. Weight is a special case of that formula, where you substitute the acceleration of gravity, g, for a. We can therefore write: W = mg.1
For example, if an object has a mass of 10 slugs2, its weight near the surface of the Earth is 10 x 32.2 (ft/s2) = 322 pounds (pound-force). If an object has a mass of 10 kilograms, its weight near the surface of the Earth is 10 x 9.8 (m/s2) = 98 newtons. You can measure the force of gravity on an object (i.e., its weight) by putting it on a scale.
Ques. What will be the mass of an object if its weight is 98 kg? (1 Mark)
1. 0.1 kg
2. 10.0 kg
3. 1.0 kg
4. 0.02 kg
Ans. 10.0 kg
Explanation: Weight is the force exerted on a body by gravity. This is often expressed in the formula W=mg, where 'W' is weight, 'm' is the mass of the object, and g is the gravitational acceleration.
g=9.81 on the surface of the earth.
so if W = 98N then \(m=\frac{W}{g}=\frac{98}{9.81}=10 kg\)
Ques. Which of the following method determines mass by measuring how much an object resists acceleration? (1 Mark)
1. Inertial Mass
2. Gravitational Mass
3. Newton Mass
4. None of the above
Ans. Inertial Mass
Explanation: Inertial mass is a mass parameter that gives inertial resistance to the acceleration of a body when it undergoes all types of force. Gravitational mass is calculated as the strength of the gravitational force experienced by a body when it is in the gravitational field g.
Ques. The law of _________ of mass states that the mass of a closed system must remain constant over time. (1 Mark)
1. Gravitation
2. Weight
3. Conservation
4. Quantity
Ans. Conservation
Explanation: Law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as the system's mass cannot change, so the quantity can neither be added nor be removed.
Ques. What is the weight of a 1 kg mass object on planet Earth? (1 Mark)
1. 9.8 pounds
2. 1 Newton
3. 1 pound
4. 9.8 Newtons
Ans. 9.8 Newtons
Explanation: Given:
Mass of object, m=1 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g=9.8m/s2
Weight, W = m×g
= 1×9.8 N
= 9.8 Newtons
Ques. Two objects with _______ volume always have the same mass. (1 Mark)
1. Same
2. Different
3. Equal
4. More
Ans. Same
Explanation: Equal volumes of different substances have different masses. Example: Mass of iron is much more than the mass of an equal volume of wood. This is because the particles of iron are more closely packed than those of wood. In other words, iron is denser than wood.
Ques. Which measurement would be different if you were on the Moon versus the Earth? (1 Mark)
1. Mass
2. Velocity
3. Density
4. Weight
Ans. Weight
Explanation: All planets have gravity; however, the strength of gravity is directly related to the mass and diameter of the planet. The weight of a 22-pound object on Earth would be about 3.7 pounds on the moon.
Ques. Mass is a _________ quantity and weight is a _________ quantity. (1 Mark)
1. vector, vector
2. tensor, scalar
3. vector, scalar
4. scalar, vector
Ans. scalar, vector
Explanation: Mass is a measure of the quantity of matter. hence it is a scalar quantity. Weight: Force by which the earth pulls an object is called the weight of that object. Hence it is a vector quantity.
Also check:




Comments