Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
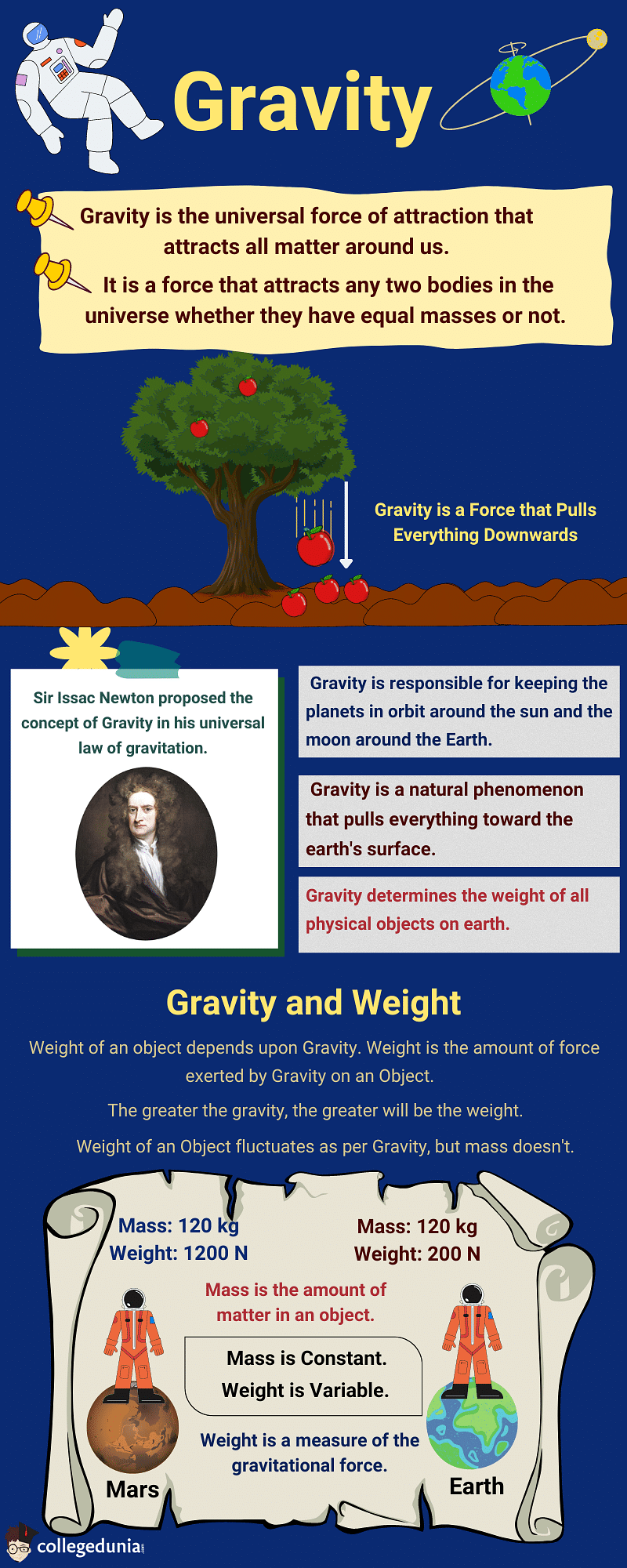
Gravity is the universal force of attraction that attracts all matter around us. It is a fundamental force that attracts two objects with masses toward each other.
- Gravity is a force that is exerted by different objects on one another due to their masses.
- It is also known as Gravitational Force.
- It is a natural phenomenon that pulls everything toward the earth's surface.
- Gravity determines the weight of all physical objects on earth.
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Gravitation
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Gravity, Gravitational Force, Universal Law of Gravitation, Force, Acceleration due to Gravity, Gravitation, Mass
What is Gravity?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Gravity is a fundamental force acting between any two objects having mass. It is one of the four major forces that govern the universe alongside Electromagnetic Force, Strong and Weak Nuclear forces,
- Sir Issac Newton proposed the concept of Gravity in his universal law of gravitation.
- It is defined as a force that attracts any two bodies in the universe whether they have equal masses or not.
- It is responsible for keeping the planets in orbit around the sun and the moon around the Earth.
- It is not detectable as it is one of the weakest forces due to the large separation distance.
- Newton (N) is the SI unit of gravity.

The video below explains this:
Relation Between G And g Detailed Video Explanation:
Read More:
History of Gravity
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Ancient scholars have tried to come up with their own explanations of why things fall on the ground despite flying up in the sky. Greek philosopher Aristotle thought that objects have a natural tendency to move toward the center of the universe which is the middle of the Earth.
- Nicolas Copernicus realized that not Earth but the Sun is at the center of the solar system.
- Sir Isaac Newton extended Copernicus’ work and came described the motion of celestial bodies.
- He said that all objects must exert some force of attraction on one another.
- In his famous 1687 work, Newton proposed Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation.
- In the twentieth century, Albert Einstein took a different approach to explaining gravity.
- Deviating from the Newtonian concept, Einstein said that pace and time are not separate entities but a single four-dimensional continuum.
- He defined gravity as the warping of space and time.
Read More: Gravitation Important Questions
Gravity Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Sir Isaac Newton explained Gravitational force as a force of attraction that exists between two objects having mass. Force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as
F ∝ M1M2 and F ∝ 1/R2
F ∝ M1M2/R2
From this equation, Gravity Formula is derived as
| \(F_g = \frac{Gm_1m_2}{r^2}\) |
Where
- Fg is the Gravitational Force acting between m1 and m2.
- G refers to the Gravitational Constant whose value is 6.67 × 10 -11m3/kg.s2.
- m1 and m2 are the masses of given two objects.
- r is the distance between the centers of two objects.
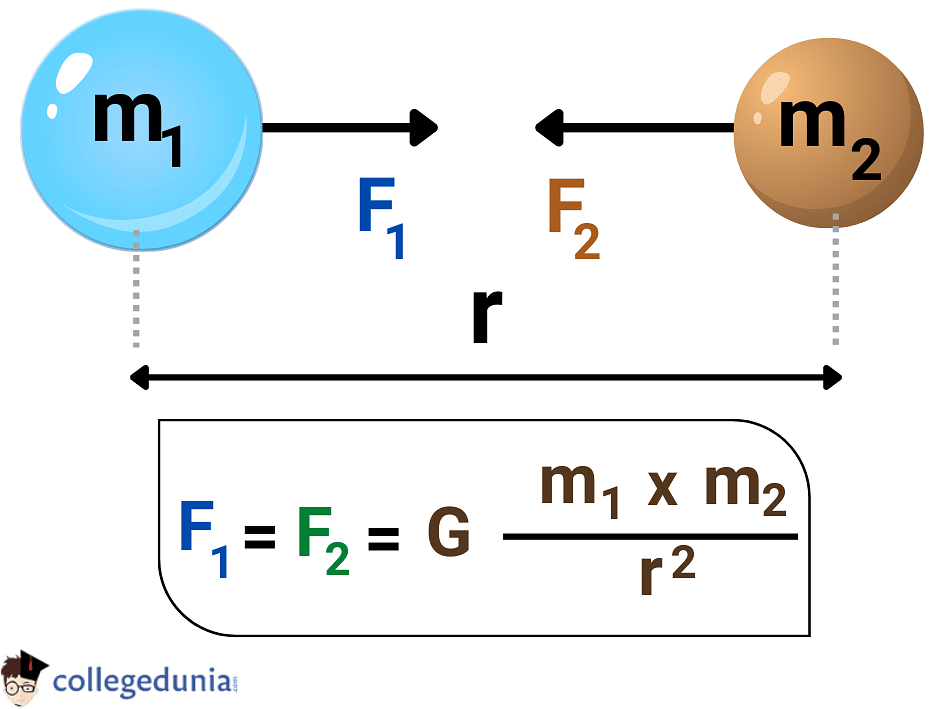
Gravity Formula
Solved ExampleExample: The mass of a body is given as 1000 Kg. The mass of the earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg and the radius of the earth is 6.38 x 106 m. Calculate the gravitational force acting on the body. Solution: According to the question,
Using the Gravitational Force Formula, Fg = [6.67 ×10–11 × 1000 × 5.98 x 1024] / ( 6.38 x 106)2 Fg = [39.8 ×1016] / [40.7 × 1012] Fg = 0.9778 x 104 Fg = 9.778 N Therefore, the force of gravity acting on the body is 9.778 N. |
Relationship between Gravity and Weight
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Weight of an object is the force of gravity acting on it. It is the product of the mass of the object, and the acceleration due to gravity.
- It changes depending on the measure of gravitational force acting on the object.
- The weight of an object is zero in case of no gravitational force.
- The SI unit for weight is also Newton (N).
- It is denoted as Fg.
Mathematically, Weight Formula is given as
| Fg = mg |
Where
- Fg is the Weight of the object in Newton (N).
- m is the Mass of the object in kg.
- g is the acceleration due to Gravity (9.8 m/s2).
Gravity
Read More: Gravitation MCQs
Examples of Gravity
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Gravity is a fundamental phenomenon that makes life possible on earth. Some of the examples of gravity are listed as follows:
- The gases in the Sun are held together by gravity.
- We have an atmosphere around the earth's surface due to the presence of gravity.
- The force of attraction, i.e. the gravity between the earth and the moon causes tides in the ocean.
- Gravity causes the moon to revolve around the earth and the earth to revolve around the Sun.
Check More:
| Relevant Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gravitational Potential Energy | Value of g on Moon | Newton's Laws of Motion |
| Force of Attraction Formula | Force and Laws of Motion | Gravity Waves |
Facts About Gravity
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Here are some important facts about Gravity:
- It is the weakest yet the most dominant of the four fundamental forces in the universe.
- Despite being the weakest force, it holds together the entire solar system and galaxies.
- The speed of the free fall is consistent over the earth’s surface which means all objects fall at the same speed.
- The value of g is calculated to be 9.8 m/s.
- The value of the Gravitational Constant G is about 6.67259 x 10–11 N m2/kg2.
- An object needs to travel 7 miles a second to leave Earth’s gravitational pull behind.
- Black Holes are placed with so much gravity that even light cannot escape from them.
Things to Remember
- Gravity is a universal force that attracts a body towards the center of the earth or any other physical body having mass.
- It is the weakest among the four fundamental forces that govern the universe.
- it is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the interacting objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two.
- Gravity Formula is given as F = GM1M2/ R2.
- The speed of free fall due to gravity is the same over the earth’s surface. This speed on earth is 9.8 m/s.
- Weight is the measure of the force of gravity acting on an object or a body.
- The relation between gravity and weight is given as w = mg.
Previous Years Questions
- Gravitational field is… (Haryana PMT 2009)
- Three uniform spheres of mass M and radius R earth are kept in such…
- Gravitational force is required for… (NEET 2000)
- The dimensional formula for the gravitational constant… (BCECE 2005)
- What will be the formula of mass of the earth in terms… (NEET 1996)
- The acceleration due to gravity at a height of 1km above the earth… (NEET 2017)
- The work done in shifting a particle of mass… (UP CPMT 2011)
- If suddenly the gravitational force of attraction between earth… (JMI-EEE 2005)
- The force of gravitation is… (AIIMS 2007)
- A man of 50 kg mass is standing in a gravity-free space at a… (NEET 2010)
- Assuming that the gravitational potential energy of an object… (NEET 2019)
- A body starts to fall freely under gravity. The distance… (Chhattisgarh PMT 2004)
- If the gravitational force between two objects were proportional… (NEET 1994)
- Two astronauts are floating in gravitational-free space after… (NEET 2017)
Sample Questions
Ques. What is Gravity? (3 Marks)
Ans. Gravity is a force that attracts any object having mass towards the center of the earth. The concept of Gravity was given by Sir Isaac Newton. It is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe apart from the weak force, the strong force, and the electromagnetic force. Albert Einstein defined gravity as a curvature of space-time induced by the uneven distribution of mass rather than a force. It is the force that controls the motion of the planets and the Moon. It is referred to as an attractive force because it constantly attracts masses to one another while never separating them.
Ques. What is the Universal Law of Gravitation? (3 Marks)
Ans. Sir Issac Newton proposed the Universal Law of Gravitation in the year 1680. According to Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation, the force of attraction between any two particles in the universe is exactly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their distance.
Thus, it can be said that
- Gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the center of mass of the given objects.
- It is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the given objects.
Ques. What is Gravitational Acceleration? (3 Marks)
Ans. Gravitational Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of a body falling freely toward the earth’s surface increases. It is denoted by the letter g and is independent of an object's form, size, and mass.
The Gravitational Acceleration Formula is:
g = GM/R2
- G is the gravitational constant.
- M is the mass of the earth.
- R is the radius of the Earth.
Ques. What are the factors that determine if a planet would have an atmosphere or not? (2 Marks)
Ans. There are two factors that determine whether a planet will have an atmosphere. They are as follows:
- Acceleration due to the gravity of the planet.
- Temperature at the surface of the planet.
Ques. What are the properties of the force of gravity? (3 Marks)
Ans. The properties of Gravity are as follows:
- It is an attractive force that pulls together two objects rather than pushing them away.
- It is a force present at a very large distance that is always present between two objects irrespective of their medium.
- Gravity is proportional to the masses of the objects.
Ques. Calculate the gravitational force if the two masses are 30kg and 50kg separated by a distance of 4 m. (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- m1 = 30 kg
- m2 = 50 kg
- r = 4m
- G = 6.67259 x 10–11 N m2/kg2
Using the Gravitational Force Formula,
F = [Gm1m2]/r2
Fg = [6.673 ×10–11 × 30 × 50] / 16
F = 62.55 x 10–11N
Thus, the force of gravity is calculated as 62.55 x 10–11N.
Ques. Assume that two objects attract each other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the distance between the two objects is doubled, what is the new attraction force that resulted between the two objects? (2 Marks)
Ans. The new attraction force that resulted between the two objects will be 4 units. Since the distance between two objects is increased 2 times, then force should be decreased by a factor of (22) = 4.
Thus, the new force (F) = (16 units) / 4 = 4 units
Ques. What is the speed of Gravity on Earth? (1 Mark)
Ans. Gravity is measured by the acceleration it gives to free-falling objects. At the earth’s surface, the acceleration of gravity is calculated as 9.8 meters per second.
Ques. Is there a connection between Gravity and Black Holes? (2 Marks)
Ans. A black hole is a region of space-time with an area of immense gravity as a lot of mass is accumulated into a very small space. Here, the gravity is so strong that even the light cannot escape. The surface of the black hole is called the ‘event horizon’. It is the boundary where the escape velocity needed to escape its gravitational pull is greater than the velocity of light.
Ques. Are there any drawbacks of Gravity? (2 Marks)
Ans. Yes, there are some drawbacks of the force of gravity which are as follows:
- Gravity of the Earth may draw asteroids from space and if these asteroids hit the earth's atmosphere, they can cause catastrophic damage on earth.
- The force of gravity may cause an object to fall from greater heights, resulting in numerous deadly mishaps for humans.
Check-Out:



Comments